PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
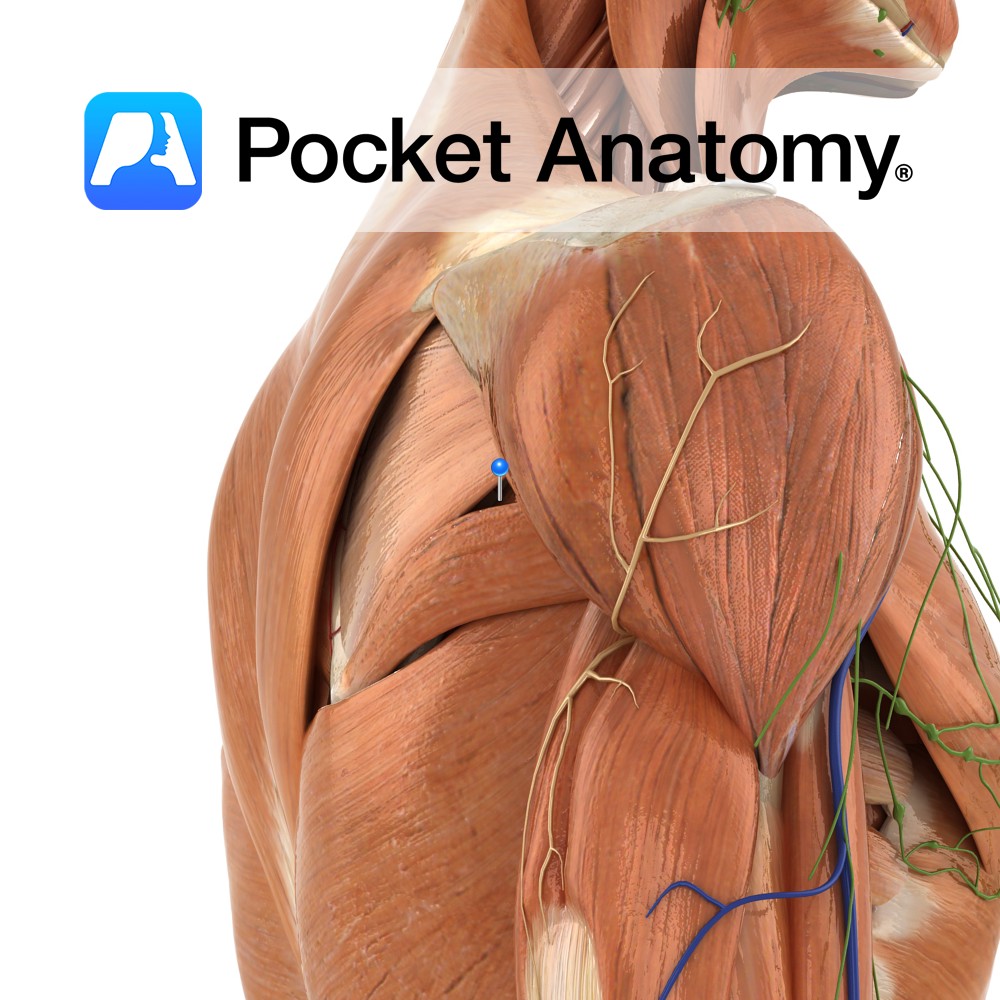
Anatomy Origin: Upper two-thirds of posterior surface of lateral border of scapula. Insertion: Inferior facet of greater tubercle of humerus. Key Relations: -The tendon of the muscle passes across and is united with the posterior capsule of the shoulder joint. -One of the four muscles of the rotator cuff muscle group. Functions -Lateral rotation of
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
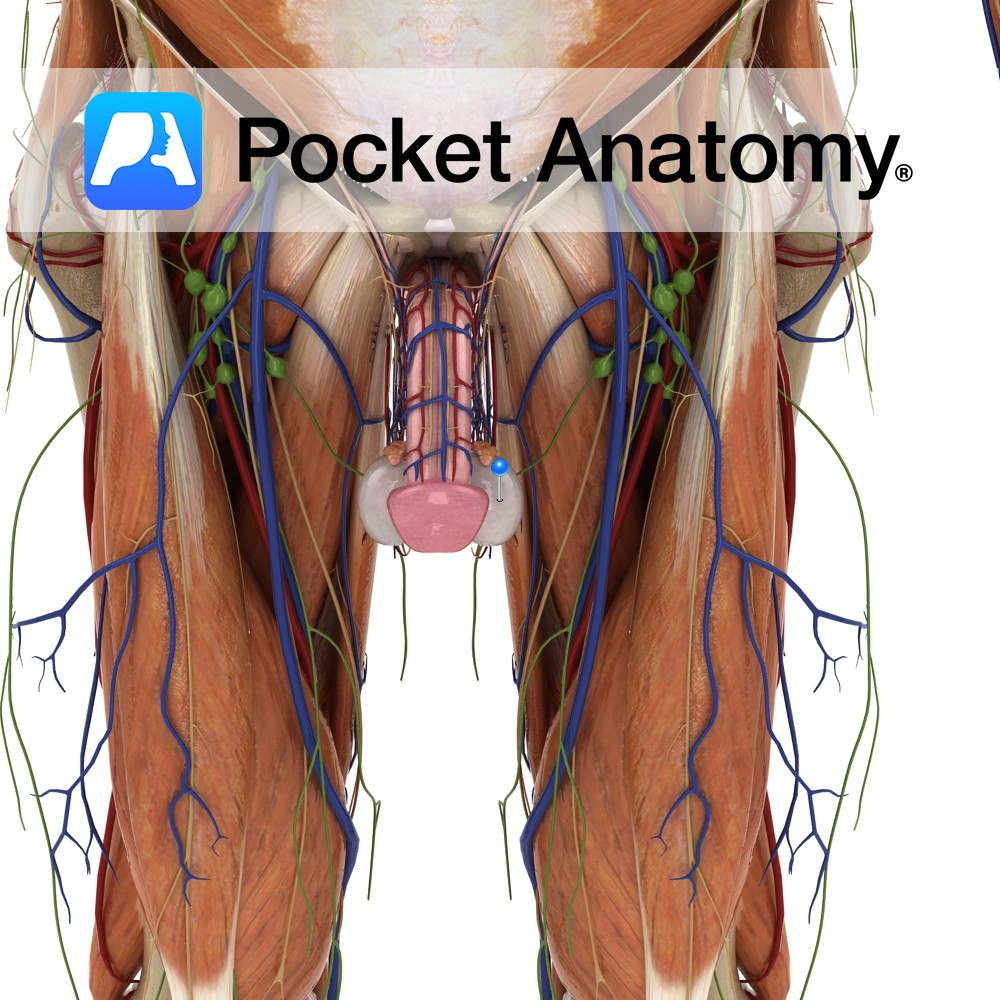
