PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
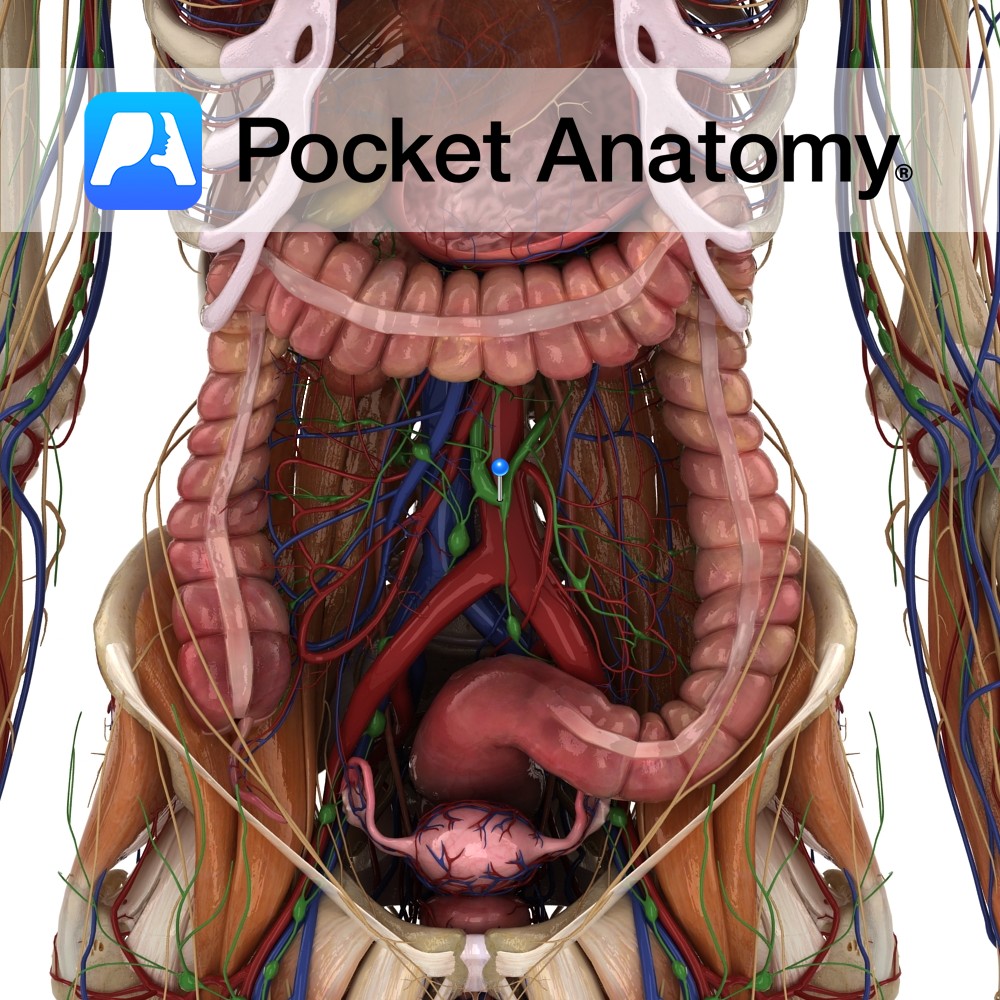
Anatomy Also known as Cisterna Chyli, a sac (constituting the start of the Thoracic Duct) receiving lymph from both Lumbar Trunks and the Intestinal Trunk. Physiology The lymphatic ducts of the small intestine begin in the villi as specialised capillaries called Lacteals. Lacteals take up lymph and also absorbed fats, the milky combination then called
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
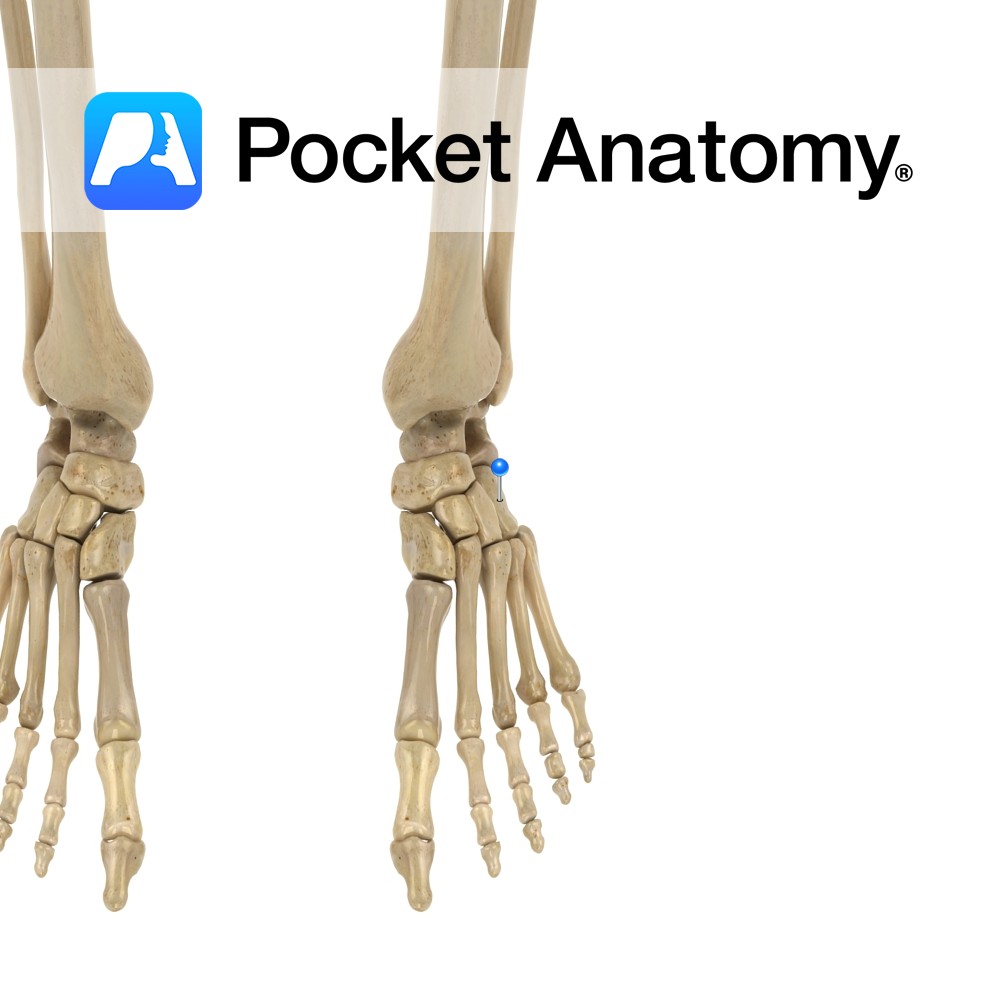
