PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
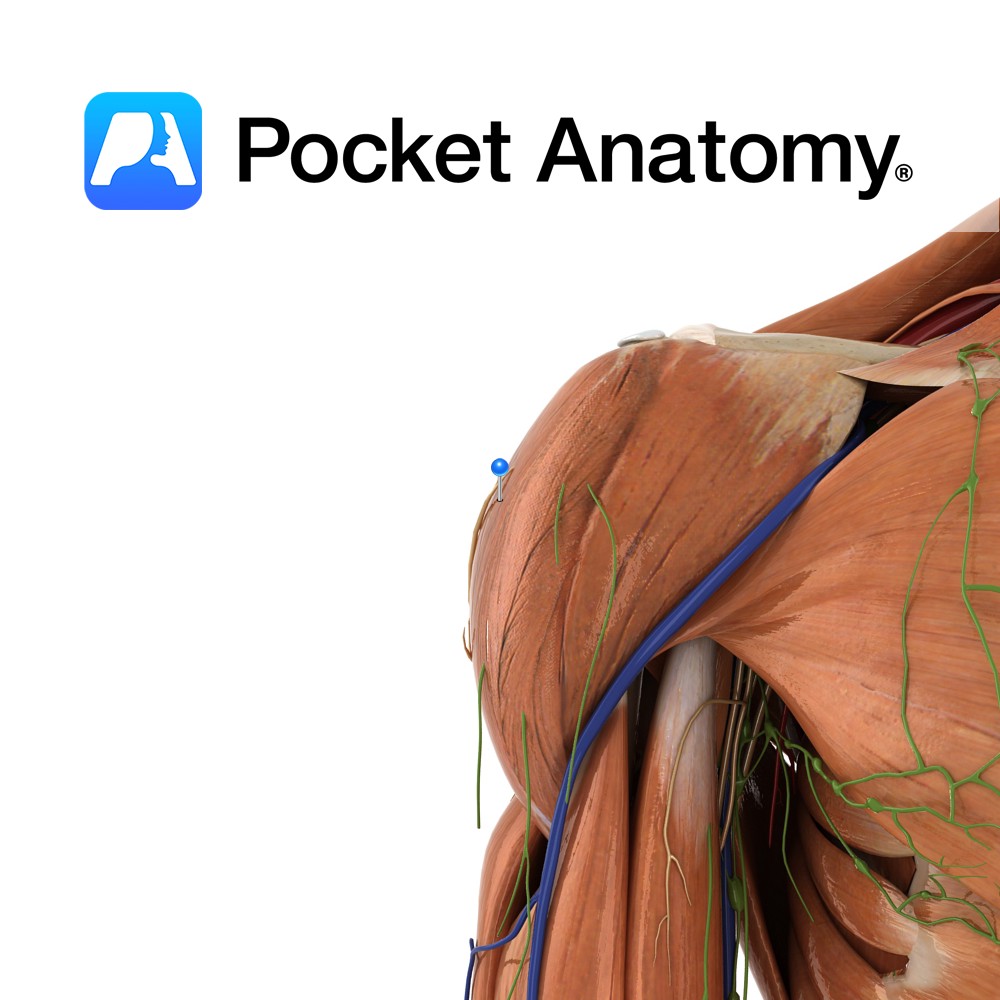
Anatomy The axillary nerve arises from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus and exits through the quadrangular space along with the anterior circumflex humeral artery and posterior circumflex humeral vein. Supply Supplies the deltoid, teres minor and triceps brachii (long head), as well as carrying sensory information from the skin covering the inferior region
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
