Anatomy
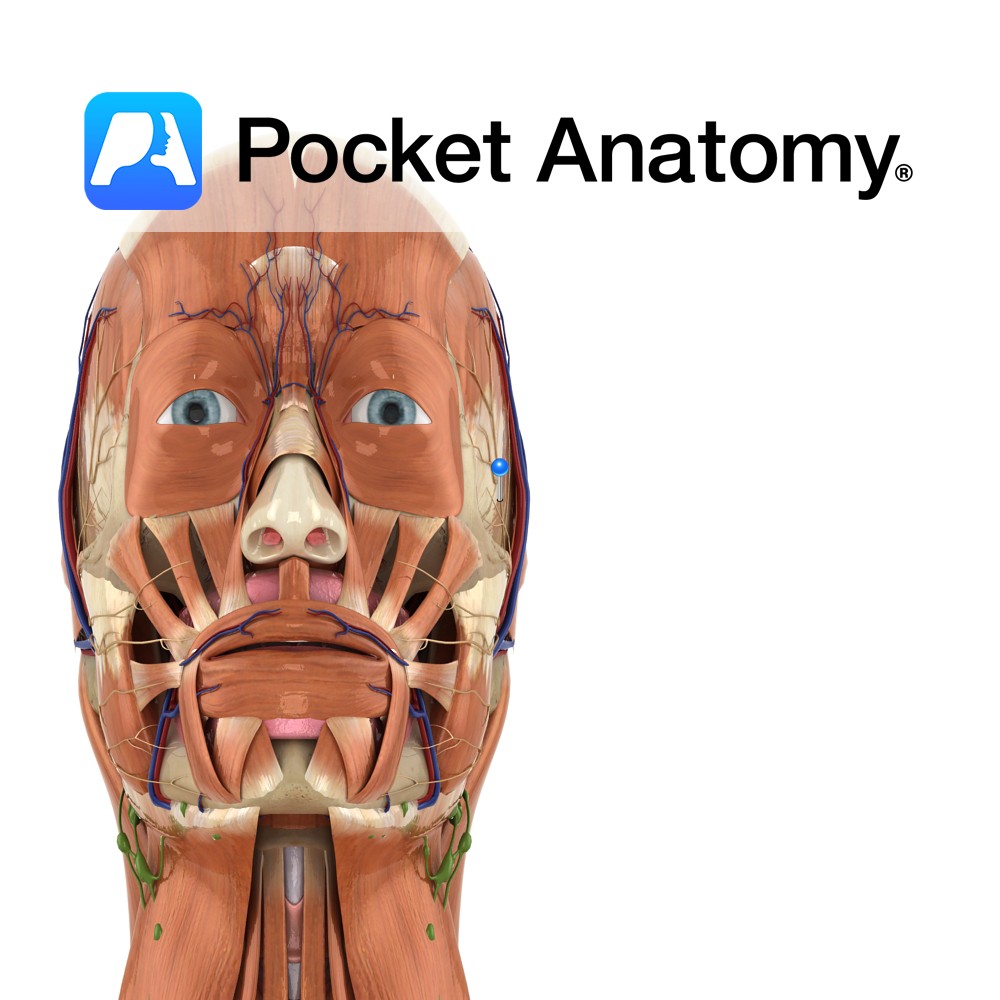
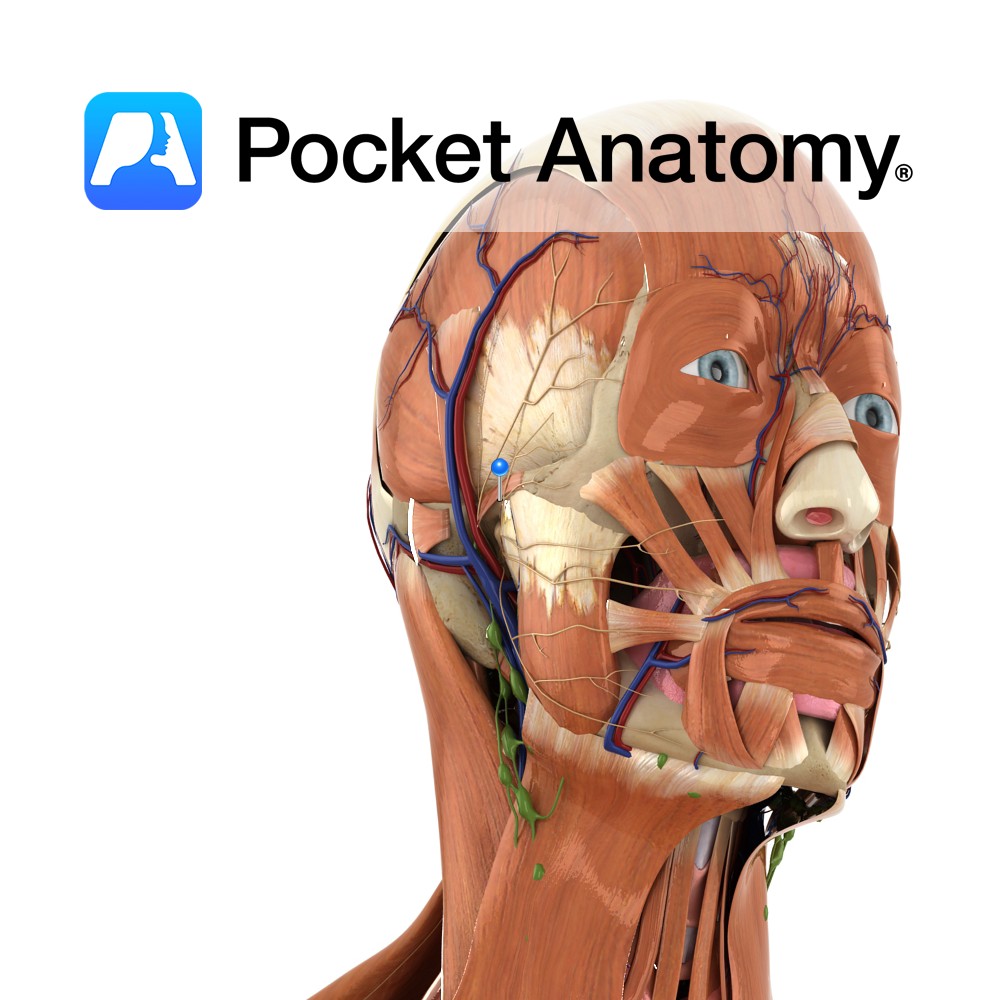
Branch of the facial nerve (also known as the seventh cranial nerve).
Facial nerve:
Has a motor and sensory origin that join together to form the nerve. It passes through the internal auditory meatus through the facial canal and finally exits from the stylomastoid foramen, and into the parotid gland where it divides into its terminal branches (temporal, zygomatic, buccal, mandibular, and cervical nerves).
Supply
Facial nerve:
Motor control to the muscles of facial expression, posterior digastric muscle, stapedius and the stylohyoid muscle. Also sends parasympathetic fibres to the sublingual and submandibular gland. It contains general sensory as well as taste fibres from the anterior two thirds of the tongue.
Clinical
Facial nerve:
A sign of facial nerve damage is the loss of the corneal eye reflex. Normally both eyes blink in response to stimulus.
Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?