Anatomy Male gonad [organ that makes gametes – sperm – through a process (spermatogenesis) that involves a type of cell division (meiosis) that produces cells that are haploid, ie have half the chromosome complement of other – diploid – cells; female gamete is ovary, its meiotic product are eggs], produces sperm and testosterone, ellipsoid (about
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
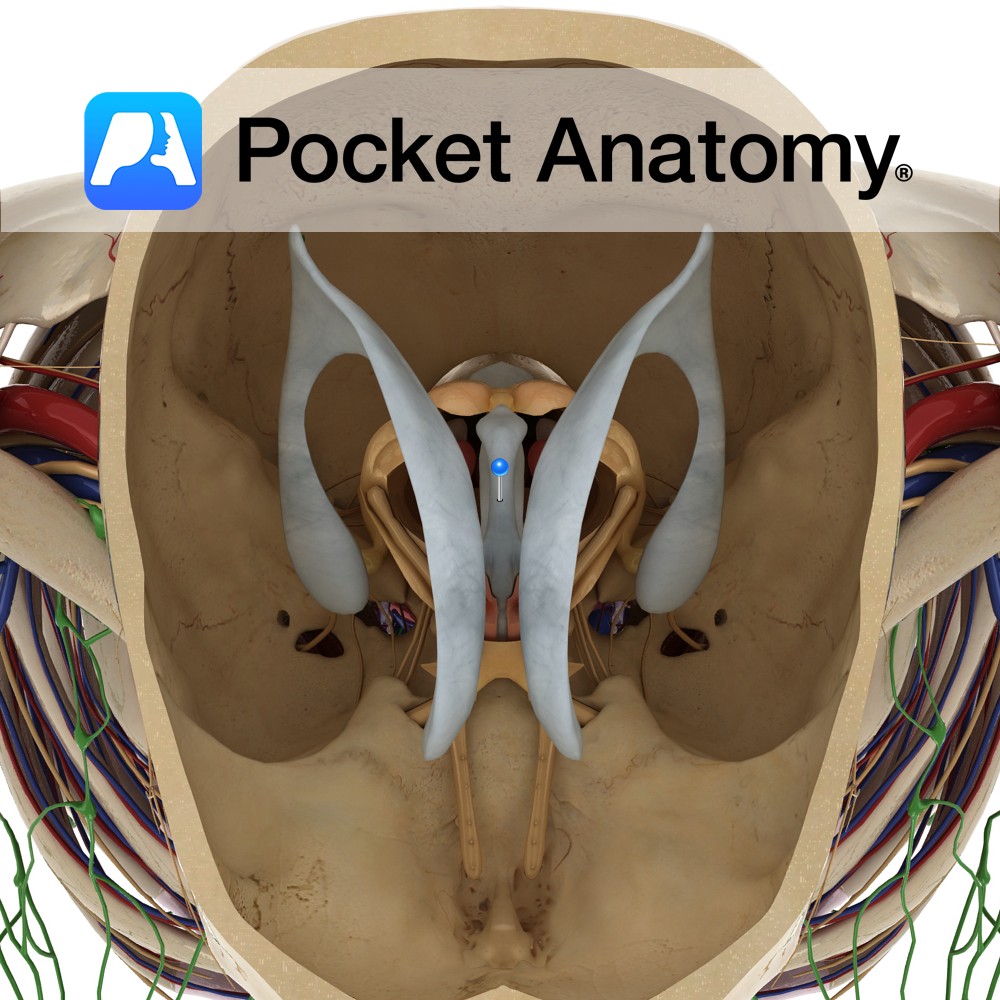
Anatomy Is a slit-like cavity lined with ependymal cells, located between the two thalami and is a part of the