PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
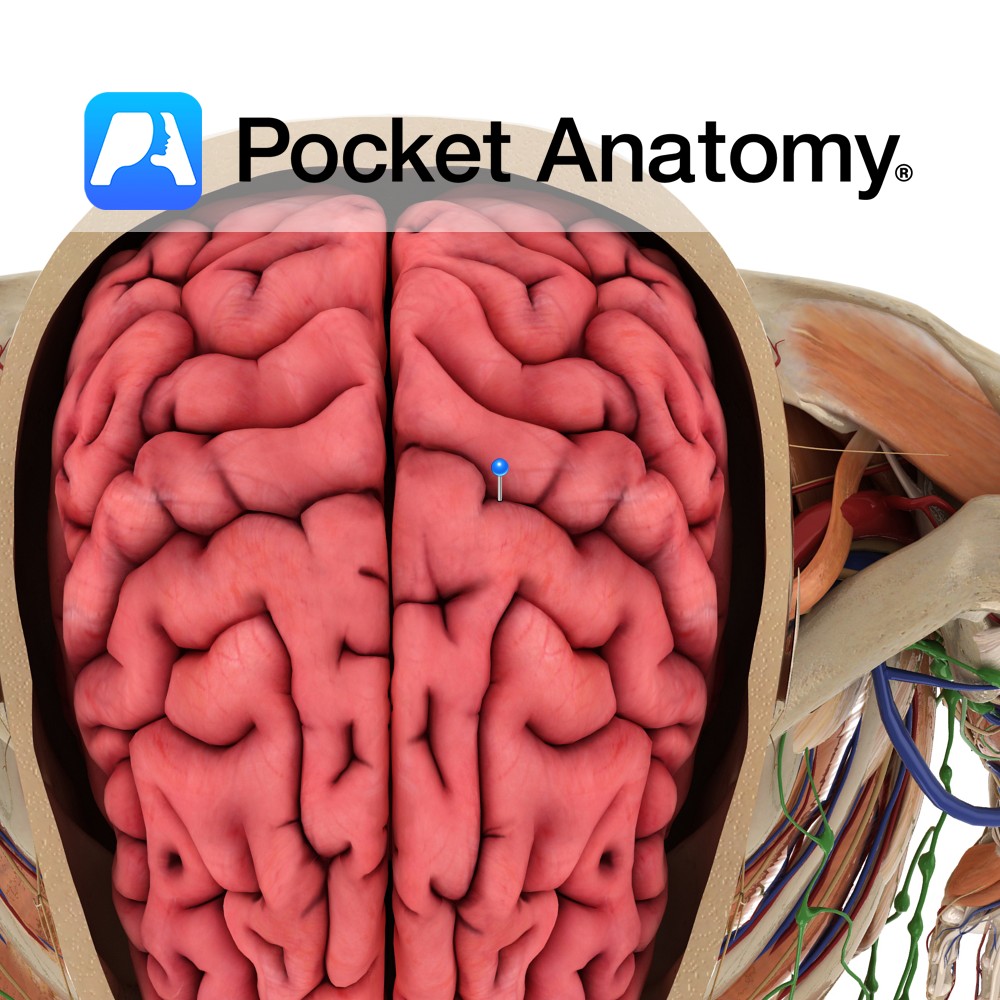
Anatomy A sulcus separating the precentral gyrus in front from the postcentral gyrus behind and forming the boundary between frontal and parietal lobes. It extends anteroinferiorly from the great longitudinal fissure along the lateral aspect of the cerebral hemisphere before terminating near the lateral sulcus. Functions The anterior and posterior walls of the central sulcus
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
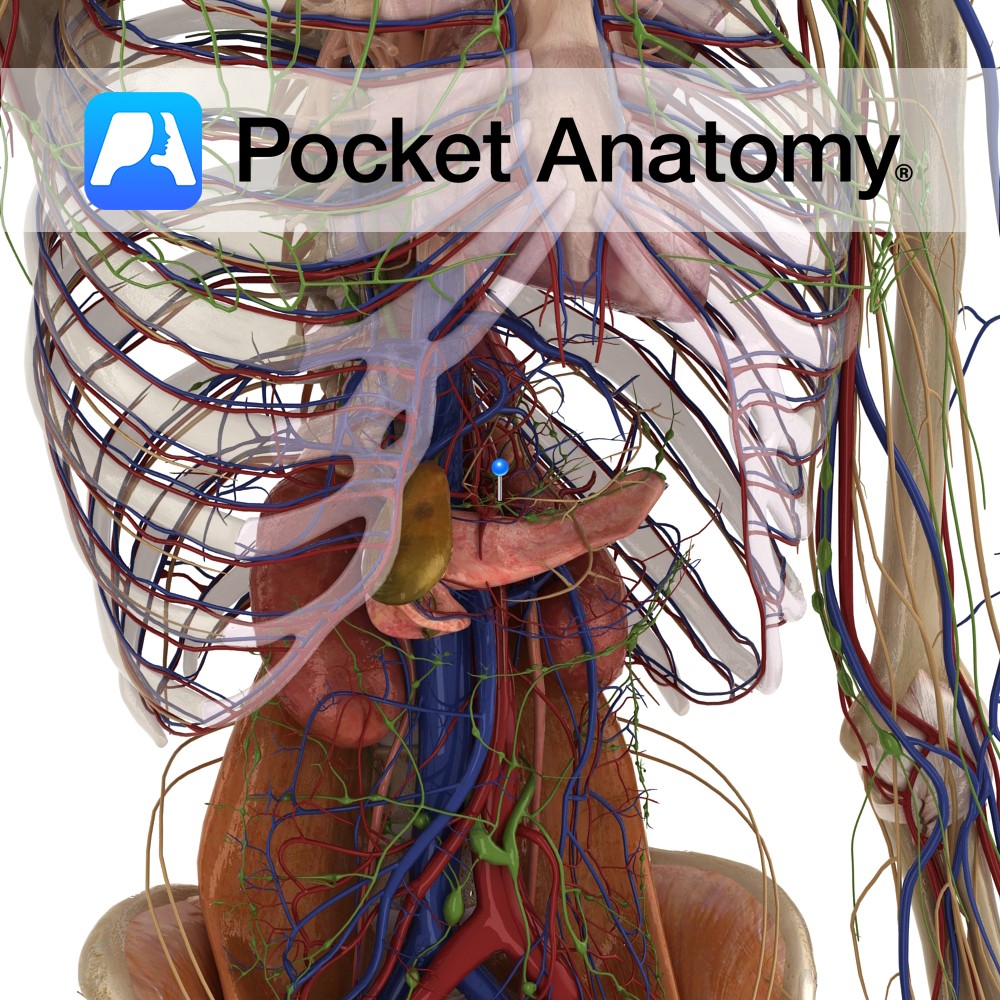