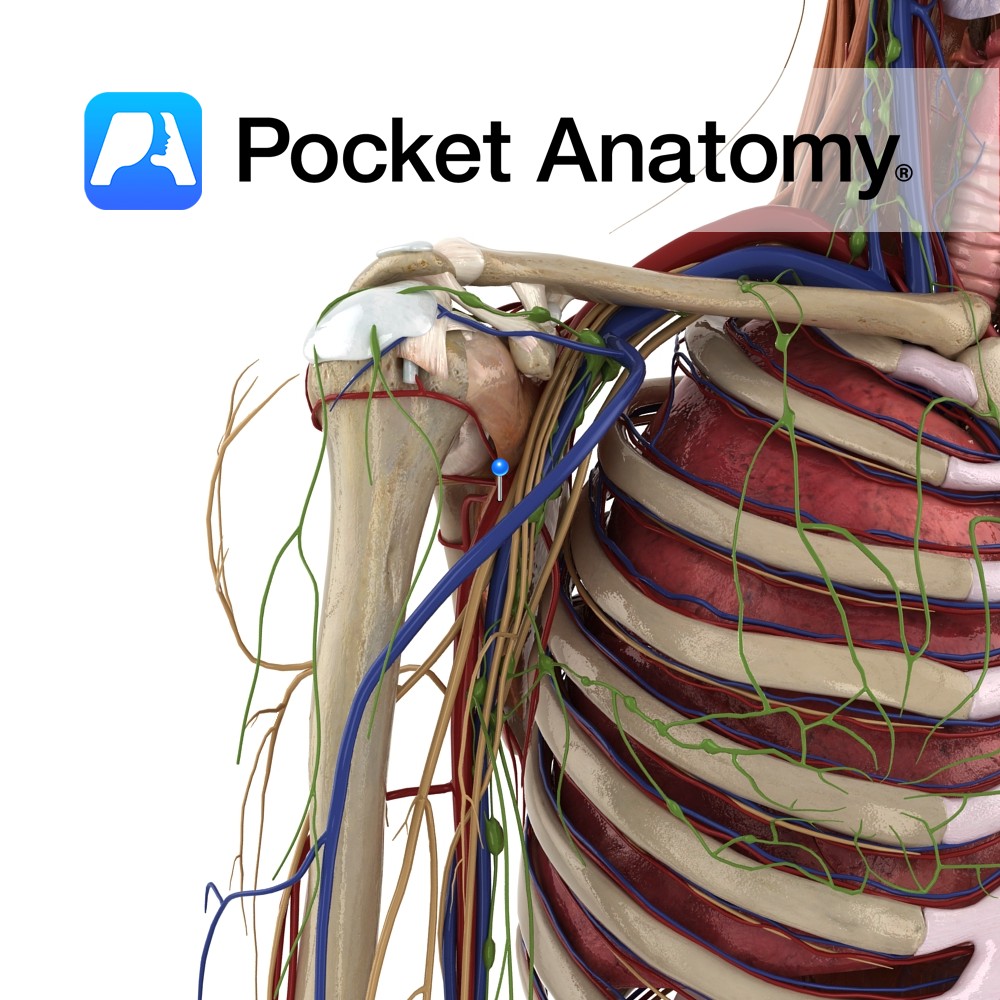
Anatomy Course Continuation of the subclavian artery after it passes the lateral margin of the first rib. It passes through the axillary inlet in association with the axillary vein, which is anterior to the artery. Separated into three parts by the pectoralis muscles. Supply Supplies the distal aspect of the arm. Clinical Fracture of the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
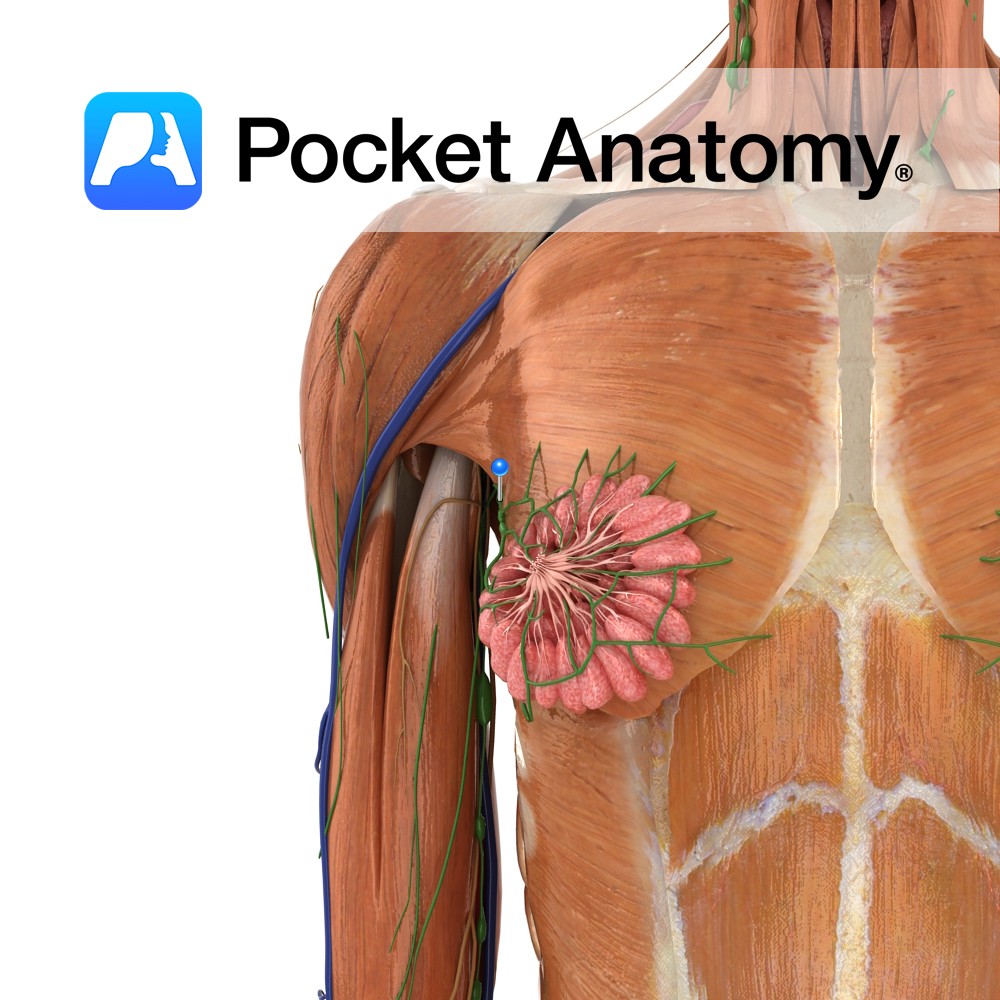
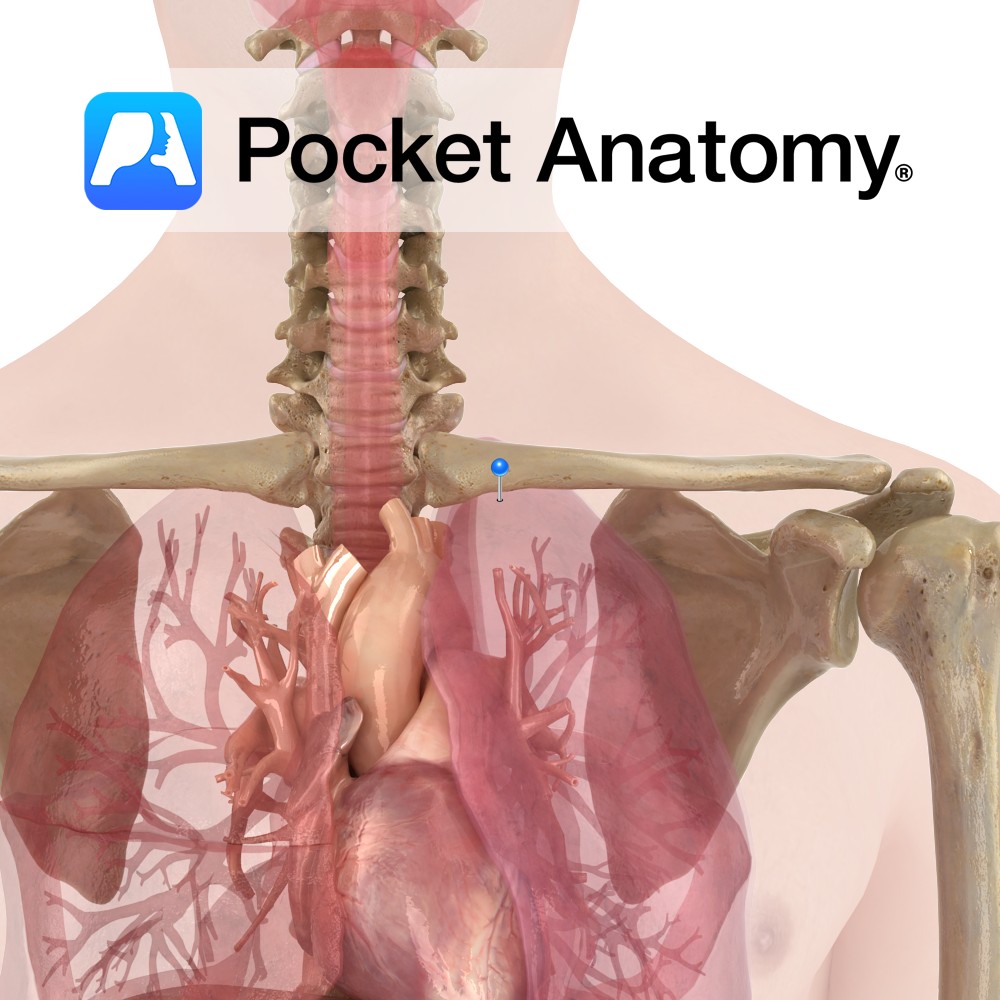
