PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
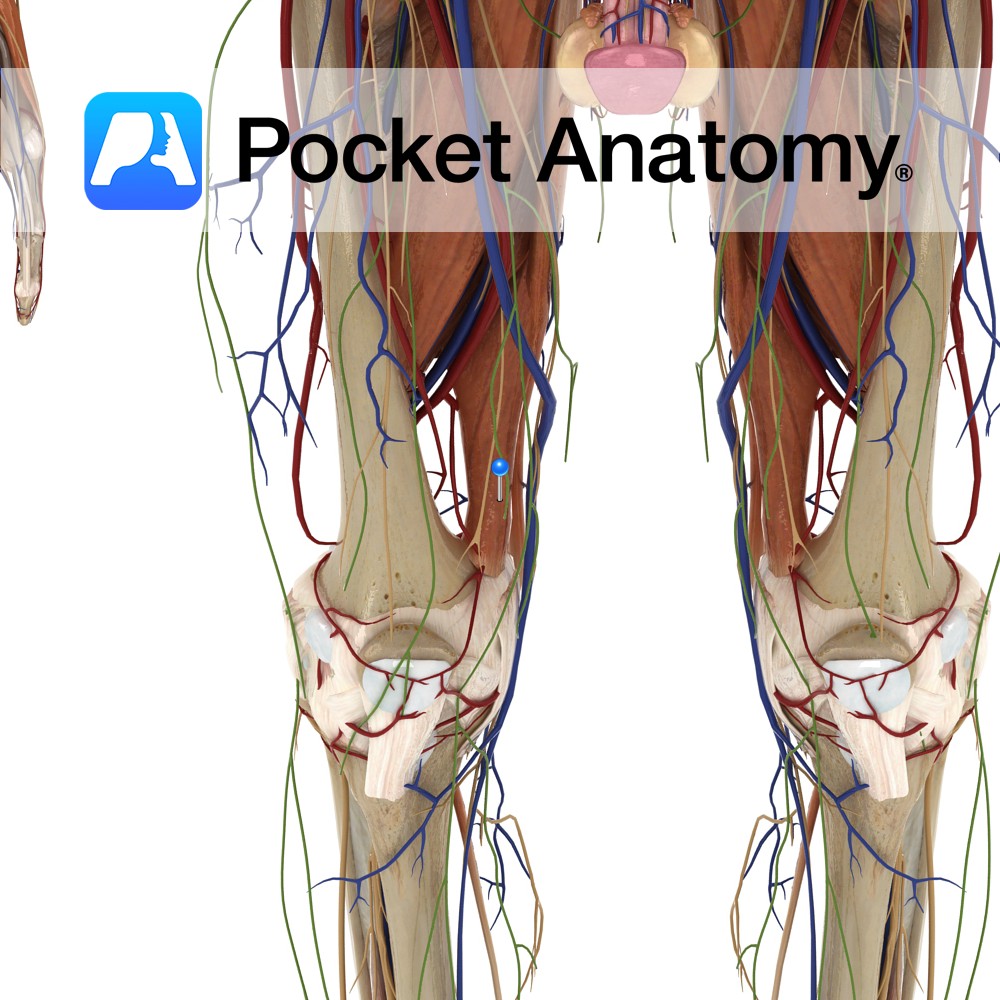
Anatomy Origin: Adductor part: Ischiopubic ramus. Hamstring part: Ischial tuberosity. Insertion: Adductor part: Gluteal tuberosity, linea aspera and the medial supracondylar line. Hamstring part: Adductor tubercle and supracondylar line. Key Relations: -One of the six muscles of the medial compartment of the thigh. -Anterior to adductor magnus are pectineus, adductor brevis, adductor longus and the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Body of the pubis, inferior to the pubic crest. Insertion: Middle third of the linea aspera of the femur. Key Relations: -One of the six muscles of the medial compartment of the thigh. -Anterior to adductor longus is the spermatic cord in males, the great saphenous vein, and near its insertion the femoral
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
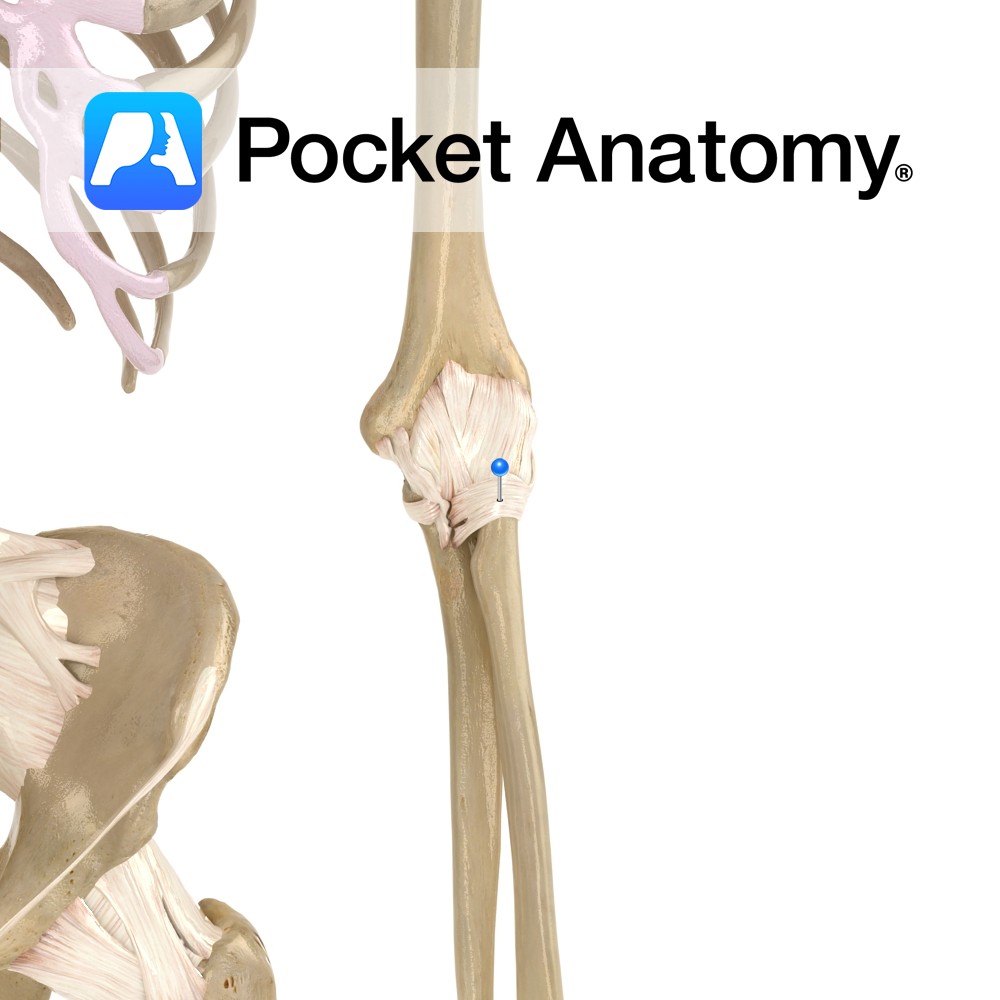
Anatomy A strong fibrous band which encircles the head of the radius. It attaches to the anterior and posterior border of the radial notch of the ulna. The superior margin of this ligament blends with the fibrous membrane of the elbow joint capsule. The ligament also blends laterally with the radial collateral ligament. Functions The
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Motion The ankle joint is a synovial hinge joint and is approximately uniaxial. It involves the articulation between the talus of the foot and the inferior surface and medial malleolus of the tibia and the lateral malleolus of the fibula. The ankle is primarily capable of hinge like plantar flexion (e.g. when pushing down an