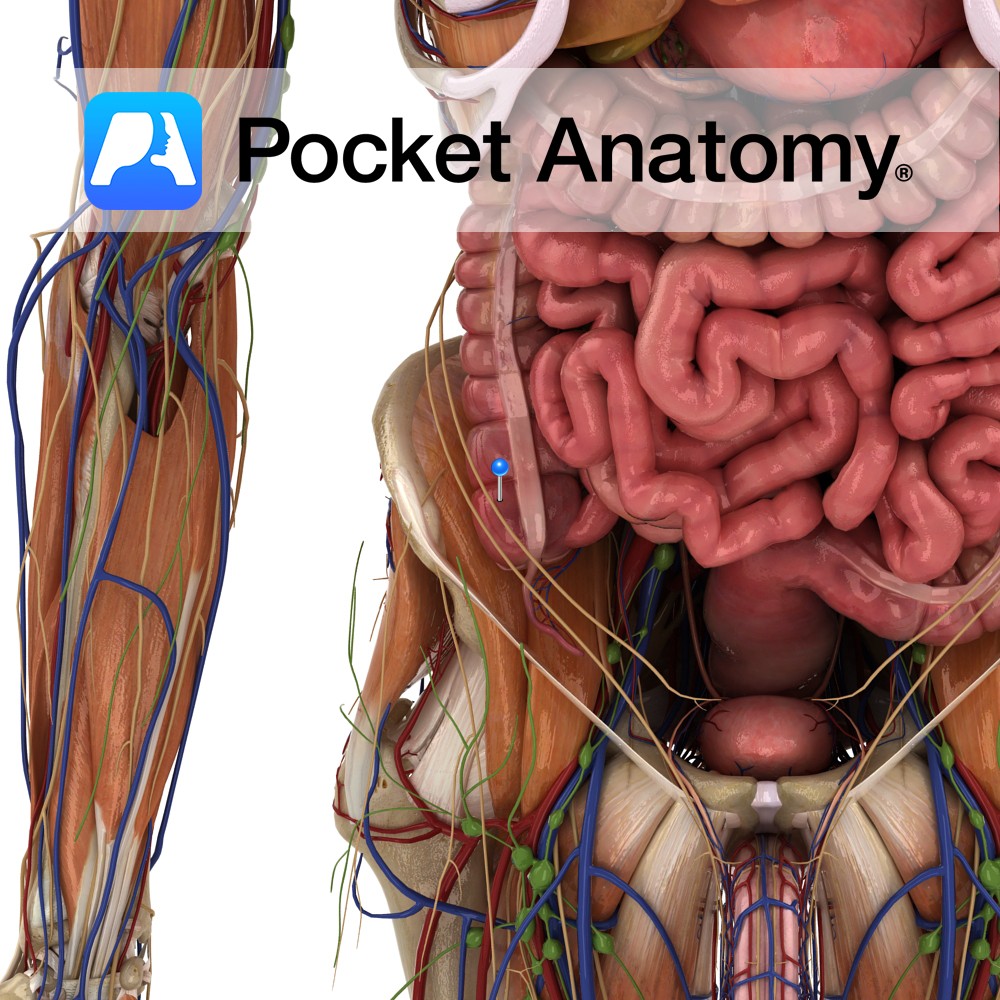
Anatomy Course: Also known as the celiac artery, it is one of three midline branches of the abdominal aorta (along with the superior and inferior mesenteric arteries). It travels anteriorly to the upper border of L1 after entering the abdominal cavity through the diaphragm at T12, branching into splenic, hepatic, inferior phrenic, and gastric arteries.
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
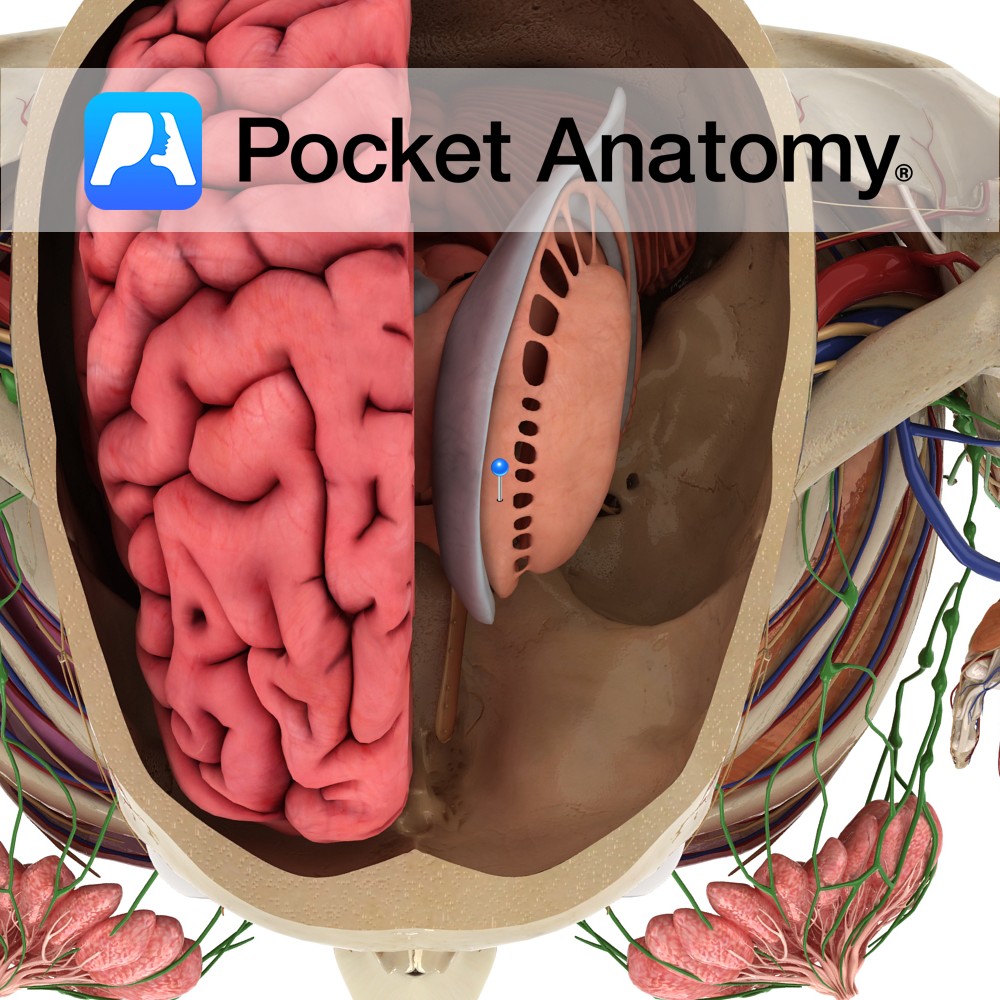
Anatomy Pouch-like (Latin; caecus – blind), usually (95%) peritoneal, 1st section of large intestine, between ileum (intervening ileo-cecal valve) and ascending colon, both valve and ceco- colic junction arising at upper surface, lower surface blind, appendix arising below and behind ileo-cecal valve (also called vermiform process, thin, 2-20cms, can pass up behind cecum, in/medial/left behind
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy The caudate nucleus comprises a head, body and tail. The head of the caudate is rounded and forms the anterior portion of the wall of the lateral ventricule. Its fibers pass through the internal capsule to be in continuity with the putamen. The body of the caudate is continuous with the head, adjacent to
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
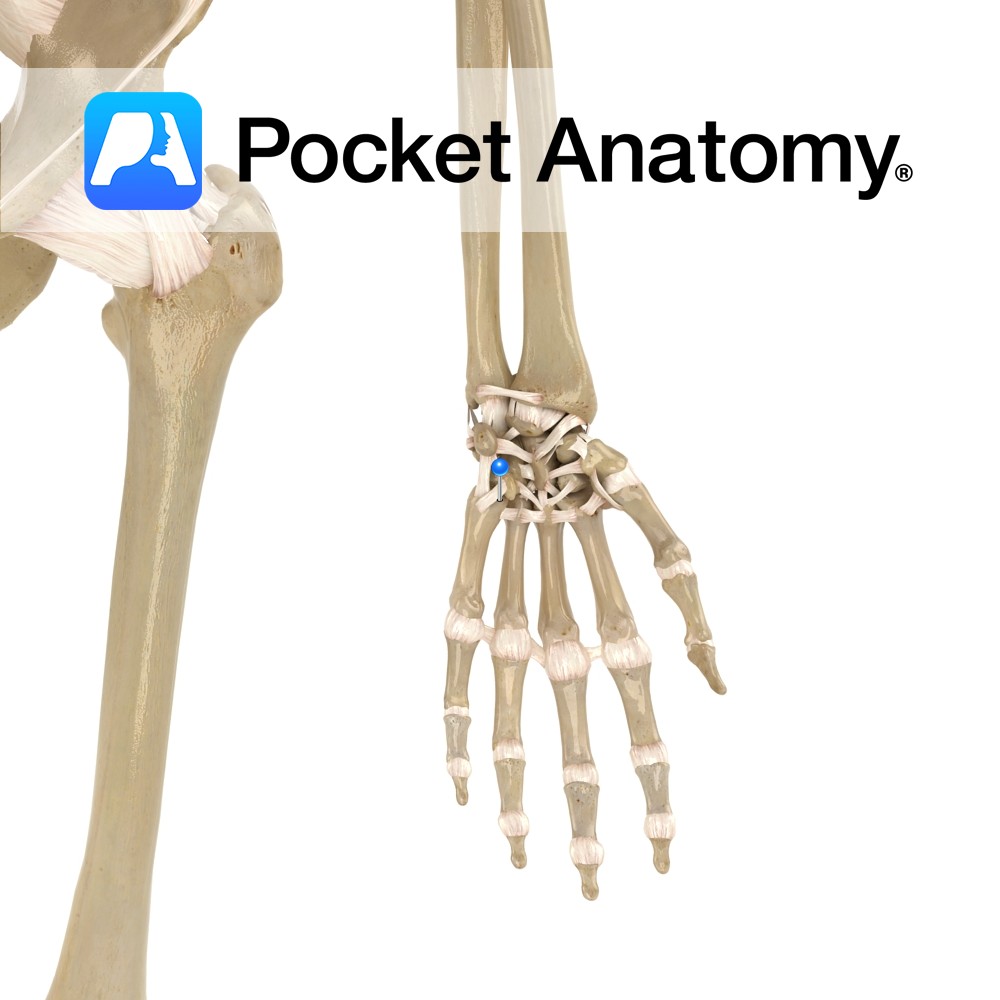
Motion The carpometacarpal joints of the 2nd to 5th fingers are synovial plane joints. The carpal bones of the wrist articulate with the second to fifth metacarpals. The second metacarpal articulates with the trapezoid primarily and also with the trapezium and capitate. The third metacarpal articulates with the capitate. The fourth metacarpal articulates with the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
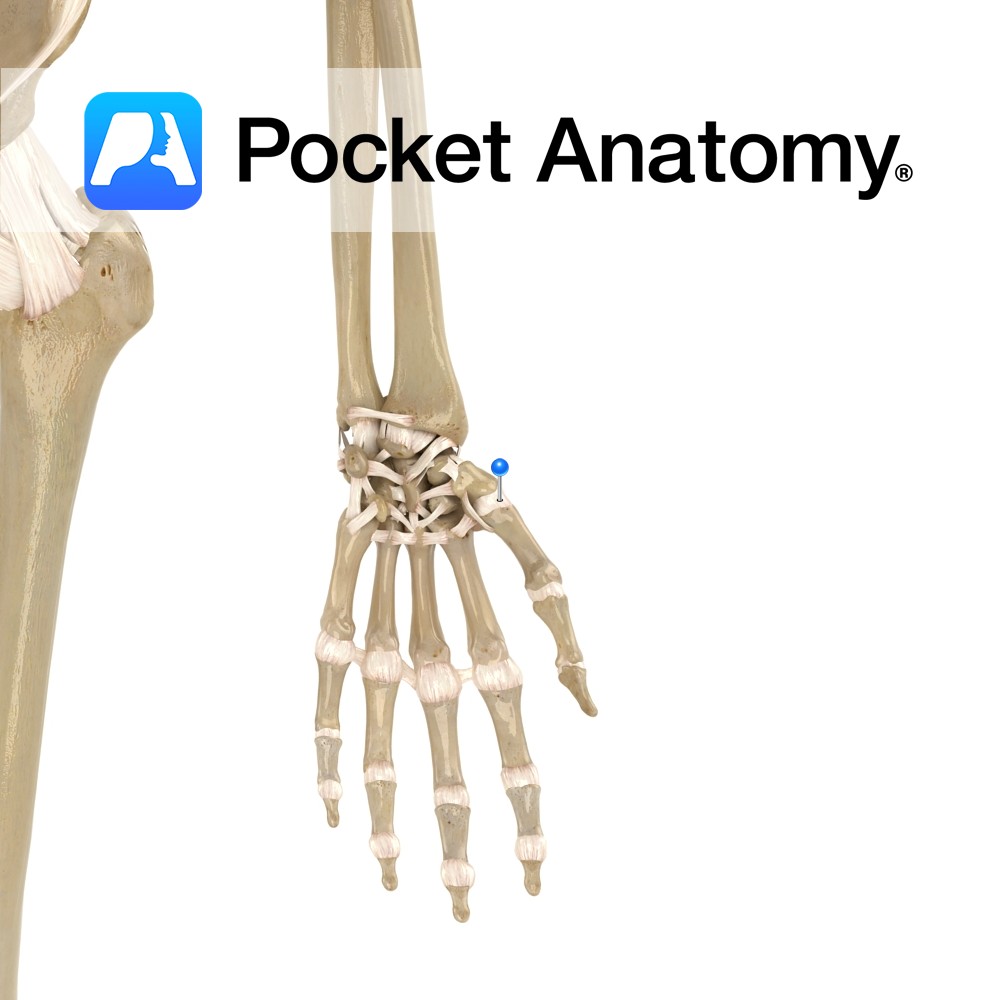
Motion The carpometacarpal joint of the thumb is a condyloid synovial saddle joint between the trapezium and the first metacarpal. It is separate from the other CMCs in the hand. It allows flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, circumduction and opposition (medial rotation with flexion). The joint is allows much more mobility than the other CMC joints.
