PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
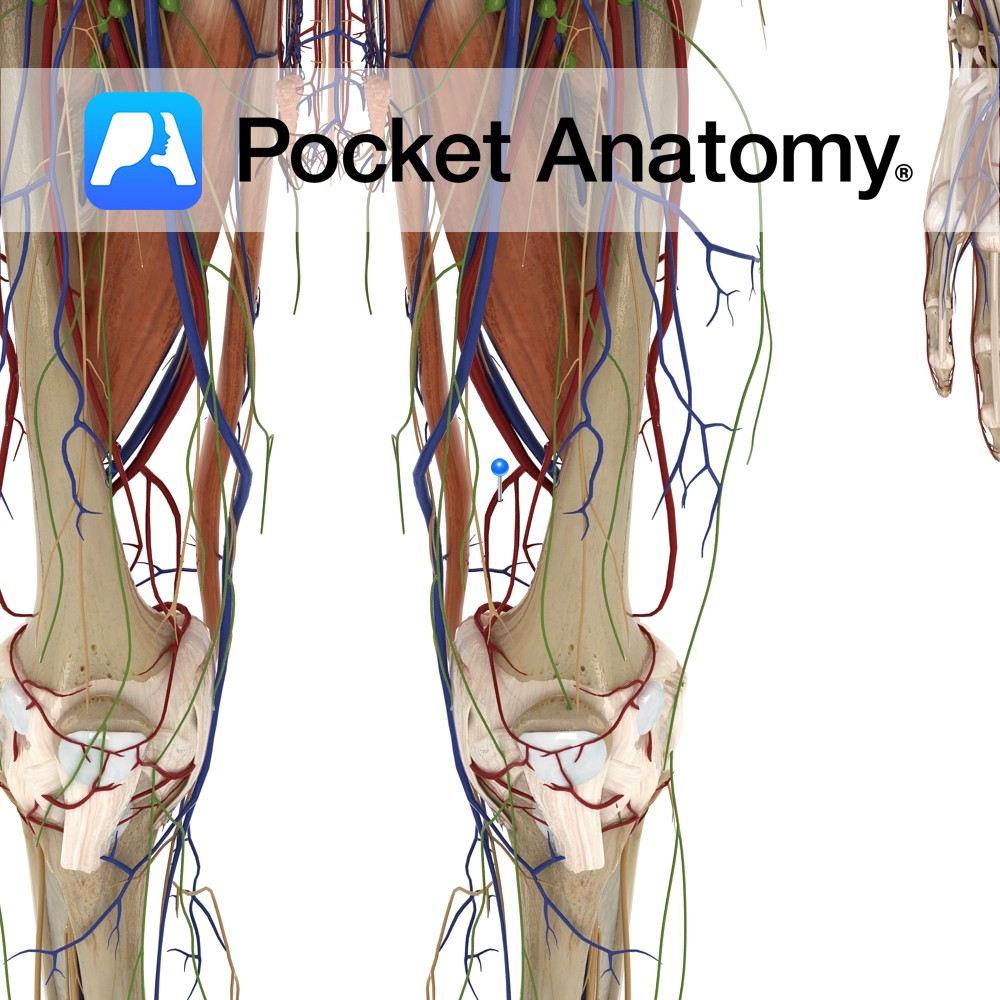
Anatomy Course Branches off the femoral artery just before it passes through the adductor magnus. Immediately branches into its saphenous and articular branches. Supply It supplies the knee via its branches. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
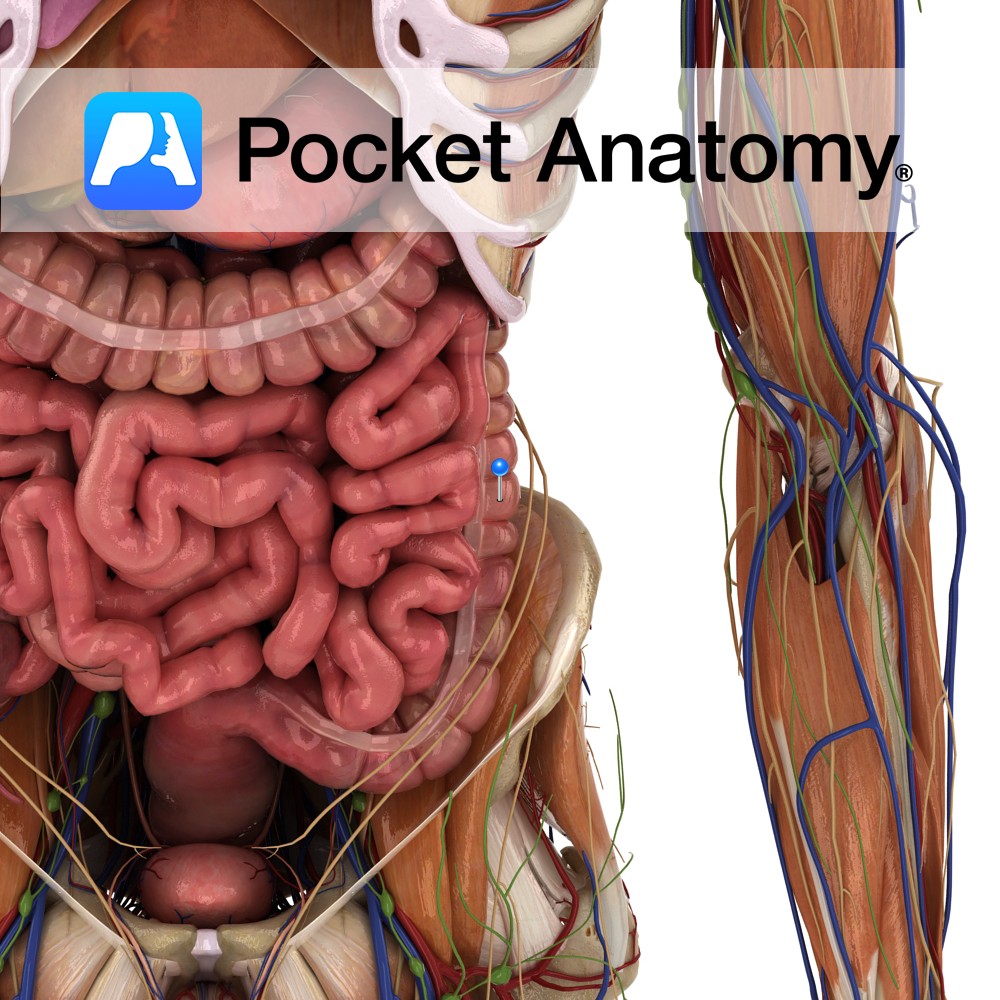
Anatomy Starts at splenic (left colic) colon flexure, at first directly behind transverse colon, front and sides covered by