Anatomy Cluster/group of nodes, in armpit. Afferent vessels bring lymph from arm, thoracic walls, breast, upper parts of abdominal walls. Efferent vessels pass filtered lymph on via the Subclavian Trunk to the Lymphatic (Thoracic) Duct; R empties into the R Subclavian Vein, L into L Brachiocephalic (aka Innominate) Vein, each through semilunar valves (which prevent
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
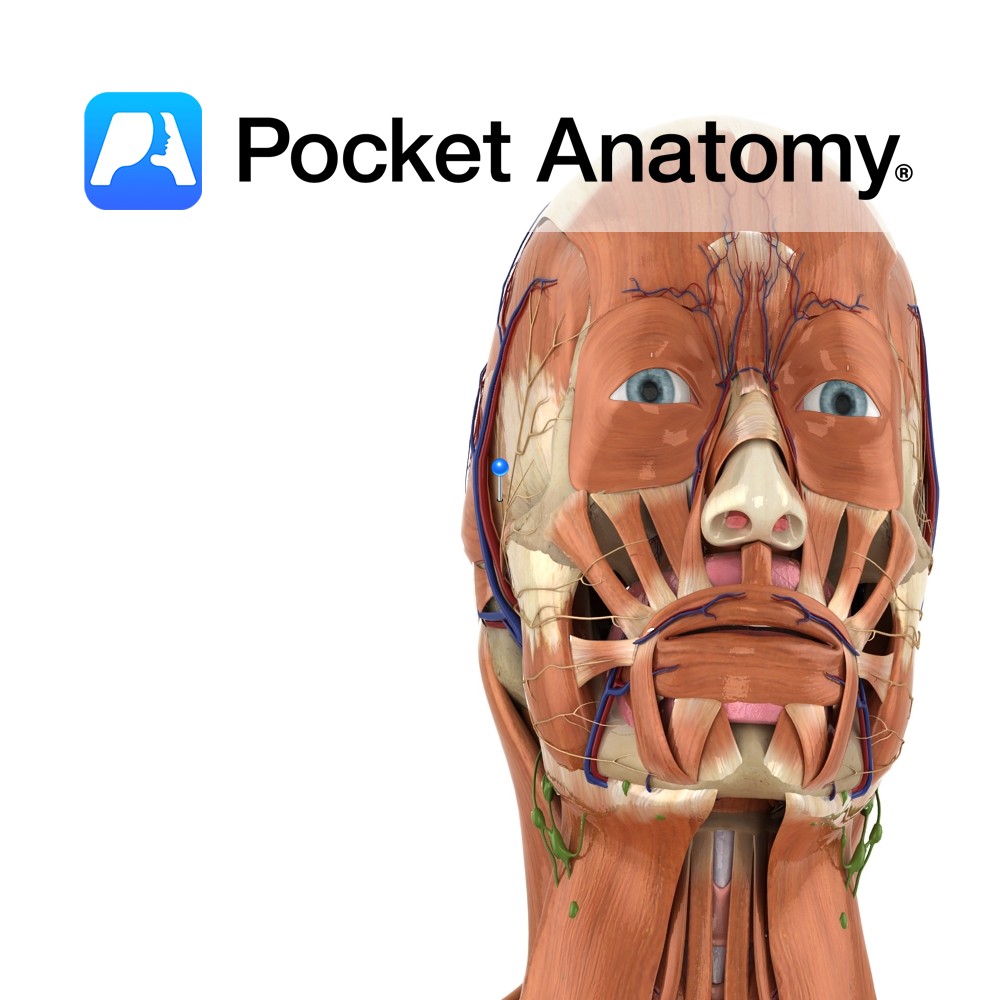
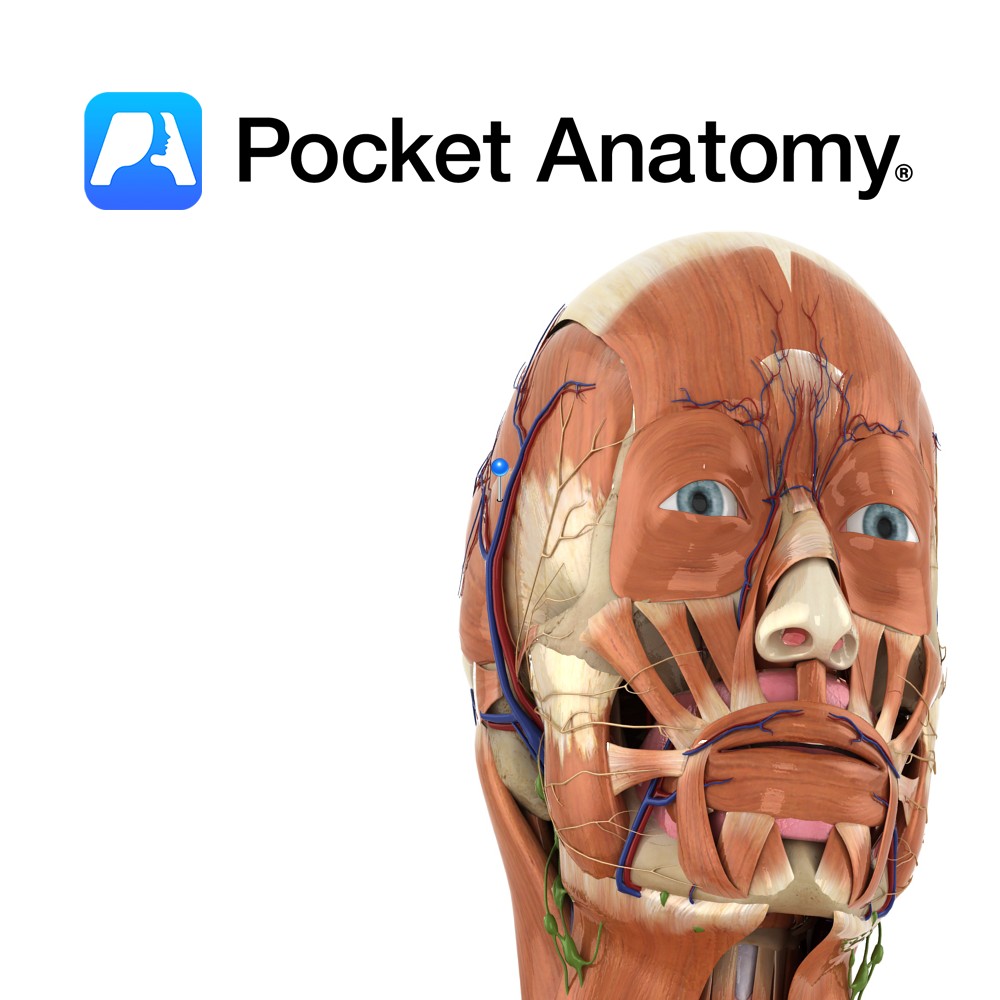
Anatomy Course Composed of two different roots of the mandibular nerve, which pass along both sides of the middle meningeal artery. It travels with the superficial temporal artery and vein to the neck of the mandible. It then travels anteriorly to cross the zygomatic process of temporal bone giving off branches along its route. Supply
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Epicranial aponeurosis on the lateral aspect of the head. Insertion: Upper part of the auricle. Key Relations: Lies superior to the ear on the lateral surface of the head. Functions Elevates the ear. Supply Nerve Supply: Facial nerve (CN 7) Blood Supply: Superficial temporal artery. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Functions The ventilation /perfusion ratio is higher at the apex of the lung, meaning more air reaches the apex than blood to carry it. paCO2 is decreased and paO2 increased in this area (similar findings to pulmonary embolism or emphysema, though not pathological). Moderate exercise increases perfusion in the apical lung, hence increasing V/P ratio.
