PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
Anatomy Course A superficial vein that joins the great and small saphenous veins. It starts where the first dorsal digital vein of the foot meets with the great saphenous vein and connects to the small saphenous vein where it meets the fifth dorsal digital vein of the foot. Drain Receives tributaries from the dorsal digits
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
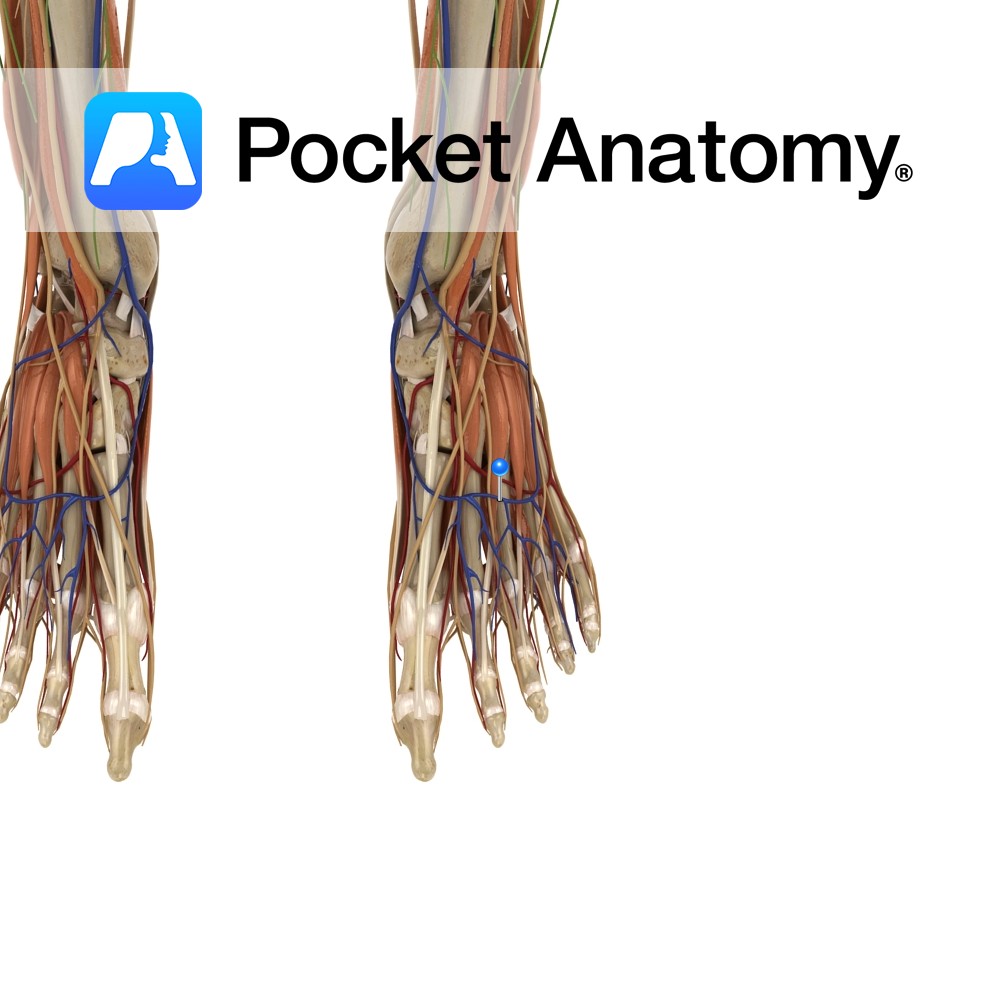
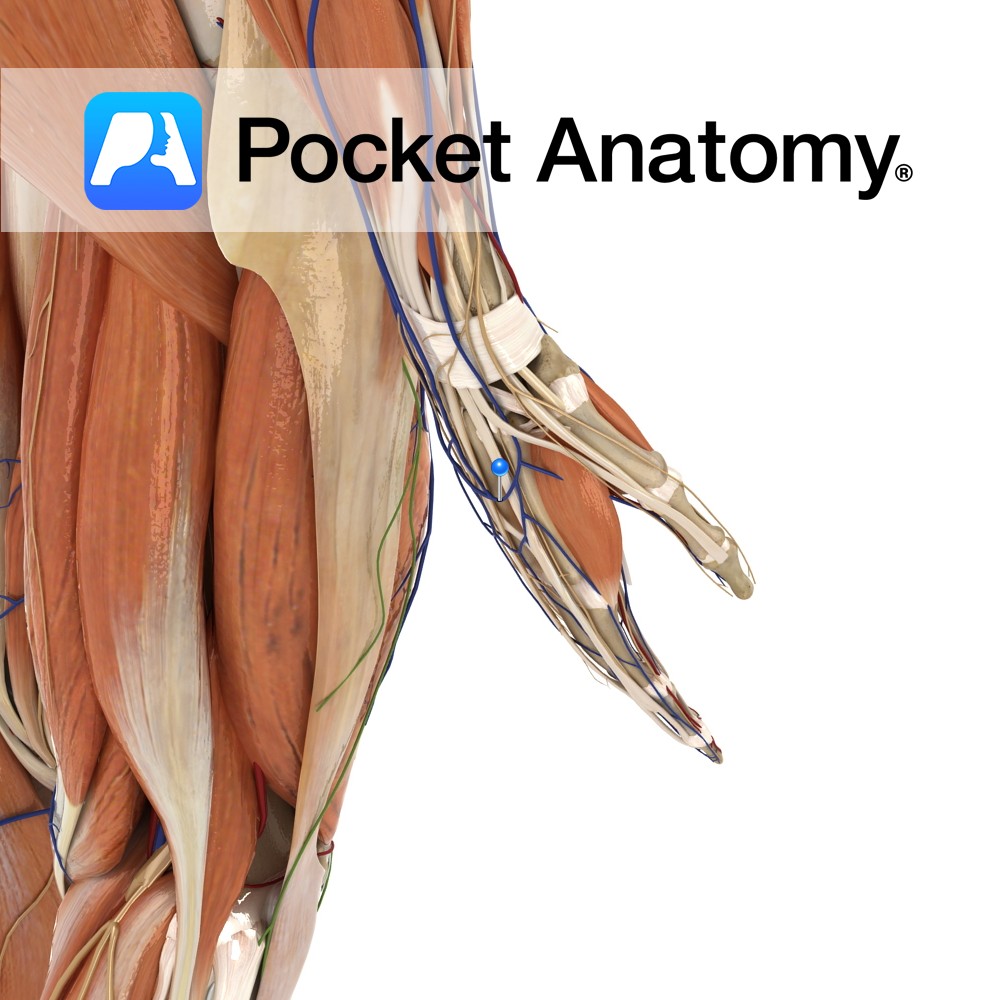
Anatomy Course A complex network of veins on the dorsum of the hand created by the dorsal metacarpal veins. The network gives rise to several veins, the most important being the cephalic and basilic vein. Drain Drains the dorsum of the hand. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