peritoneum, descending outside (lateral to) left kidney, then psoas, over aponeurosis of transversus abdominis and quadratus lumborum, past iliac crest down to be continuous with sigmoid colon at top of lesser pelvis (ie true pelvis, ie
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
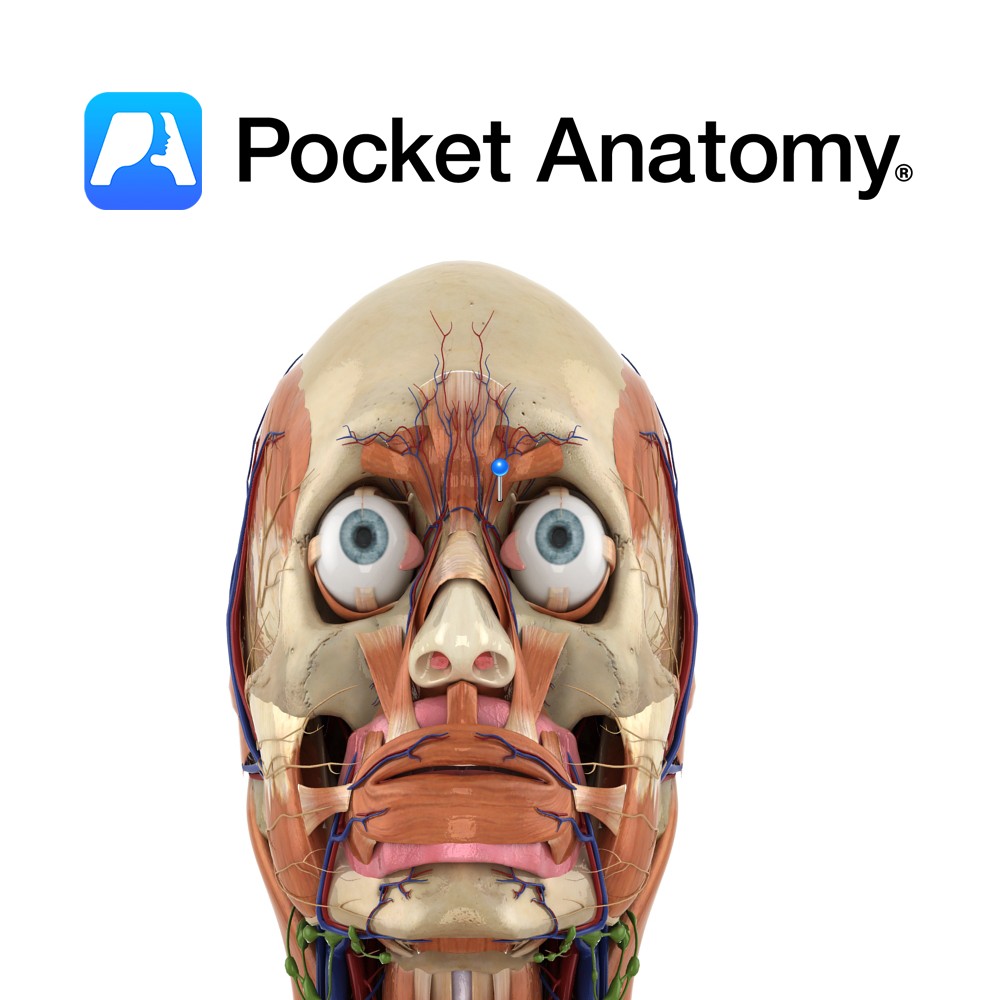
Anatomy Origin: Medial orbital rim adjacent to the lacrimal bone. Insertion: Medial aspect of the bony orbit. Key Relations: Inserts inferior to the corrugator supercilii. Functions Depresses the eyebrow. Supply