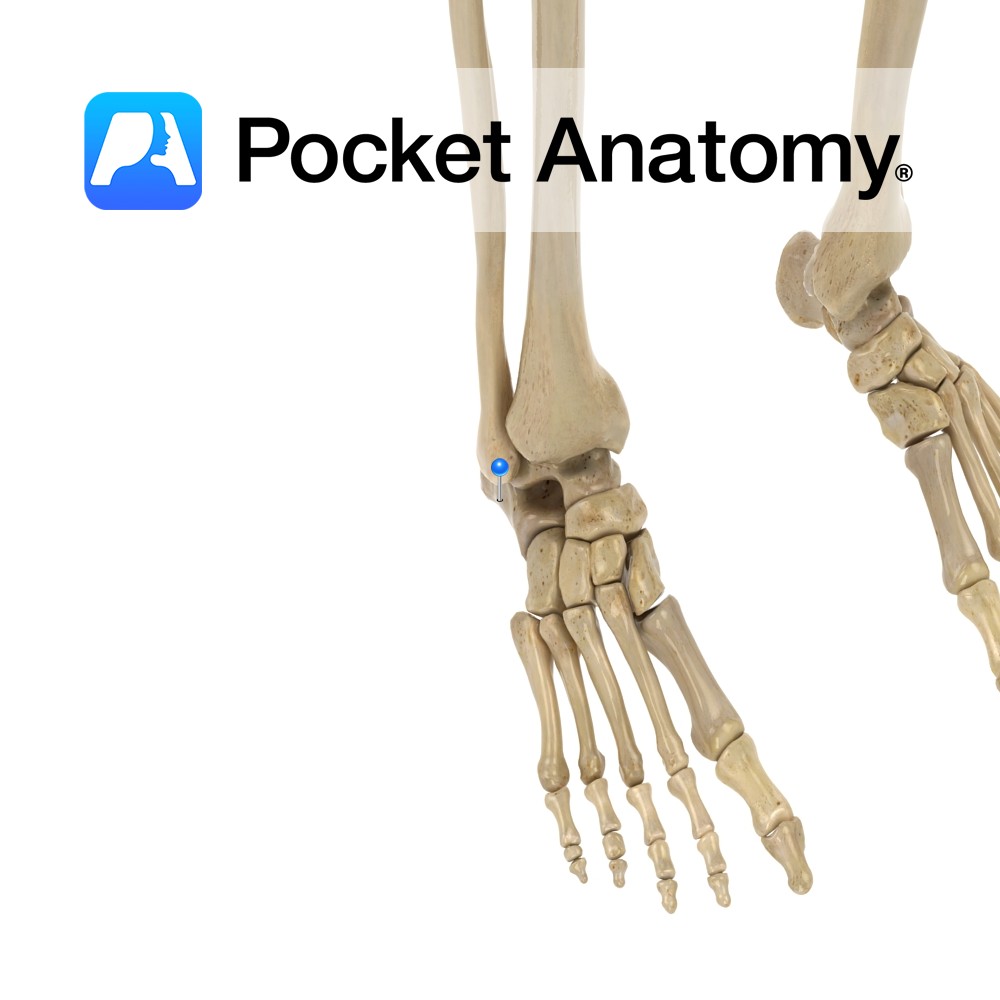
Anatomy Tarsal bone. Articulates proximally/back with calcaneus, forward with 4th and 5th (laterally) metatarsals, in/medially with lateral (3rd) cuneiform and sometimes the navicular. Cuboid + navicular + 3 cuneiforms = midfoot (form arches of foot). Clinical Damage to nearby muscles, ligaments, joints, can lead to partial dislocation (subluxation) cuboid, with lateral foot pain and weakness
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
