PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
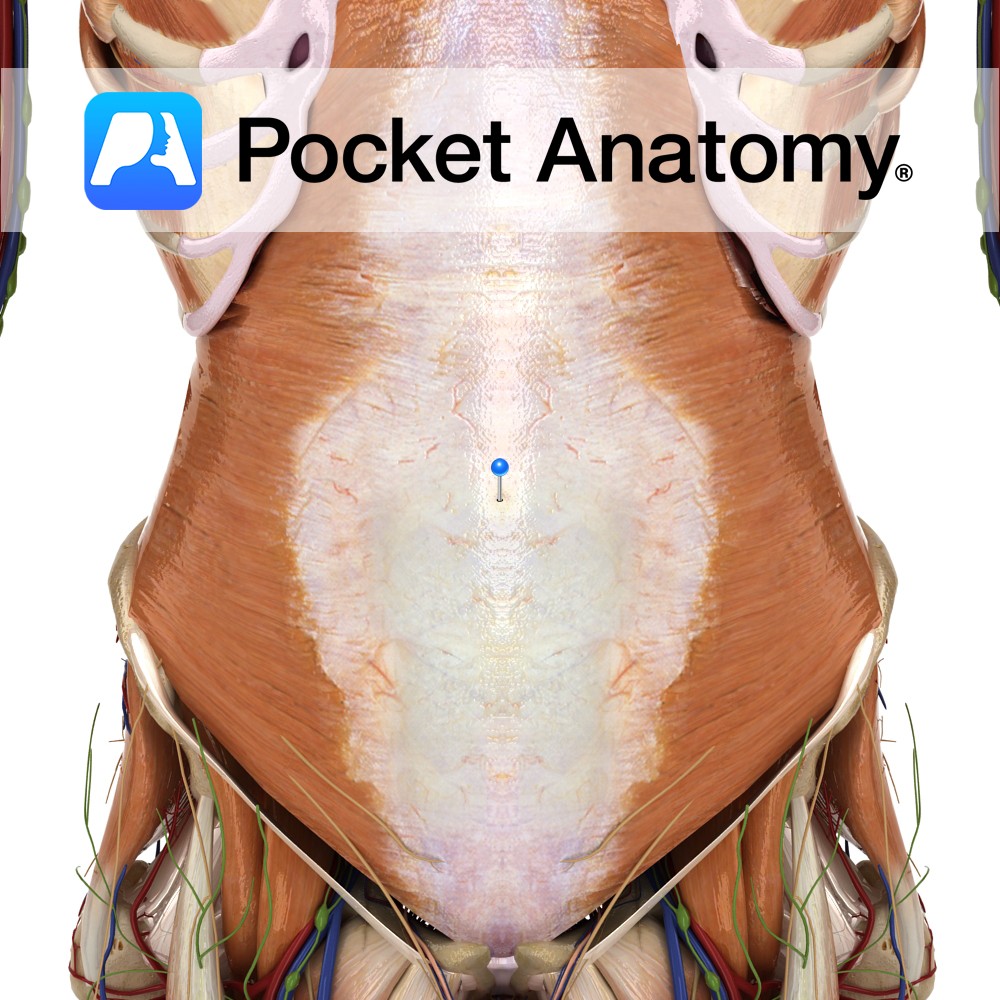
Anatomy A continuous fascia that lines the abdominal cavity, deep to the transverse abdominis muscle, and continuous into the pelvic cavity. Superiorly: it blends with the fascia of the inferior of the diaphragm. Posteriorly: it blends with the thoracolumbar fascia. Laterally: with the