Nerve Supply: Facial nerve, temporal branch (CN 7). Blood Supply: Opthalmic artery. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
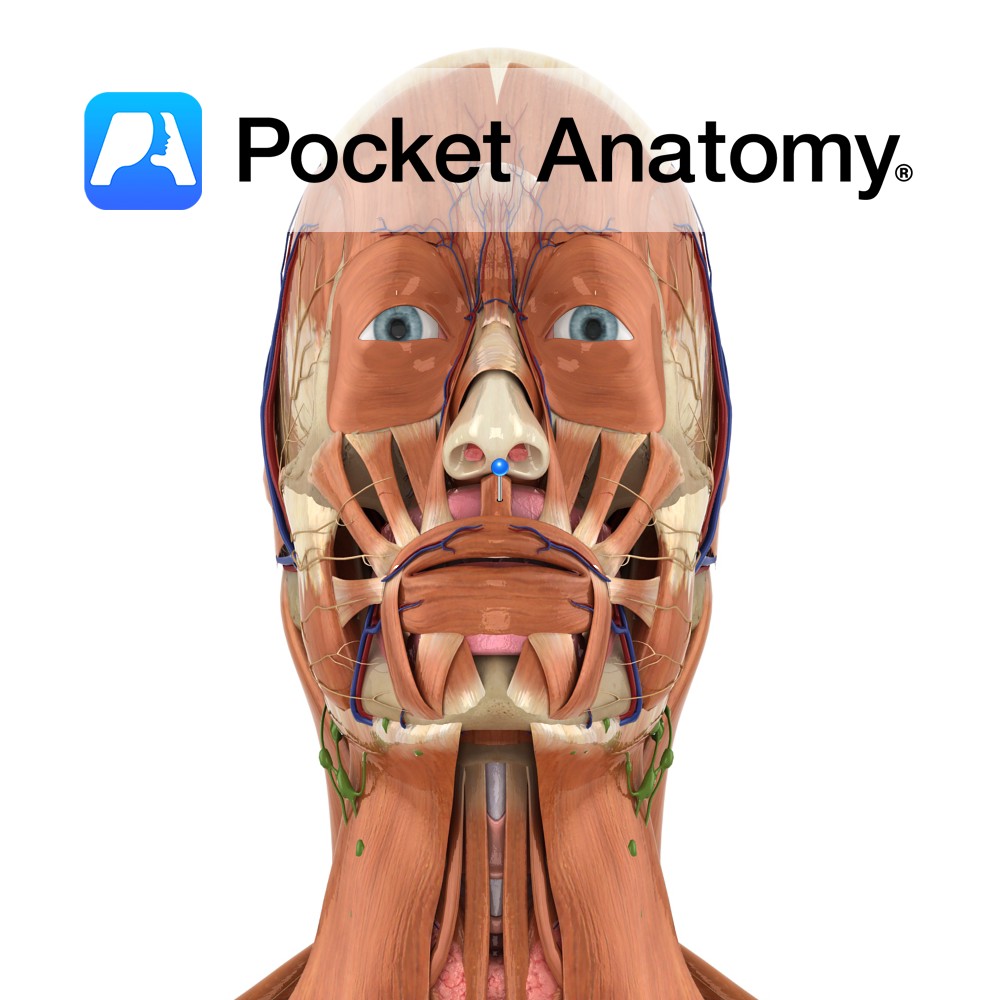
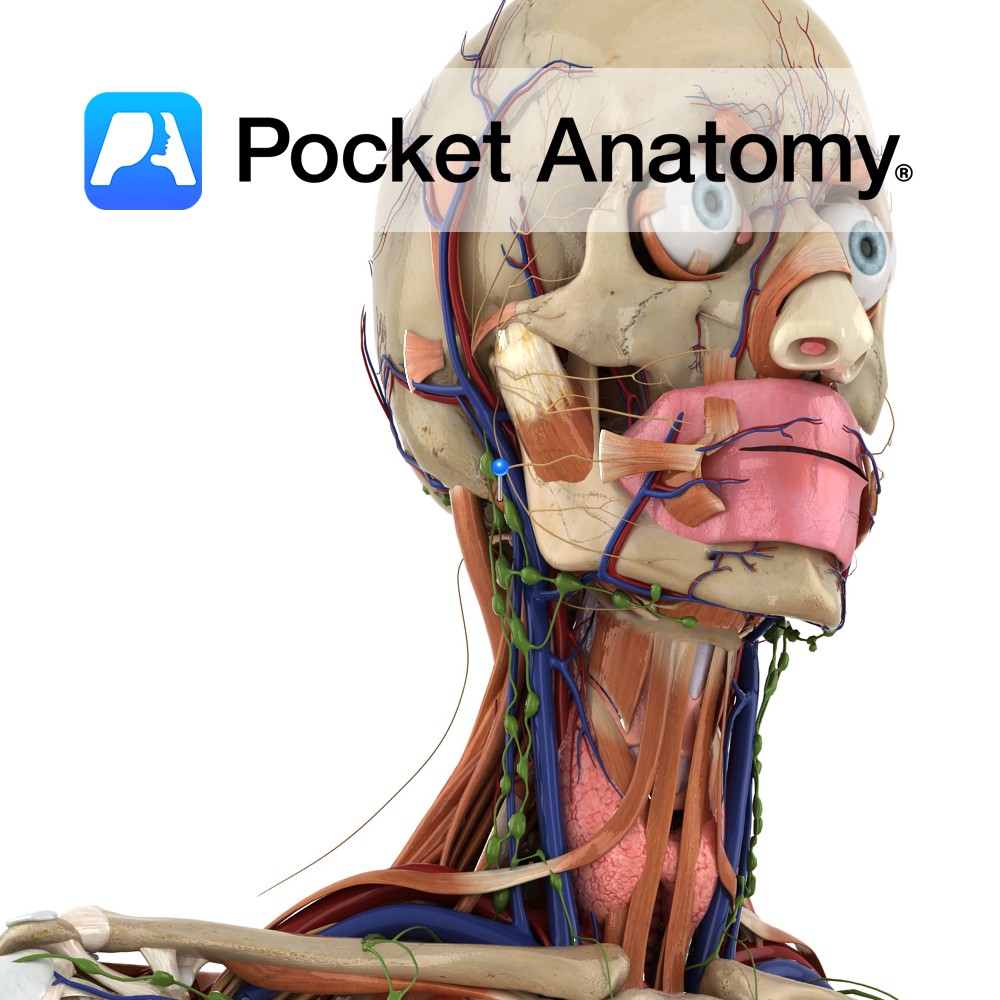
Anatomy Origin: Maxilla above medial incisor. Insertion: Lower part of nasal septum. Key Relations: Lies inferior to the nose. Functions Depresses the nasal septum. Supply Nerve Supply: Buccal branch of the facial nerve (CN 7). Blood Supply: Superior labial branch of the facial artery. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