series of fluid-filled cavities, which make up the ventricular system. It is connected anteriorly to the lateral ventricles via the interventricular foramen of Monro. The anterior wall is formed by the lamina terminalis. The lateral
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course The ascending portion of the thoracic aorta is that directly from the heart to the arch of the aorta. It begins at the base of the left ventricle of the heart, and is contained in the pericardium for its course. Supply All blood that is circulated throughout the systemic circulation passes through the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
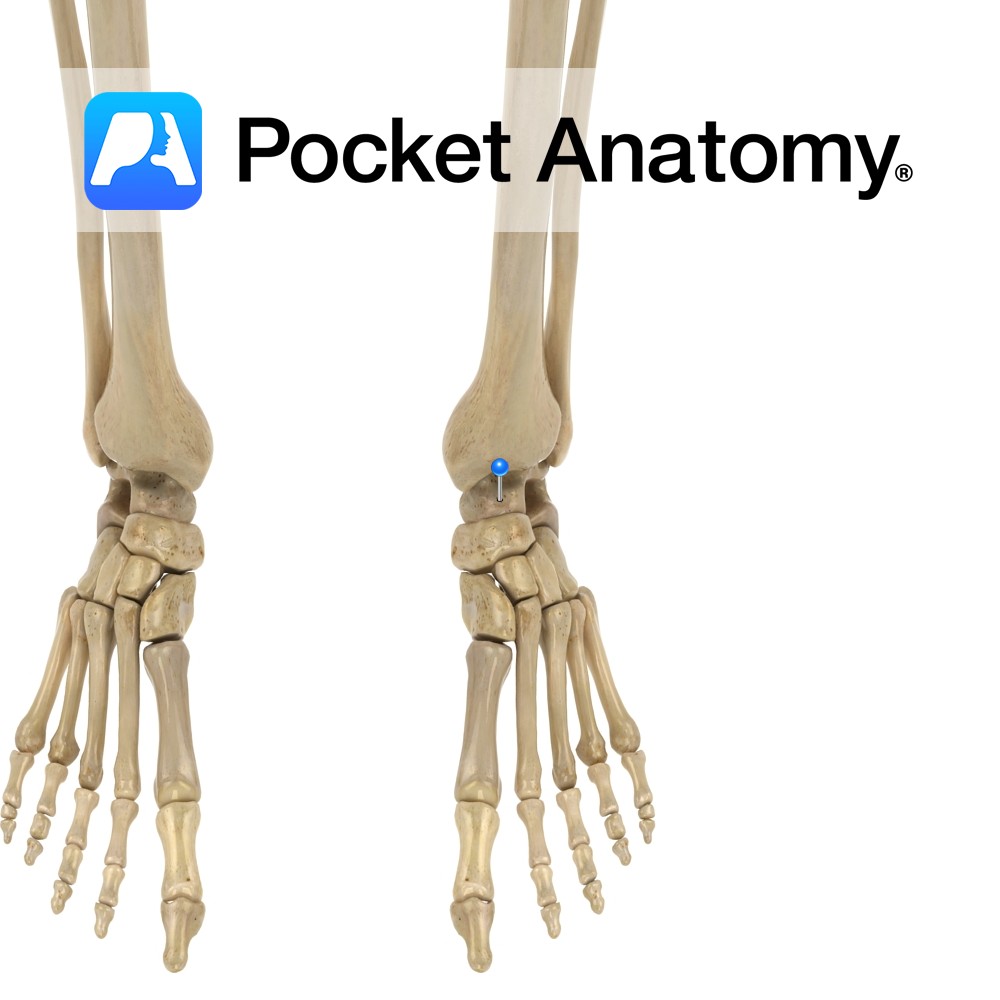
Anatomy Anklebone. Tarsal bone, irregular shape (boxing glove from above), transmitting weight of body to foot through articulations up with malleoli of tibia and fibula (talocrural joint – hinge), down with calcaneus (subtalar joint) and forward with navicular (along with calcaneocuboid joint, forms transverse talar joint). Clinical Fractures can be difficult to treat, can lead
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
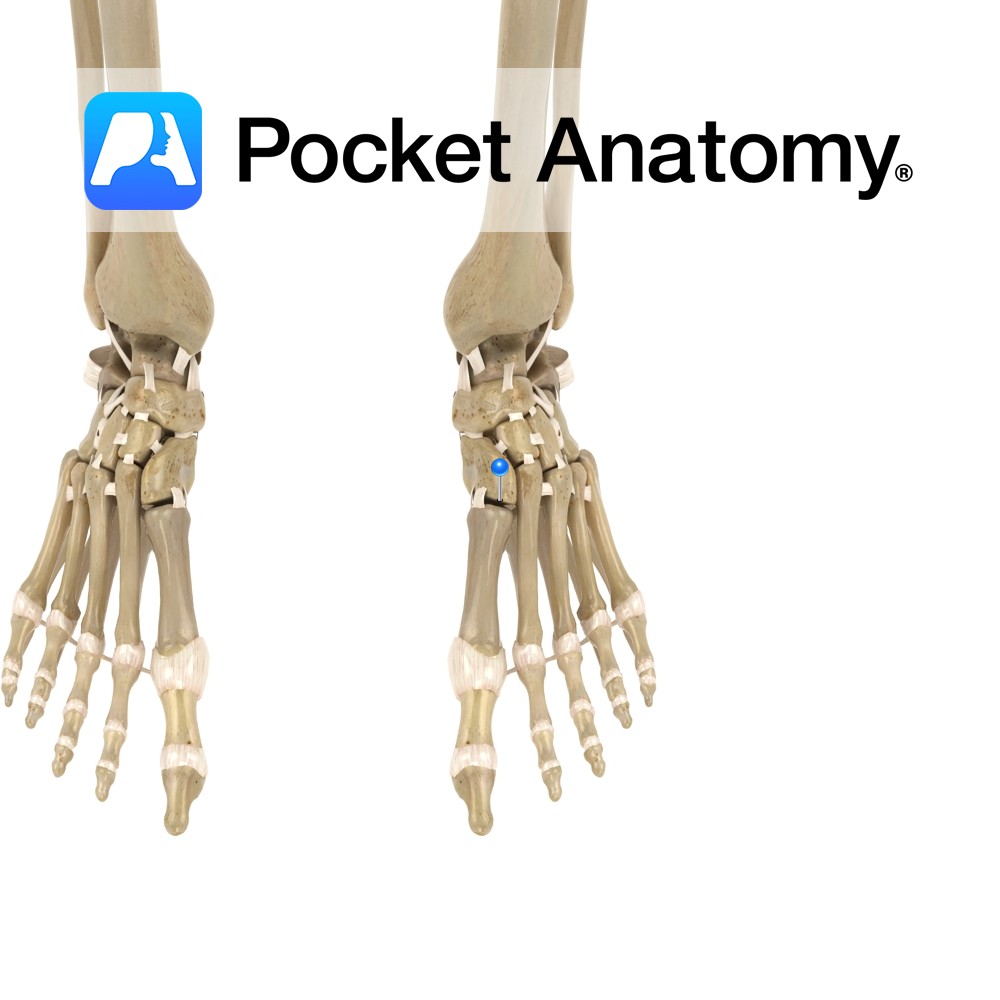
Motion The tarsometatarsal joints are synovial plane joints found in the foot. They are formed by the articulations between the five metatarsal bones and the cuneiform and cuboid bones. The 1st metatarsal articulates with the medial cuneiform, the 2nd with the intermediate cuneiform, the 3rd with the lateral cuneiform, the 4th with the lateral cuneiform
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Also known as the ear canal, connecting (runs forward and down) outer (pinna) to middle ear (outer 1/3 fibrocartilage, inner 2/3 bony). Clinical Common site for infection, foreign bodies. Cerumen (ear wax) lubricates, offers some protection against infection and insects. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
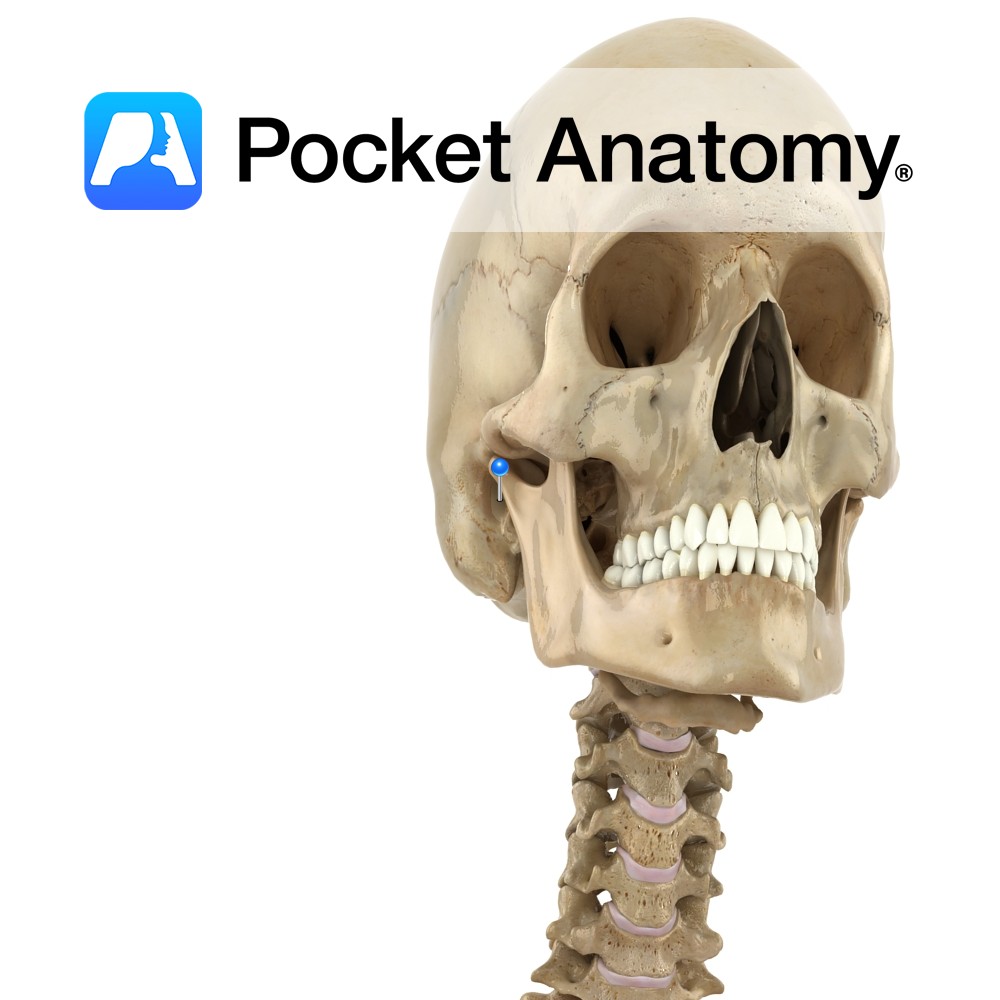
Anatomy Conical bulge from bottom surface, just behind and below external acoustic meatus. Contains small interconnected air cells/sinuses, which connect with middle ear; secrete mucus, buffer air pressure changes at eardrum. Muscles attached; splenius and