PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
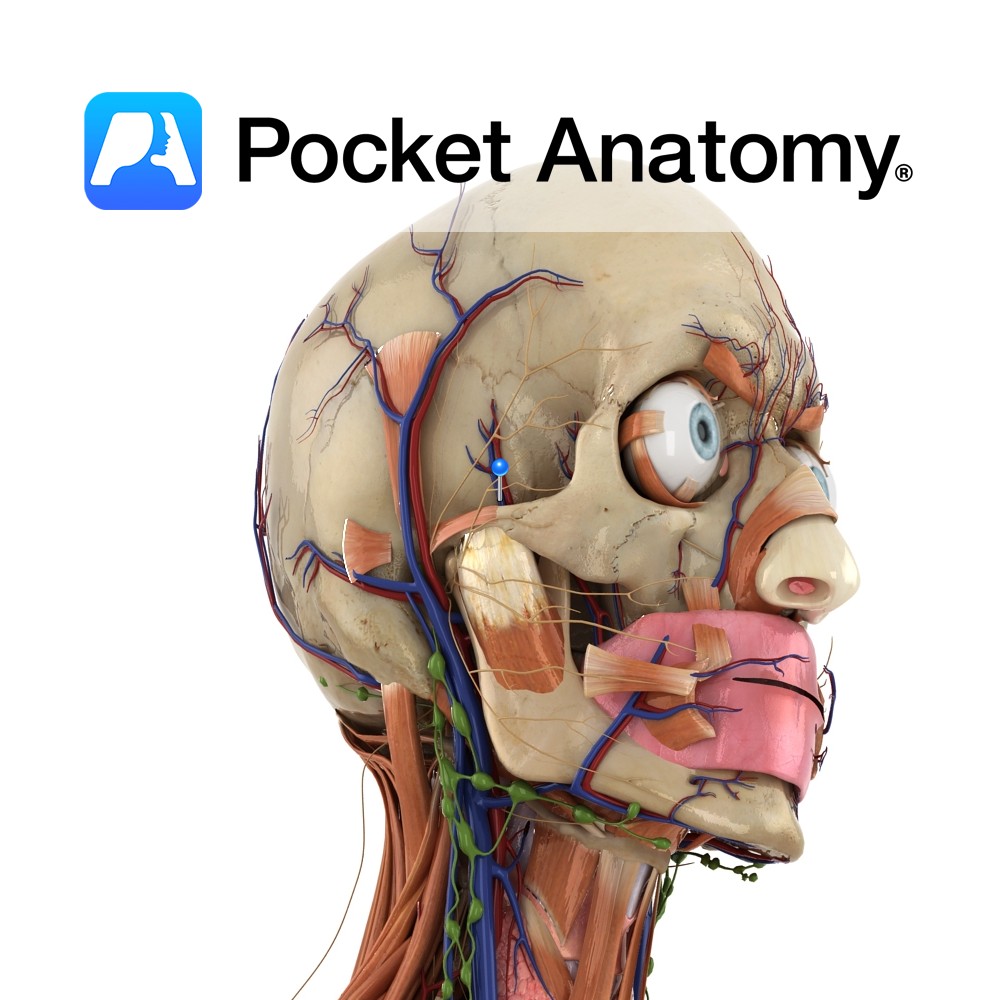
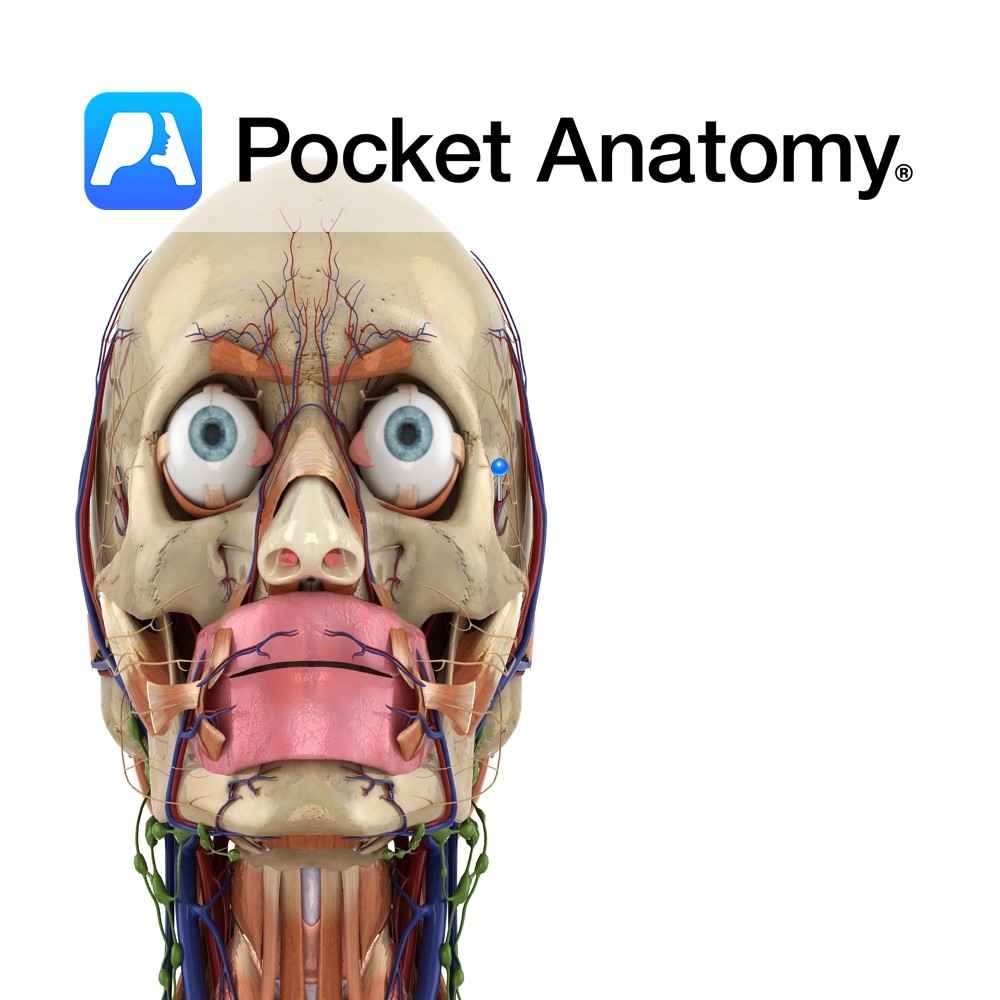
Anatomy Course Group of veins that arise from beneath the temporalis muscle and eventually drain into the pterygoid plexus. Drain Drains the deep muscles of the side of the head. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Branches of the maxillary artery that arise in the infratemporal fossa. Usually travels in conjunction with the deep temporal nerves as it rises between the pericranium and temporalis muscle. Anastamoses exists between it and the middle temporal artery. Supply Mainly the temporalis muscle. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
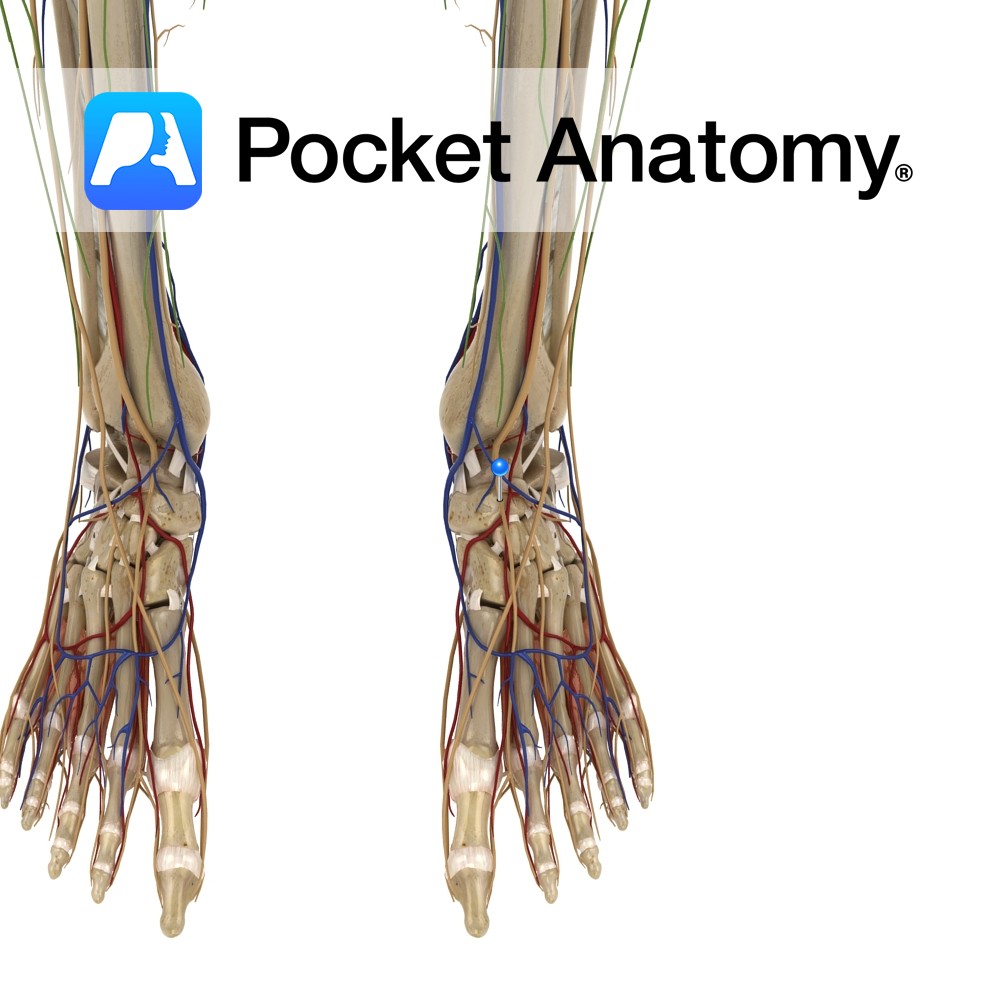
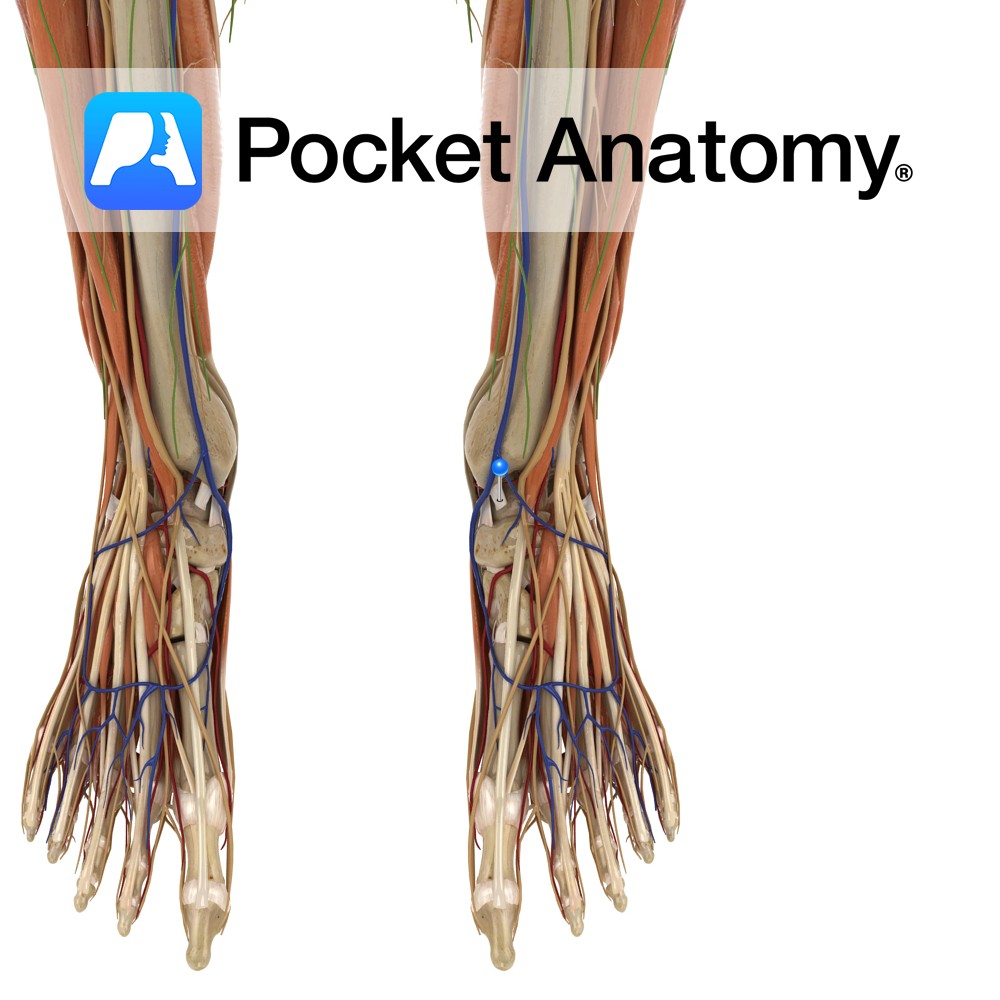