spine of the ilium. Anteriorly: in the abdomen, both sides converge and
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
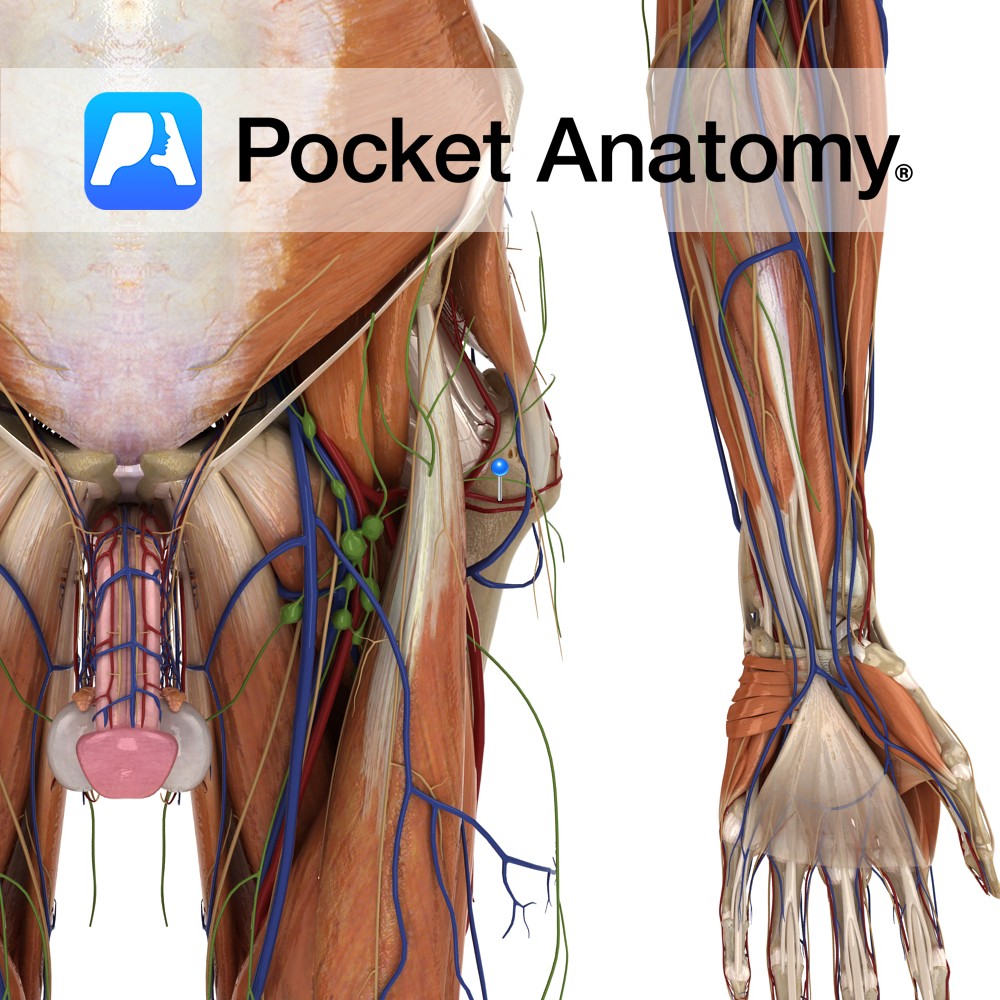
Anatomy Course This is the smallest branch from the lateral circumflex femoral artery. It travels laterally to pierce the vastus lateralis muscle. It then joins with the medial circumflex femoral artery contributing to