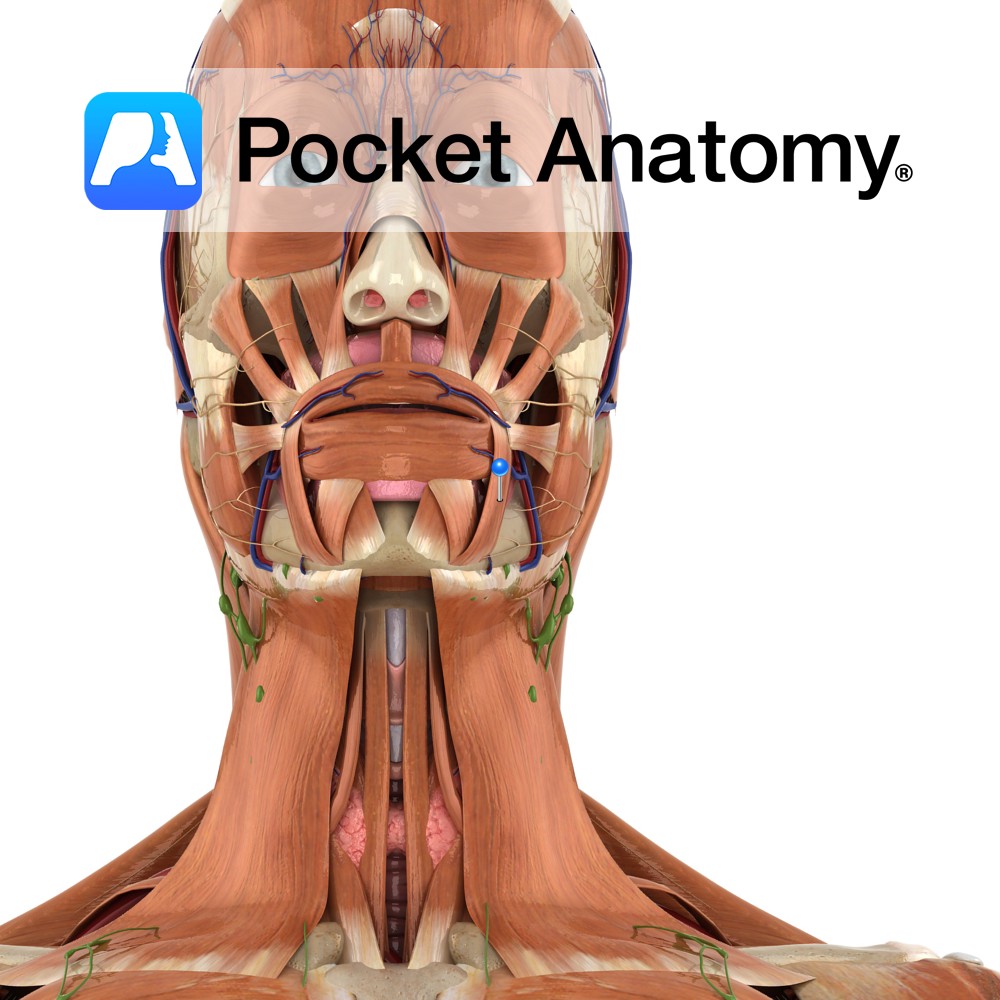
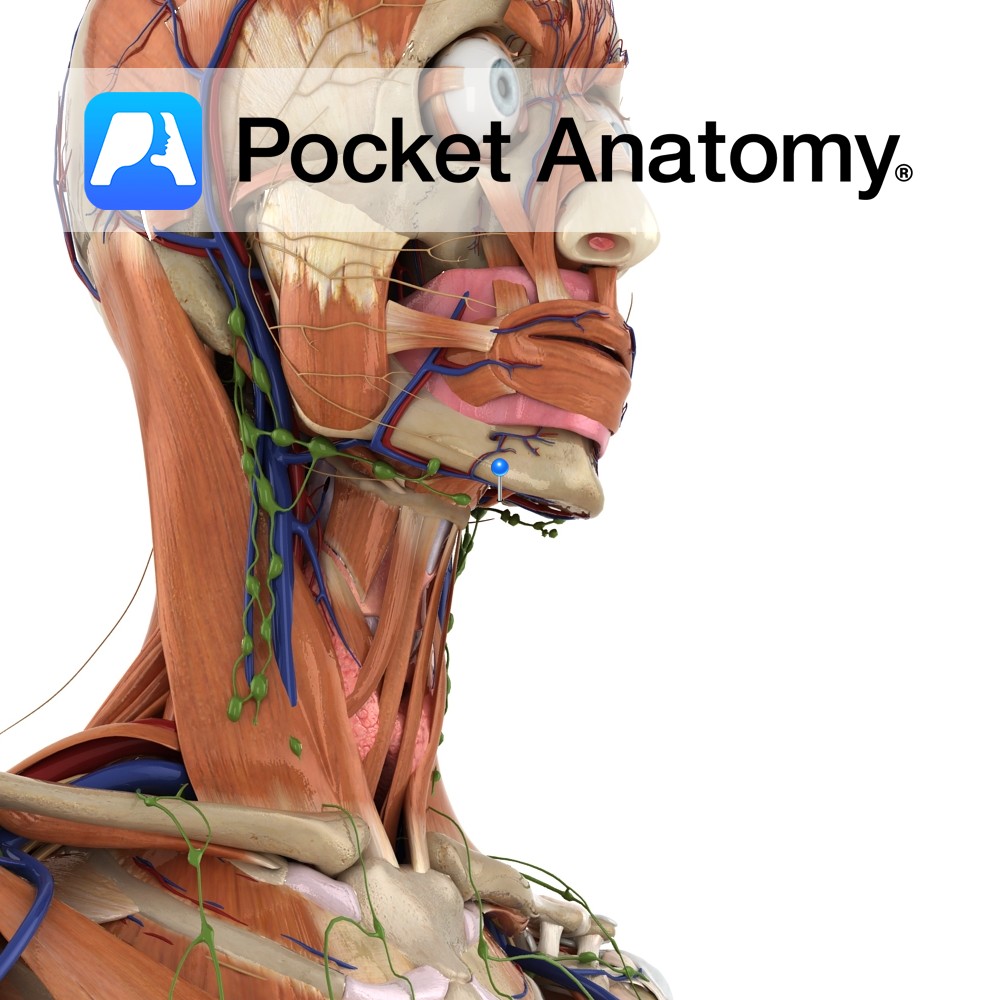
Anatomy Origin: Anterior part of the oblique line of the mandible. Insertion: Lower lip at the midline. Key Relations: Merges with fibres from the same muscle on the opposite side and from orbicularis oris. Functions Draws lower lip downwards and laterally. Supply Nerve Supply: Buccal and mandibular branches of the facial nerve (CN 7). Blood
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
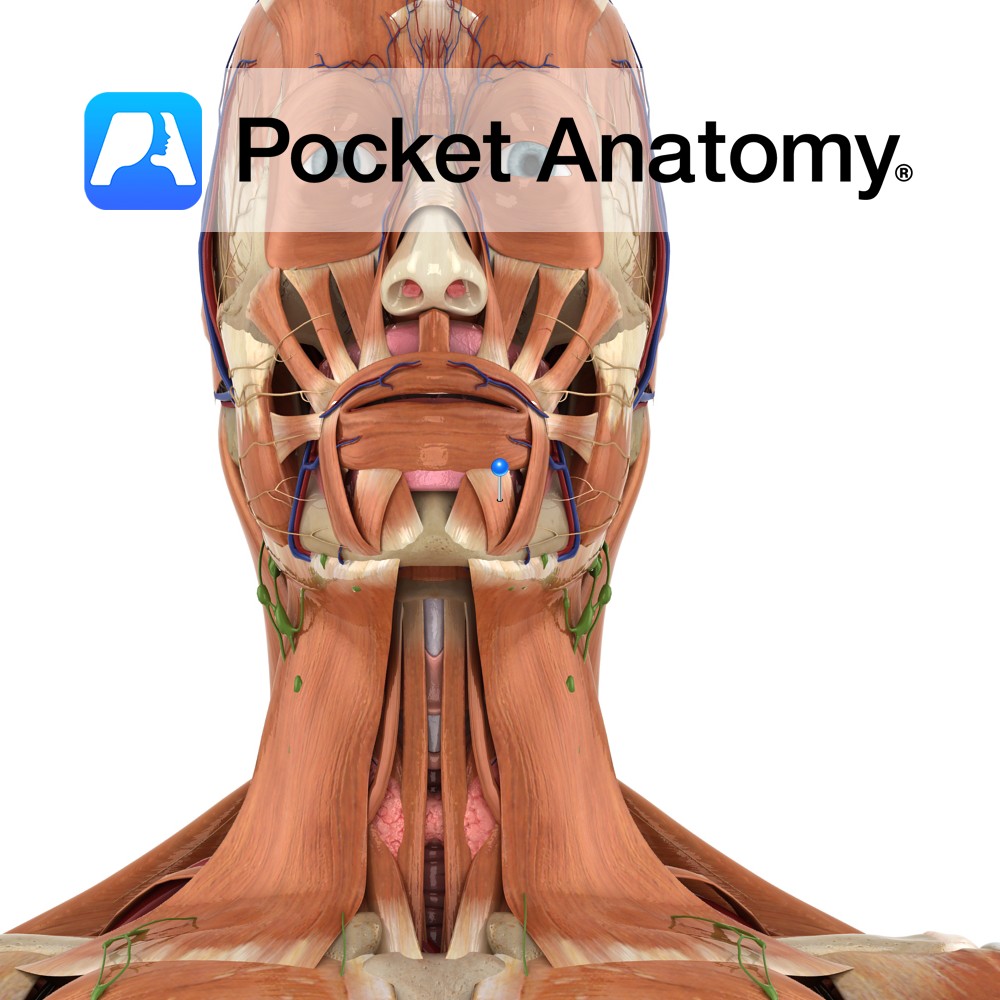