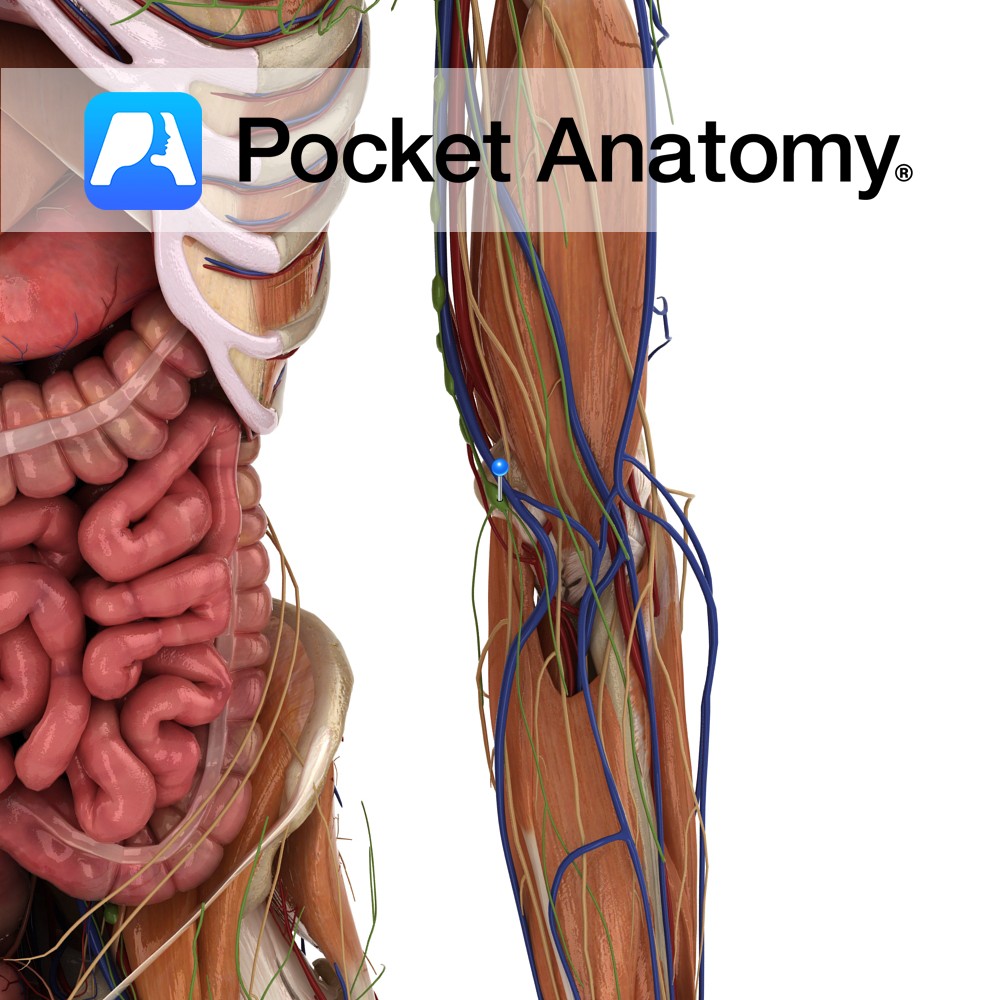
Anatomy Also known as epitrochlear nodes, near the elbow, above epicondyle. There are superficial and deep sets of cubital nodes, receiving afferent drainage of forearm and the hand, efferents thence passing up to superficial and deep Axillary lymph nodes. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
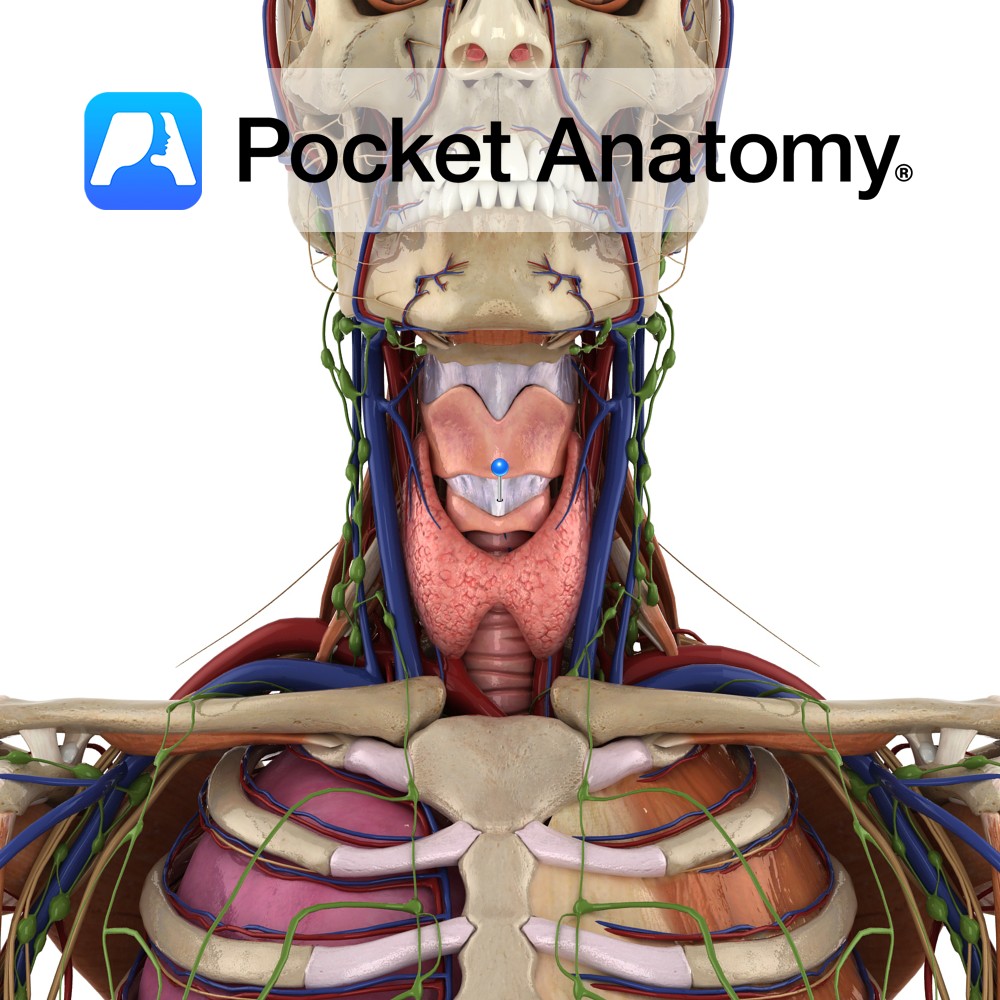
Anatomy A thickening of the median portion of the anterior cricothyroid membrane. It begins as a broad band attaching to the anterior superior aspect