the anastomosis around head of the femur. Supply The transverse branch of the lateral circumflex artery supplies the head and neck of
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
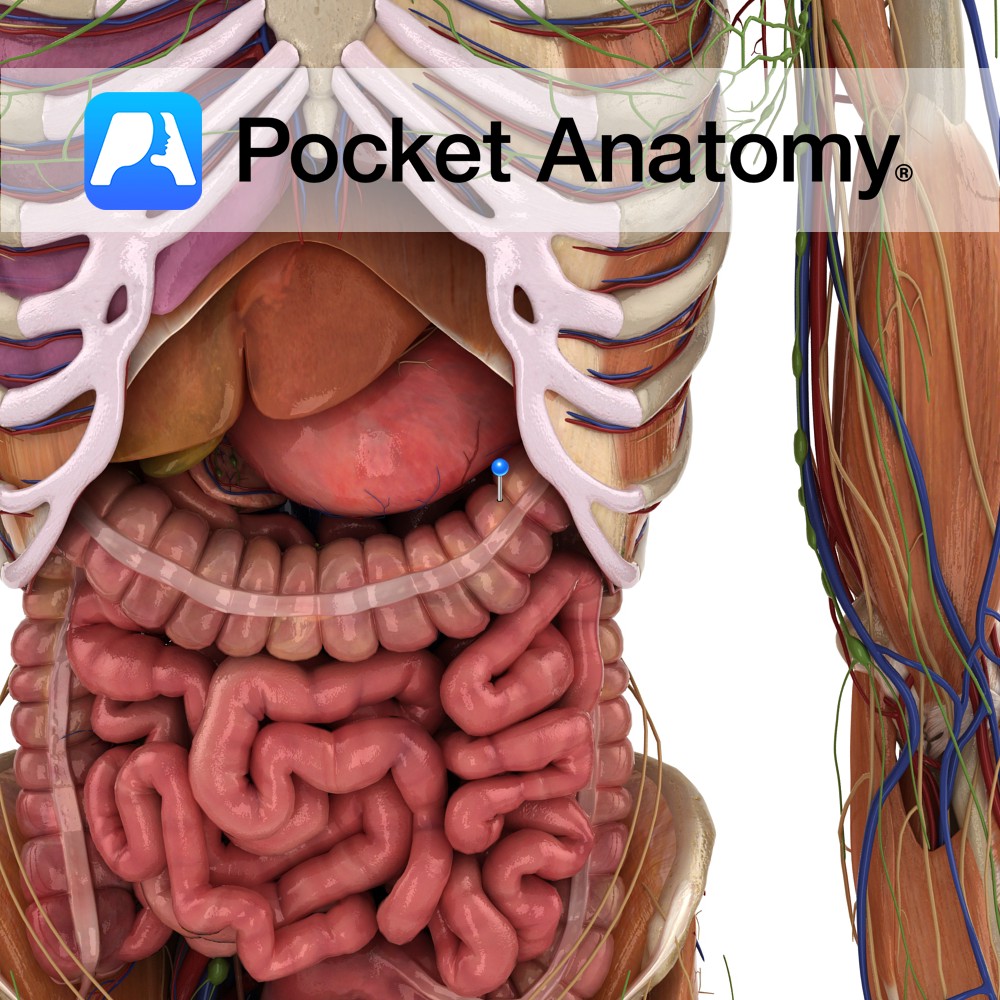
Anatomy Part of colon from abrupt outward curve of right colic (hepatic) flexure in right to abrupt inward curve of splenic (left colic) flexure in left