Anatomy
Origin:
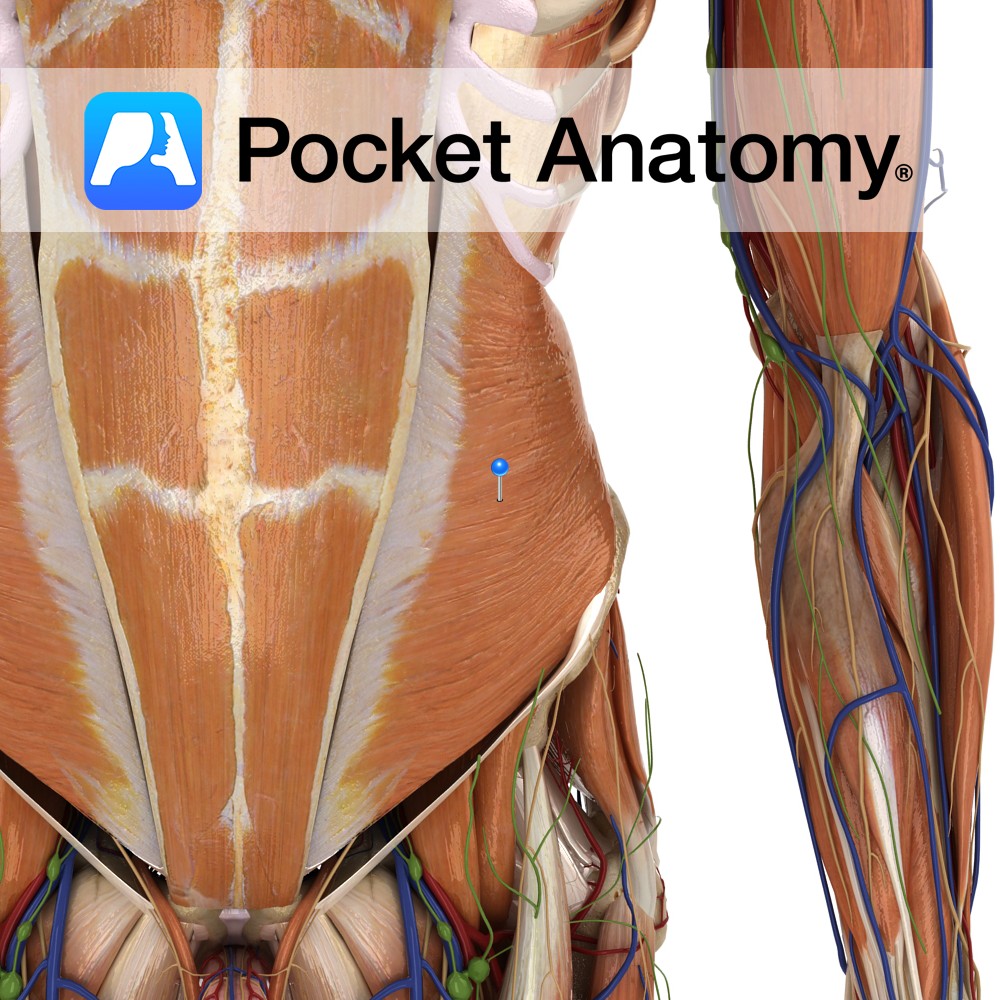
Thoracolumbar fascia, iliac crest and the lateral two thirds of inguinal ligament.
Insertion:
Inferior border of 9th /10th to 12th ribs, aponeurosis to linea alba, pubic crest and pectineal line.
Key relations:
-Deep to the external obliques.
-Muscle fibres run superomedially.
Functions
-Compresses abdominal cavity and raises intrabdominal pressure e.g raking leaves.
-Flexes (contracting bilaterally) and rotates (contracting unilaterally) the vertebral column (trunk).
Supply
Nerve Supply:
Anterior rami of thoracic spinal nerves (T7 to T12).
Blood Supply:
Superiorly by: lower intercostal arteries.
Inferiorly by: either the deep circumflex iliac or iliolumbar artery.
Clinical
The internal oblique forms part of the superior wall of the inguinal canal.
Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?