Anatomy Origin: External oblique line of the mandible. Insertion: Angle of the mouth. Relations: Arises on the lateral surface of the mandible inferior to the canine, pre molar and 1st molar teeth. Functions Depresses angle of mouth (antagonises levator anguli oris and zygomaticus major). e.g. as in expressions of sadness or grief.. Supply Nerve Supply:
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
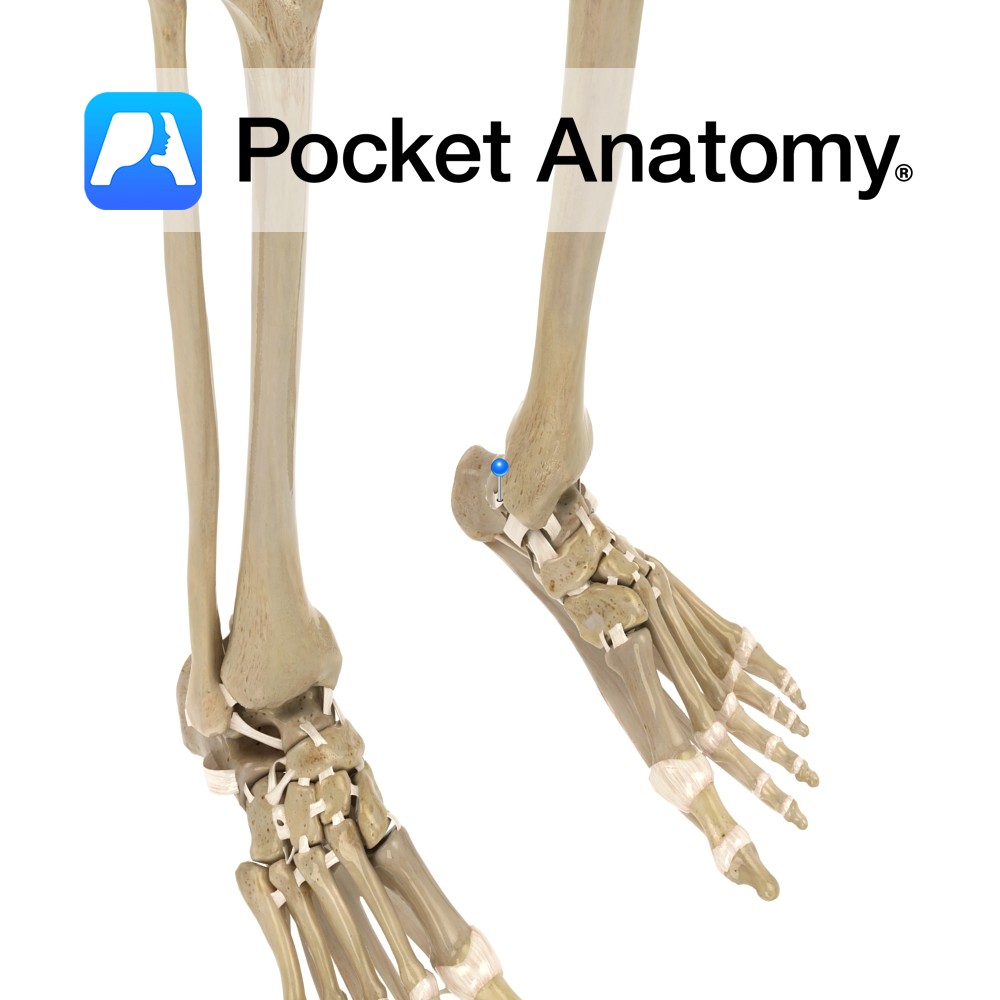