Anatomy Course Branch of the common peroneal nerve that descends in the deep compartments of the leg on the interosseous membrane. Descends down the leg with the anterior tibial artery until it reaches the ankle, where it gives off its terminal branches. Supply Motor innervation to the deep muscles of the leg and muscles of
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
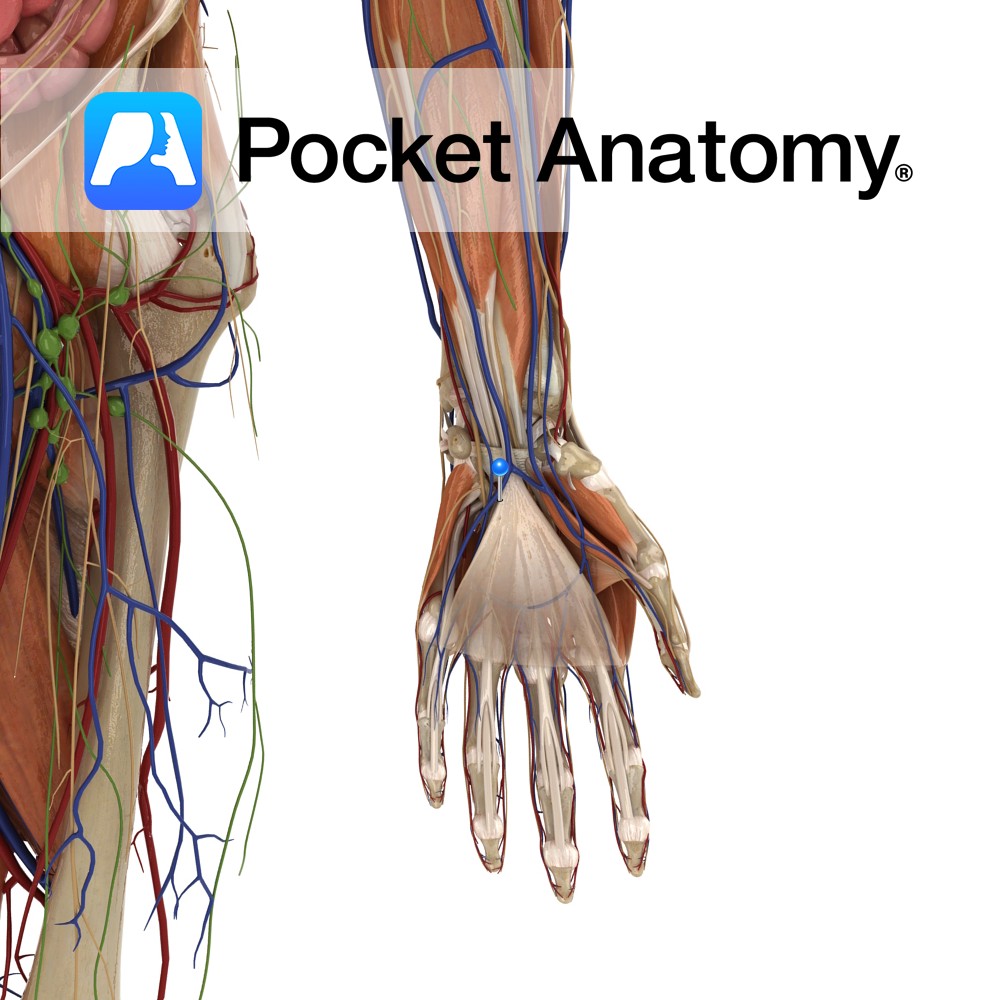
Anatomy Course Branch of the medical aspect of the ulnar artery. Proceeds around the hook of the hamate in order to reach the anastomotic network of the deep palmar arch. Supply Supplies the deeper components of the palm. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
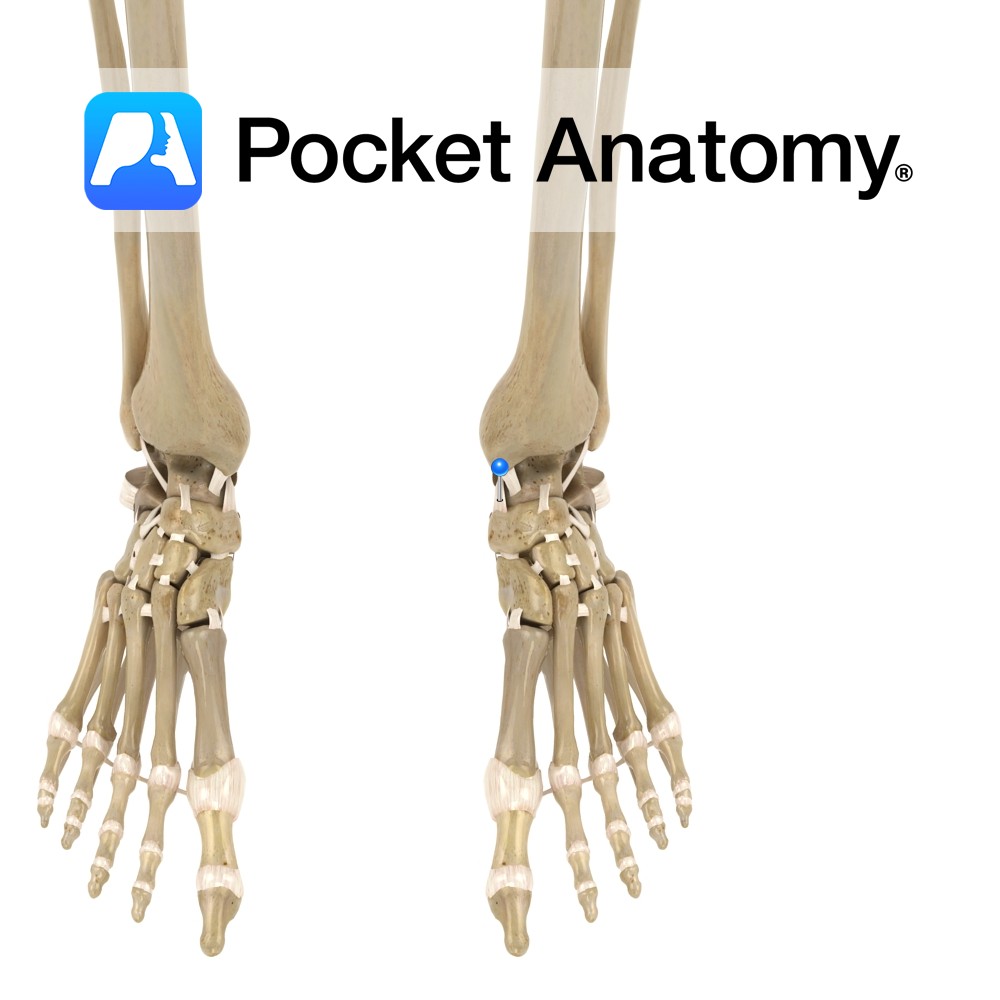
