PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
Anatomy Origin: Floor of temporal fossa and its overlying fascia. Insertion: Medial surface of coronoid process of mandible and anterior border of ramus of mandible. Key Relations: -Superficial to the muscle are the masseter and the temporal branches of the facial nerve. -One of the four muscles of mastication. Functions -Elevates the mandible to occlude
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
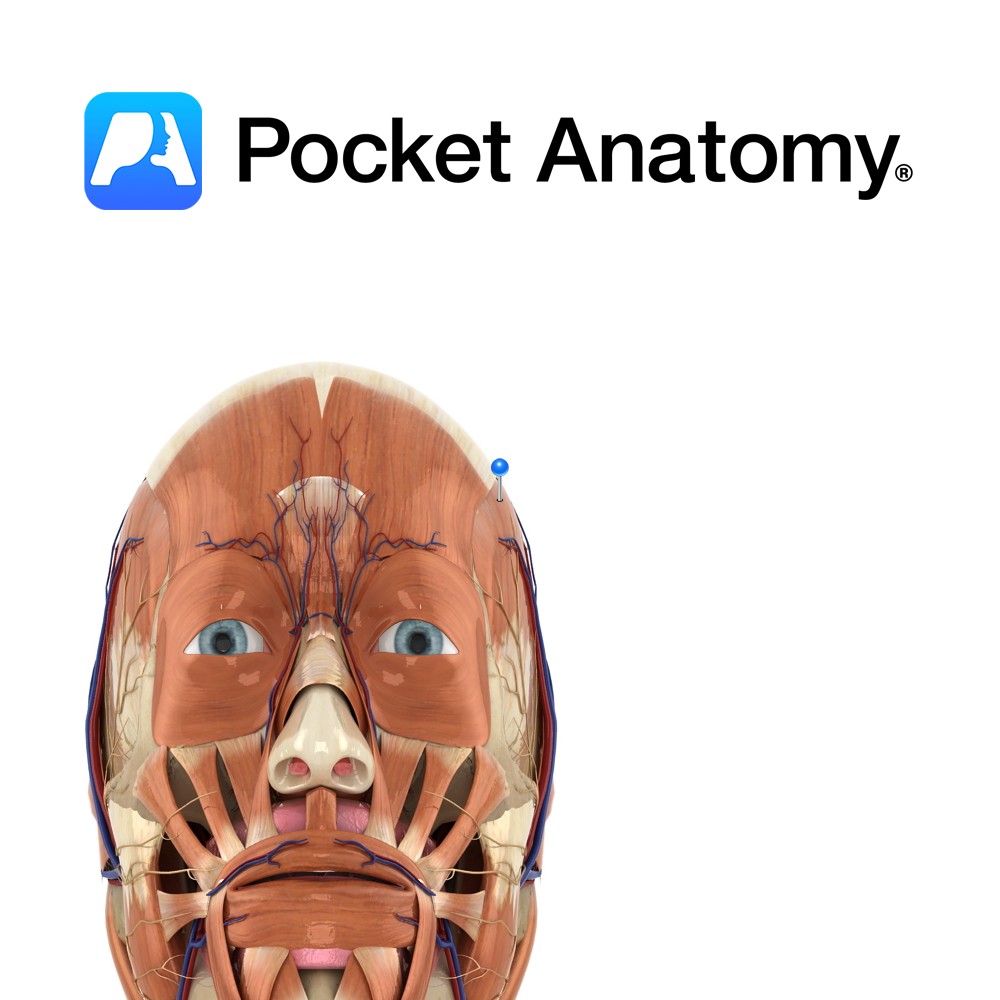