Anatomy The posterior tibiotalar ligament attaches from above the medial malleolus of the tibia to the medial side and medial tubercle of the talus. Functions Medial support and stability to the ankle joint. Clinical A very strong ligament. It gets damaged when an eversion force is placed on the ankle, putting the ankle into external
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Mastoid notch on medial side of mastoid process of temporal bone. Insertion: Intermediate tendon between the two bellies which itself attaches to the body of the hyoid bone. Key Relations: -Is one of the suprahyoid muscles lying in the anterior triangle of the neck. -Forms inferoposterior boundary of submandibular triangle. -Forms superior boundary
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Digastric fossa on inside of mandible. Insertion: Intermediate tendon between the two bellies which itself attaches to the body of the hyoid bone. Key Relations: -Is one of the suprahyoid muscles lying in the anterior triangle of the neck. -Forms inferoanterior boundary of submandibular triangle. -Forms lateral boundary of submental triangle. -Superior to
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
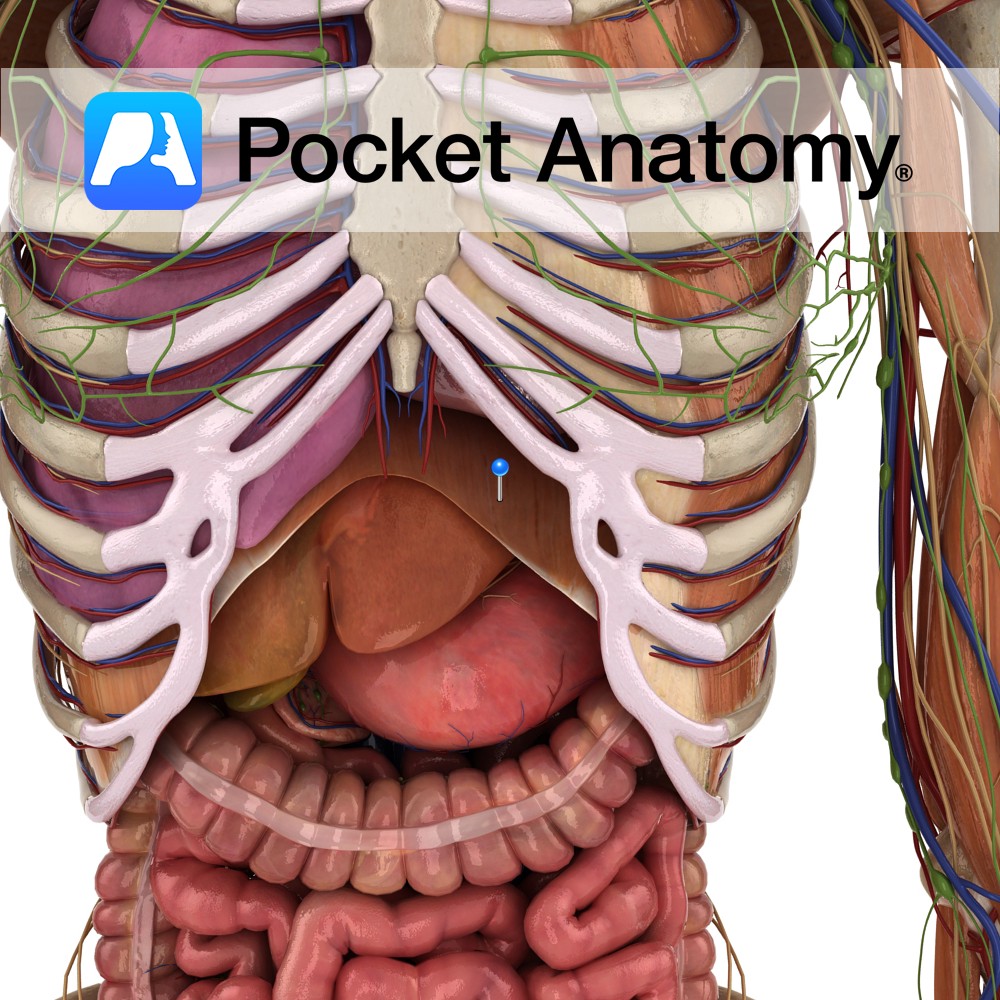
Anatomy Origin: Xiphoid process, costal margin, lower six costal cartilages, ends of 11th and 12th ribs and lumbar vertebrae L1 to L3. Insertion: Central tendon of diaphragm. Key relations: -The inferior vena cava passes through the caval hiatus of the diaphragm at vertebral level T8. -The oesophagus and vagus nerve pass through the oesophageal hiatus
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins