PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
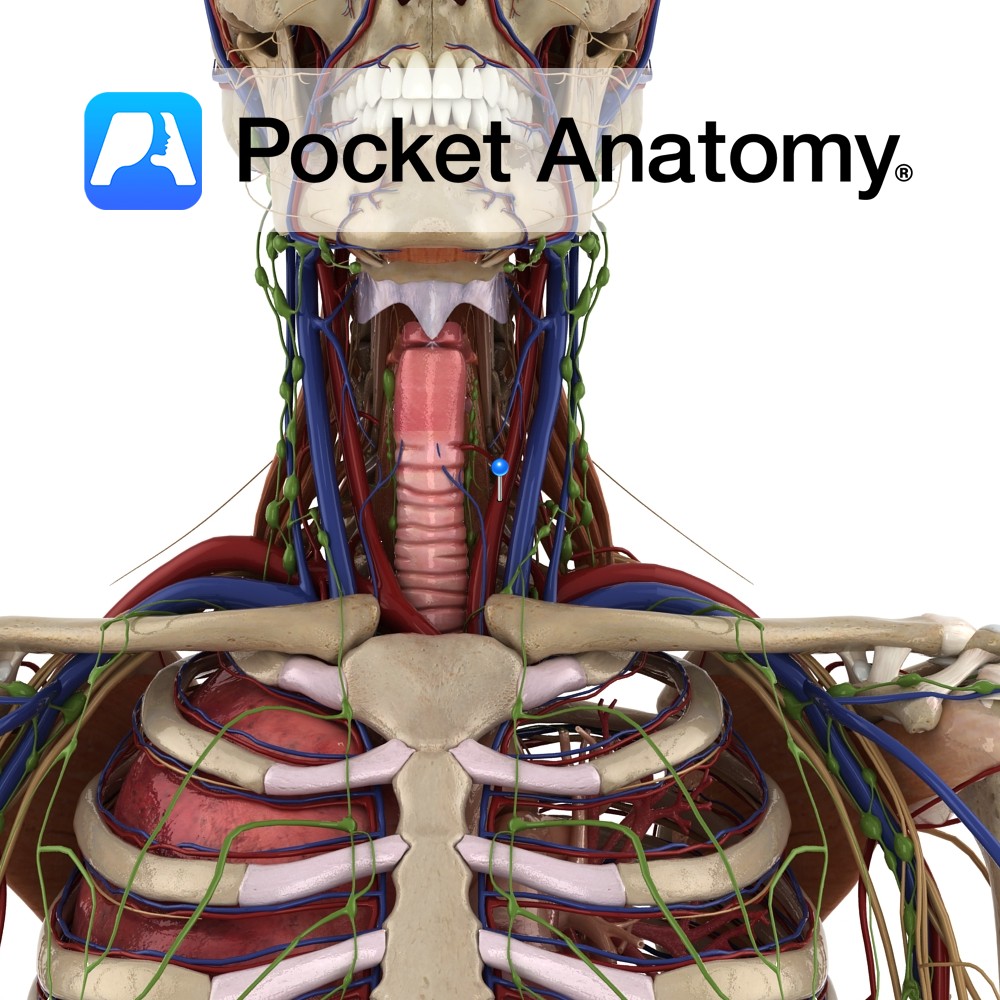
Anatomy Course Right common carotid artery originates from the right brachiocephalic trunk posterior to the sternoclavicular joint. Left common carotid originates as a main branch of the arch of the aorta and ascends to enter the neck behind the left sternoclavicular joint. Both bifurcate into the internal and external carotid arteries in the carotid triangle.