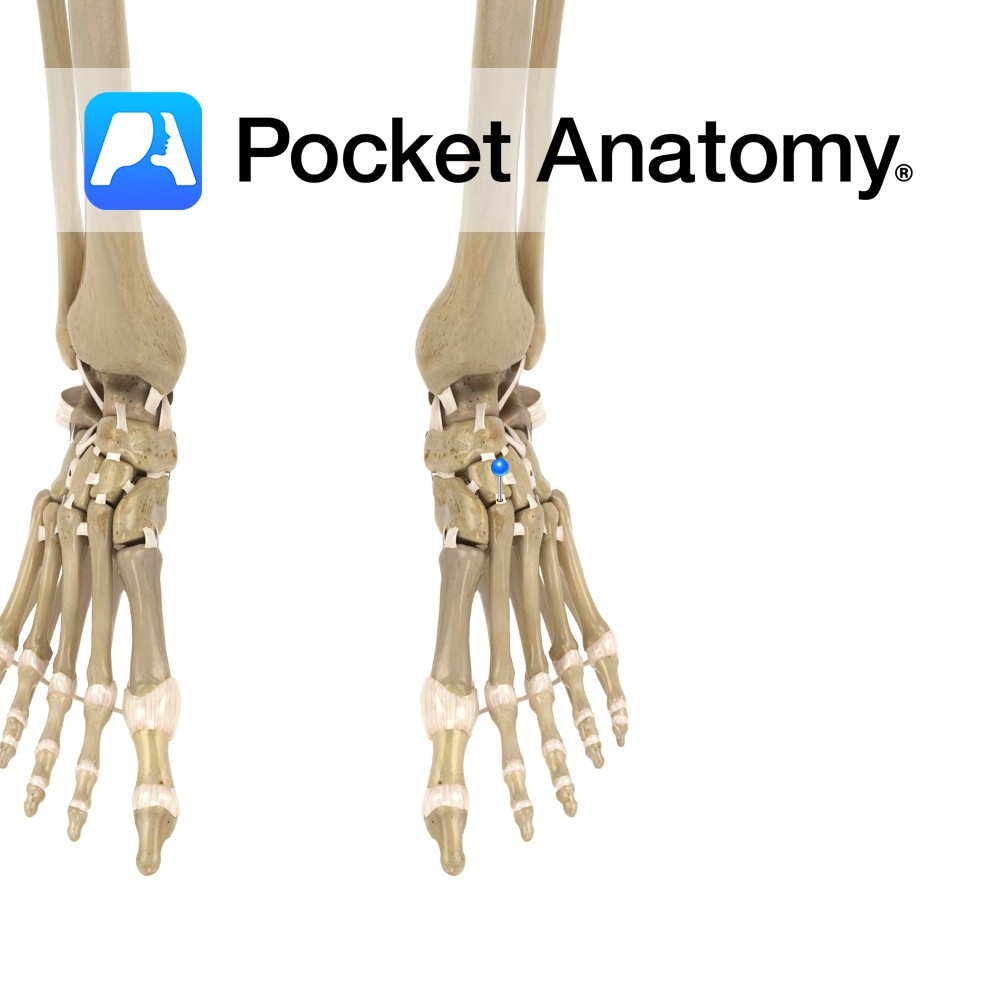
Anatomy Short, flat ligaments that attach longitudinally and obliquely from the cuboid and the three cuneiform bones, to the metatarsal bones of the foot. Functions Static stability to the tarsometatarsal joints. Clinical Injured when fractures or dislocations occur at the tarsometatarsal joint (at the first tarsometatarsal joint, called the lisfranc injury). Commonly injured when the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Attaches to the posterior border of the distal radius. It travels obliquely downwards and medially to attach to the dorsal surface of the scaphoid, lunate and trapezium bones of the hand. Weaker than the volar radiocarpal ligament. Functions Helps to stabilize the wrist joint posteriorly. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy One of the intrinsic muscles of the back. Consists of iliocostalis cervicus, thoracis and lumborum. Iliocostalis cervicis: Origin: Angles of 3rd to 6th ribs. Insertion: Transverse processes of C4 to C6. Iliocostalis thoracis: Origin: Angles of 7th to 12th ribs. Insertion: Angles of 1st to 6th ribs. Iliocostalis lumborum: Origin: Iliac crest, sacrum and
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy A thin leaf shaped cartilage situated at the inlet of the larynx. It is formed from yellow elastic fibrocartilage. It lies posterior to the root of the tongue and the hyoid bone. Its superior end is free, its inferior end is tapered and attaches internally to below the thyroid notch via the thyroepiglottic ligament.