of the cricoid cartilage and narrows as it ascends to attach to the lower aspect of the thyroid cartilage. Functions Binds the cricoid and thyroid cartilage while limiting the anterior posterior
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
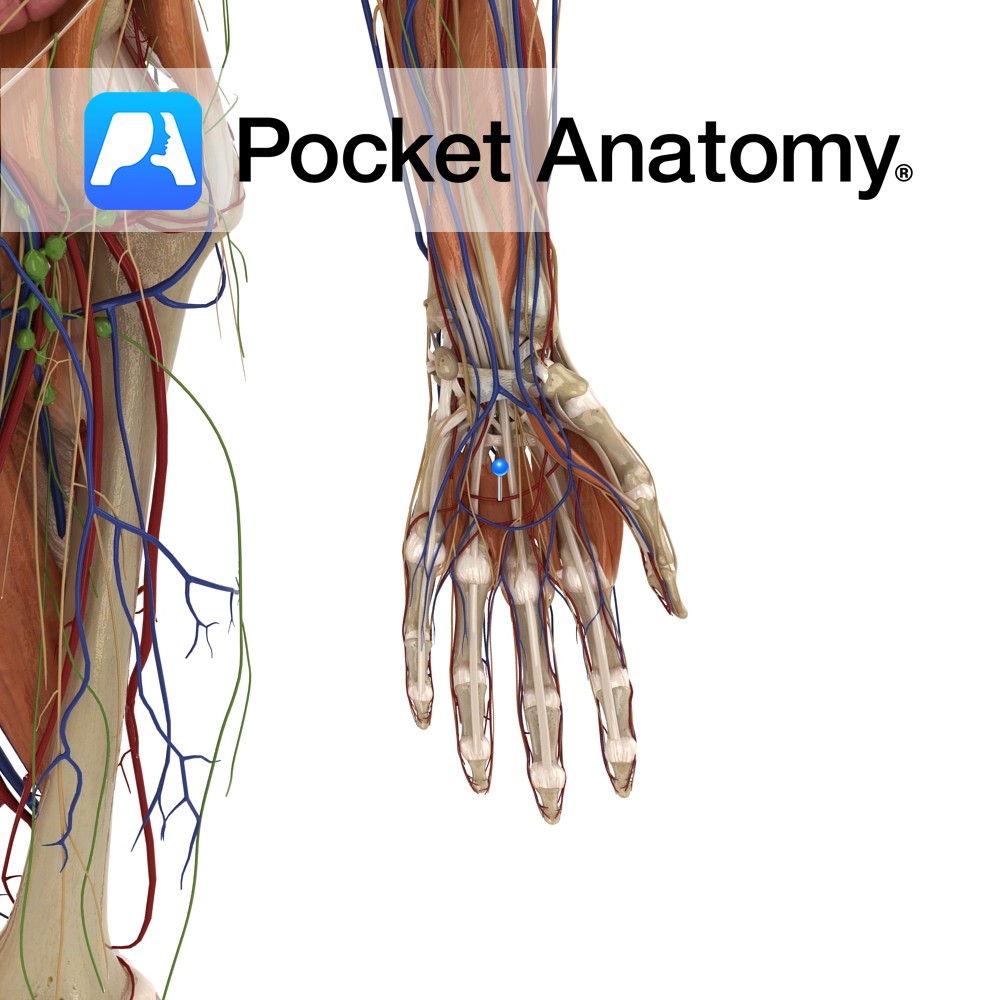
Anatomy Course A complex network of vessels that originate mostly from the radial artery but also from the ulnar artery via its deep palmar branch. It is situated on the base of the metacarpals bones. Supply Supplies the deeper components of the palm. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