longissimus capitis, digastric, sternocleidomastoid. Vignette Mastoid, ie breast-shaped. Easily felt just behind earhole, medial to pinna. Mastoiditis usually an extension
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
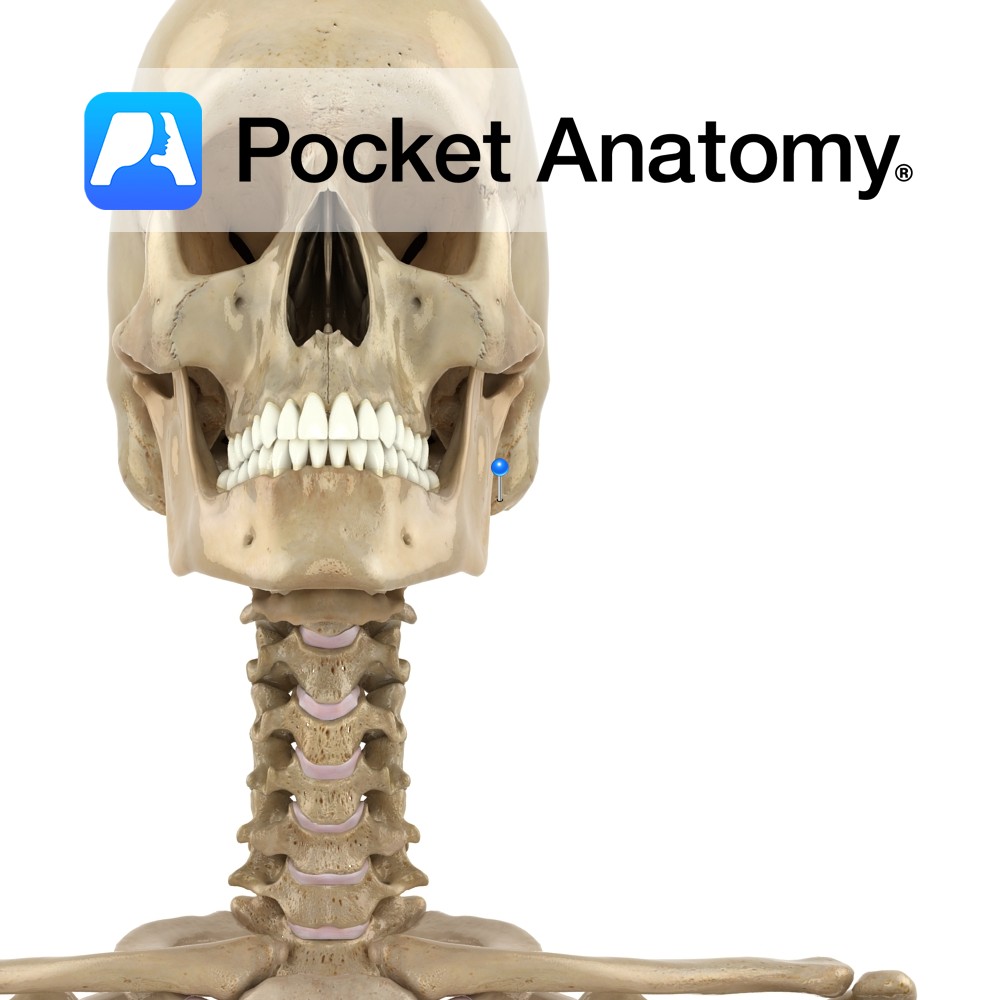
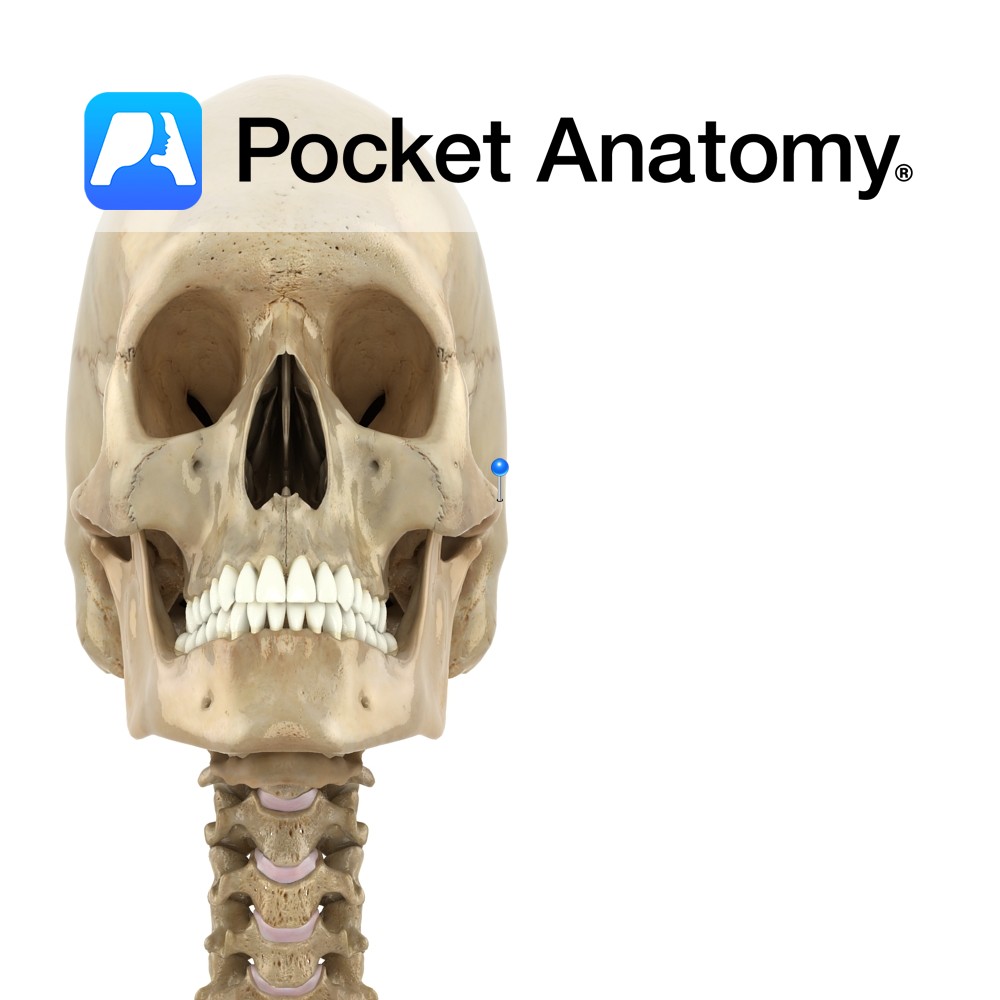
Anatomy An arched process out and forward from temporal bone. Forms an arch at side of skull with the temporal process of the zygomatic bone, in which the upper extremity of the ramus of the mandible inserts (its condylar head at the back contributing to the TMJ, and its coronoid process at the front taking
