PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
Anatomy Origin: Lateral and medial processes of the calcaneal tuberosity and plantar aponeurosis. Insertion: Lateral surface of the base of the 5th proximal phalanx. Key relations: -Lies on the lateral surface of the foot. -The lateral plantar vessels and nerve located medially. Functions Abducts the 5th toe at the metatarsophalangeal joint. Supply Nerve supply: Lateral
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
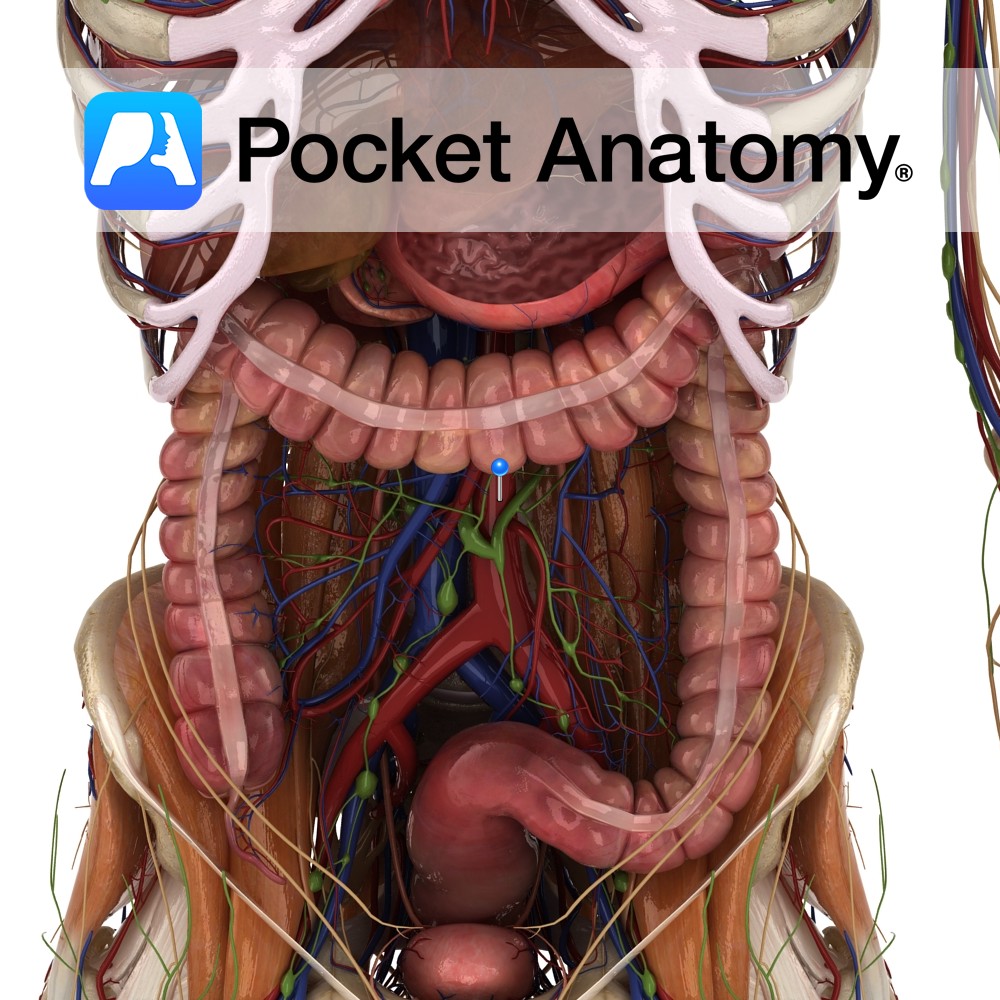
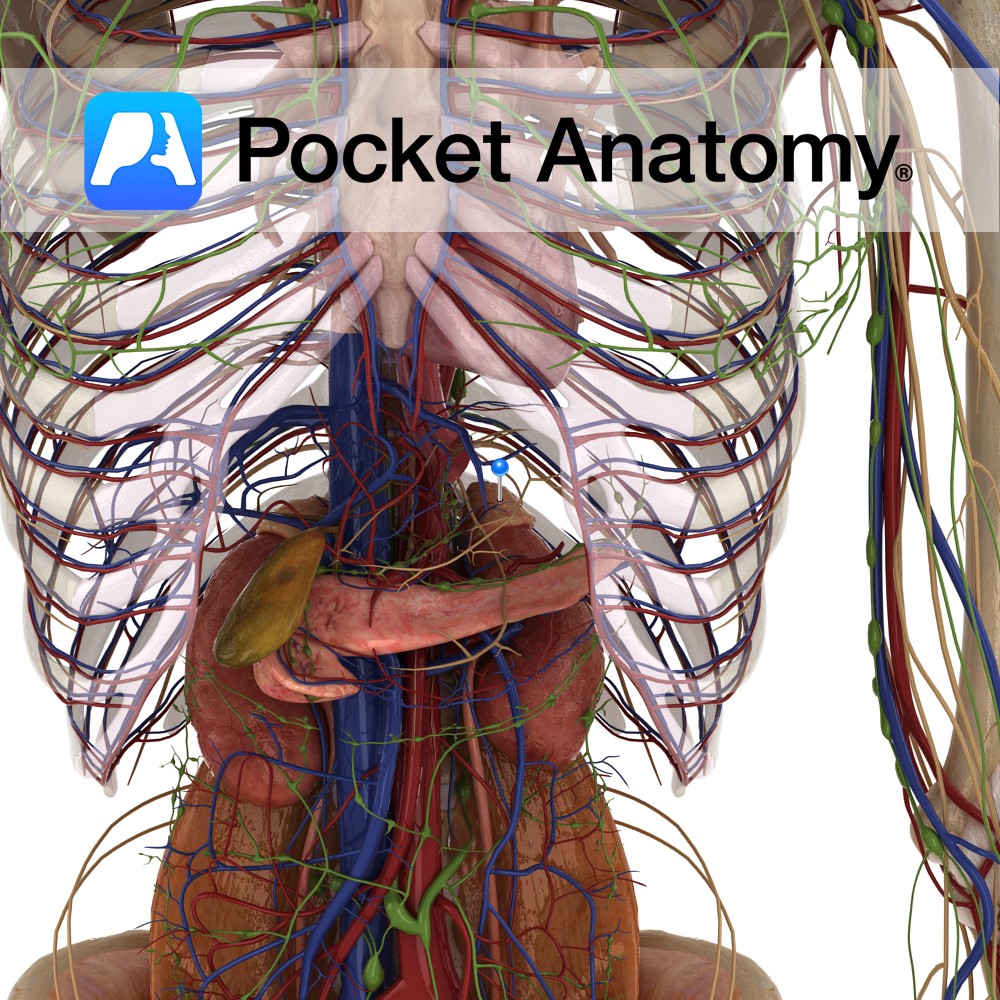
Anatomy Course Enters the abdomen as a continuation of the thoracic aorta by passing through the aortic hiatus