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
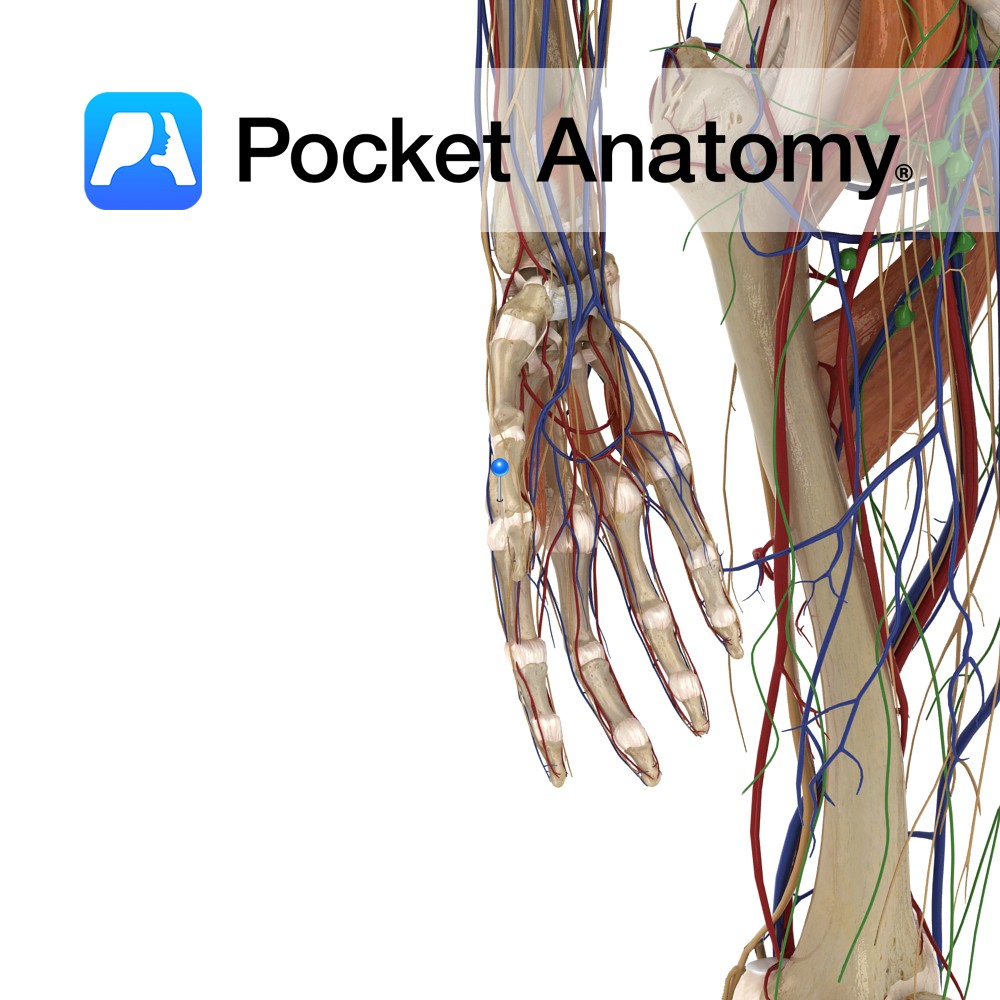
Anatomy Origin: Middle thirds of posterior of radius and ulna and intervening interosseus membrane. Insertion: Lateral aspect of base of 1st metacarpal. Key Relations: -Its tendon together with the tendon of extensor pollicis brevis forms the anterior boundary of the anatomical snuff box. -One of the six muscles in the deep posterior compartment of the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Tubercles of scaphoid and trapezium and adjacent flexor retinaculum. Insertion: Proximal phalanx and extensor apparatus of the thumb. Key Relations: Is one of the muscles of the thenar eminence of the hand. Functions -Abduction of the thumb at the carpopmetacarpol and metacarpophalangeal joints. -Also assists in thumb opposition and extension. Supply Nerve Supply:
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
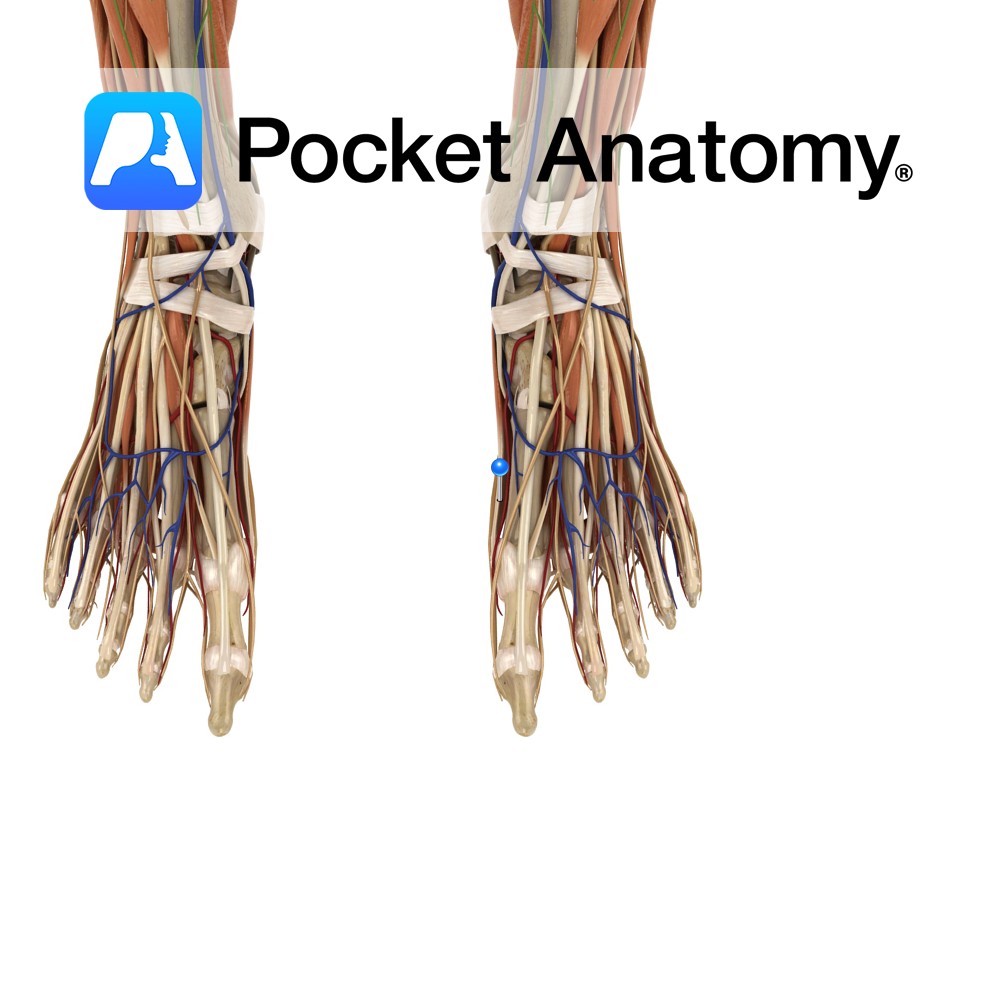
Anatomy Origin: Medial process of the calcaneal tuberosity, flexor retinaculum and plantar aponeurosis. Insertion: Medial surface of the base of the proximal phalanx of the hallux (big toe). Key relations: Lies on the medial surface of the foot and contributes to a soft tissue bulge on the medial part of the sole of the foot.
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
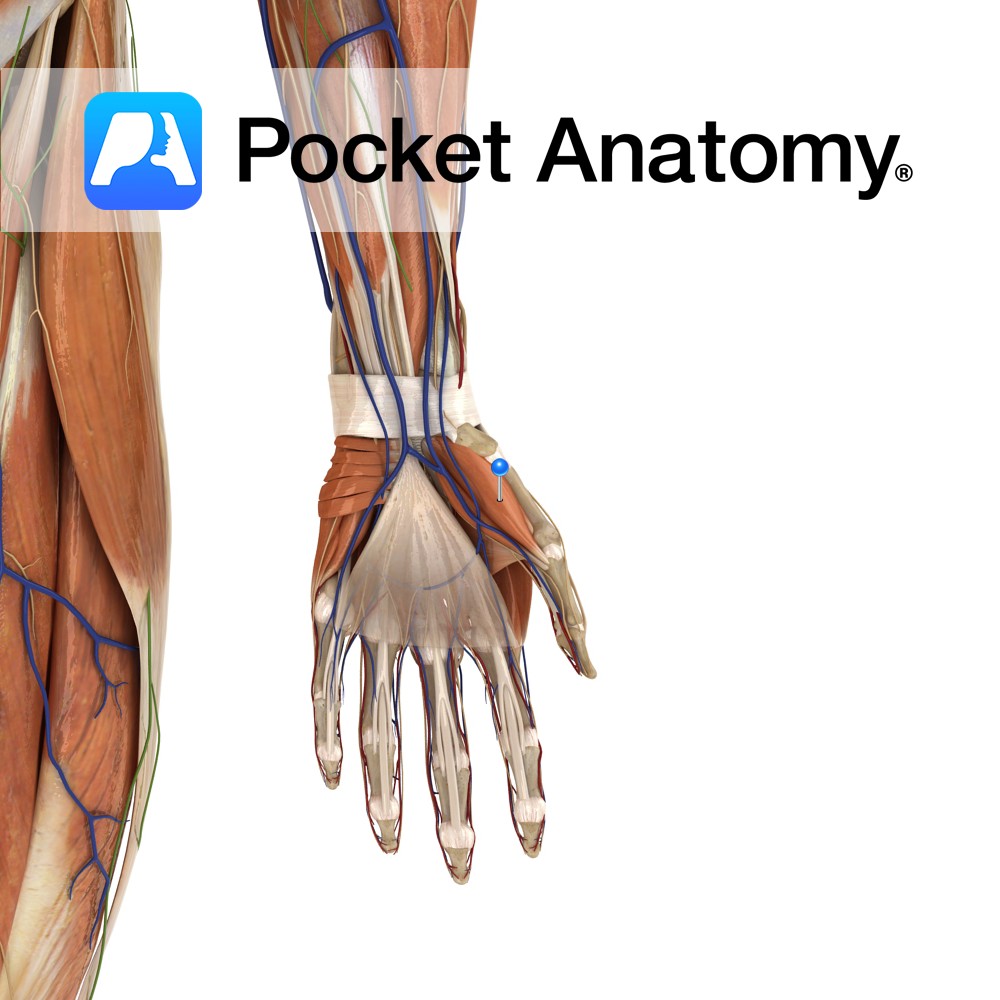
Anatomy Origin: Pisiform and tendon of flexor carpi ulnaris. Insertion: Ulnar aspect of the base of the proximal phalanx of the little finger and ulnar border of the extensor apparatus of the little finger. Key Relations: Is one of the muscles of the hypothenar eminence of the hand. Functions Abduction of the little finger at
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins

.jpg)