Anatomy The tibionavicular ligament attaches from above the medial malleolus of the tibia to in front of the navicular tuberosity, down to the calcaeonavicular ligament. Functions Medial support and stability to the ankle joint. Clinical A very strong ligament. It gets damaged when an eversion force is put on the ankle, placing the ankle into
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Attaches from above the medial malleolus on the anterior surface of the tibia, to the medial surface of the talus. It lies deep to the tibionavicular and tibiocalcaneal parts of the deltoid ligament. Functions Medial support and stability to the ankle joint. Clinical A very strong ligament. It gets damaged when an eversion force
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Anterior fibres from lateral third of the clavicle. Lateral/middle fibres from the acromion. Posterior fibres from the spine of the scapula. Insertion: Deltoid tuberosity of the humerus. Key Relations: Its origin mirrors the insertion of trapezius. Functions -Powerful abductor of the arm after 15°.* -Anterior fibres flexes and medially rotates the arm at
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Anterior fibres from lateral third of the clavicle. Lateral/middle fibres from the acromion. Posterior fibres from the spine of the scapula. Insertion: Deltoid tuberosity of the humerus. Key Relations: Its origin mirrors the insertion of trapezius. Functions -Powerful abductor of the arm after 15°.* -Anterior fibres flexes and medially rotates the arm at
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Anterior fibres from lateral third of the clavicle. Lateral/middle fibres from the acromion. Posterior fibres from the spine of the scapula. Insertion: Deltoid tuberosity of the humerus. Key Relations: Its origin mirrors the insertion of trapezius. Functions -Powerful abductor of the arm after 15°.* -Anterior fibres flexes and medially rotates the arm at
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy There are four deep transverse metatarsal ligaments which link all the metatarsals. They attach on the dorsal surface of the head of the metatarsals from one to two, two to three, three to four and four to five. The ligament also blends with the planter ligaments of the adjacent metatarsophalangeal joints. Functions They enable
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)