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Epididymis (head – receives spermatozoa, body, tail – reabsorbs fluids and concentrates sperm) is a single coiled tube, 20-24 feet long, enveloping/investing/covering the back and top of the testis, its head continuous with and receiving immature sperm (can’t swim or fertilise) from efferent ducts at back of testis, passing them on (mature, typically after
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Layer of tough, dense, fibrous tissue that covers the upper portion of the cranium. Attaches posterior to occipitalis, anteriorly to frontalis, and laterally to auriculares anterior and superior. Posteriorly and laterally, its fibers are continued to the external occipital protuberance and zygomatic arch, respectively. Dorsally, it is firmly connected to the skin by the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
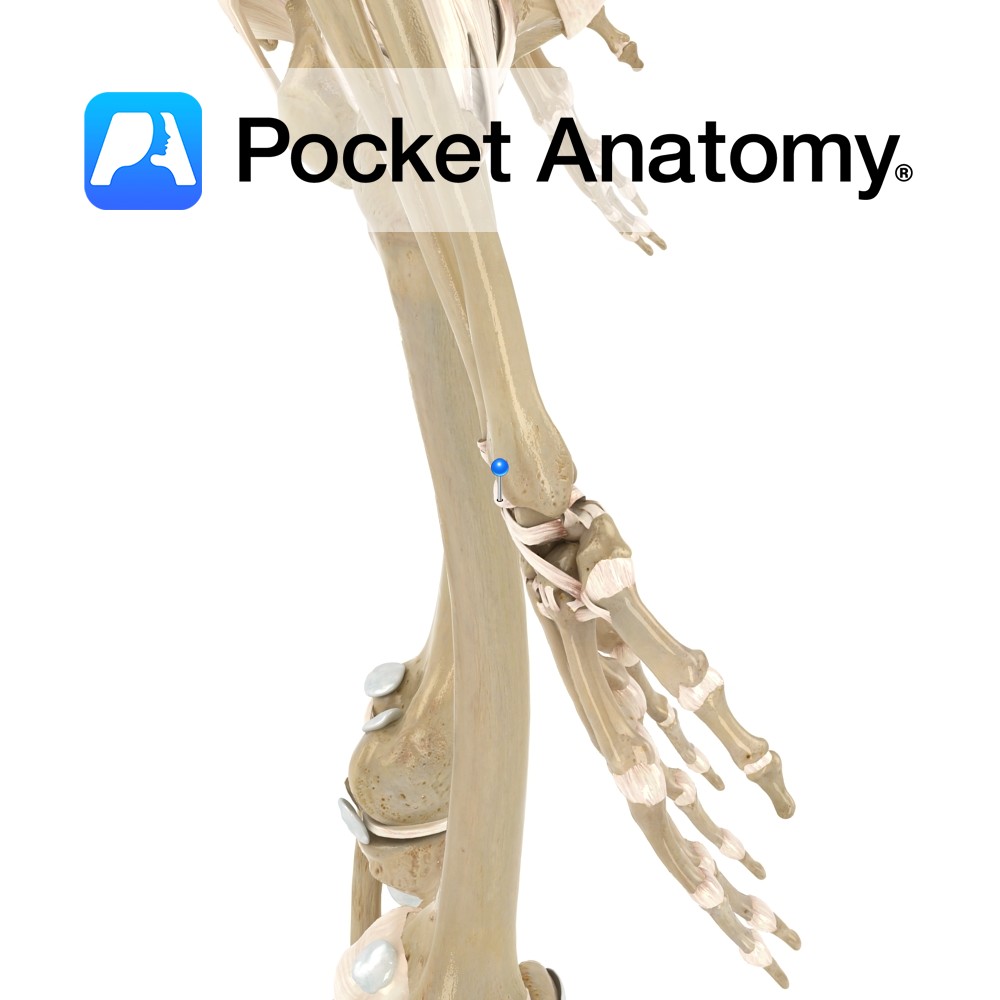
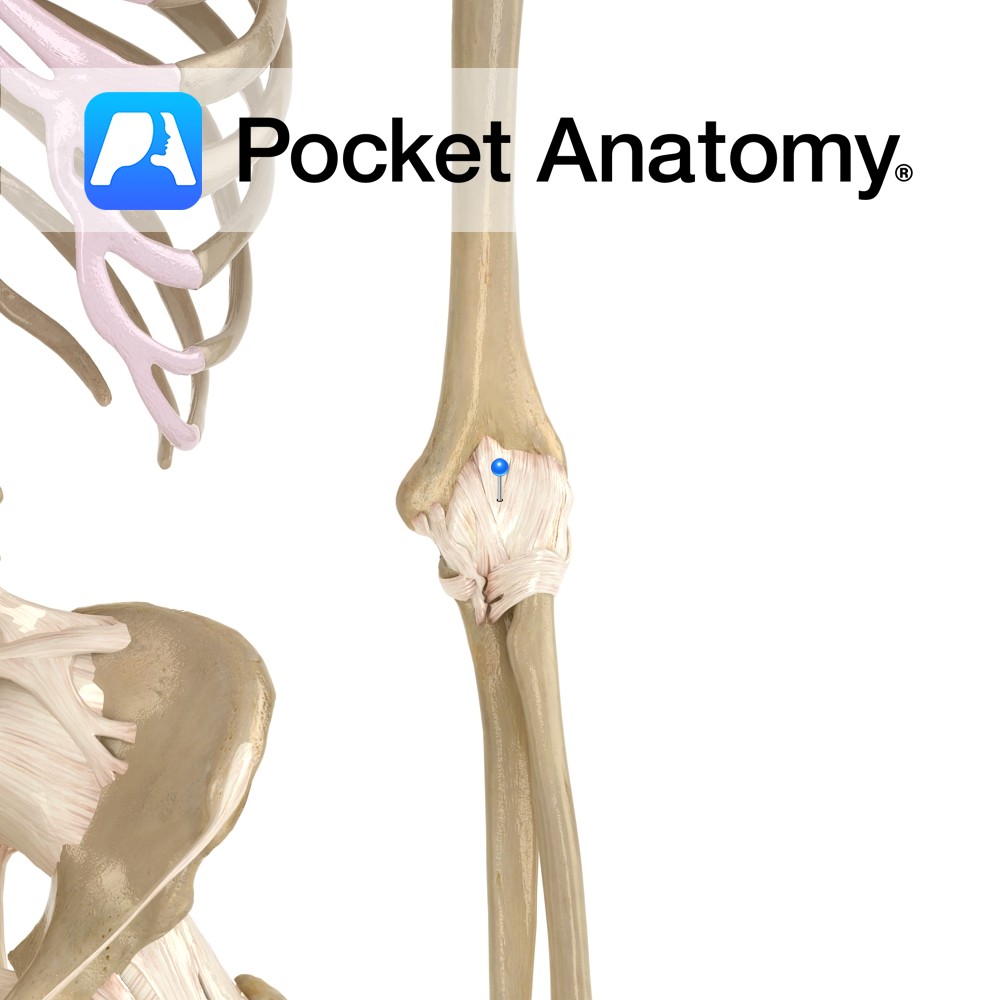
Anatomy The joint capsule attaches to the articular margins of the ulna, radius and humerus. It attaches to the margins of the olecranon, coronoid process and radial fossae. Distally, it blends with the annular ligament. The capsule is thinner anteriorly and posteriorly. Functions The capsule supplies static stability to the elbow joint. Interested in taking
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Functions The main function of the pinna is to collect sound and direct it into the ear canal; it acts as a filter, in that it selects the sound waves that are with the frequency range of human hearing. Anatomy Also known as the external ear, the pinna is the visible portion of the ear
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins