PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
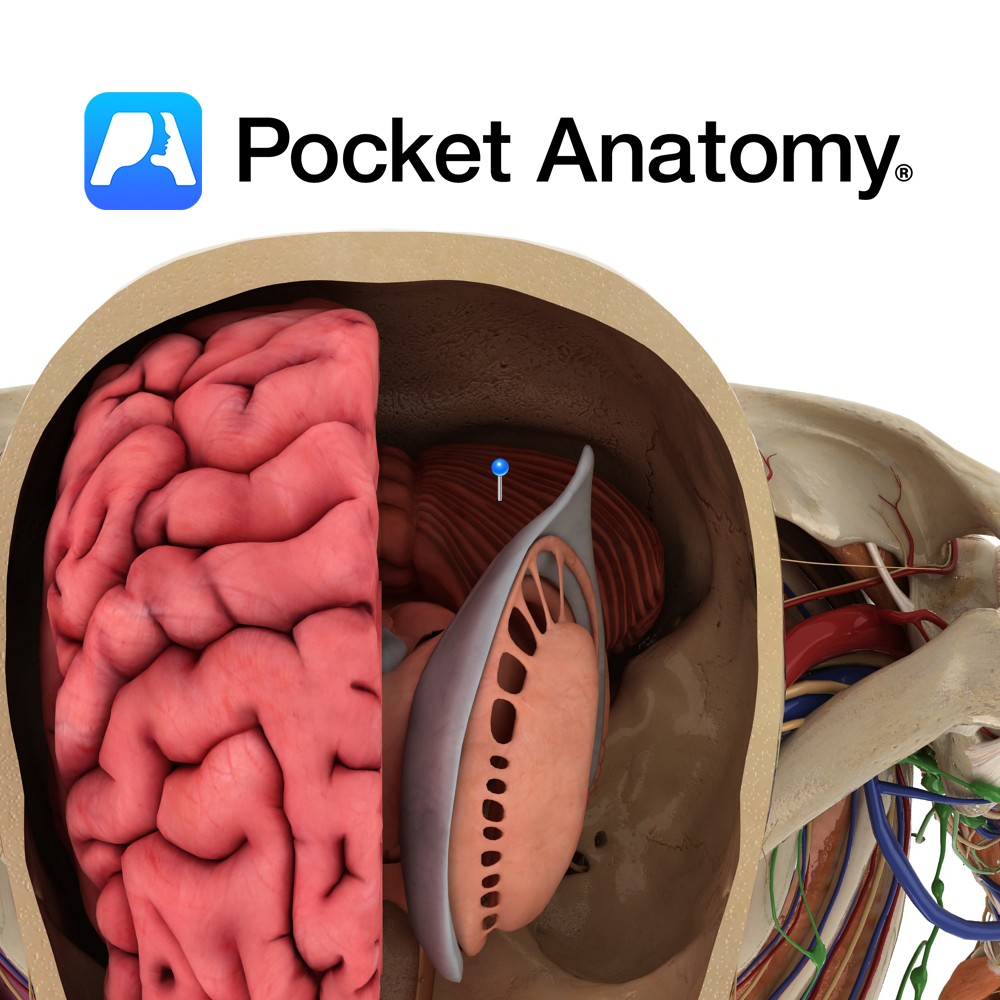
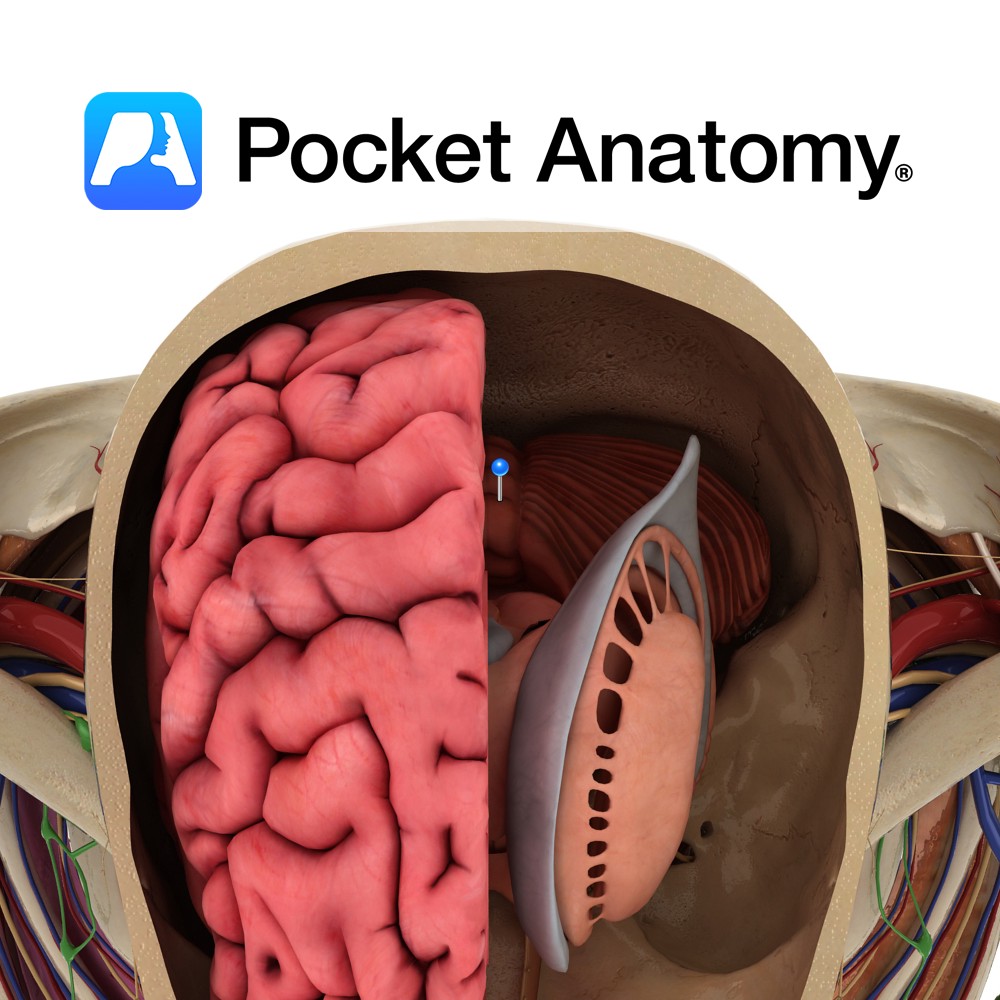
Anatomy Located in the posterior cranial fossa, inferior to the cerebrum and posterior to the pons and medulla and forms the roof of the 4th ventricle. Composed of two cerebellar hemispheres, connected by the midline vermis. The dural tentorium cerebelli separates the cerebellum below from the occipital lobes above, while the dural falx cerebelli intervenes
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Located in the midline, between the two cerebellar hemispheres. It is further subdivided into nine areas, from anterior to posterior, as follows: lingula, central lobule, culmen, declive, folium, tuber, pyramid, uvula and nodule. Blood Supply: Supplied by branches of the superior, anterior inferior and posterior inferior cerebellar arteries. Clinical Cerebellar vermis lesions are characterised
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
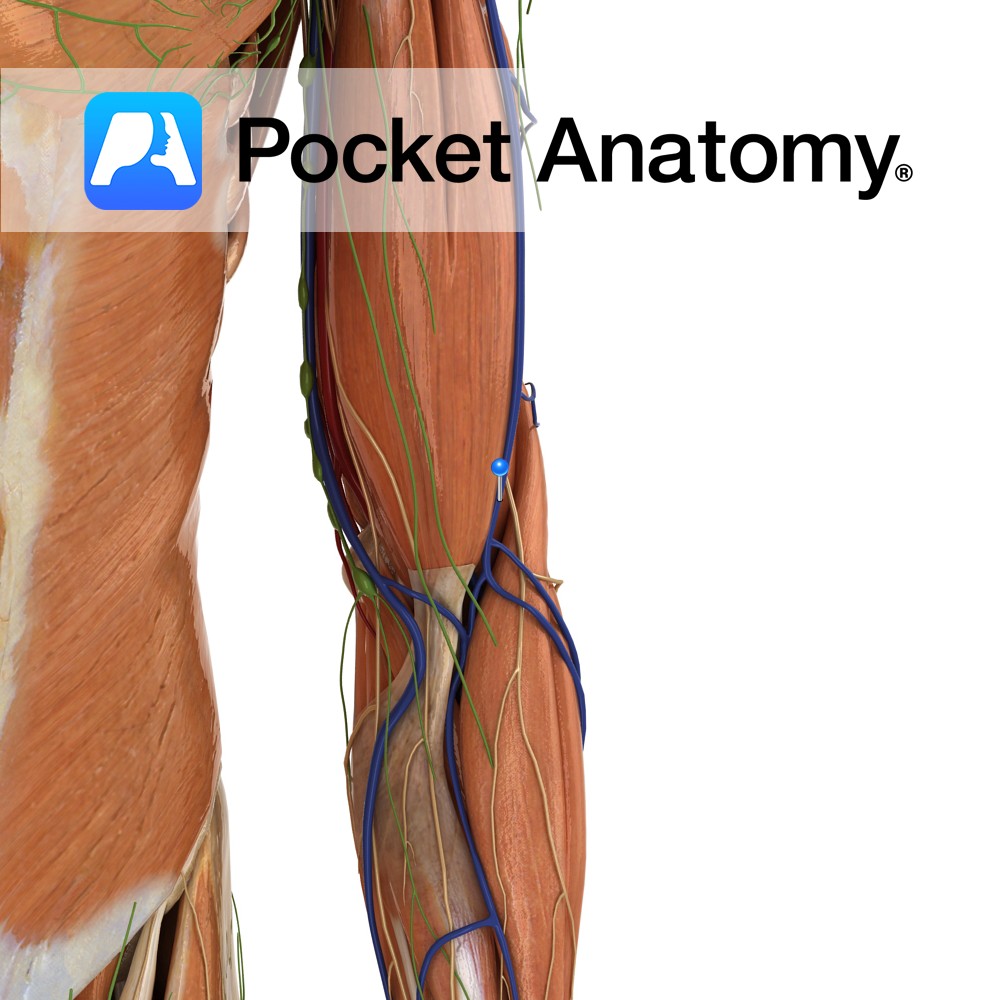
Anatomy Course Originates from the left side of the dorsal venous network found on the dorsum of the hand on the metacarpal bones. It travels superficially on the lateral aspect of the arm and forearm until it passes between