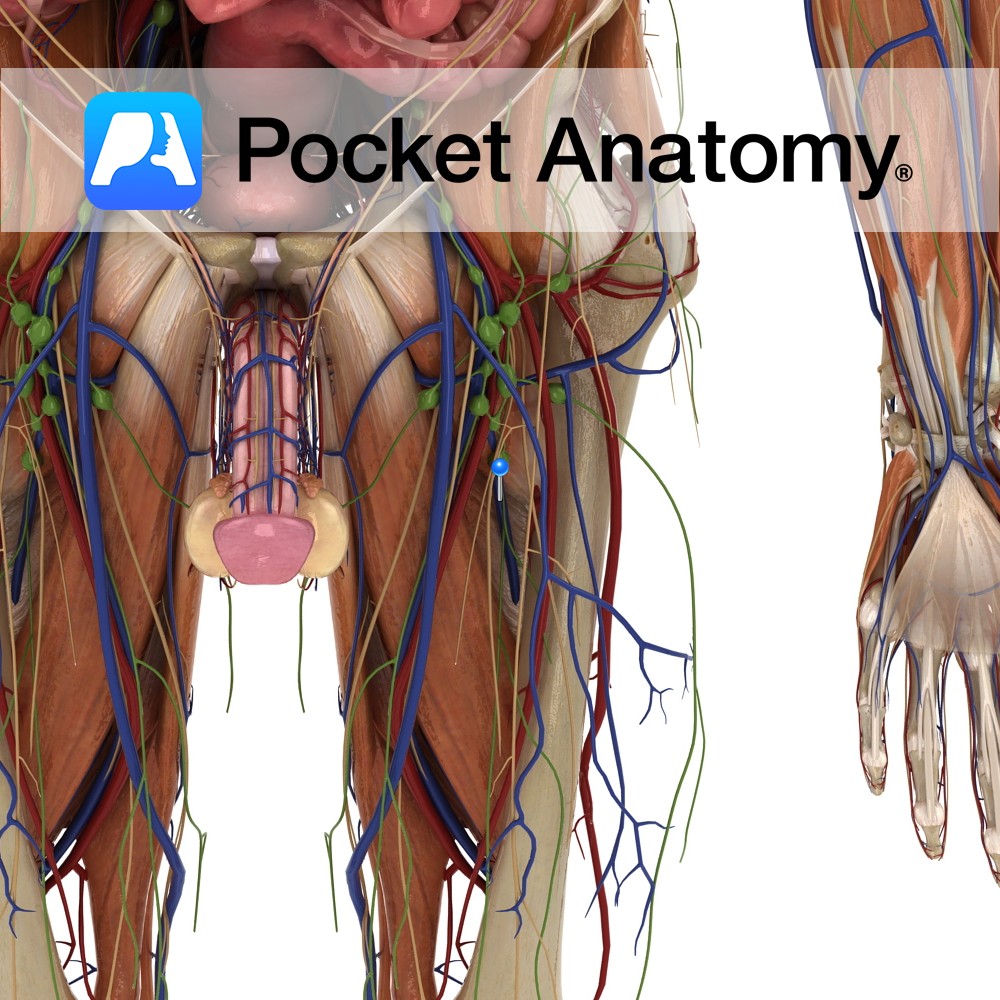
Anatomy Course Its origin is highly variable but receives many vessels as it rises up the leg alongside its corresponding artery until it eventually joins the femoral vein and the inferior border of the ischial tuberosity. Drain Drains the inner thigh. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
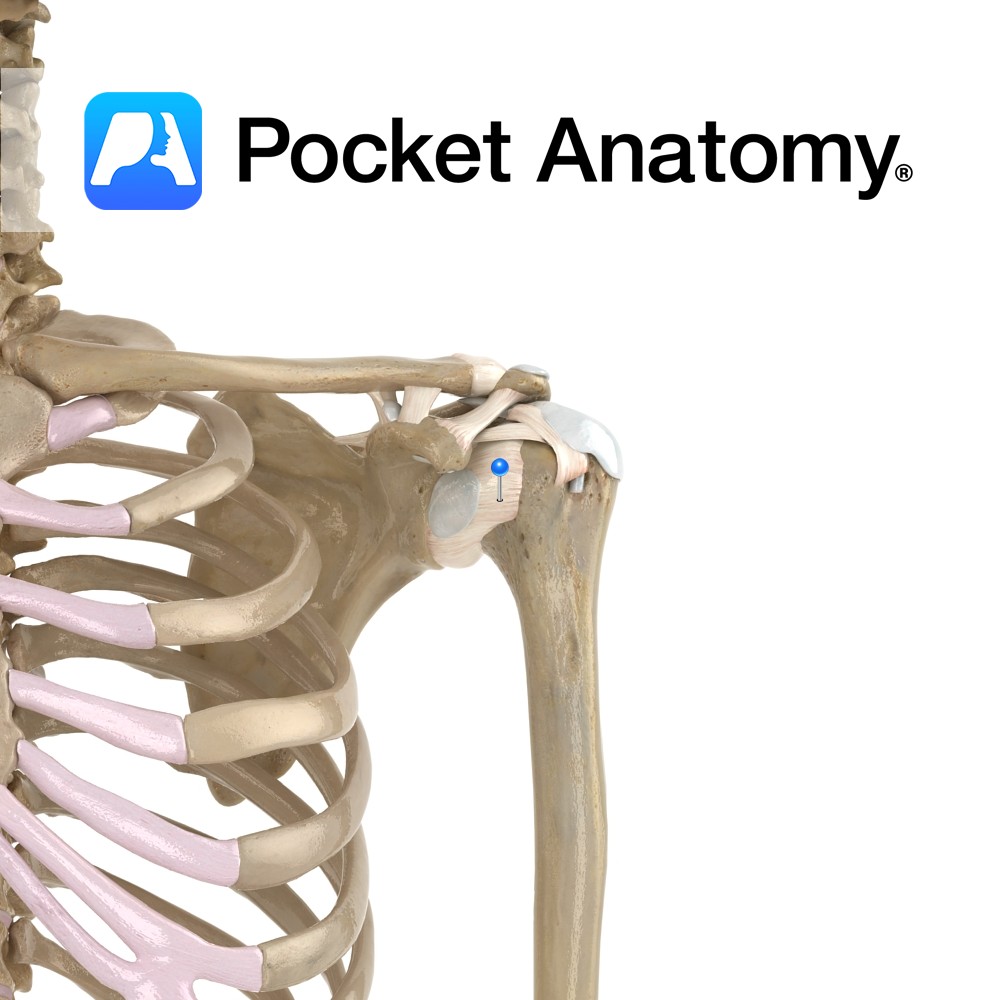