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
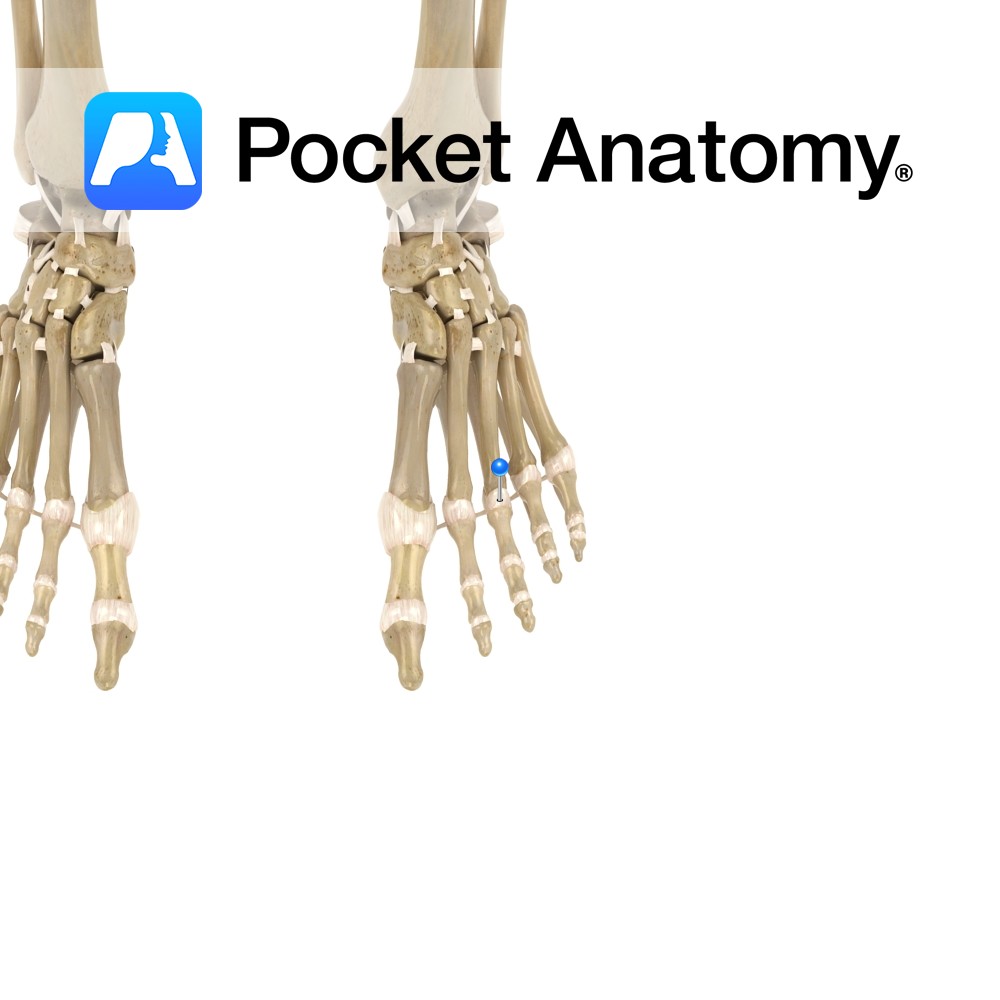
Anatomy Attach from the lateral and medial sides of the heads of the metatarsals to the base of the corresponding phalangeal joints. Functions To reinforce the joint laterally and medially. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
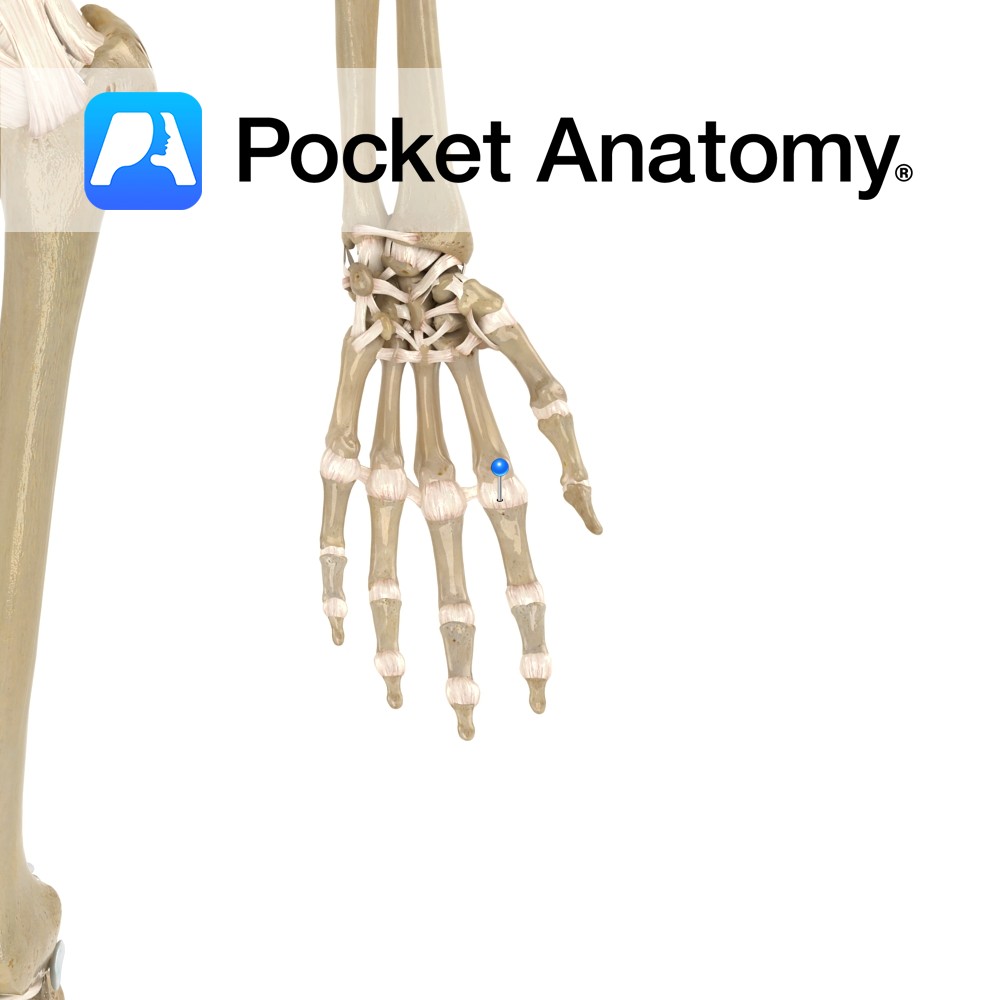
Anatomy The metacarpophalangeal ligaments attach from the distal heads of metacarpals two to five on the radial and ulnar surfaces, then attaching to the base of the corresponding phalangeals. Functions To reinforce laterally the metacarpophalangeal joint. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course All the colic veins follow their corresponding arteries and eventually empty into the superior and inferior mesenteric veins. Drain Left colic drains the descending colon, the right colic drains the ascending colon and the middle colic drains the transverse colon. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Branch of either the superior mesenteric artery or the ileocolic artery (inconsistent). Along its path it crosses anteriorly to the gonadal vessels, right ureters and the psoas major muscle. Supply Supplies both the ascending and transverse colon. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Branch of the inferior mesenteric artery, which travels retroperitoneally and divides into ascending and descending branches. Supply Supplies the descending and transverse colon. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
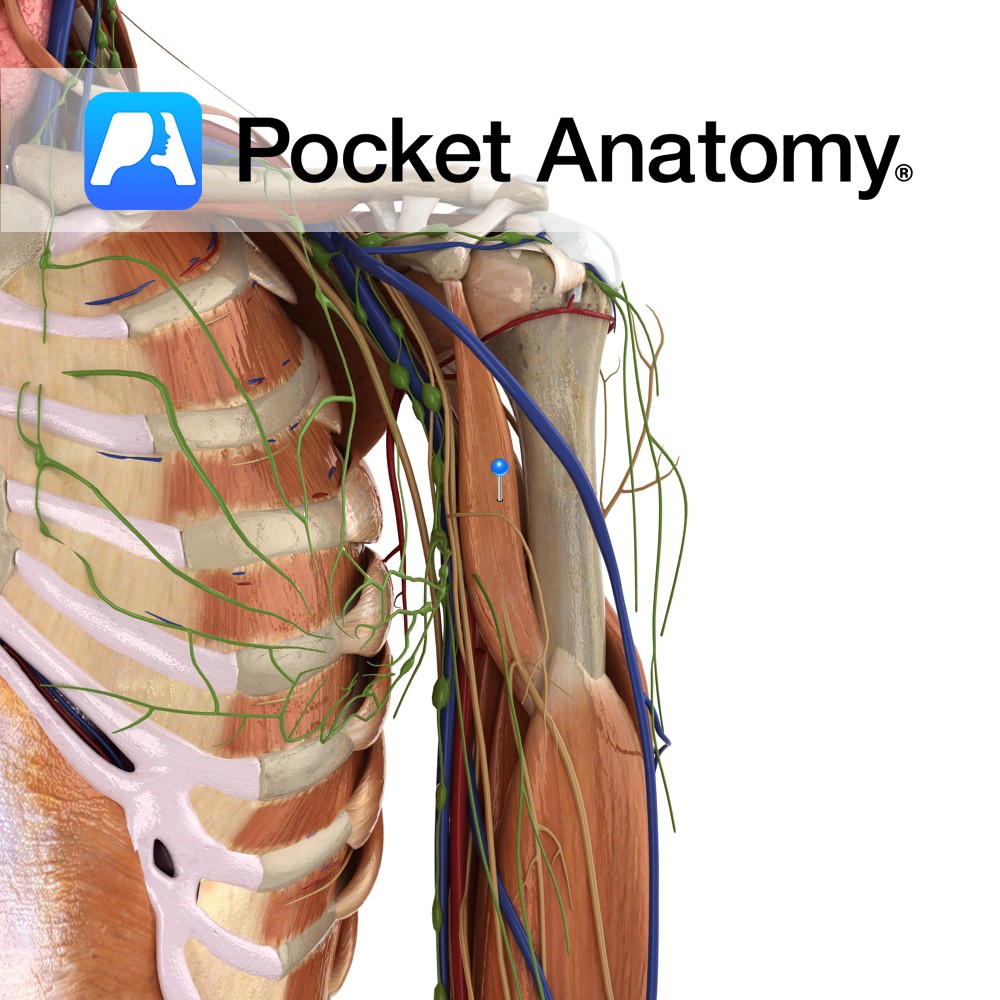
Anatomy Origin: Apex of coracoid process (with short head of biceps brachii). Insertion: Midway on medial border of humerus between the origin of triceps brachii and brachialis. Key Relations: Musculocutaneous nerve perforates it in the axilla as its route of entry to the arm. Functions -Flexes the arm at the shoulder joint. -Adducts the arm
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
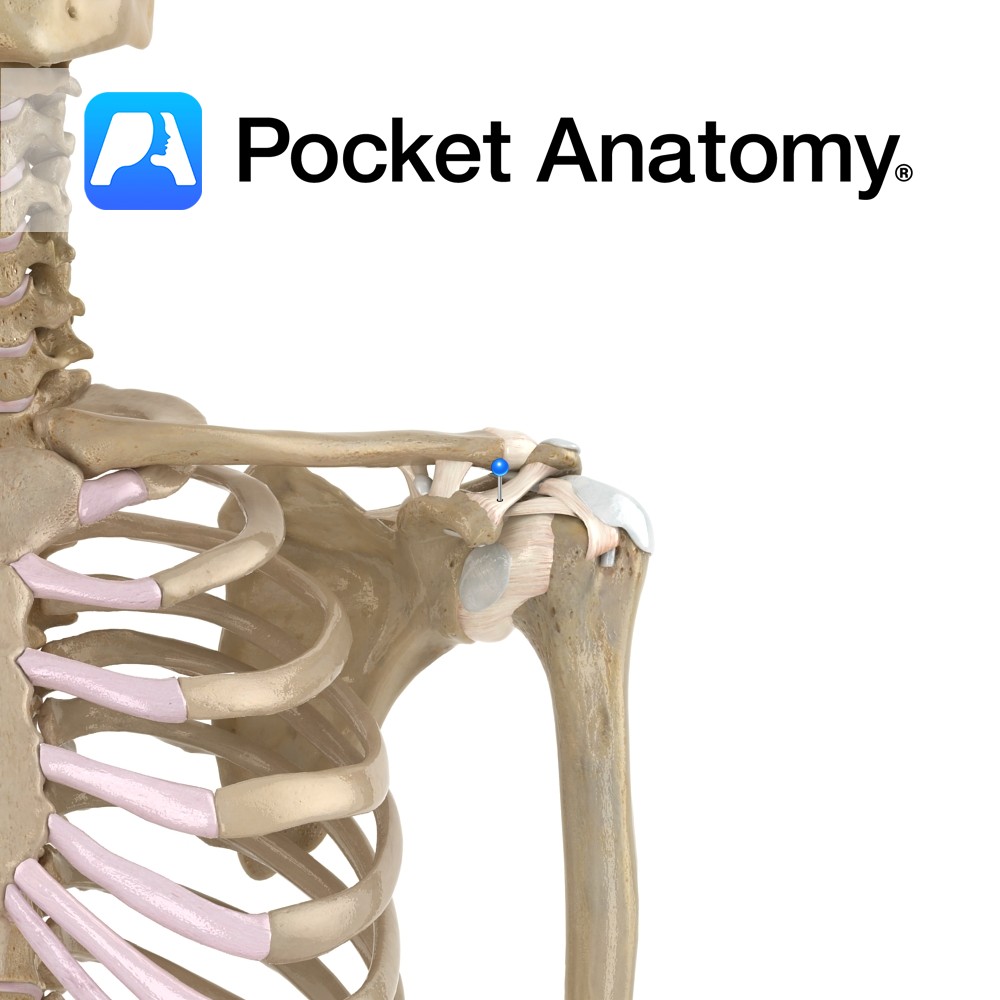
Anatomy A triangular shaped ligament. Its apex attaches just lateral to the acromioclavicular joint. Its broad base attaches along the lateral border of the coracoid process. Functions Helps to maintain the position of the acromion on the clavical, and stops superior distraction. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
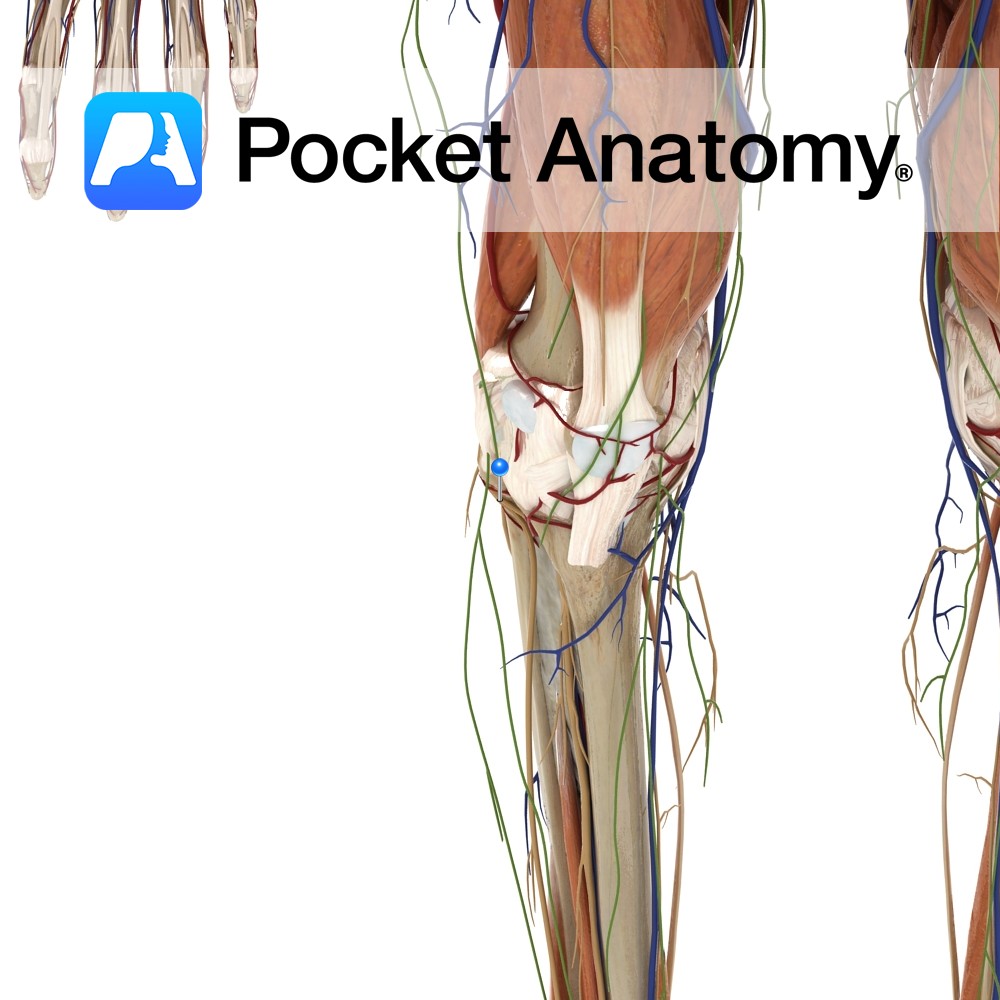
Anatomy Course Originates from the dorsal branches of the fourth and fifth lumbar nerves as well as the first and second sacral nerves. Makes an oblique descent on the lateral aspect of the popliteal fossa until it reaches the head of the fibula, which it encircles. Divides into the superficial peroneal and deep peroneal nerve.
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
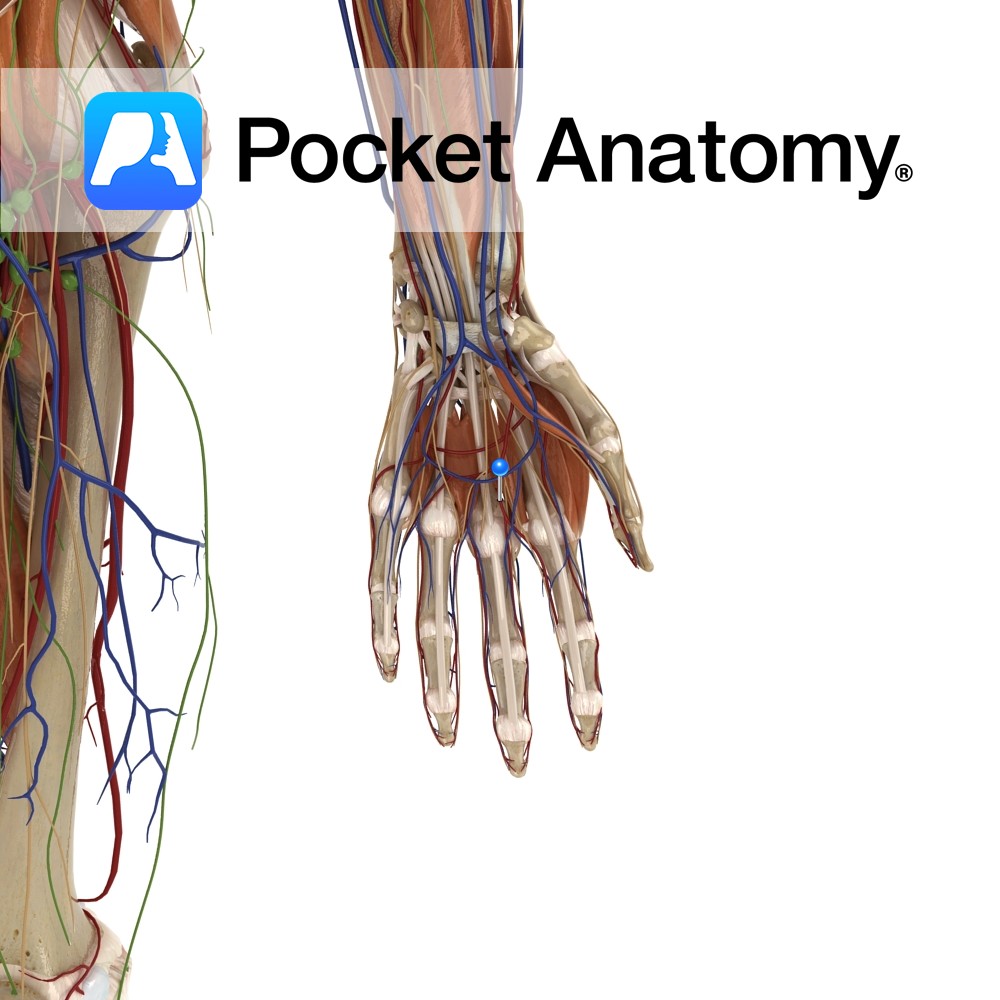
Anatomy Course Branches from the superficial palmar arch which then proceed distally on the anterior aspects of the lumbrical muscles. Supply Supplies the little finger, ring finger, middle finger and medial aspects of the index finger. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins


.jpg)
.jpg)