the deltoid and pectoralis major muscle where it promptly empties into the axillary vein. Drain Drains
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Arises from the lateral aspect of the axillary artery. Travels behind the coracobrachialis muscles and the short head of the biceps brachii and anterior to the neck of the humerus. Anastamoses with the posterior circumflex humeral artery. Supply Supplies the glenohumeral joint and the neck of the humerus. Interested in taking our award-winning
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
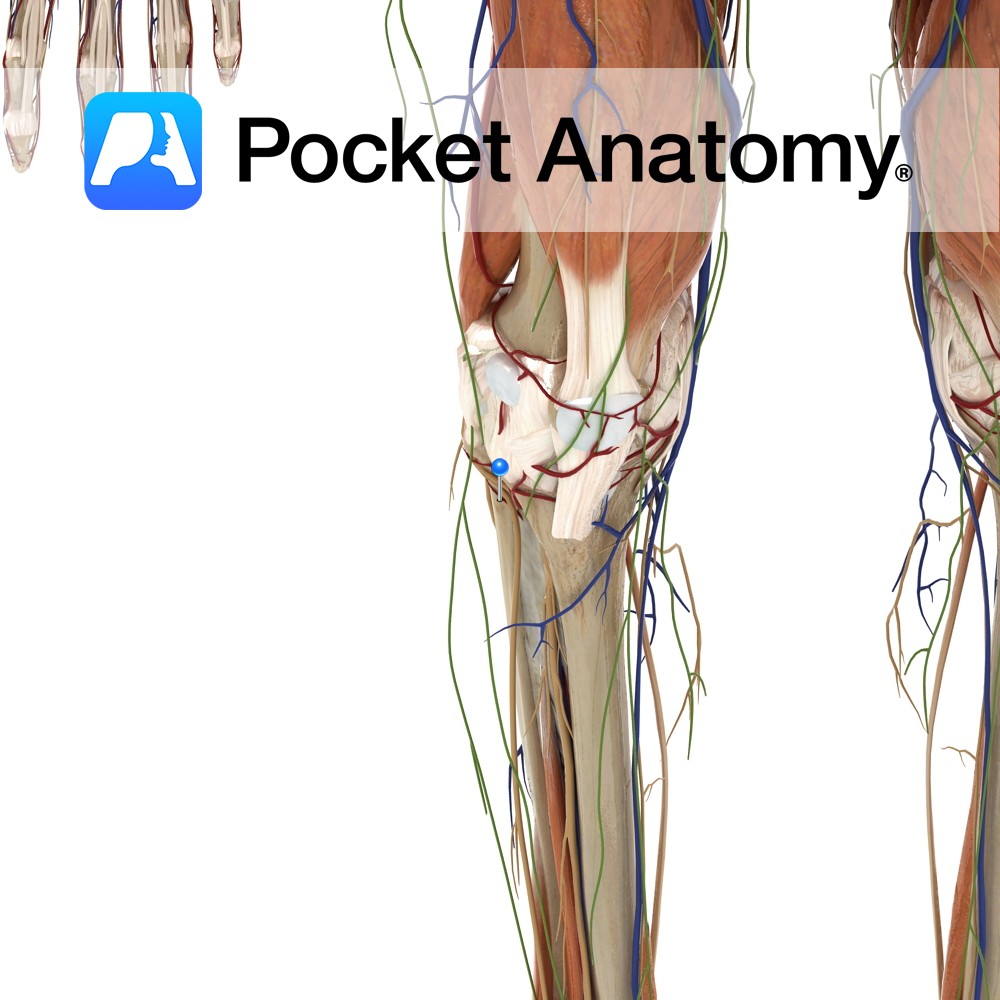
Anatomy Course Branch of the anterior tibial artery. Travels laterally through the soleus muscle as well as continuing around the neck of the fibula. It ends by contributing to the anastomotic network of the knee. Supply Supplies the soleus muscle and other adjacent muscles. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Pedicles project posteriorly from either side of the back of the vertebral body, joining laminae which themselves meet at the midline (from where a spinous process projects back and down) to complete the neural arch (enclosing the vertebral foramen). Where pedicle meets lamina each side, a transverse process, to which muscles and ligaments attach,
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Pedicles project posteriorly from either side of the back of the vertebral body, joining laminae which themselves meet at the midline to complete the neural arch (enclosing the vertebral foramen). A spinous process projects back and down from this junction; muscles and ligaments attach to it. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Pedicles project posteriorly from either side of the back of the vertebral body, joining laminae which themselves meet at the midline (from where a spinous process projects back and down) to complete the neural arch (enclosing the vertebral foramen). Adjacent laminae above and below are connected by the ligamenta flava. Interested in taking our
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
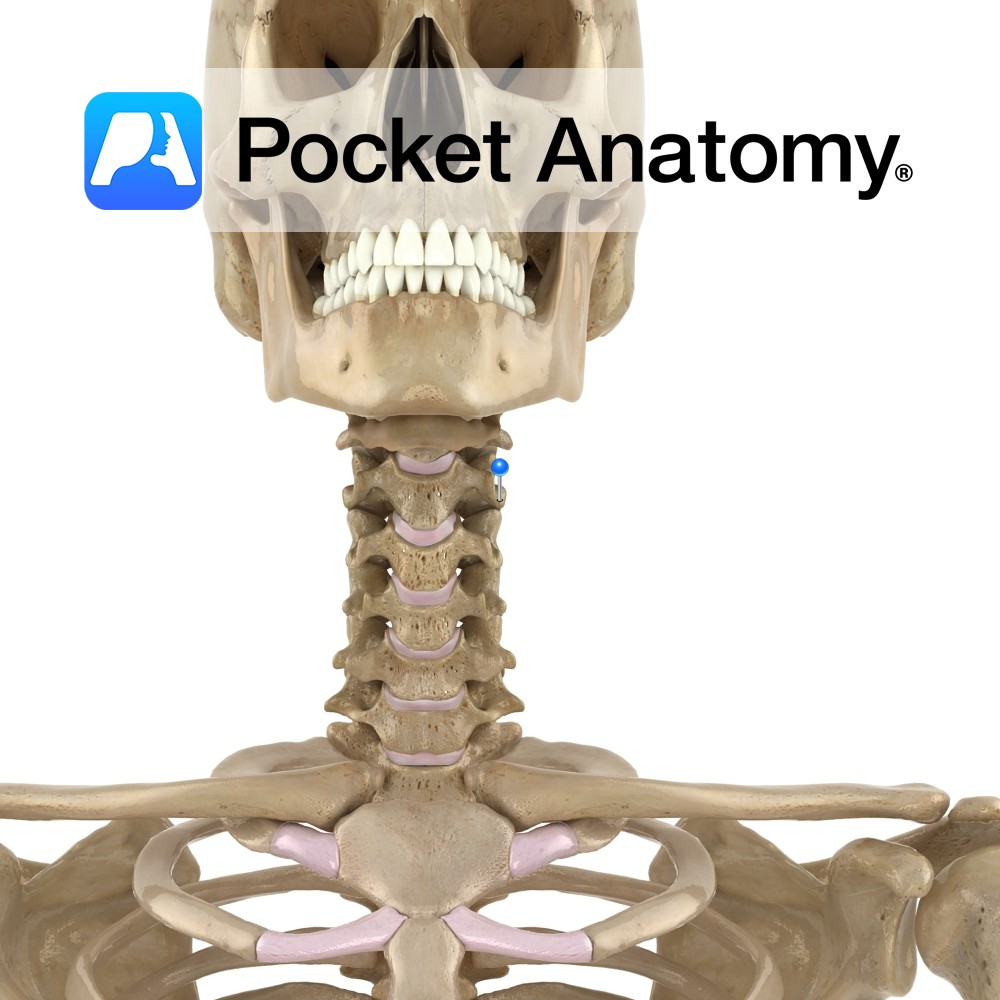
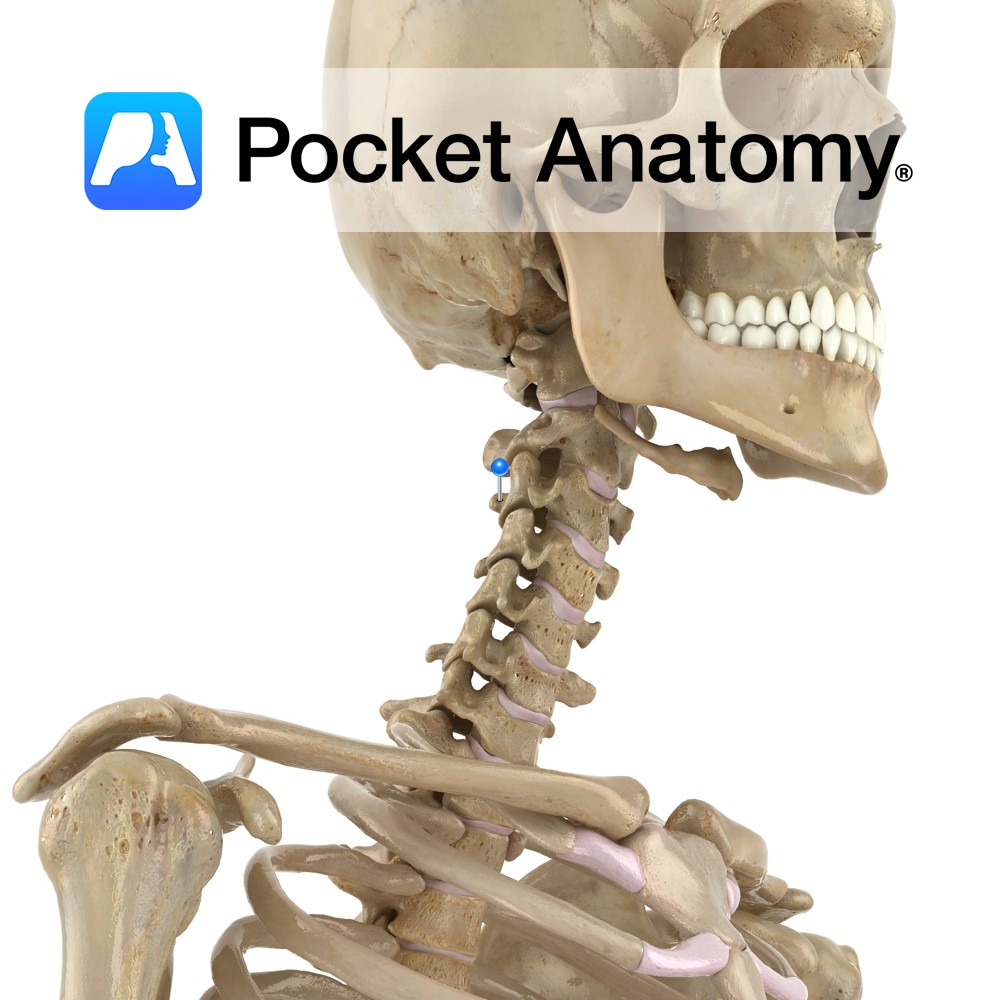
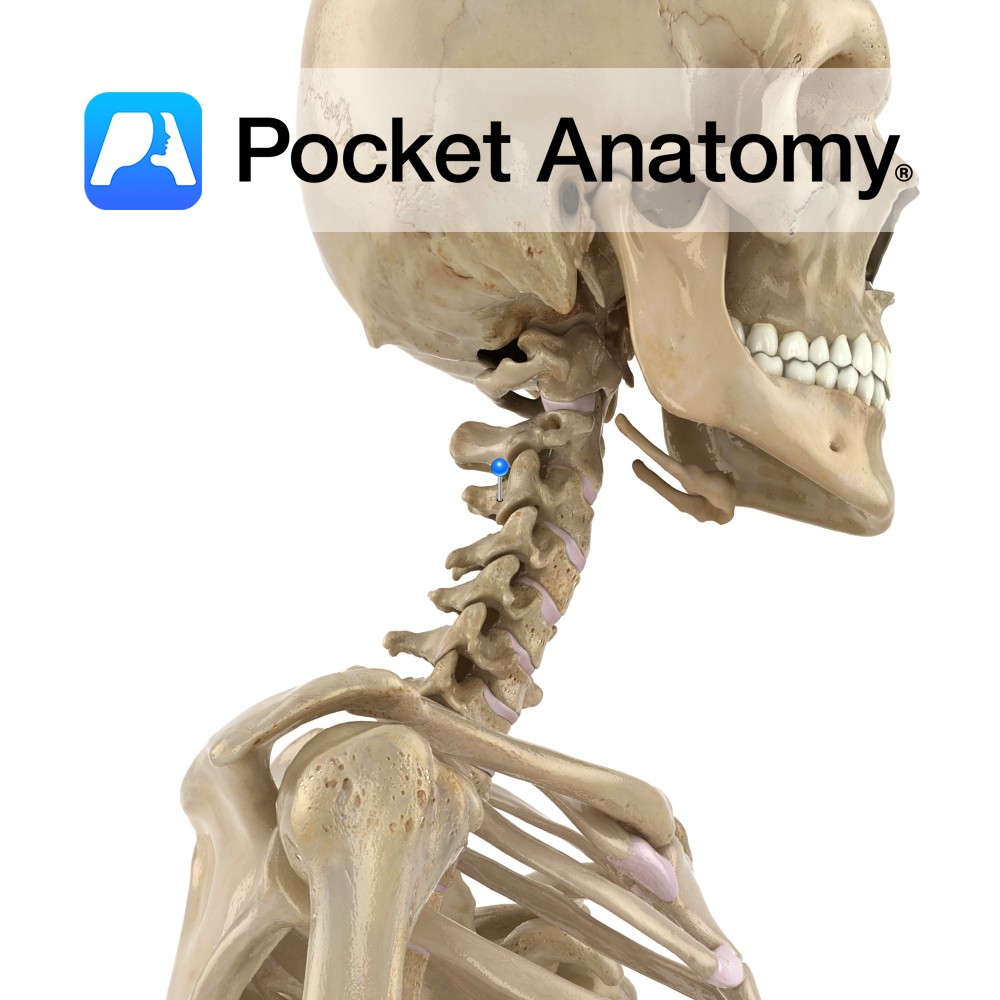
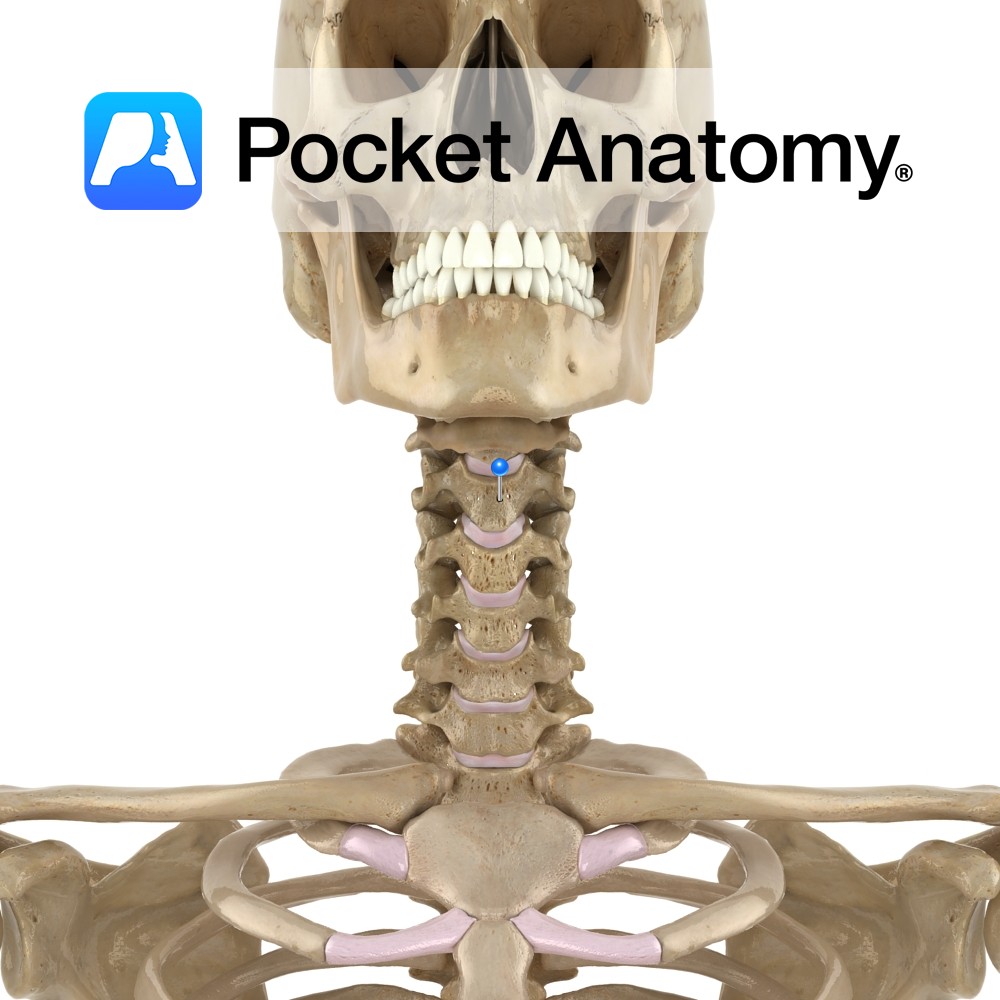
Anatomy Cylindrical, broader side-to-side, upper surface lipped at sides, lower surface indented at sides. Articulates with vertebrae above and below through fibrocartilaginous discs that allow some vertebral movement and provide shock absorption. No articular facets (unlike those on thoracic for articulation with ribs). Clinical The cervical (and lumbar) spine exhibits flexion, extension and some lateral
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Complex 3D/multiplanar structure, the pea-sized glans and shaft (variably hooded by the labia minora and curtained by the upper/anterior junction/commissure of the labia majora) the only distinctly visible surface element. There is also an internal portion of the shaft and a much bigger associated cluster of tissue, some clearly distinguishable anatomically/histologically (such as paired
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins

.jpg)