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
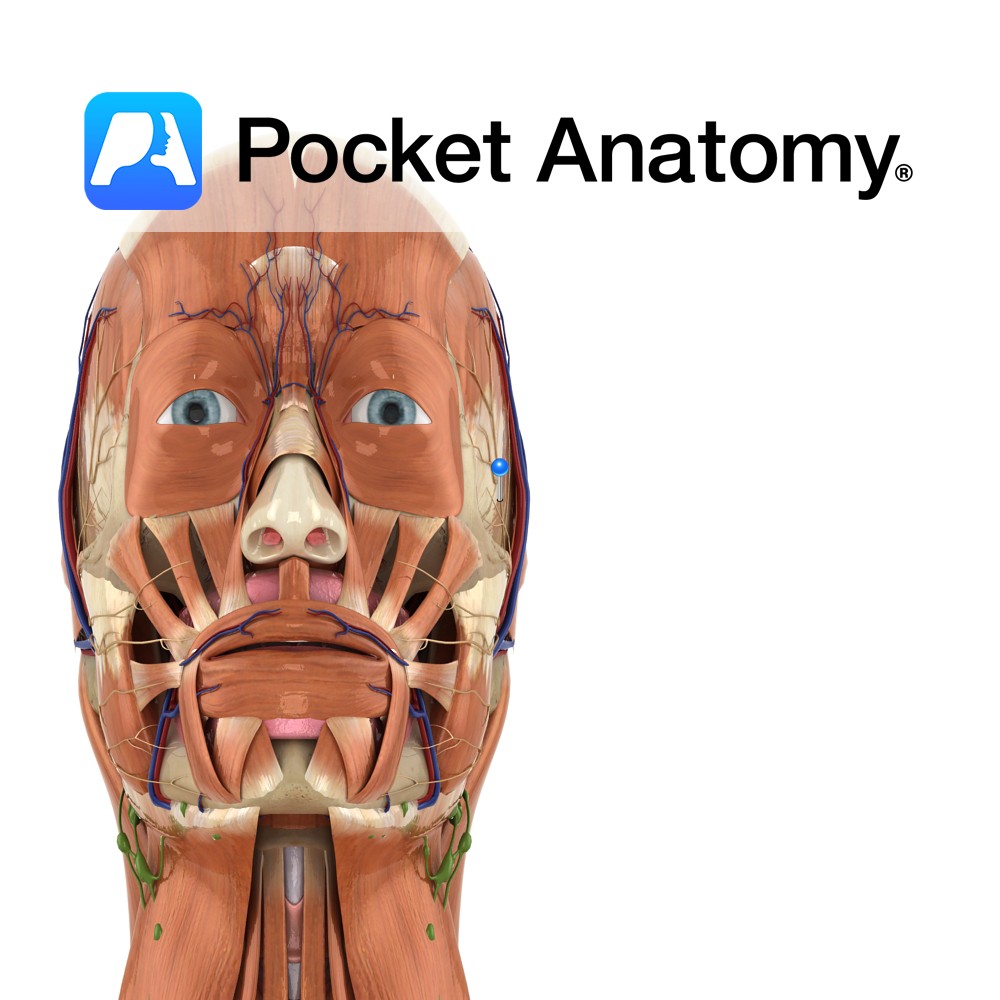
Anatomy Branch of the facial nerve (also known as the seventh cranial nerve). Facial nerve: Has a motor and sensory origin that join together to form the nerve. It passes through the internal auditory meatus through the facial canal and finally exits from the stylomastoid foramen, and into the parotid gland where it divides into
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins

.jpg)