PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
Anatomy Course A network of nerve fibers running from the spine to neck, axilla and forearm. It is divided into roots (C5, C6, C7, C8, T1), trunks (superior, middle and inferior), divisions (3 anterior and 3 posterior), cords (lateral, posterior and medial), and terminal branches (musculocutaneous, axillary, radial, median and ulnar nerves). Supply Responsible for
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
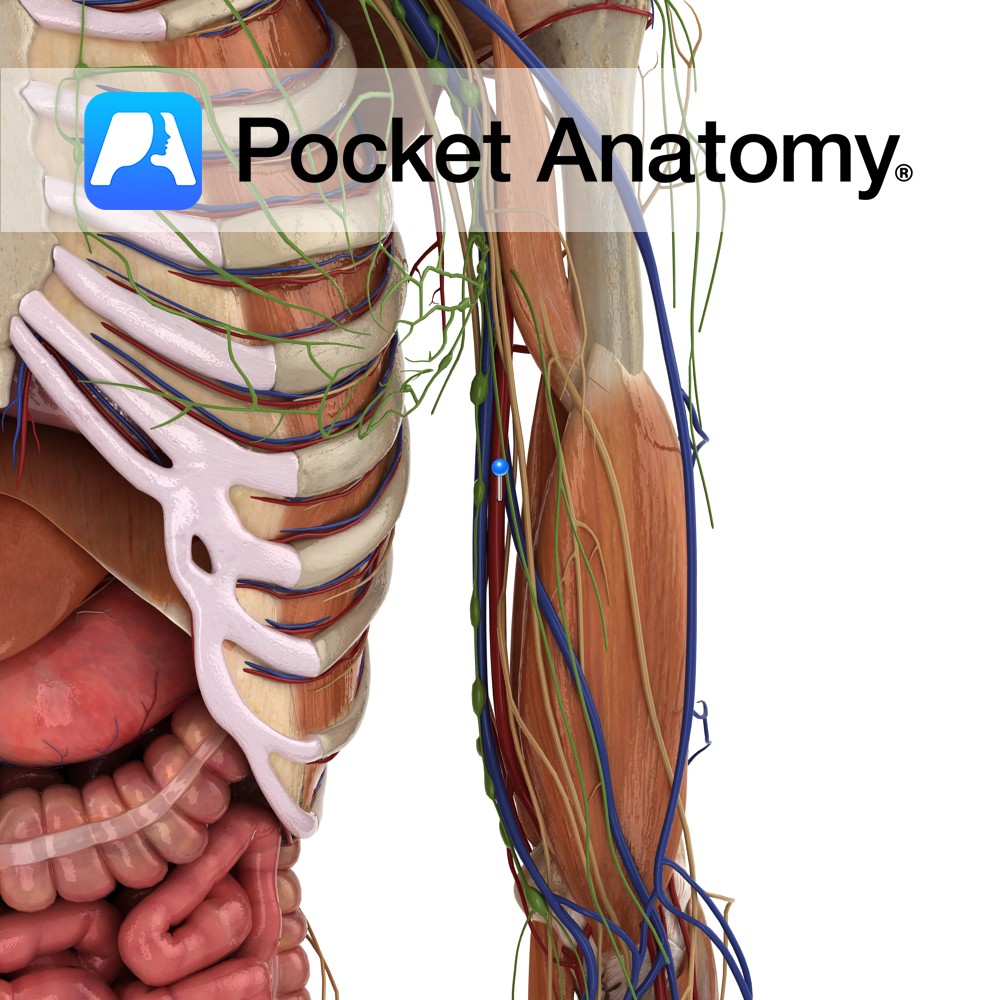
Anatomy Course Continuation of the axillary artery after it has passed the inferior border of the teres minor muscle. It continues to proceeds downwards on the ventral surface of the arm until it reaches the cubital fossa, where it bifurcates in the radial and ulnar arteries. (Bifurcation sometimes occurs higher in the arm in some