hypochondrium, convex down, most mobile part of SI, largely covered by peritoneum, connected by transverse mesocolon (mesentery in SI, called mesocolon in LI – double layer of peritoneum caused
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
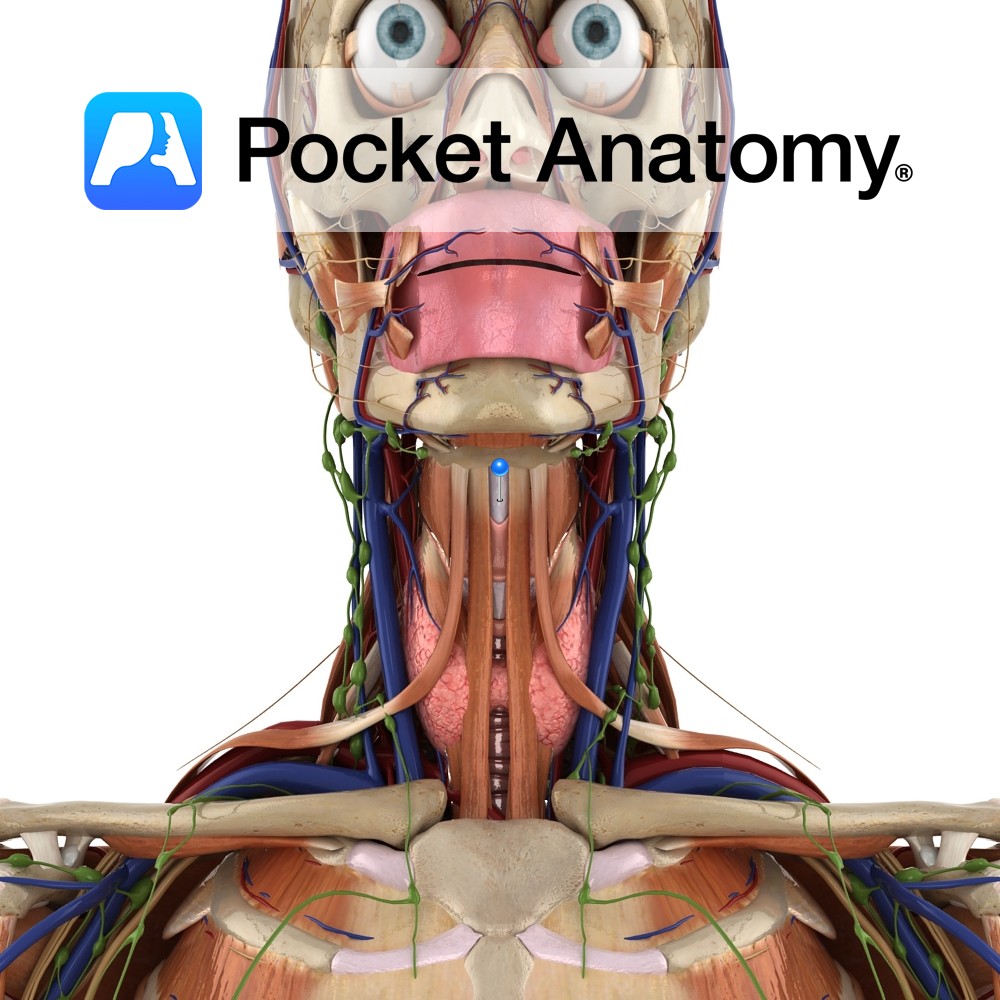
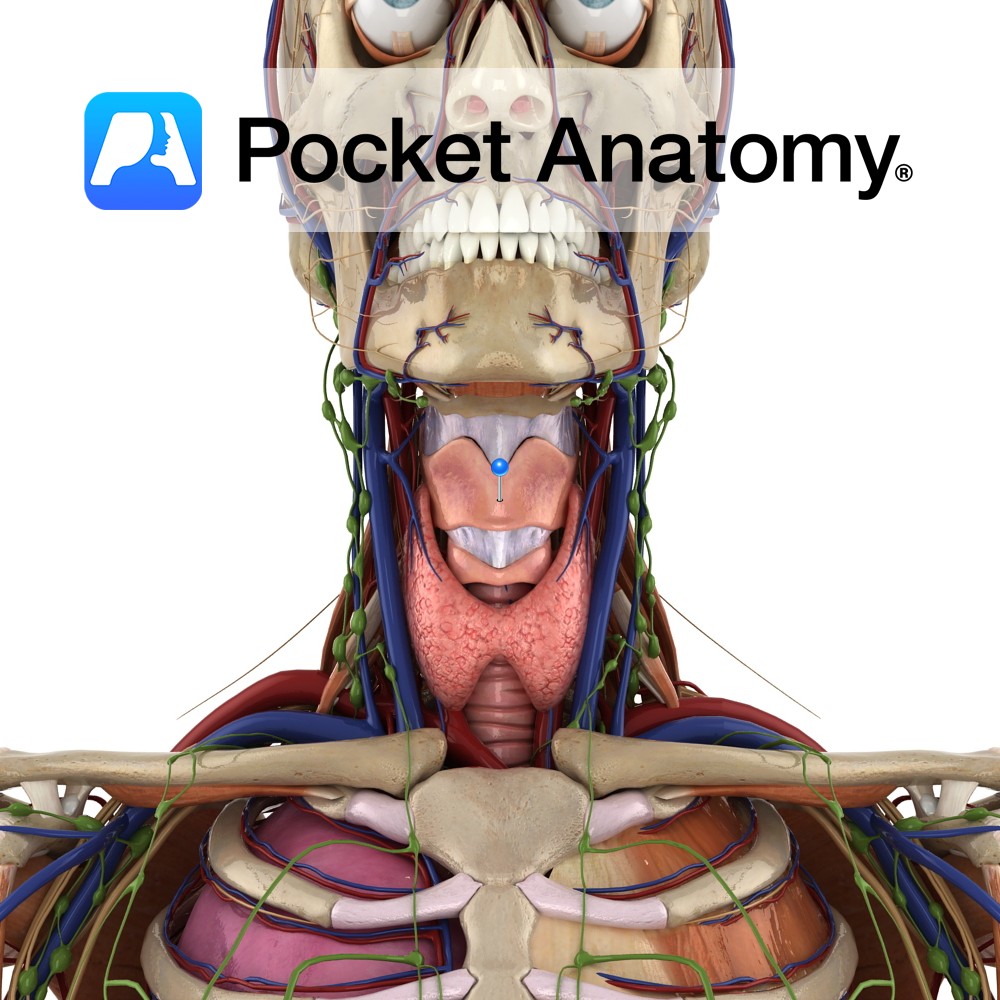
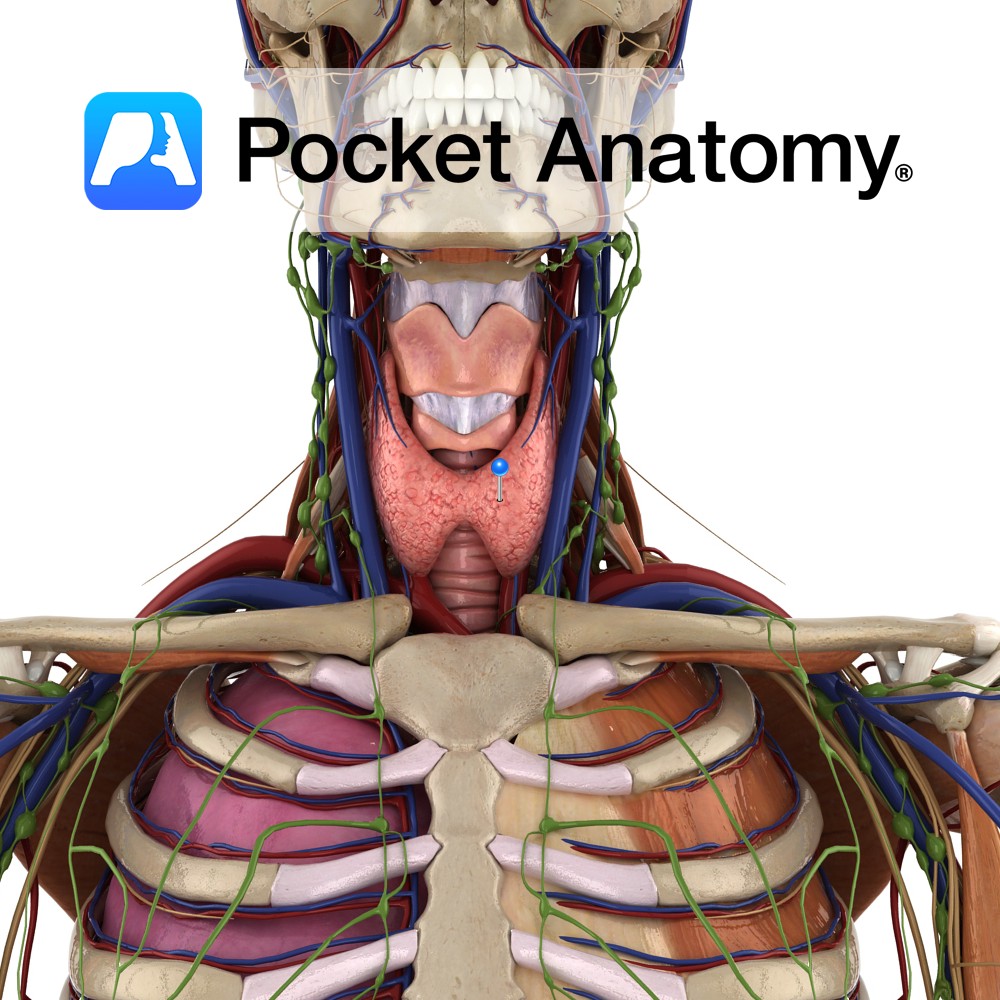
Anatomy Connects the superior borders of the thyroid laminae and superior horns to the hyoid bone above. It is thickened in the midline as the median thyrohyoid ligament. Functions Helps to hold the thyroid in place. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy The largest part of the larynx. It comprises of two quadrangular lamina, fused along the inferior two thirds to form the laryngeal prominence. The posterior border of each lamina projects as superior and inferior horns. The superior horns attaches to the hyoid bone via the thyrohyoid membrane. The inferior horns articulate with the cricoid
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Largest endocrine gland, in neck, ductless, butterfly-shaped (2 conical lobes, apex up, connected by isthmus), behind infrahyoid (strap) and sternocleidomastoid muscles, partially wrapping around posterior structures – thyroid and cricoid cartilages (attached to them, so moves on swallowing), trachea, esophagus. Encapsulated, between the 2 layers of which, posteriorly, are 2 parathyroid glands each side.
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
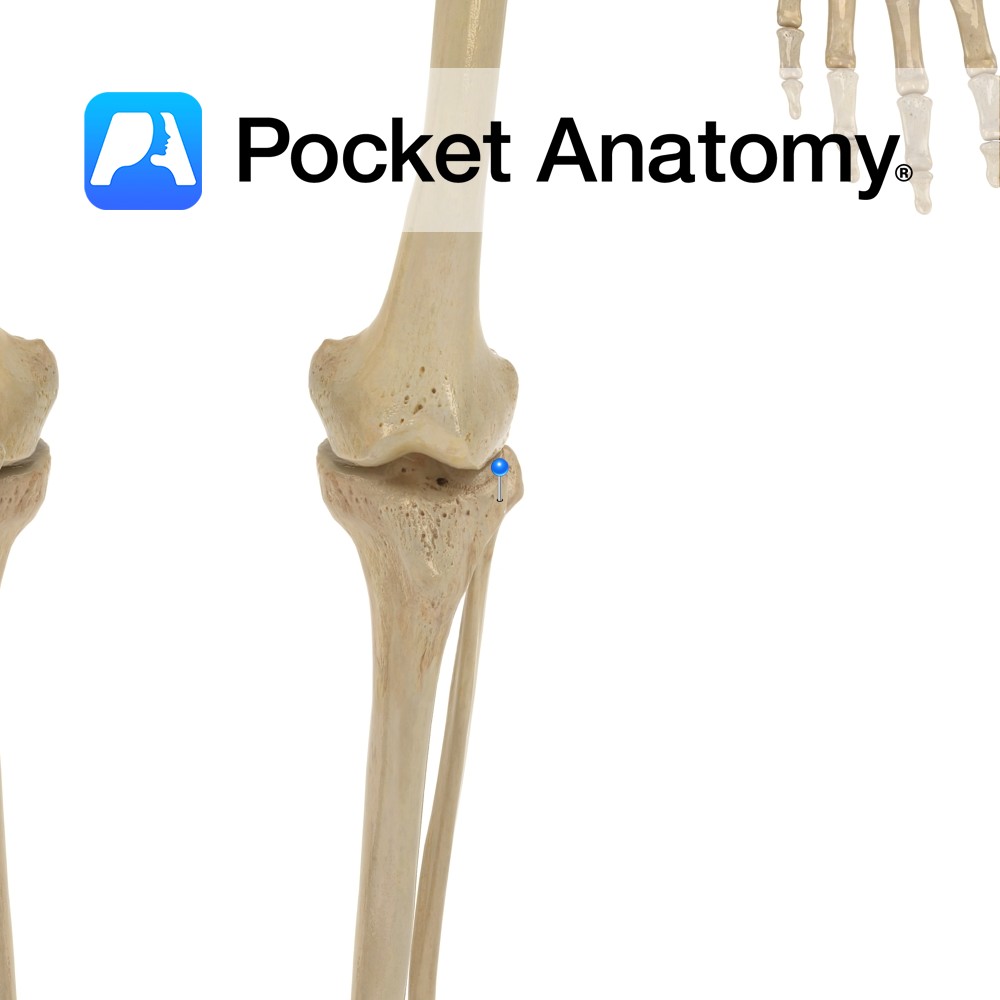