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
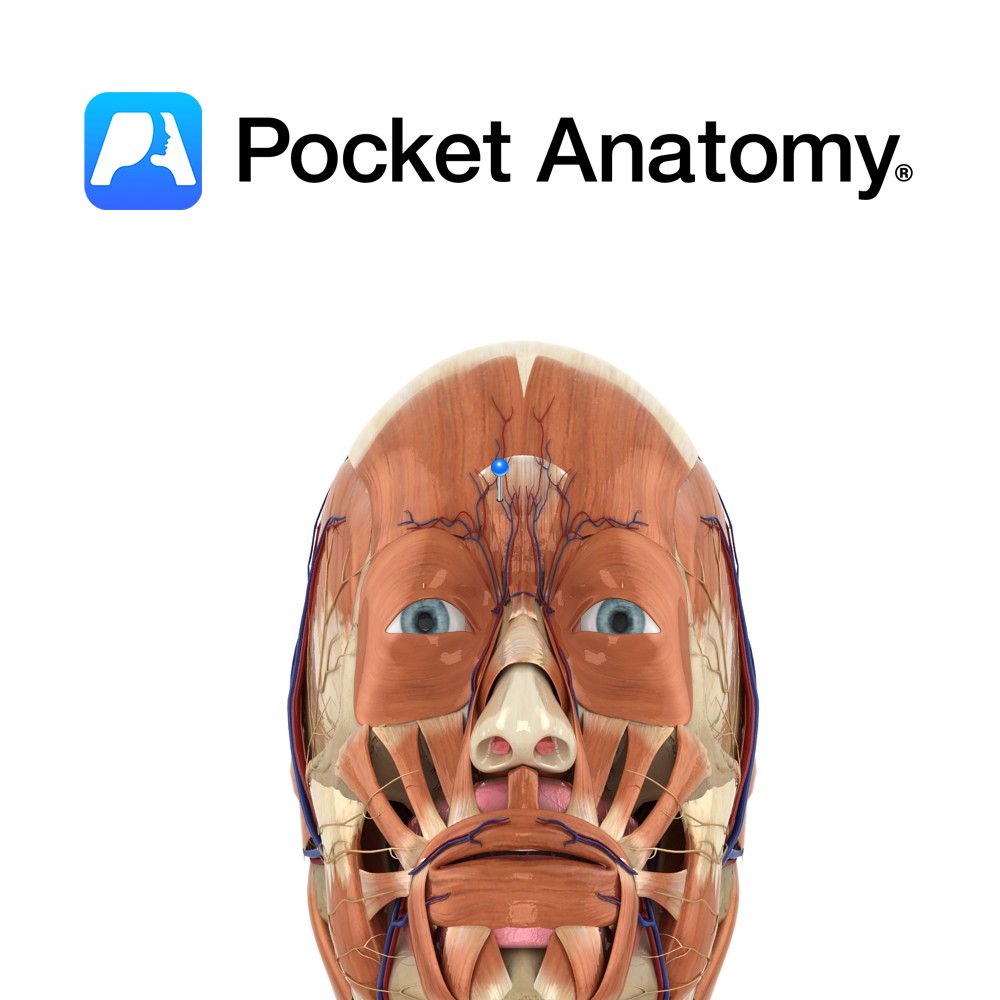
Anatomy Course Formed when the supraorbital vein and frontal vein come together. It then proceeds in a diagonal path in the crease at the base of the nose until it reaches the lower orbit where it is renamed the anterior facial vein. It is part of an anastomotic network between the cavernous sinus and the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
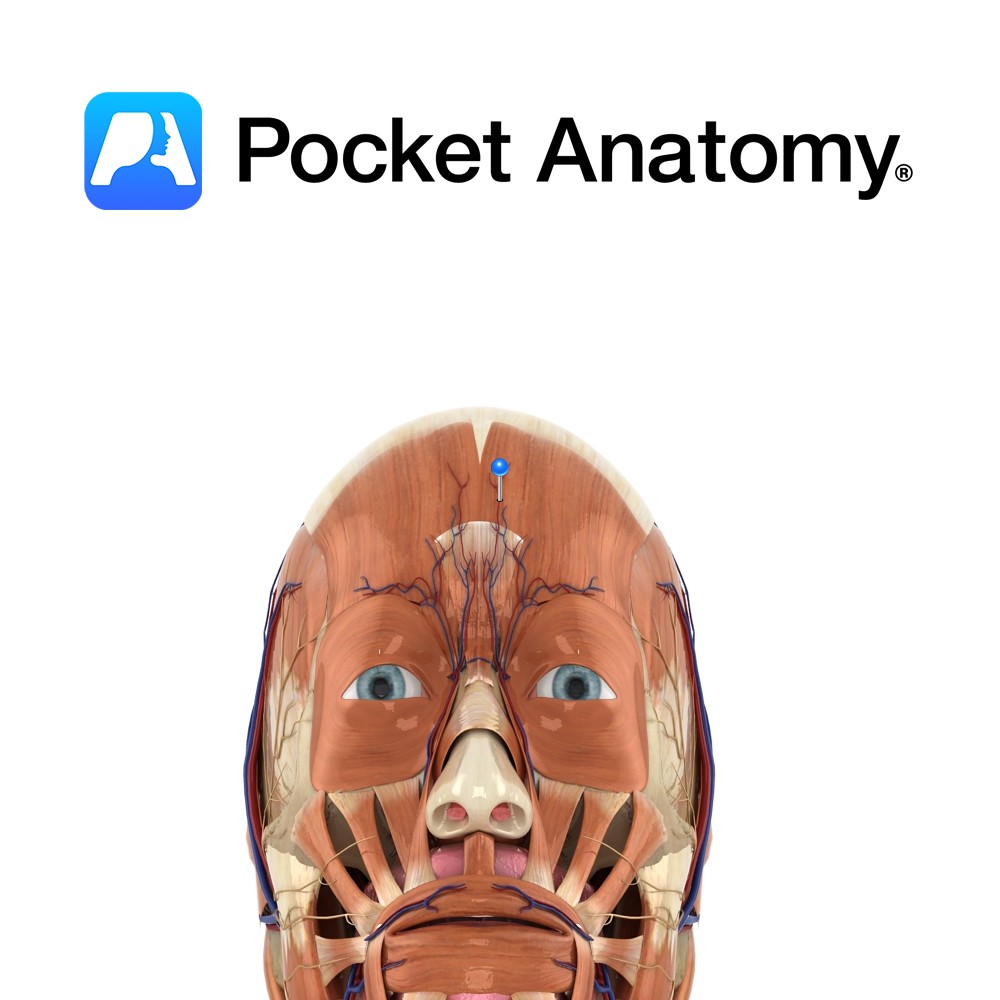
Anatomy Course One of the terminal branches of the facial artery. Ascends to the medial aspect of the eye‘s orbit, accompanied by the angular vein. There are frequent anastamoses with the dorsal nasal artery. Supply Responsible for supply to the orbicularis oculi muscle as well as the lacrimal ducts of the eye. Interested in taking
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