Anatomy Course A terminal branch of the ophthalmic artery (which is a branch of the internal carotid) – branches off where the ophthalmic artery travels posterior to the trochlea, exits the orbit medially, and ascends the forehead. Supply Along with the ophthalmic artery, it supplies the structures of the orbit of the eye, including the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
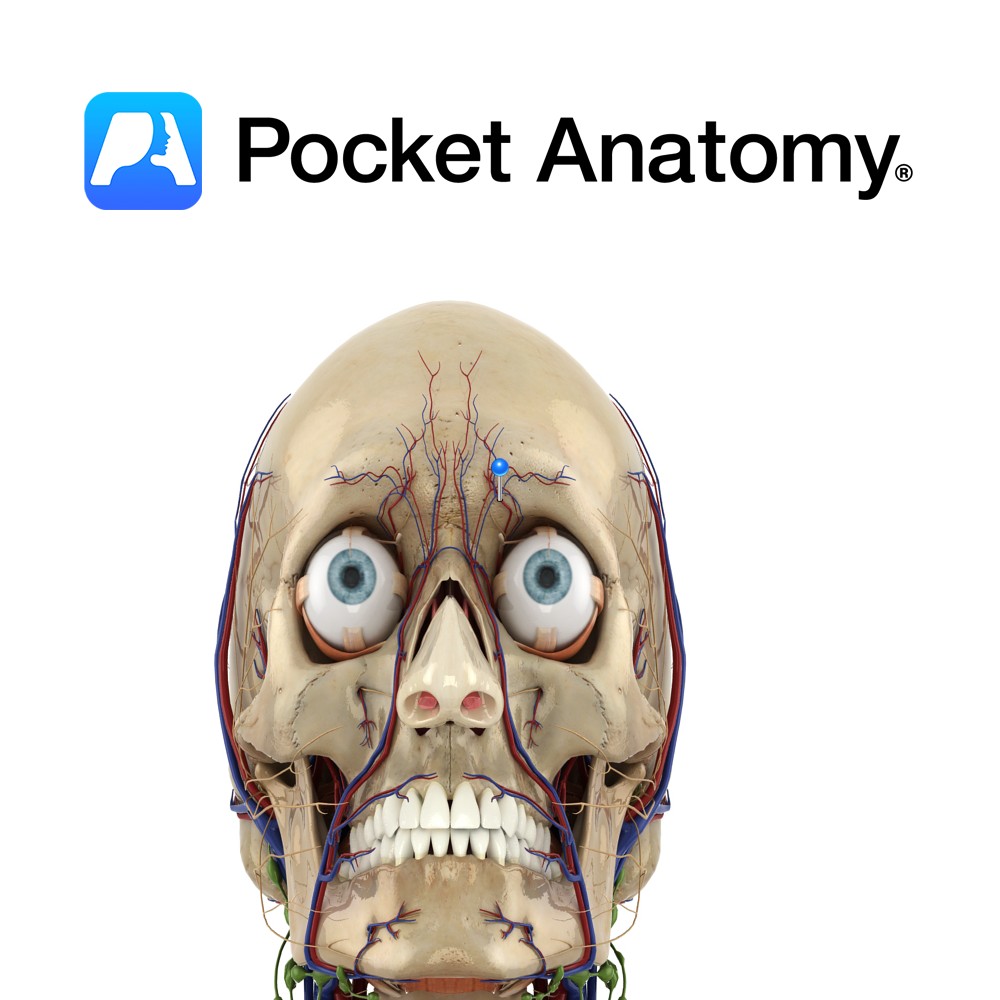
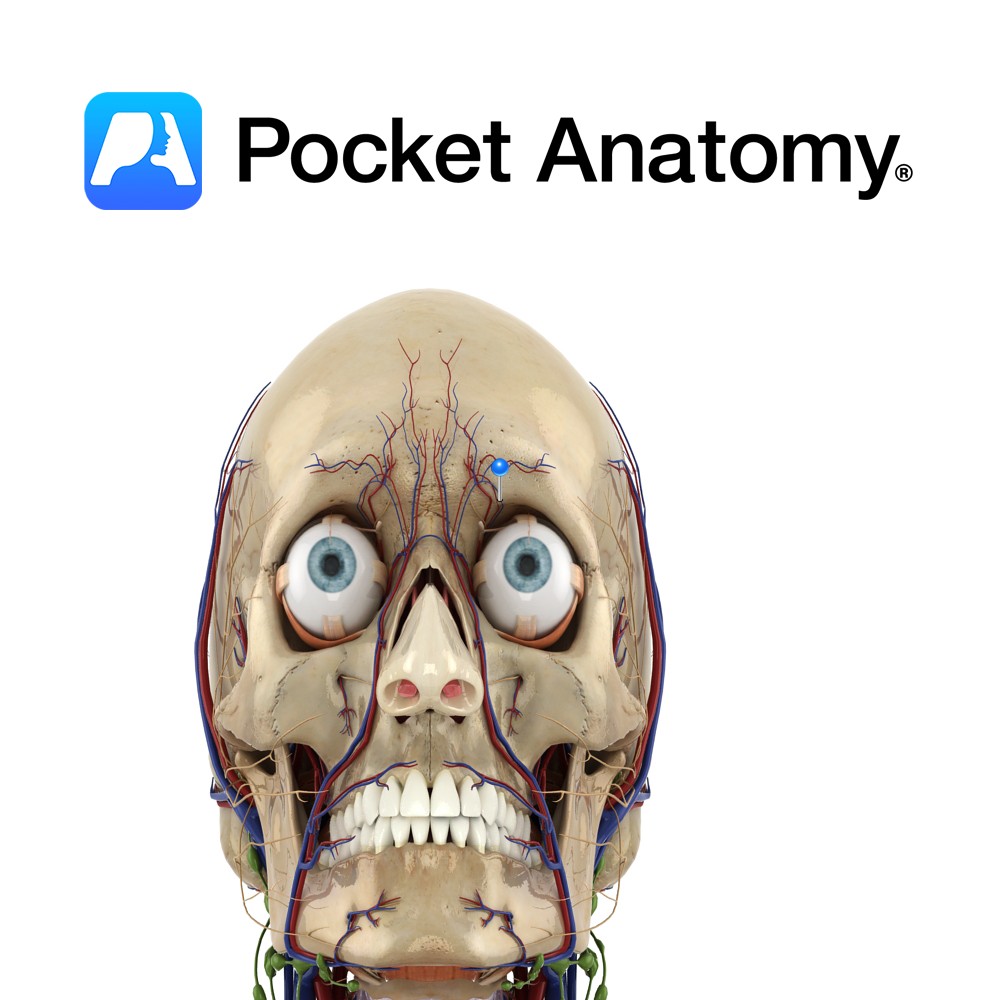
Anatomy Course A terminal branch of the ophthalmic vein. Drain Drains forehead and front of scalp. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
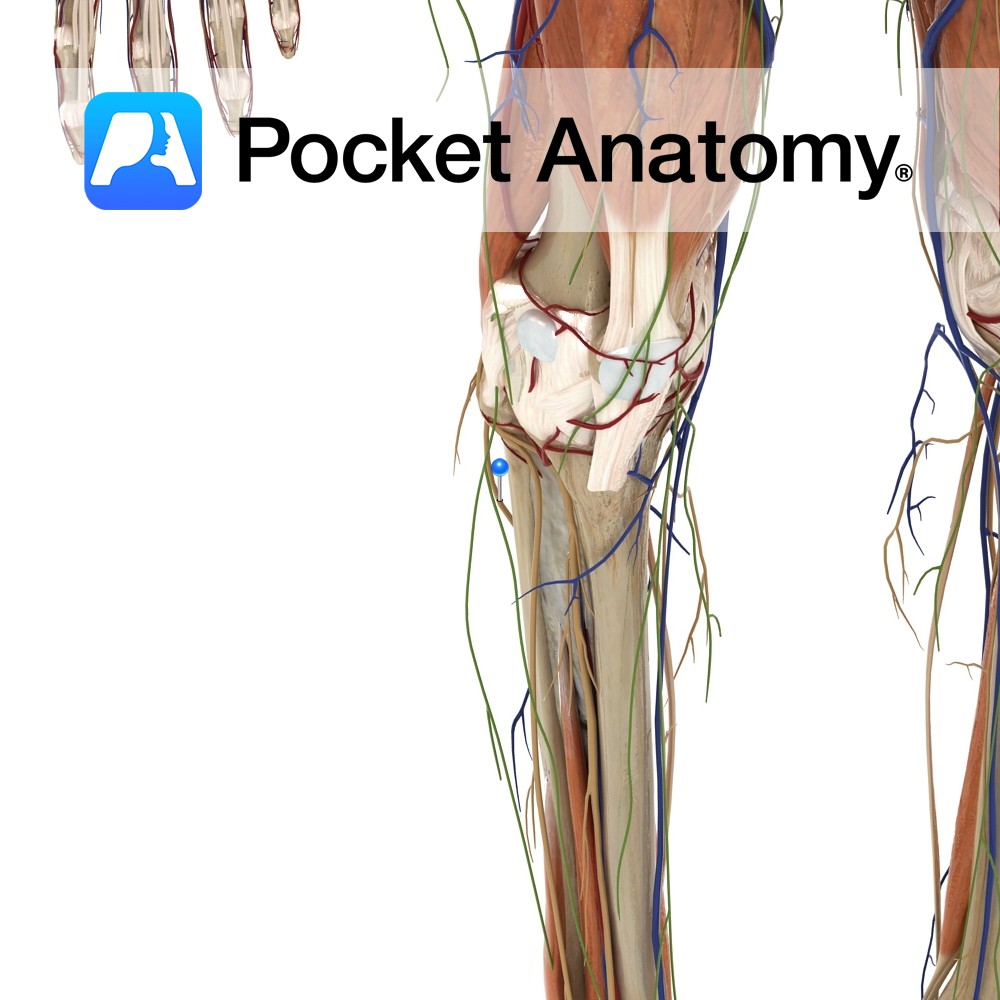
Anatomy Course The sural communicating branch of the common peroneal nerve contributes to the sural nerve. It arises from the common peroneal nerve in the popliteal space and passes over the lateral head of the gastrocnemius muscle. About halfway down the leg, it joins with the medial sural nerve to form the sural nerve. Supply
