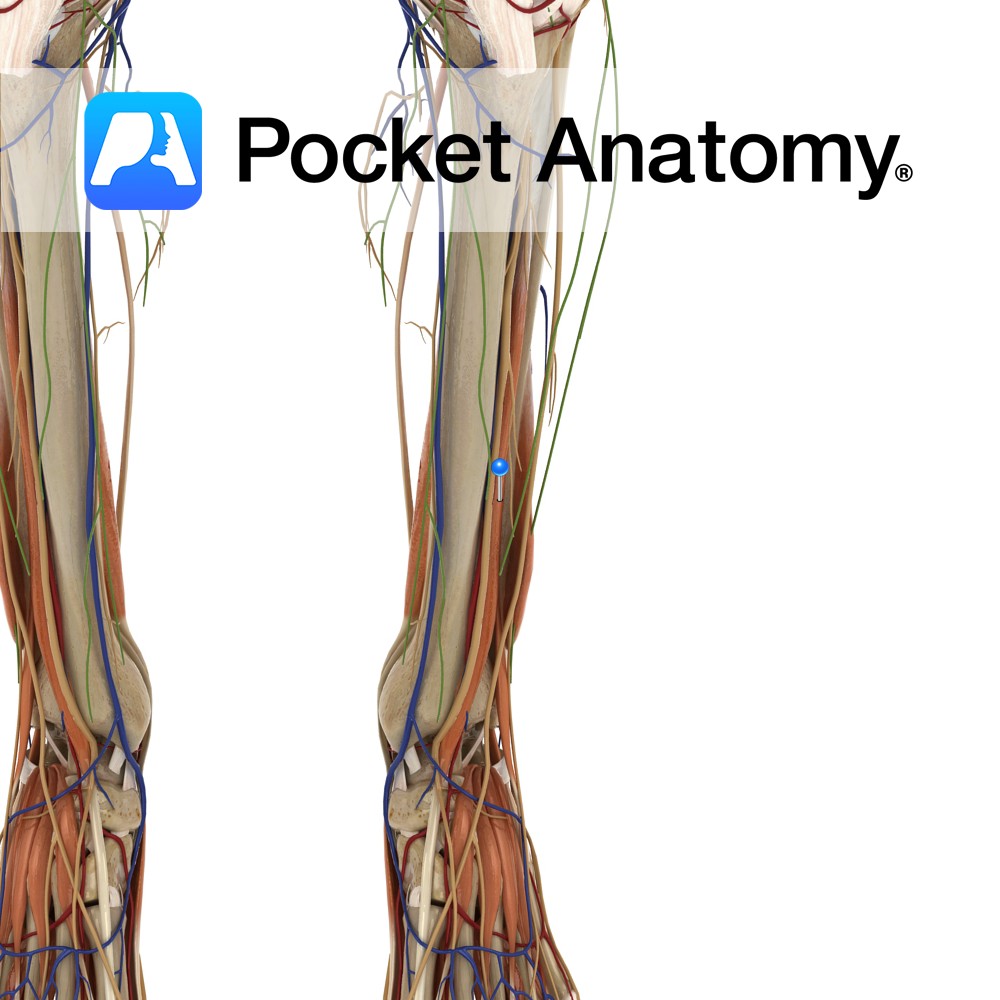
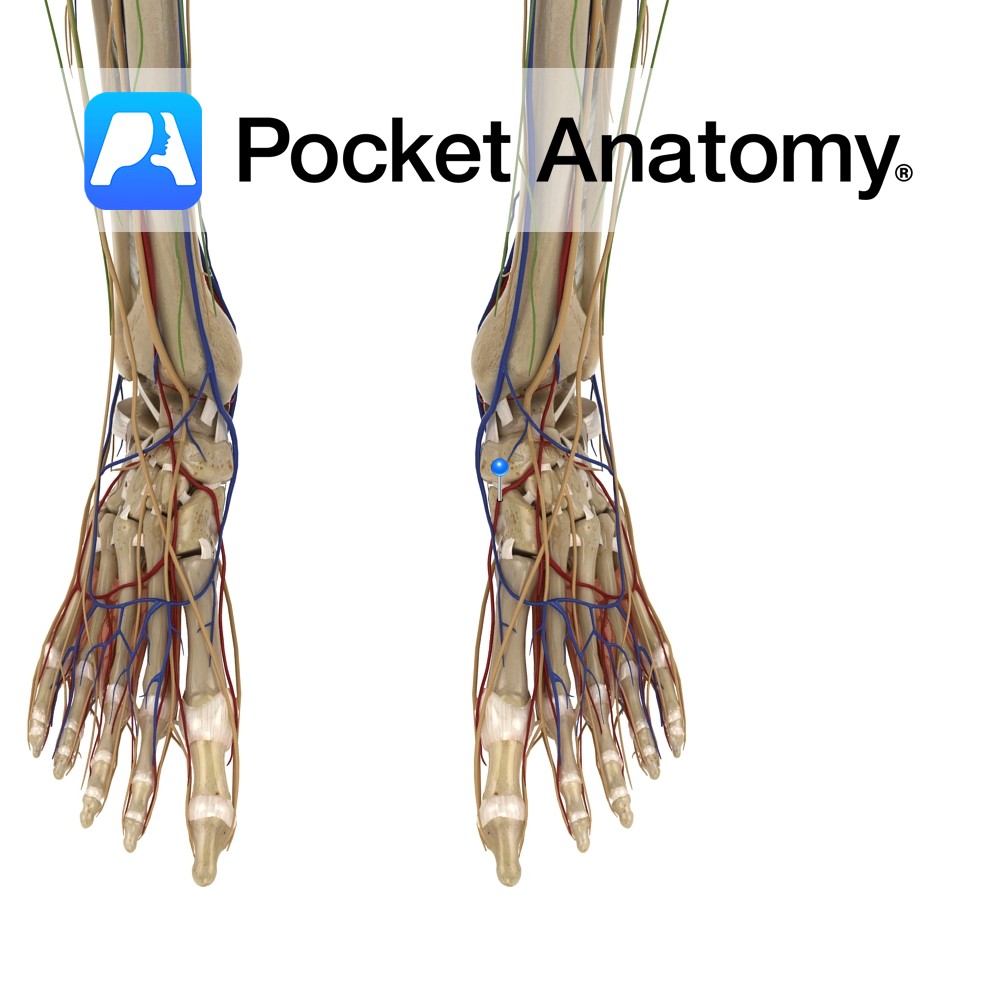
Anatomy
Origin:
Middle half of the anteromedial surface of the fibula and the interosseous membrane.
Insertion:
Dorsal surface of the base of the distal phalanx of the hallux (big toe).
Key Relations:
-One of the four muscles of the anterior compartment of the leg.
-The extensor hallucis longus tendon crosses anterior to the ankle joint between the tibialis anterior tendon medially and the extensor digitorum longus tendon laterally and is palpable in front of the ankle joint.
Functions
-Extends the hallux (big toe) at the interphalangeal and metatarsophalangeal joints e.g. walking up the stairs it extends the big toe up to clear the step.
-Assists in dorsiflexion of the ankle joint and weak inversion of the foot.
Supply
Nerve Supply:
Deep fibular (peroneal) nerve (L5).
Blood Supply:
Anterior tibial artery.
Clinical
Extensor tendinitis is inflammation of the extensor tendons of the toes such as tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis longus, extensor hallucis brevis, extensor digitorum longus and extensor digitorum brevis. The patient may present with pain and swelling on the dorsum of the foot, which may be worsened by activity e.g running or by passive stretching of the tendons. Extensor tendinitis may be caused by overuse, hill running as the extensor muscles have to work harder, tight-fitted shoes or if shoe laces are tied too tightly.
Treatment includes rest, ice, NSAIDs, better fit shoes, stretching the calf muscles and in severe cases surgery.
Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?