Functions
Moves sperm from epididymis to ejaculatory ducts (by means of smooth muscle peristalsis) in anticipation of ejaculation.
Anatomy
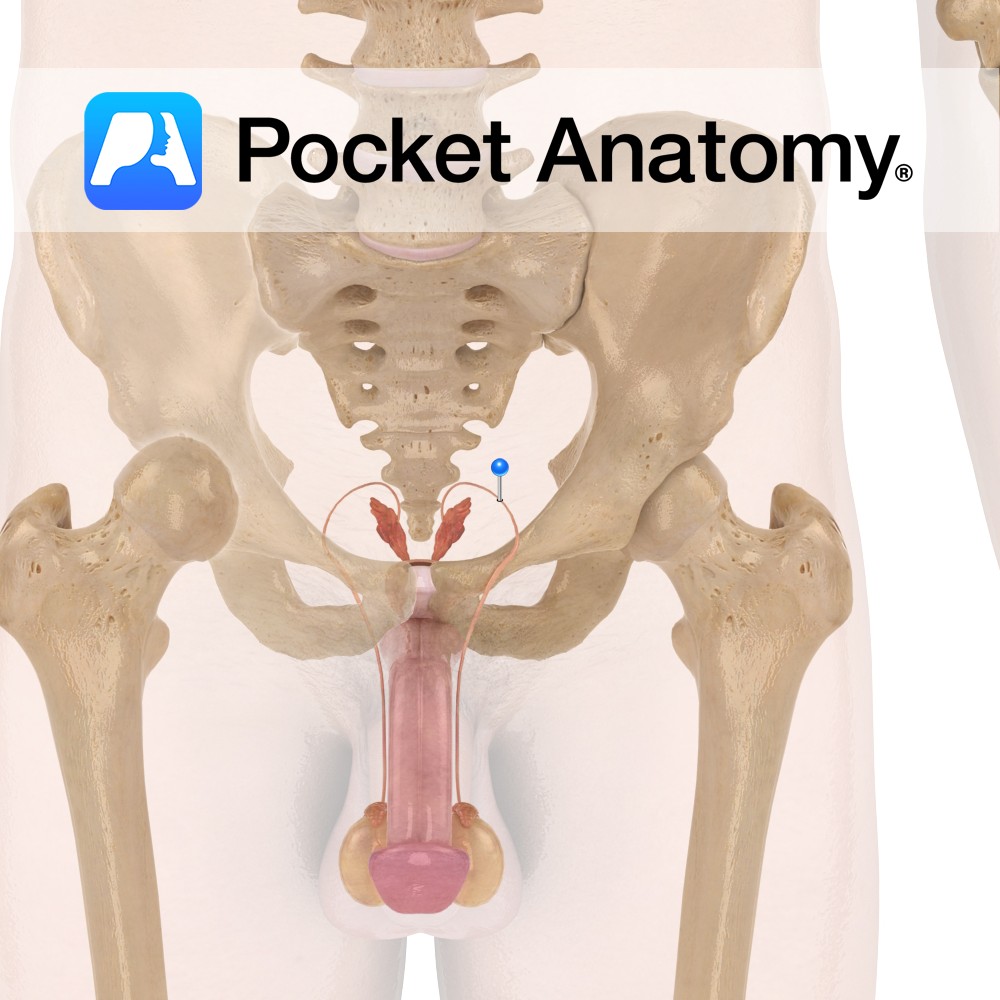
Paired structure of male reproduction, connects the epididymis to ejaculatory ducts for the movement of sperm. Usually ~30cm long, 3-5mm diameter, contain smooth muscle.
An ampulla (tortuous in shape) is often seen at the efferent end, at the fundus of the prostate. An outpouching of this forms the seminal vesicles during foetal development.
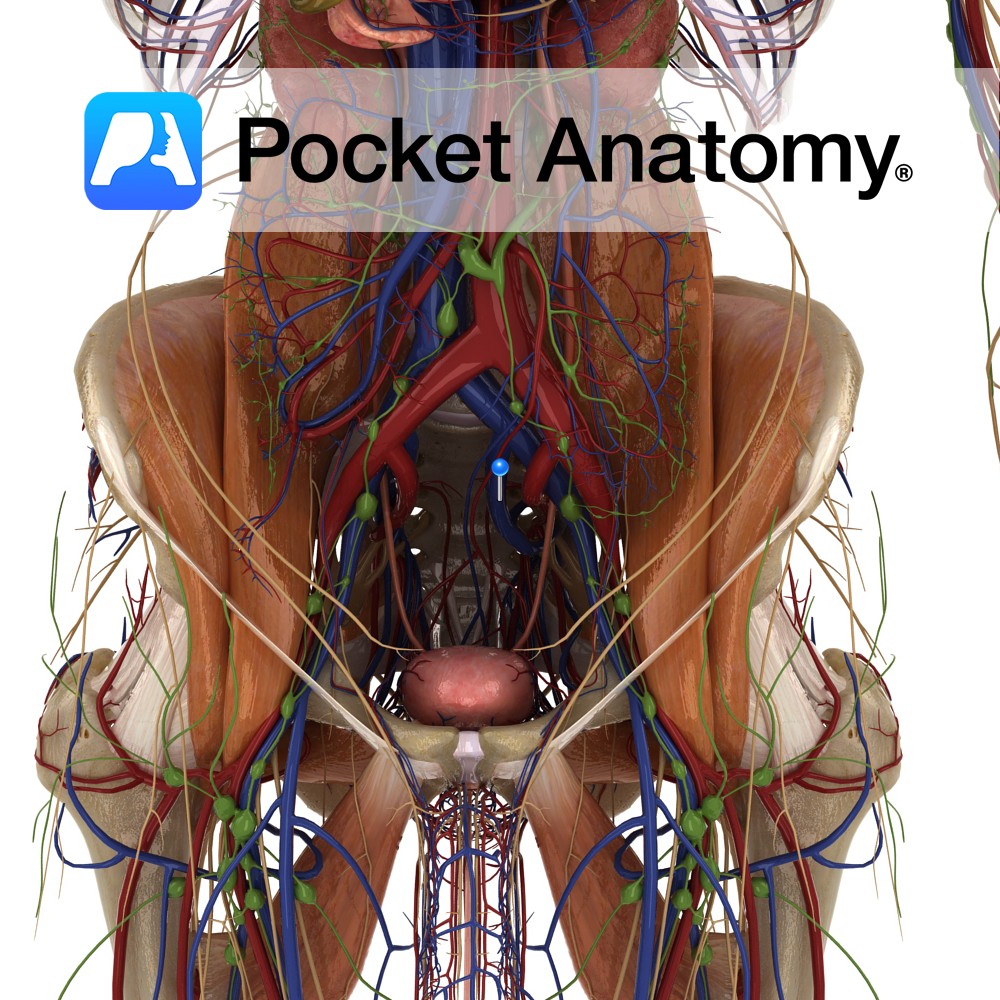
Supplied by vas deferens artery, from superior vesical artery, from internal iliac artery.
Clinical
Vasectomy involves severing the vas deferens as a means of contraception. Modern techniques obstruct the tube instead with injection of a blocking material.
Both techniques – while practically permanent – can be reversed, with varying degrees of success.
Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?