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
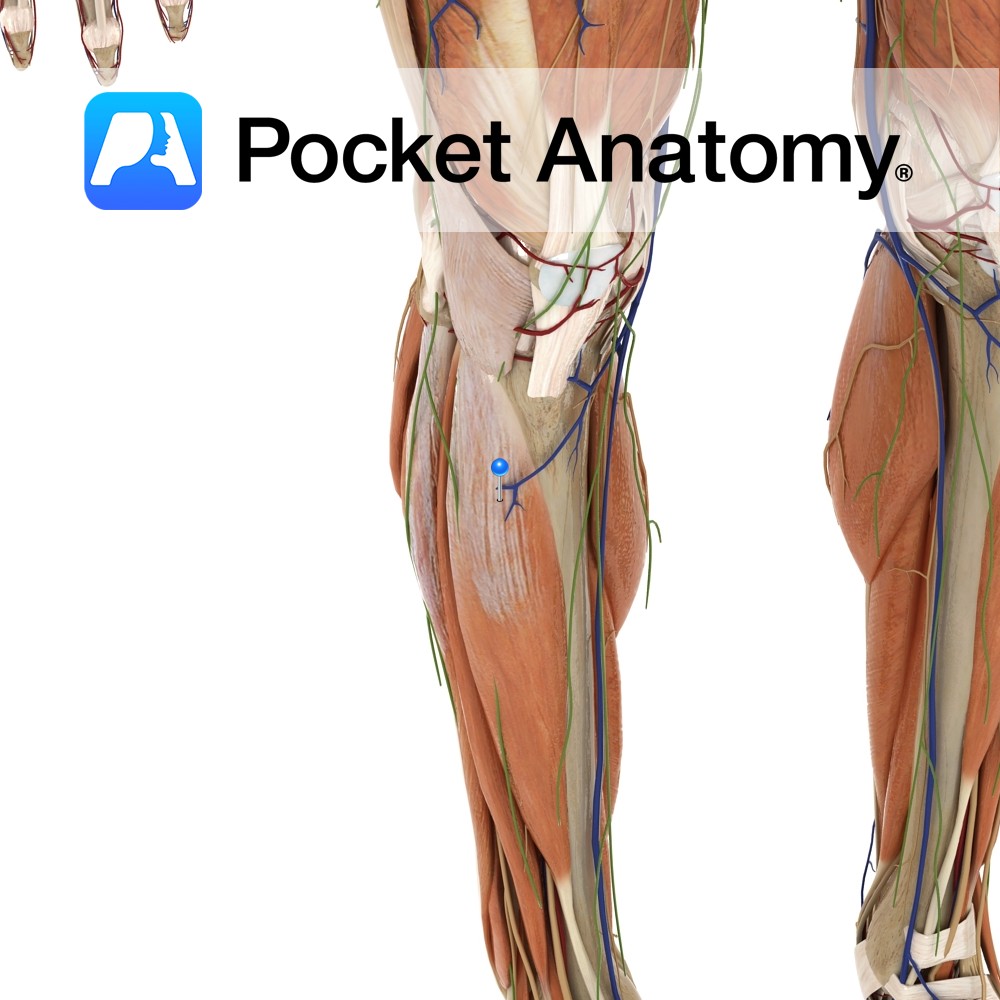
Anatomy Course Originates from the tibial nerve just above the knee joint, between the heads of the gastrocnemius muscle. It descends superficially to the gastrocnemius muscle, and penetrates the deep fascia about halfway down the calf, to run subcutaneously. It continues down the leg, and passes around the lateral malleolus to continue to supply the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Also known as extra-sutural bone. An extra, occasionally present, irregular bone, in a cranial suture. Most commonly seen in the lambdoid area. Vignette Ole Worm, 16th/17th century Danish physician. Also known as Inca bone; relatively high prevalence in Peruvian mummies. Presence of multiple wormians a marker in diagnosis osteogenesis imperfecta (Brittle Bone Disease). Interested
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy 3 distinct, separated, equally spaced, longitudinal ribbons/straps of muscle (mesocolic, free, omental) along the length of ascending, transverse, descending and sigmoid colon, visible just below serosa, shorter than other corresponding colonic layers, thus puckering the colon between them (even more on contraction), and giving rise to haustra/sacculations; converge at either end – rectum, base
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
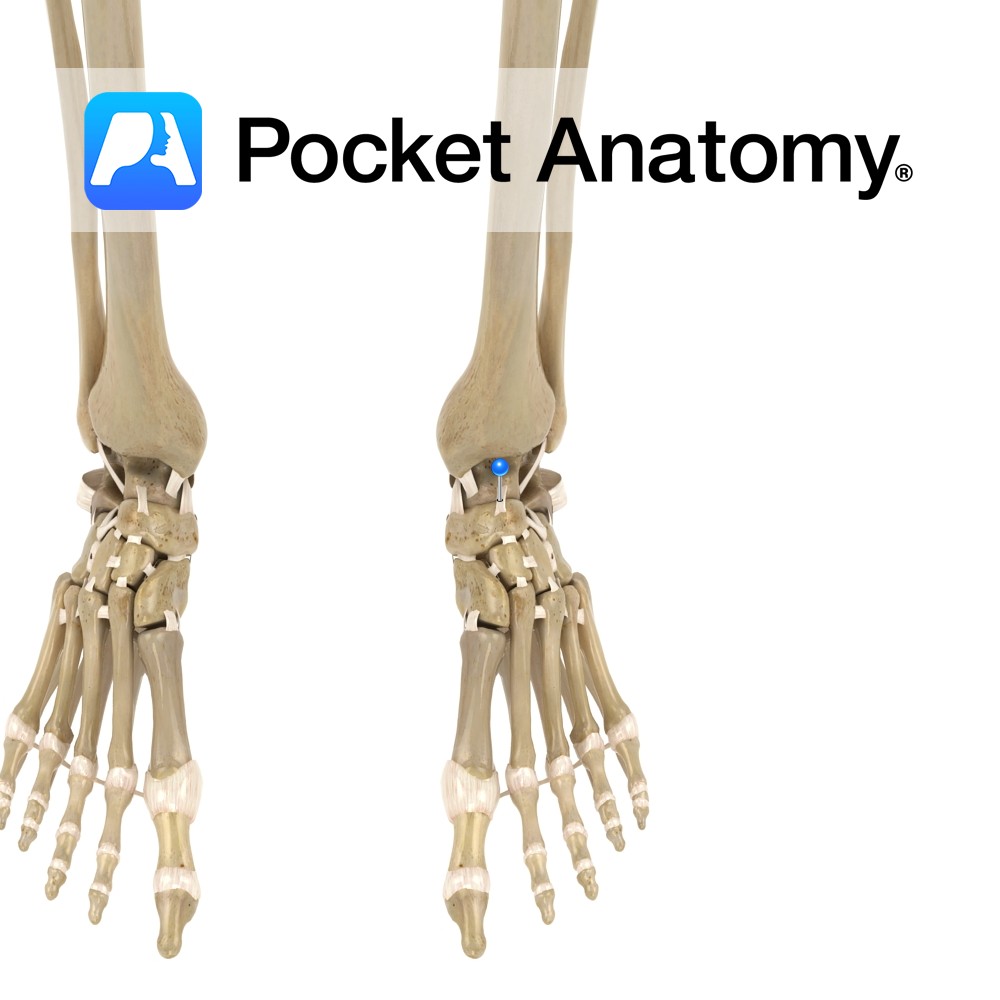
Anatomy A broad, thin ligament that connects the neck of the talus to the dorsal surface of the navicular. Functions Provides static stability to the talocalcaneonavicular joint. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
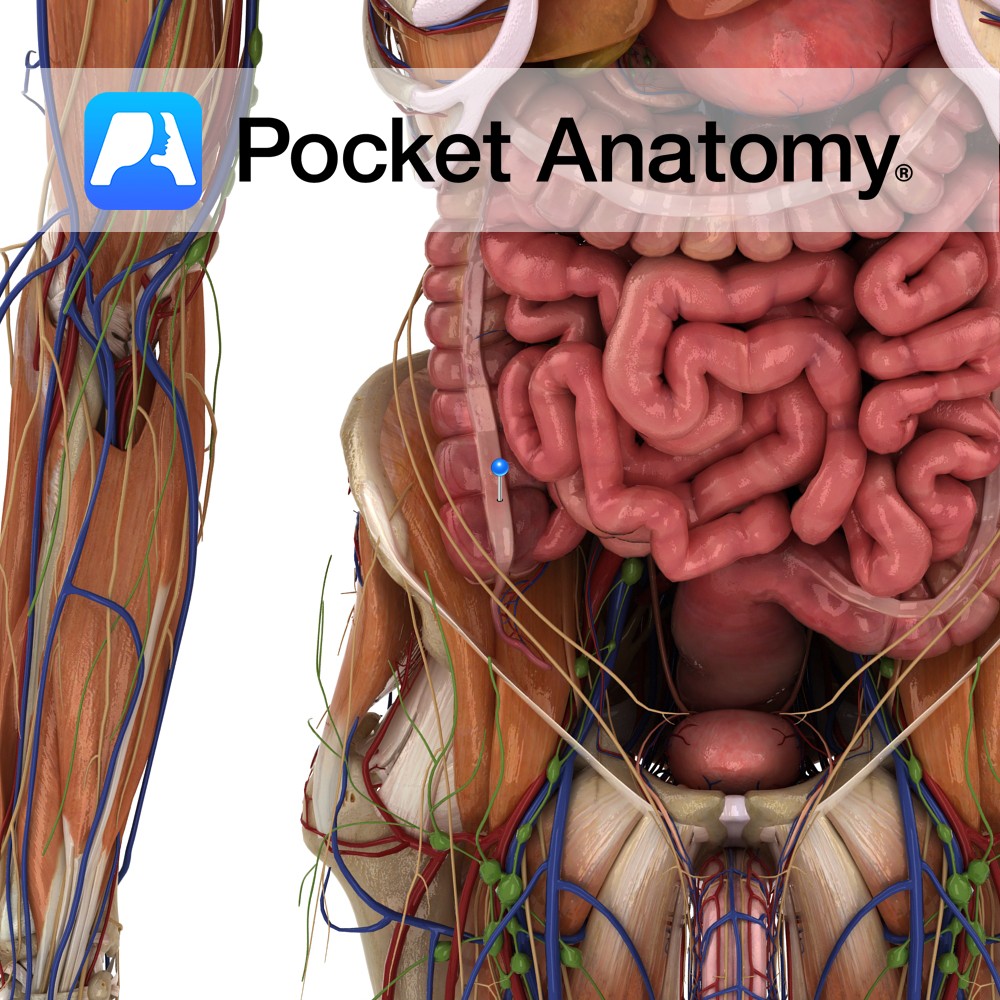
Anatomy Course Formed by the union of several veins in the abdomen that drain the region known as the embryonic midgut. It is formed in the mesentery, through which it ascends and then travels up behind the pancreas. Here it joins with the splenic vein to form the portal vein. Drain Drains the region of
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