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy One of the three layers in living bone. Surrounded and protected by Compact Bone, Marrow is spongy and sits in the Medullary Cavity, the central cavity of bone shafts. Yellow and Red Bone Marrow is produced and stored. In infants, all of the marrow is Red. Red marrow produces red and white blood cells,
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
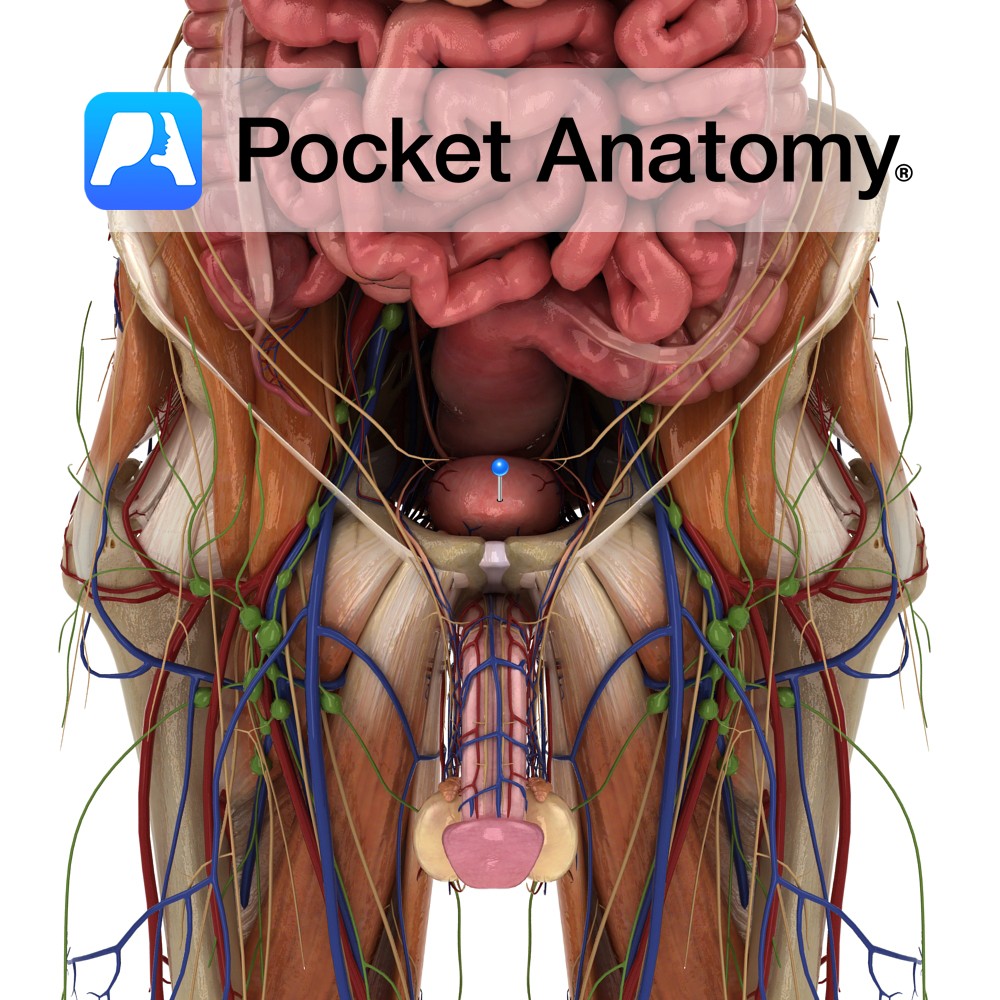
Anatomy Hollow distensible muscular organ, extra-peritoneal on pelvic floor behind pubic symphysis; 300-600 mls capacity; urine enters through ureteral openings 2-3 cms apart in posterior wall, is extruded through internal urethral orifice below (trigone the area thus bounded); dome, posterior surface covered with peritoneum; neck fixed by true ligaments of pelvis and fascia; body supported
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
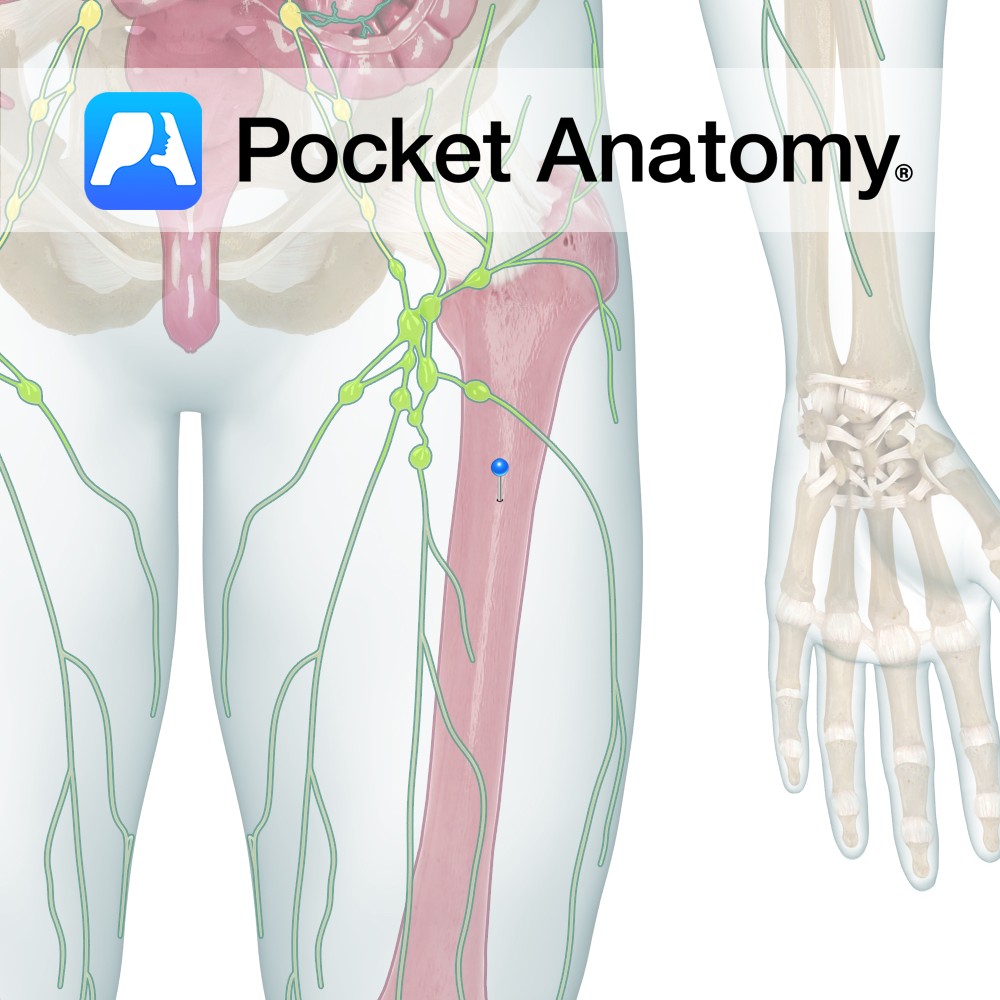
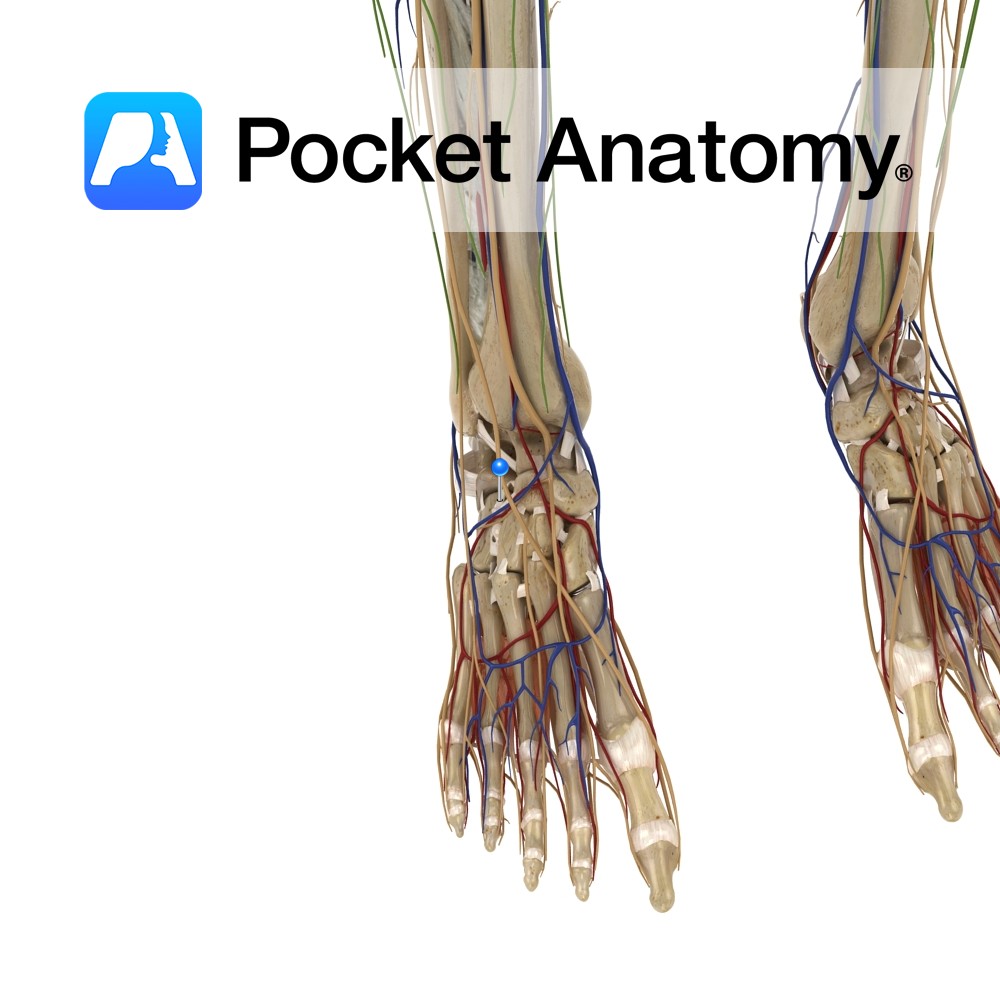
Anatomy The calcaeonavicular part of the bifurcate ligament is Y-shaped and superior to the joint. It attaches from the anterior aspect of the superior surface of the calcaneus: The dorsal lateral part of the navicular (calcaeonavicular ligament). The dorsal medial surface of the cuboid ( calcaeocuboid ligament). Functions Reinforces the lateral part of the talocalcaneonavicular
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
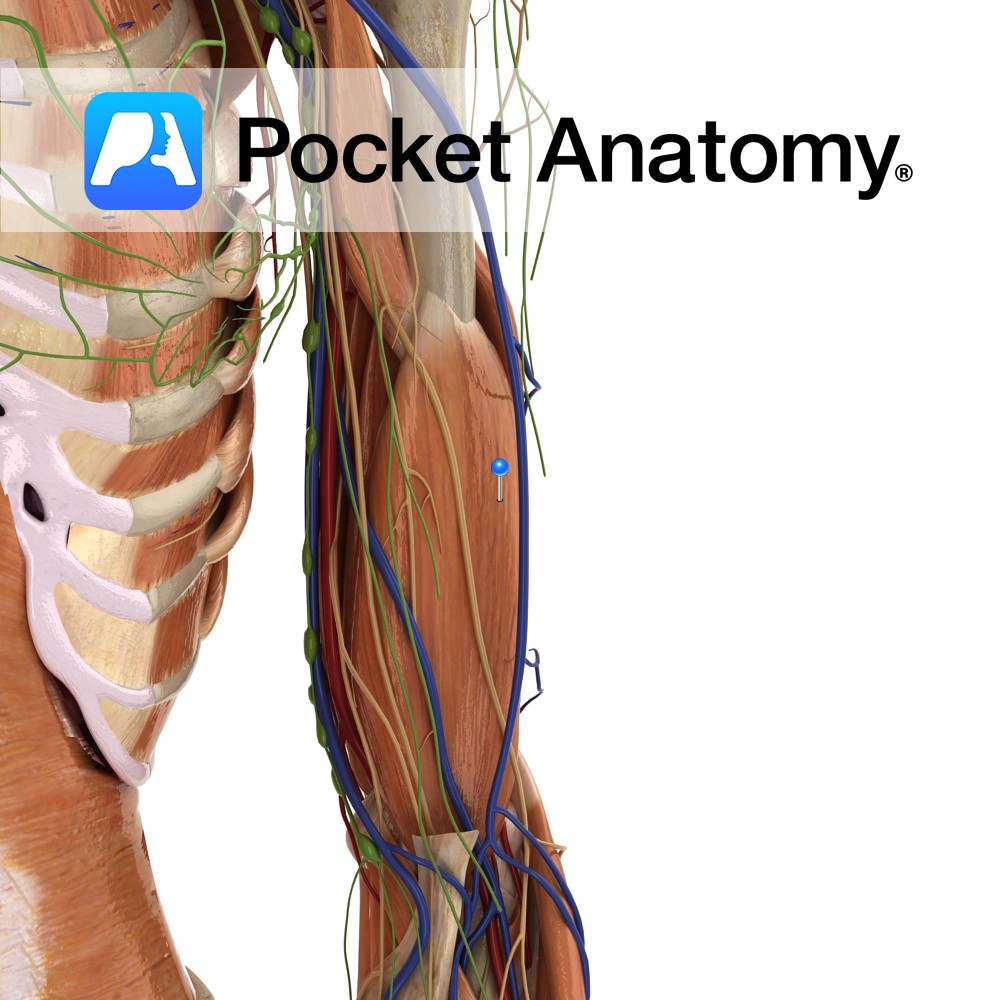
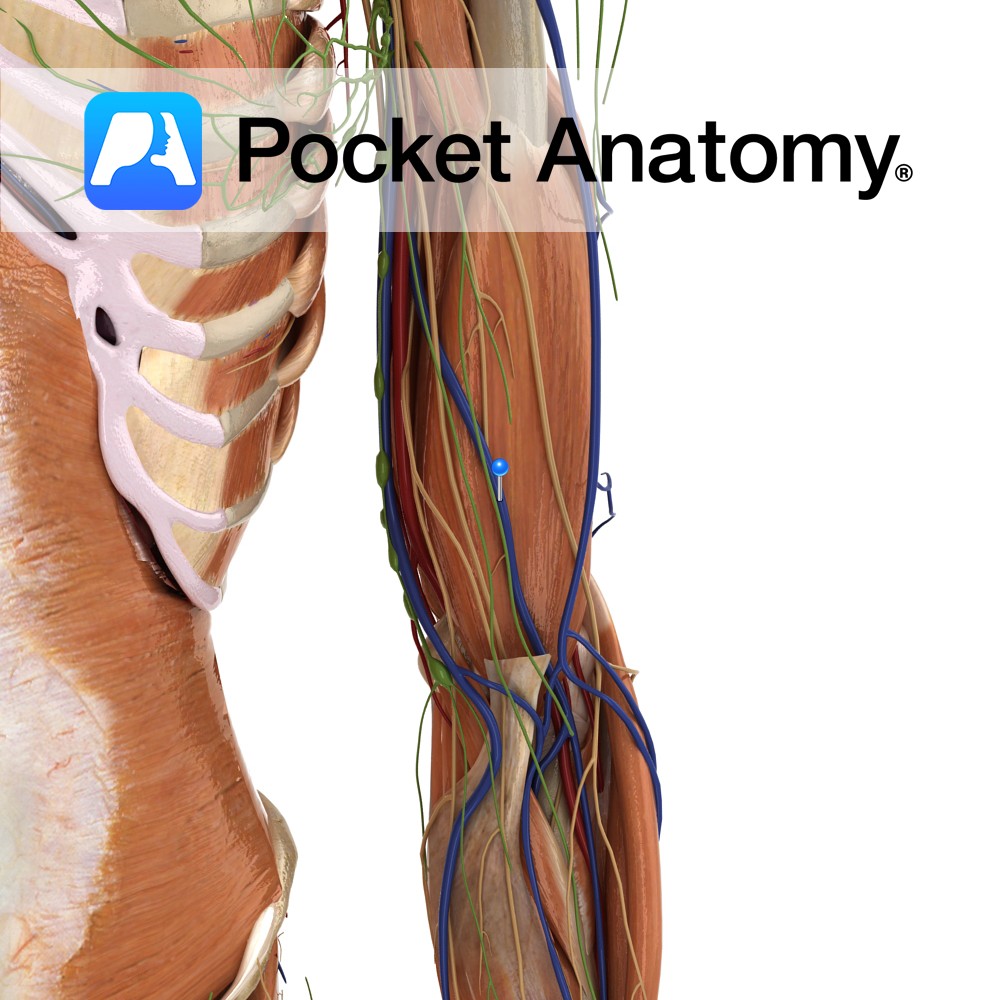
Anatomy Origin: Distal half of anterior surface of the humerus. Insertion: Coronoid process and the tuberosity of the ulna. Key Relations: -Located deep to the biceps brachii and forms part of the floor of the cubital