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Most noticeable feature – odontoid process (derived from separation and fusion of body C1 with that of C2) rising from upper surface. Also large strong spinous process. C2 has complex articulation with atlas: Pivotal junction with odontoid process at 2 joints – front of odontoid with anterior arch C1, back of odontoid with transverse
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Highest vertebra of column of 33. Forms spine/skull joint, along with C2 (axis). C1 has no vertebral body, as it is fused with that of C2 to contribute to formation of odontoid process (or dens). C1 has no spinous process; its absence affords greater range of movement of skull on C1. Superior facets (atlanto-occipital)
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
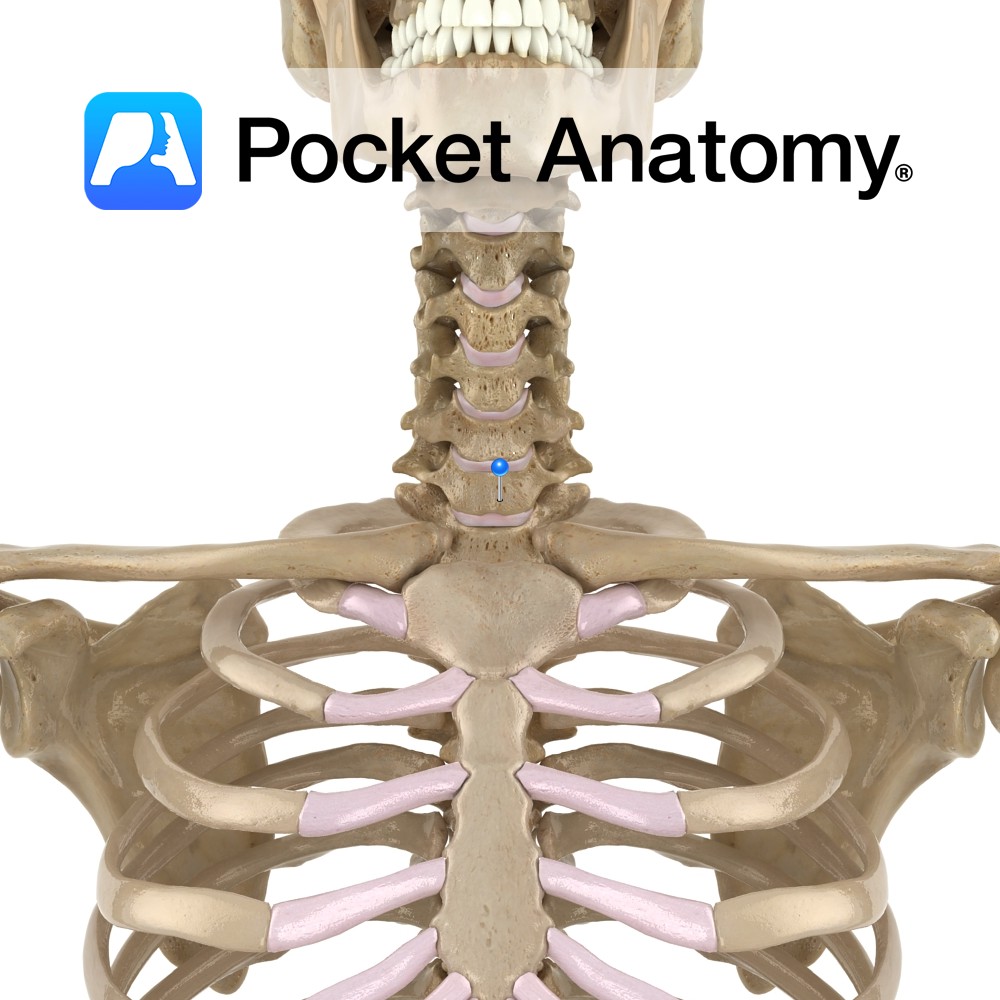
Anatomy Also called vertbra prominens. Its spinous process is thick, long, almost horizontal, ends in a tubercle to which the bottom of the ligamentum nuchae is attached. In 70% of people, this is the most prominent spinous process (30% either C6 or T1). In 1 in 500, the transverse process has a forward projection as
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
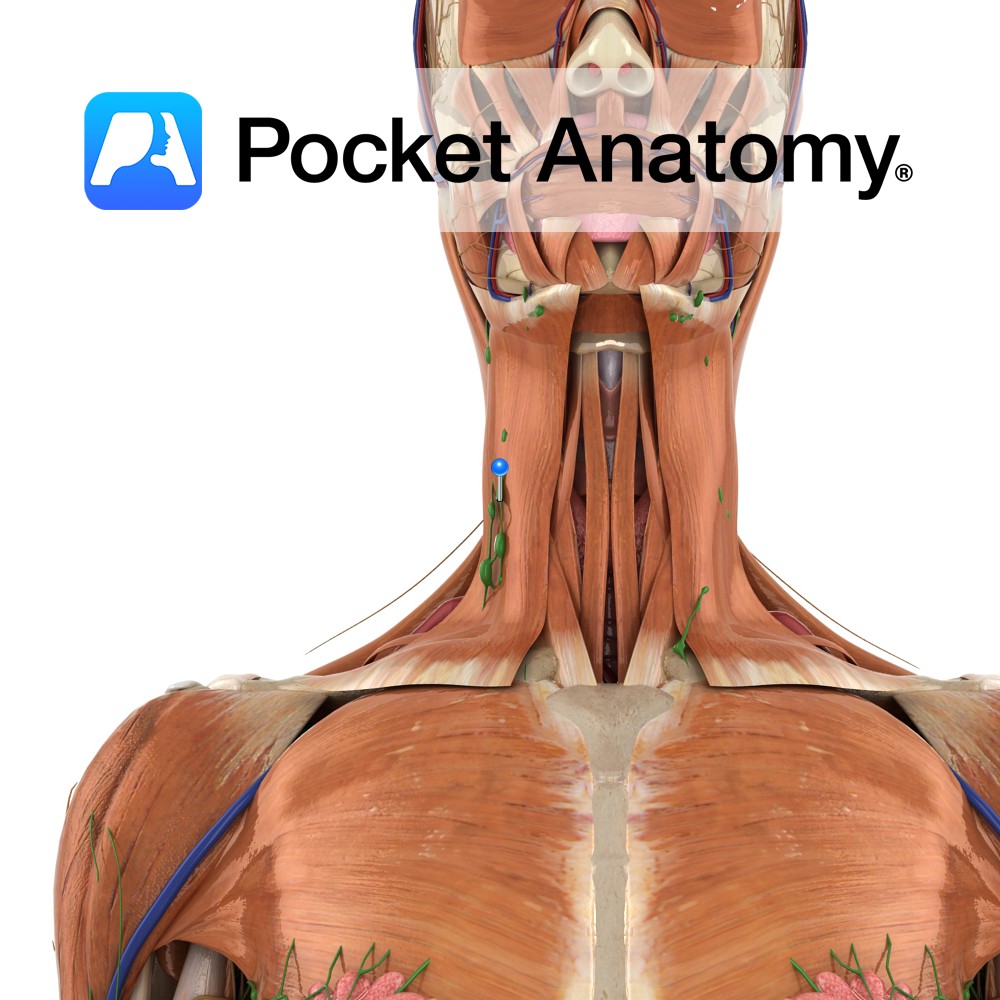
Anatomy Group/Cluster of nodes, in front and back of ears and along lower border jaw, and deeper in neck alongside blood vessels. Nodes filter the lymphatic drainage of scalp, face, nasal cavity, pharynx. Clinical Main (6) groups/clusters of nodes; Cervical, Axillary, Thoracic (Mediastinal, Bronchopulmonary), Iliac, Inguinal. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins

.jpg)
.jpg)