So, you’ve just downloaded the Pocket Anatomy app? You’re maybe spending hours spinning around the 3D models of the male and female body and have certainly been admiring the beauty of them. You’re amazed at how complex this machine is! Now, it’s high time to understand how the human body works and how each single part
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins, Teaching Anatomy
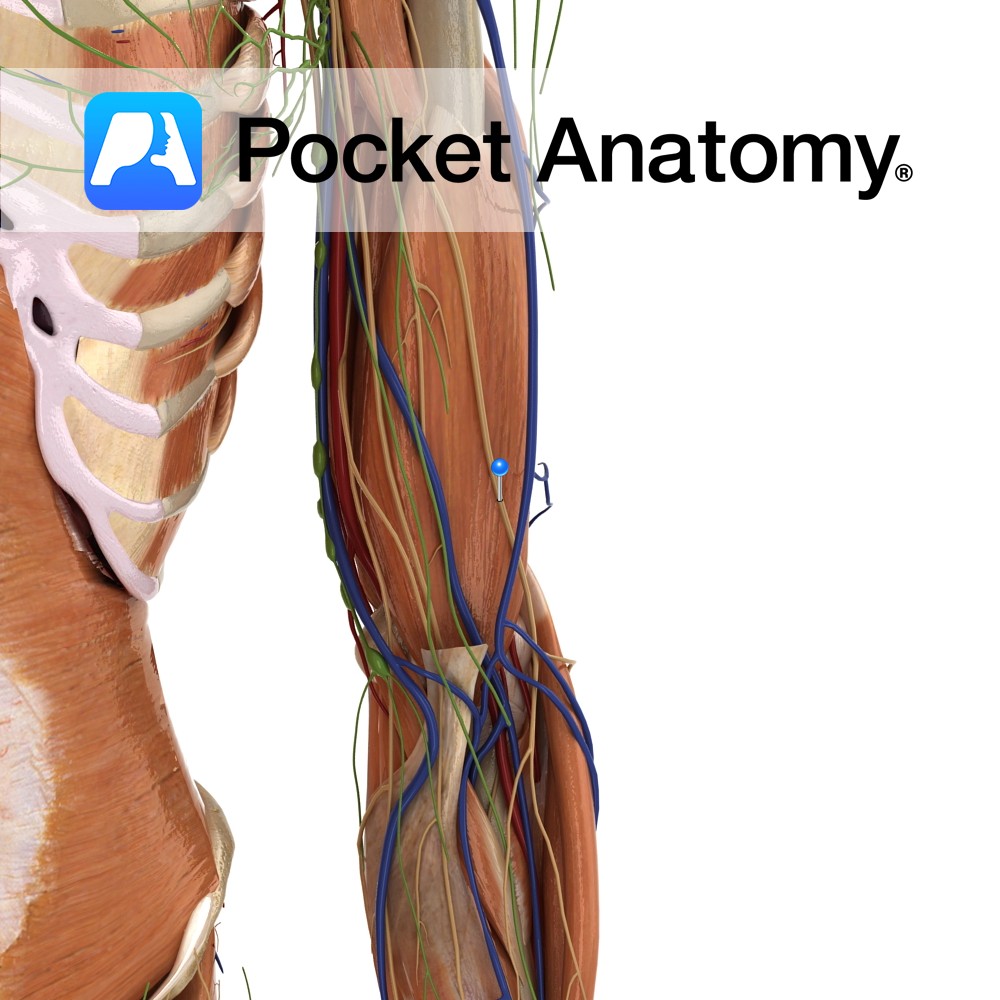
Anatomy Course A continuation of the musculocutaneous nerve in the arm. This nerve becomes the lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve once it has emerged from between the biceps brachii and the brachialis muscle, lateral to the biceps brachii tendon, passing behind the cephalic vein. It then divides into two branches, both of which run distally along