fossa. –Musculocutaneous nerve lies on its lateral surface adjacent to biceps brachii. Functions Works synergistically with biceps brachii for
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Begins with the fusion of the radial and ulnar veins at the elbow. It then travels beneath the muscles of the forearm as it travels proximally up the arm. It eventually joins the basilic vein. Drain Drains the muscles of the forearm. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course A network of nerve fibers running from the spine to neck, axilla and forearm. It is divided into roots (C5, C6, C7, C8, T1), trunks (superior, middle and inferior), divisions (3 anterior and 3 posterior), cords (lateral, posterior and medial), and terminal branches (musculocutaneous, axillary, radial, median and ulnar nerves). Supply Responsible for
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course A network of nerve fibers running from the spine to neck, axilla and forearm. It is divided into roots (C5, C6, C7, C8, T1), trunks (superior, middle and inferior), divisions (3 anterior and 3 posterior), cords (lateral, posterior and medial), and terminal branches (musculocutaneous, axillary, radial, median and ulnar nerves). Supply Responsible for
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course A network of nerve fibers running from the spine to neck, axilla and forearm. It is divided into roots (C5, C6, C7, C8, T1), trunks (superior, middle and inferior), divisions (3 anterior and 3 posterior), cords (lateral, posterior and medial), and terminal branches (musculocutaneous, axillary, radial, median and ulnar nerves). Supply Responsible for
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)