of the diaphragm at the level of T12. Descends downward slightly to the left of the midline until it bifurcates into the left and right common iliac arteries at the level to L4. The inferior vena cava
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Body and inferior ramus of pubic bone. Insertion: Pectineal line and proximal part of linea aspera of the femur. Key Relations: -One of the six muscles of the medial compartment of the thigh. -Lies posterior to pectineus, adductor longus and the anterior branch of the obturator nerve. -Posterior to adductor brevis are adductor
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
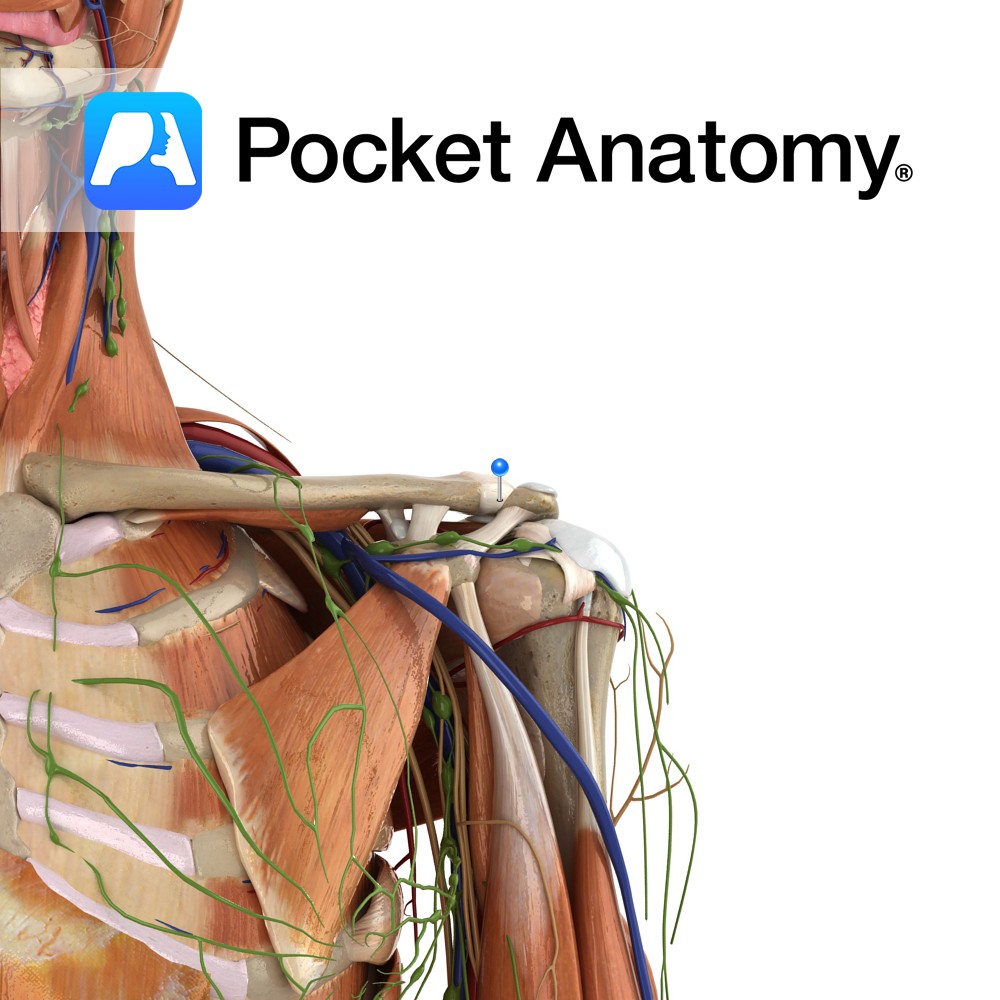