Anatomy The capsular ligament of the shoulder surrounds the glenohumeral joint. It attaches from the scapula, just outside the glenoid labrum, and medial to the supraglenoid tubercle to allow for the attachment of the biceps brachii. It attaches onto the anatomical neck of the humerus, except medial where it extends down to the surgical neck
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
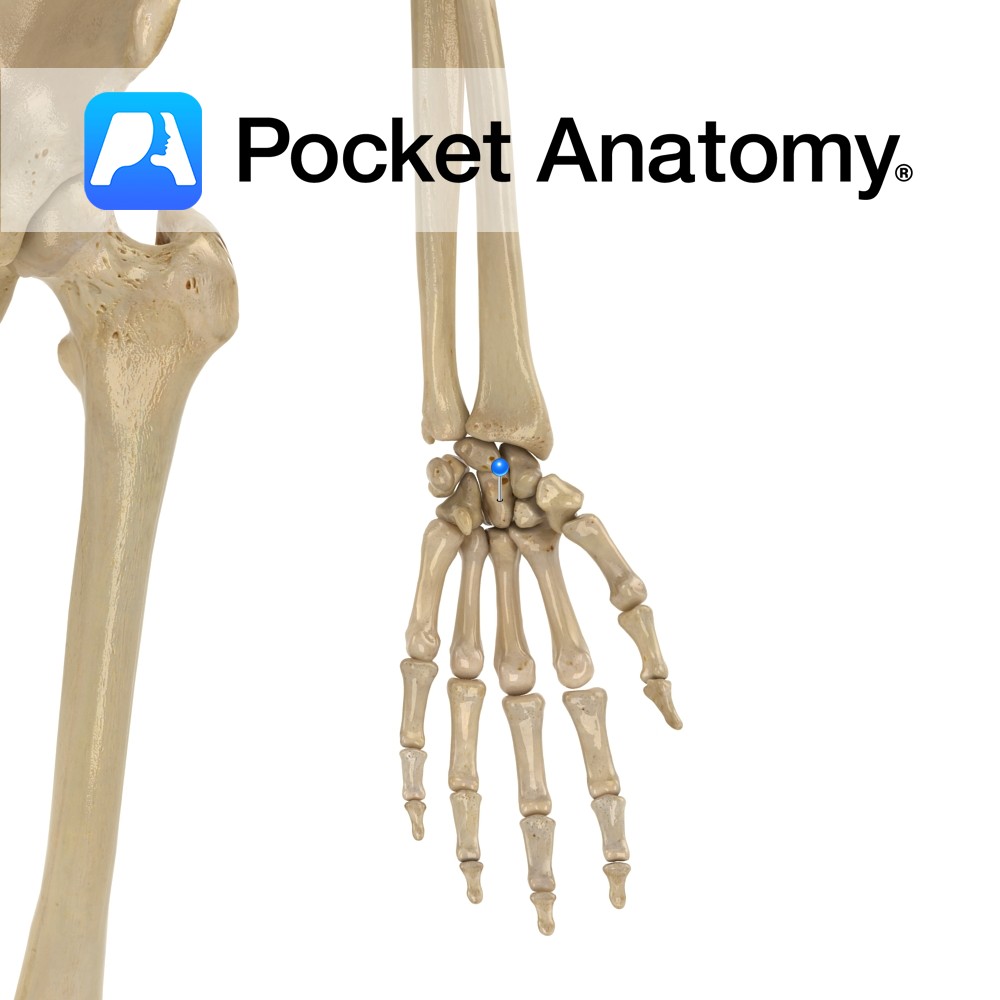
Anatomy Largest carpal bone, in centre of wrist in distal (further) row. Articulates up with lunate, down with 2nd, 3rd (mostly) and 4th metacarpals, out