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins, Teaching Anatomy
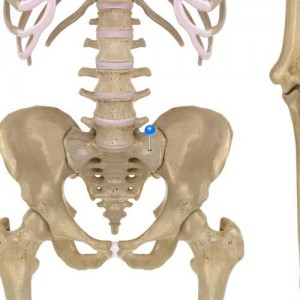
Ala of Sacrum anatomy Ala of sacrum is a large triangular surface either side of sacral base, continuous with iliac fossa (akin to adapted and joined transverse and costal processes elsewhere spine). Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins, Teaching Anatomy
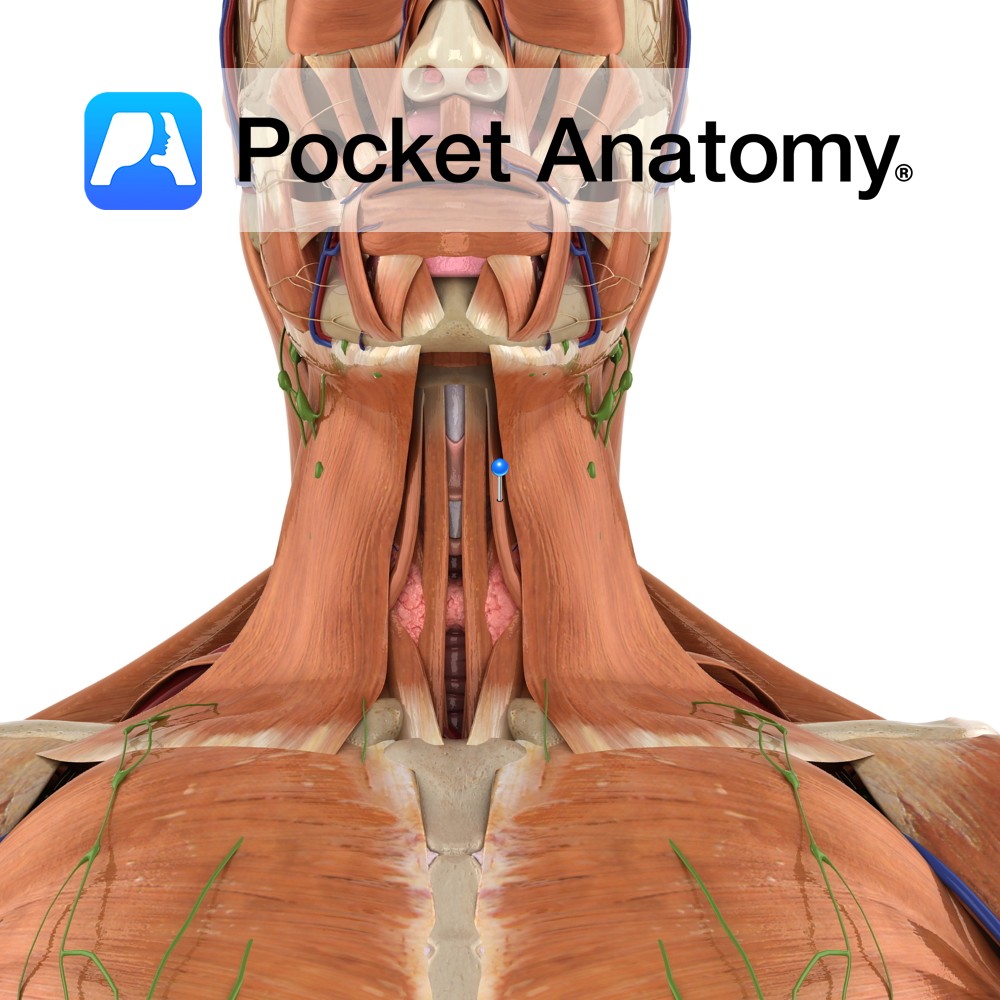
Anatomy Origin: Superior border of scapula medial to suprascapular notch. Insertion: Body of hyoid bone. Key Relations: -Is one of the infrahyoid muscles (sometimes referred to as ‘strap muscles’) lying in the muscular triangle of the neck. -Lateral to sternohyoid. Functions Depresses and fixes the hyoid bone. Supply Nerve Supply: Anterior rami of C1 to
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins, Teaching Anatomy


.jpg)