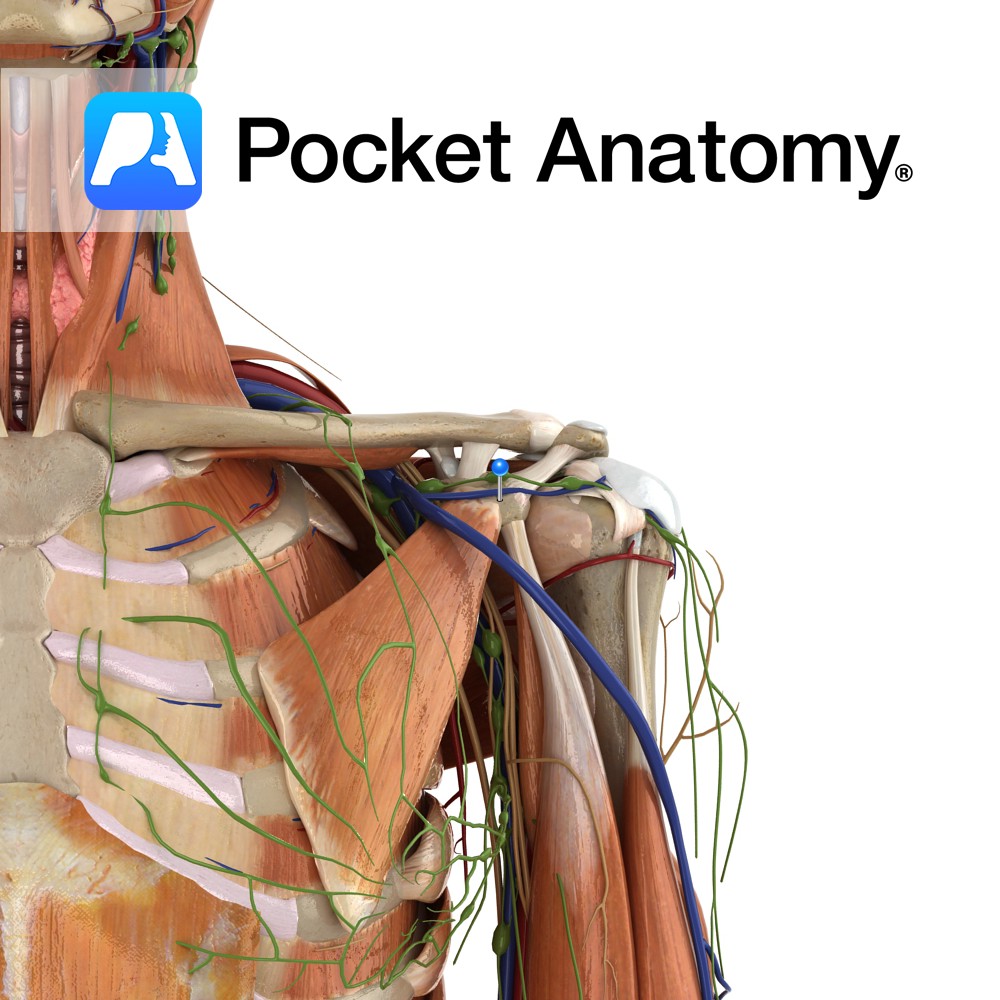
Anatomy The acromioclavicular ligament lies superiorly to the acromioclavicular joint. It is a thickening of the acromioclavicular capsular ligament. It attaches from the superior lateral end of the clavicle to the adjacent superior surface of the acromium. Functions Stabilises the acromioclavicular joint along with the coracoclavicular ligament. Clinical The acromioclavicular joint is a very unstable
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
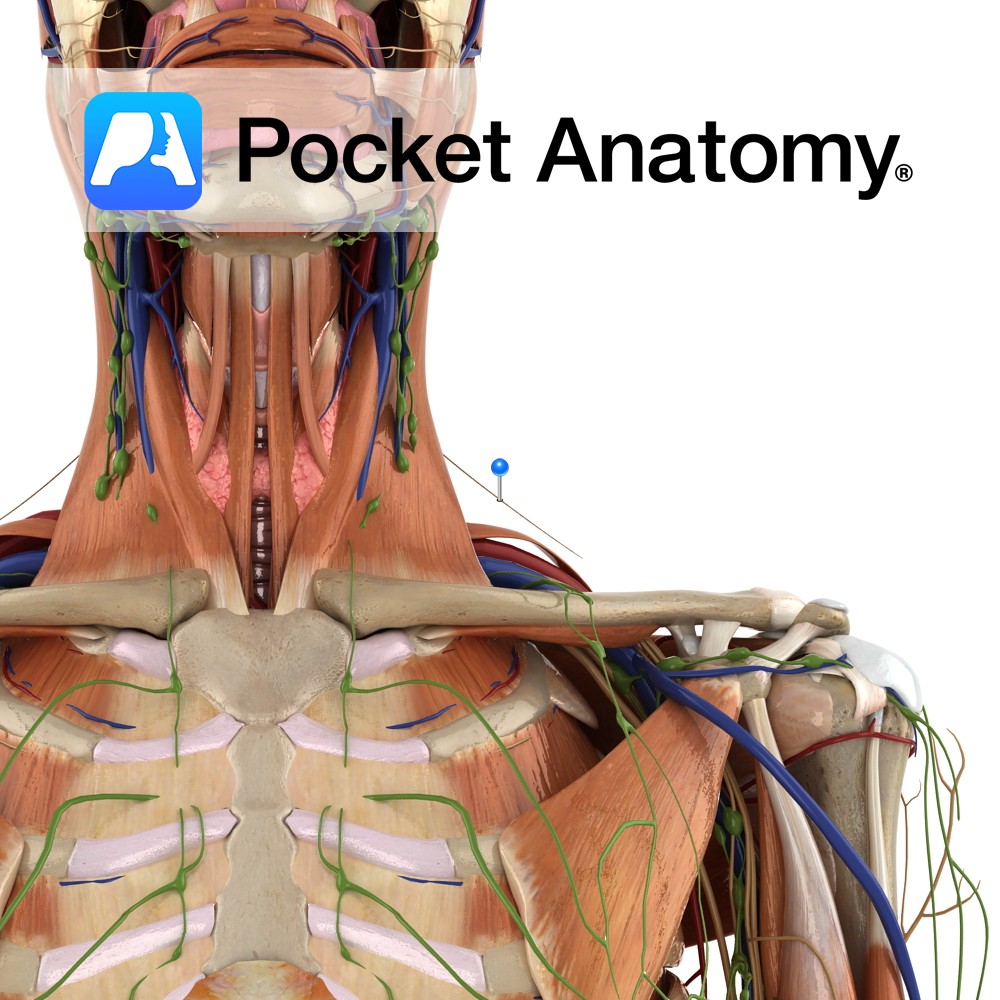
Anatomy Course Part of a network of veins that can be found in the shoulder. It follows a similar path to its corresponding artery. Drain Drains the scapular region of the back. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Also known as the eleventh cranial nerve, its spinal root enters the cranium via the foramen magnum to join the cranial root, and it then exits via the jugular foramen along with the glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves. Once out of the cranium, the cranial portion of the nerve dissociates and joins the vagus
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
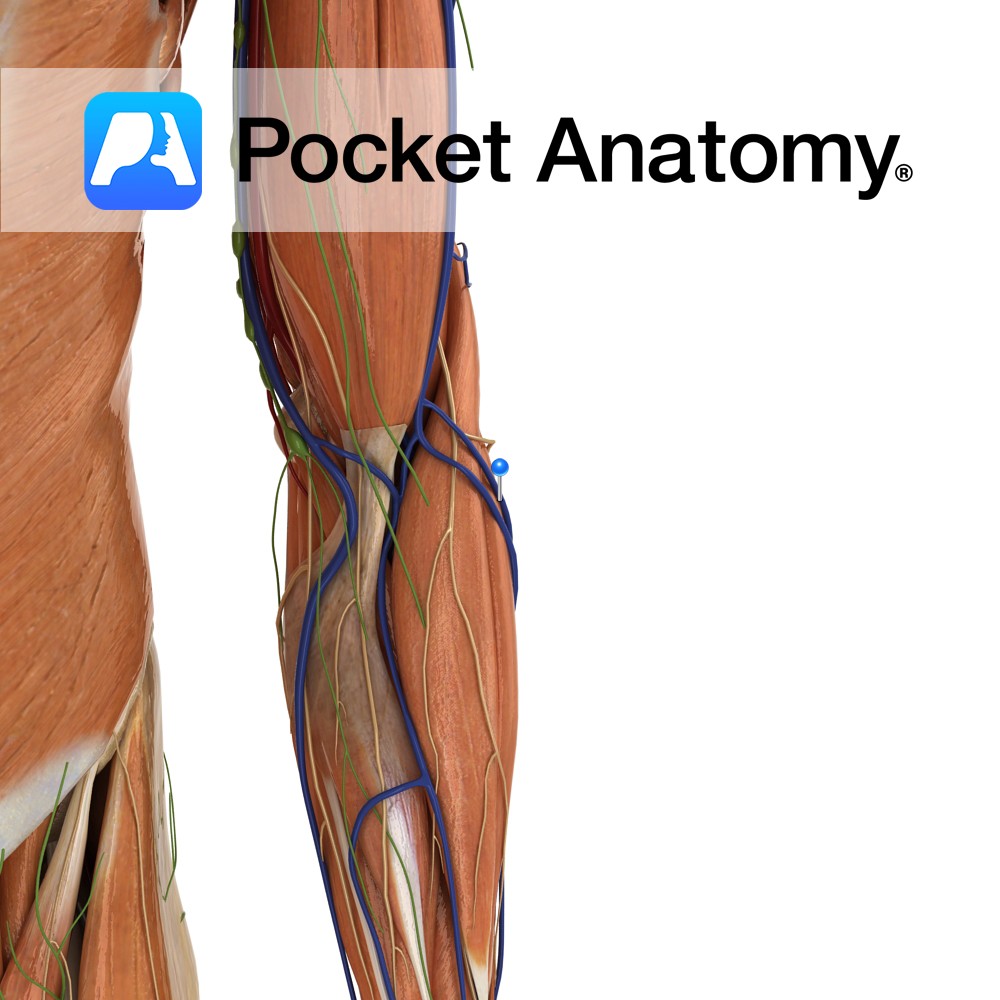
Anatomy Course Arises from a small plexus on the posterior forearm and rises on the lateral side until it joins the cephalic vein at the elbow. Drain Drains the posterior side of the forearm. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Lateral epicondyle of humerus. Insertion: Lateral aspect of olecranon of ulna and proximal quarter of posterolateral aspect of ulna. Key Relations: One of the six muscles in the deep posterior compartment of the forearm. Functions Assists triceps with extension of the forearm at the elbow. e.g. as in pushing a door closed.. Supply
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Small (triangular 2×1″, 3.5-5 gm) paired endocrine gland on top of kidneys upper abdomen, under diaphragm, retroperitoneal; secrete and release hormones involved in – regulation of metabolic rate, immune system, water-salt balance, response to stress; 2 types of tissue, cortex and medulla (encapsulated outer and inner layers); cortex is larger part, 3 zones –
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
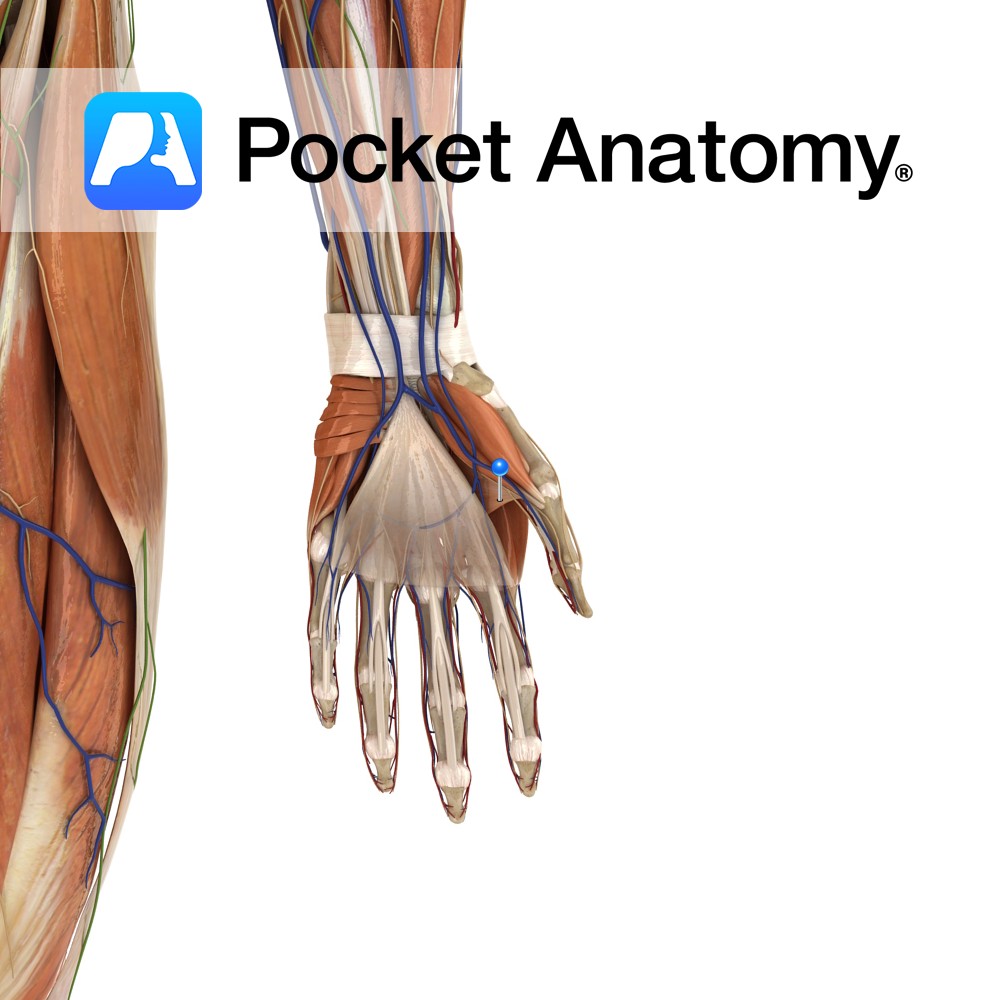
Anatomy Origin: Oblique head: capitates and bases of the second and third metacarpals. Transverse head: ulnar aspect of third metacarpal. Insertion: Base of proximal phalanx of the thumb. Key relations: The radial artery passes between the two heads on its course from the dorsal aspect to the palmar aspect of the hand where it forms
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins

.jpg)