with trapezoid and navicular, in with hamate. Attachments; part of adductor pollicis. Vignette Capit (Latin); head. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Heelbone. Largest tarsal bone, bears most weight in heel. Biggest tendon in body – Achilles – inserts into upper surface. Talus + calcaneus = hindfoot. Articulates up with talus, forward with cuboid. Clinical Joint above (subtalar) affords foot inversion and eversion and in conjunction with calcaneocuboid and talonavicular joints below (together called transverse talar
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
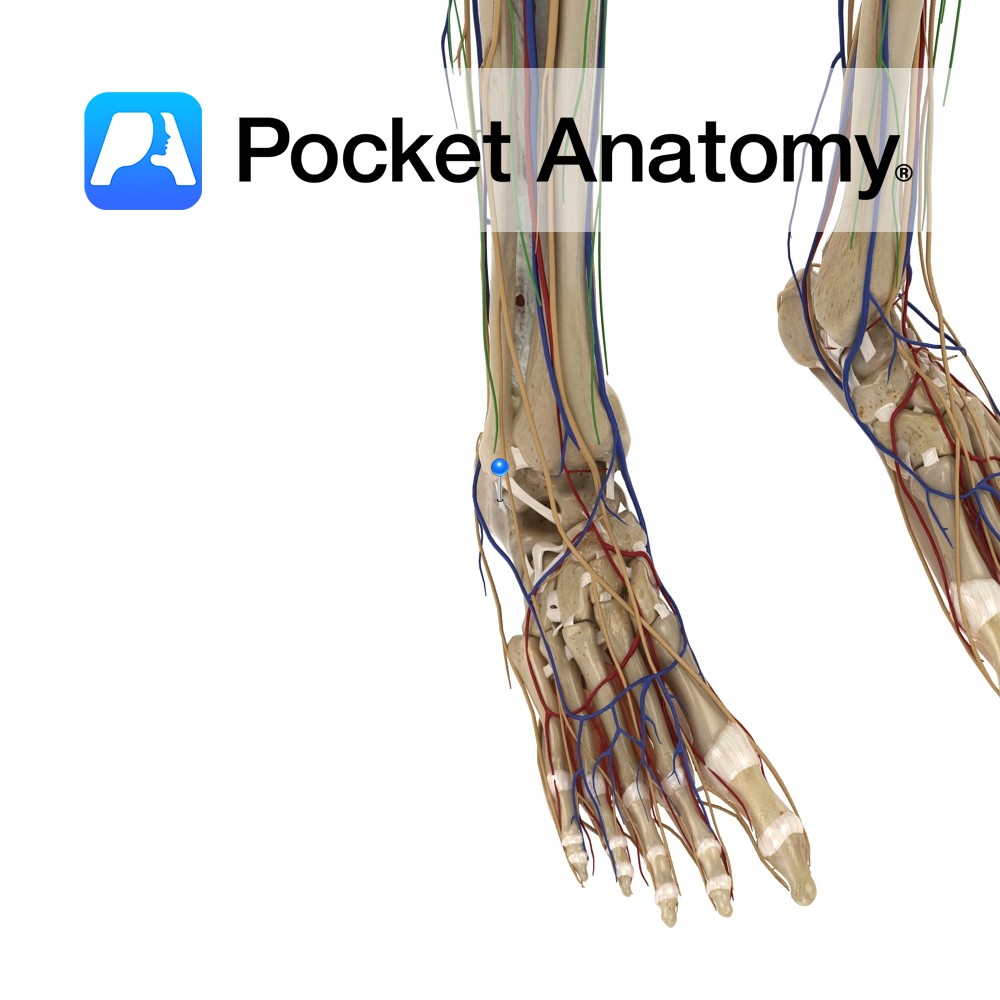
Anatomy Attaches from the posteromedial side of the lateral malleolus, above the malleolus fossa. It travels obliquely downwards and posteriorly to attach to a tubercle on the lateral surface of the calcaneus. Functions Supplies support and stability to the talocural (ankle) joint. Clinical The lateral ligaments of the ankle are the most commonly strained. The
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins