Motion
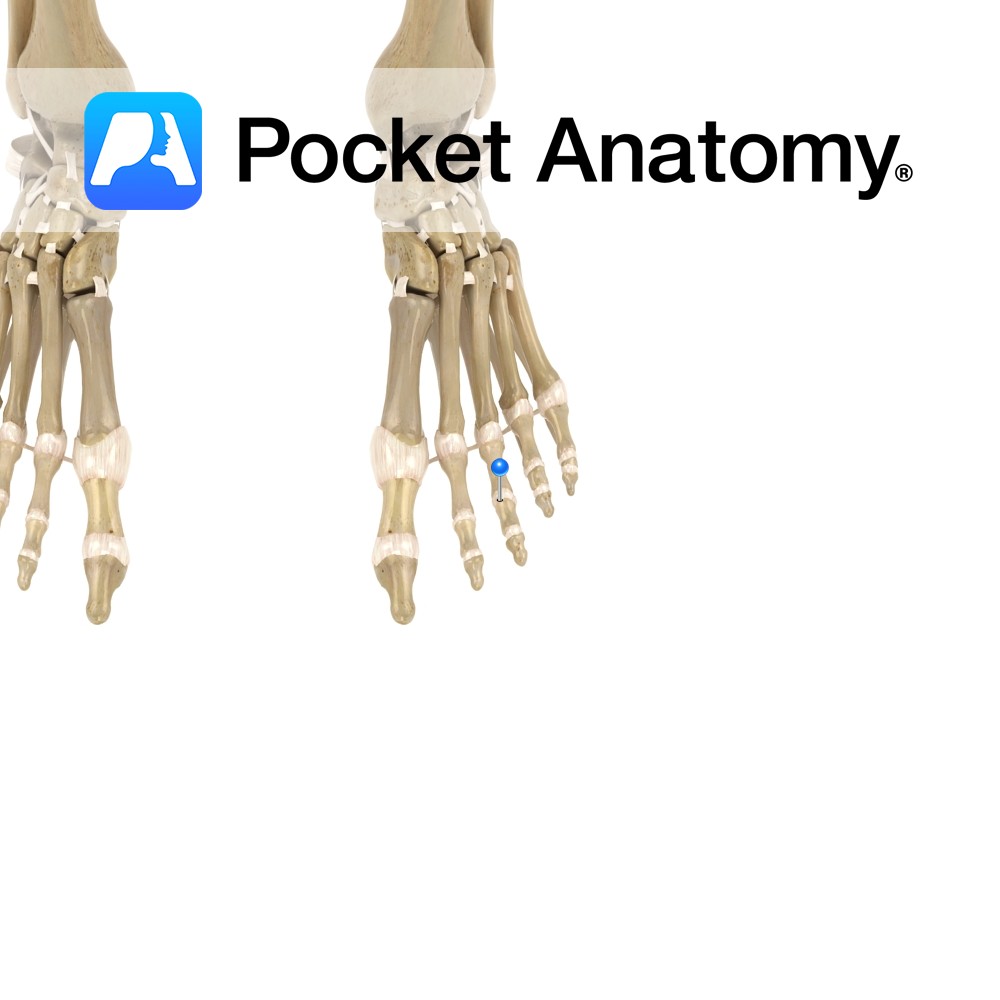
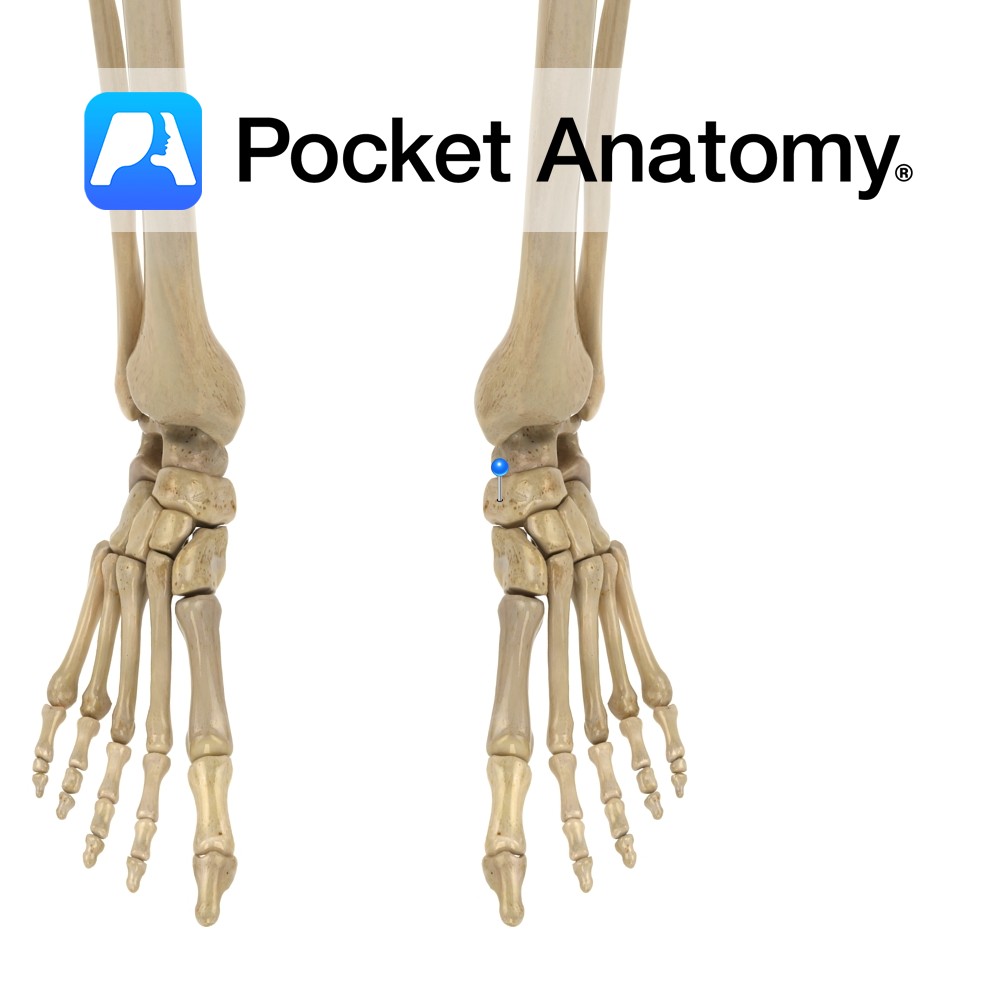
The interphalangeal joints are synovial hinge joints. They involve the articulations between the proximal, middle and distal phalanges of the toes. They allow mainly flexion and extension.
Stability
The fibrous capsules surrounding the joints plays a role in their stability.
The joints are reinforced by the following ligaments:
-Medial collateral ligament
-Lateral collateral ligament
-Plantar ligament.
Muscles
Flexion:
Flexor digitorum longus (2nd-5th digits)
Flexor digitorum brevis (1st digit only)
Quadratus plantae (2nd-5th digits)
Flexor hallucis longus (1st digit only)
Extension:
Extensor digitorum longus (2nd-5th digits)
Extensor digitorum brevis (2nd-4th digits)
Extensor hallucis longus (1st digit only)
Lumbricals.
Clinical
The distal interphalangeal joints are commonly affected by osteoarthritis.
Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?