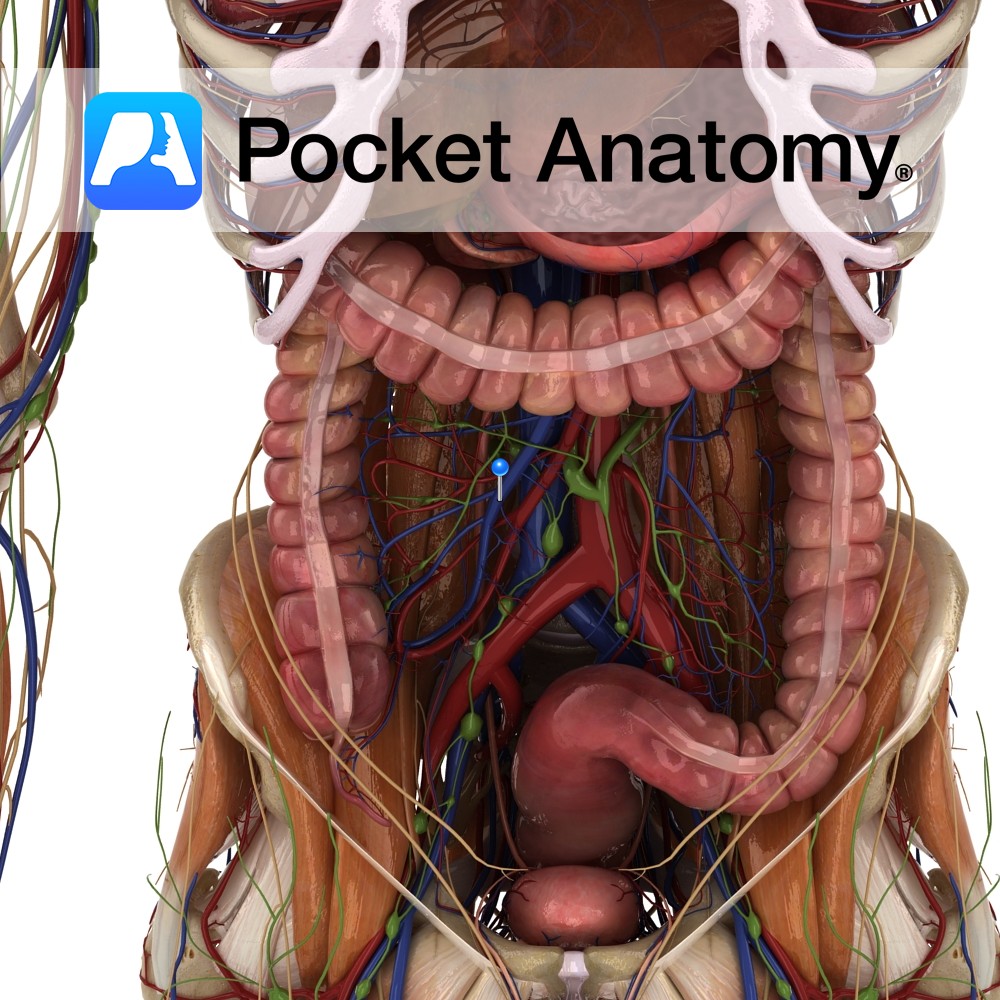
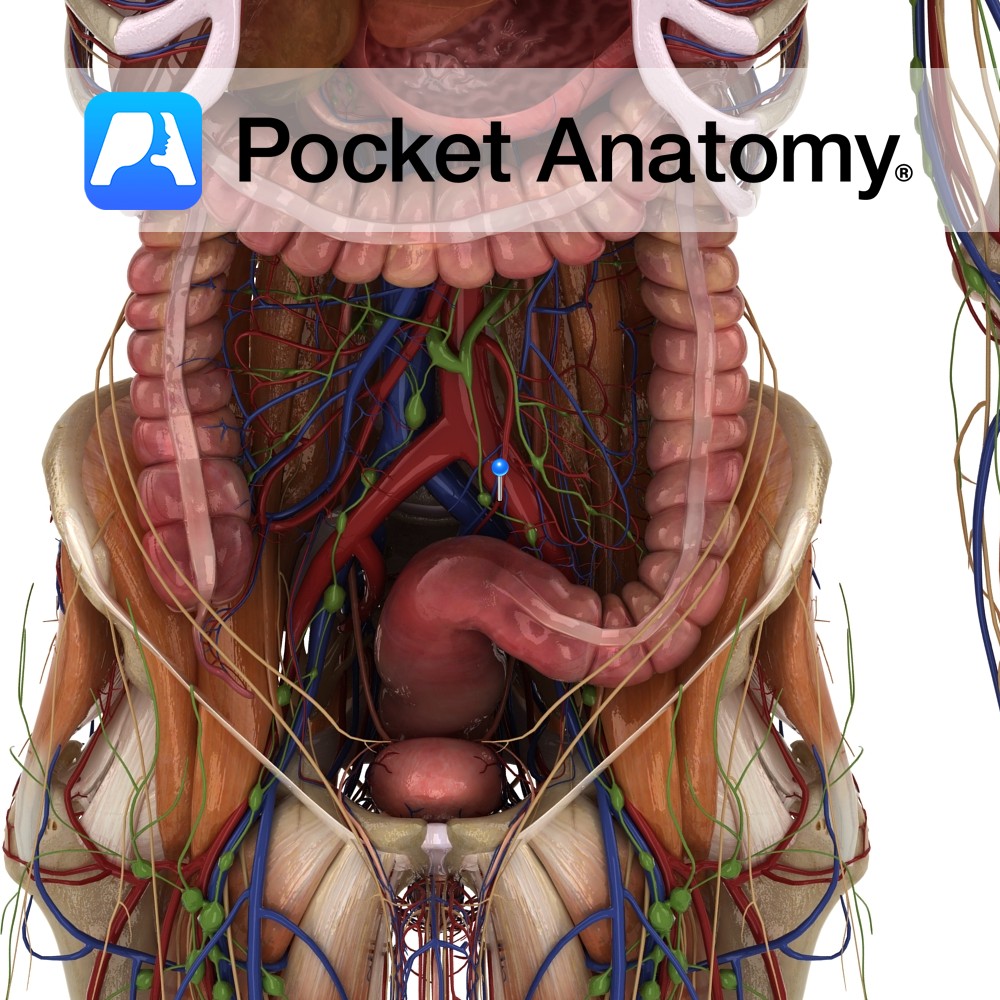
Anatomy Course One of the terminal branches of the inferior mesenteric artery. It descends in the sigmoid mesocolon and crosses over the left internal iliac artery. It divides at the vertebral level of SIII, and continues to descend by the rectum where it anastomoses with the middle and inferior rectal arteries. Supply Supplies the rectum.
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins

-bone.jpg)