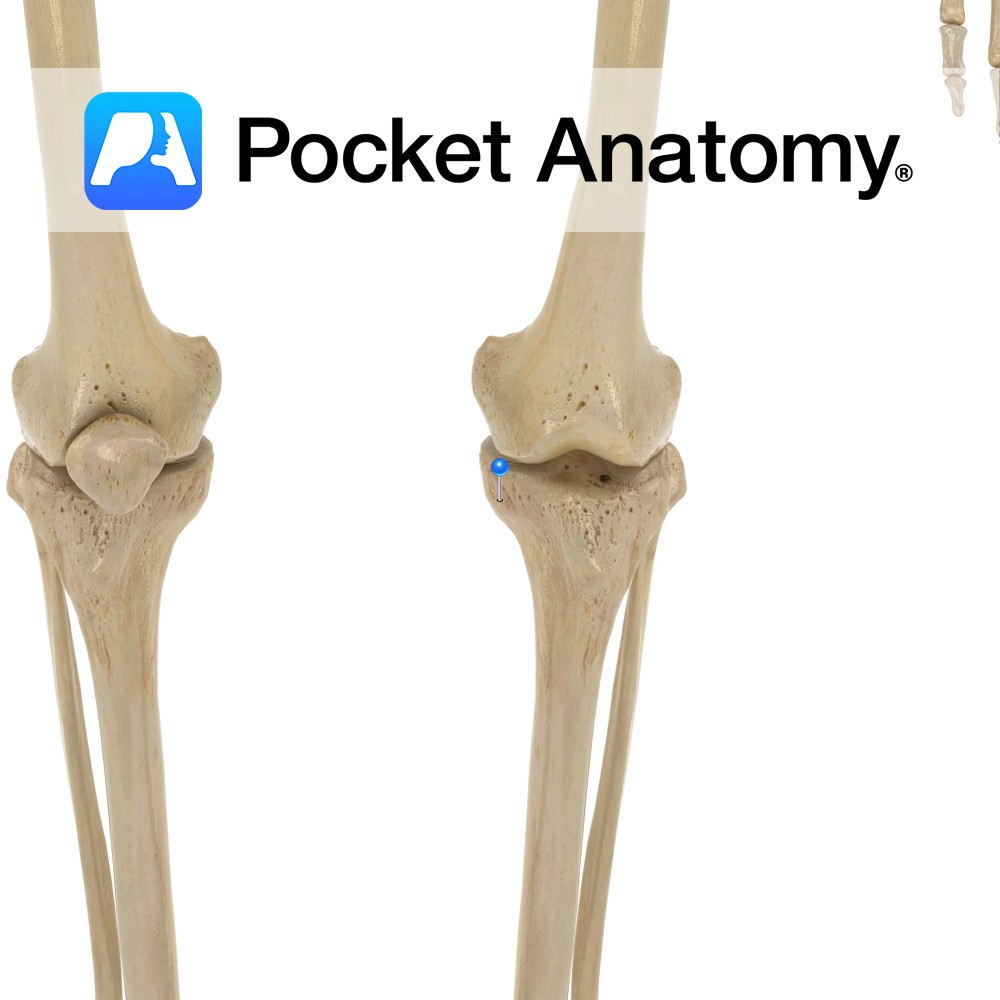
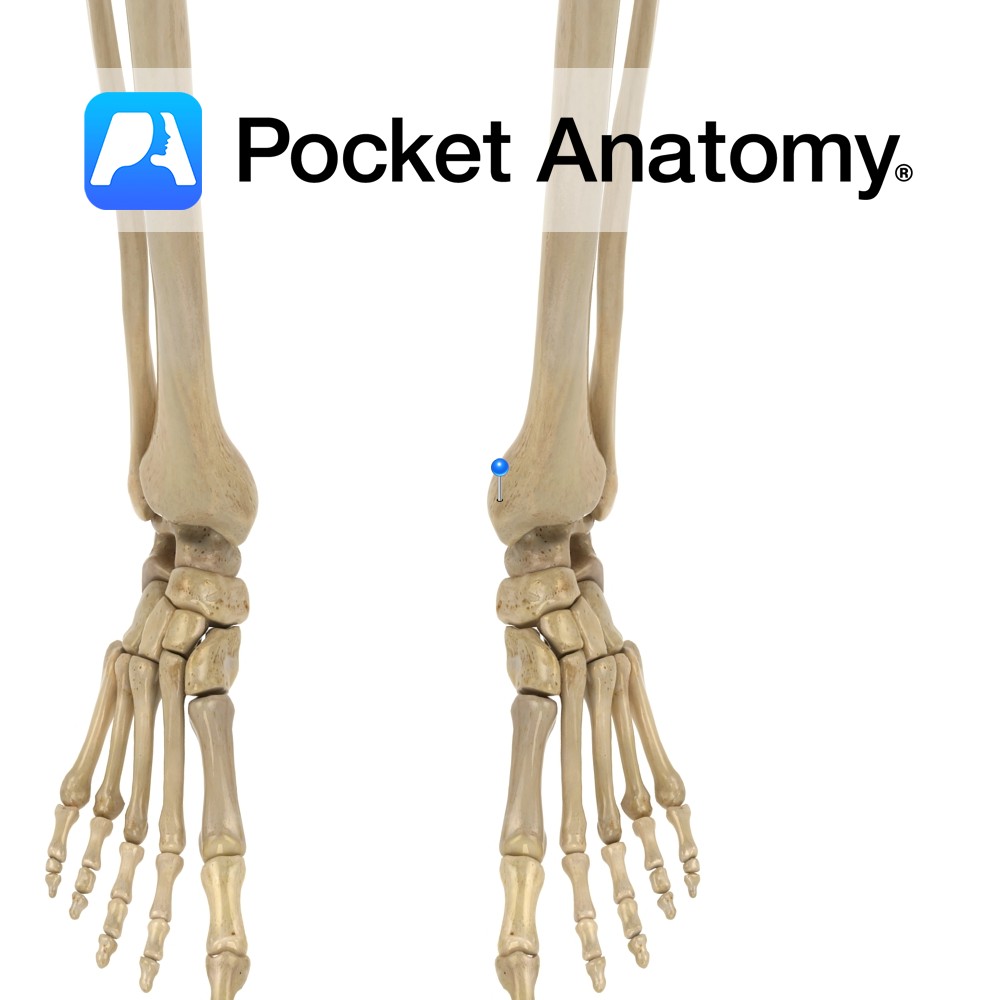
Anatomy Swelling on outside of upper extremity, articulates with head of fibula, gives attachment to iliotibial band/tract. Clinical Knee joint allows flexion, extension and small amount lateral and medial rotation. Vignette Tibia is 2nd longest behind femur, and is the weightbearing bone of the leg. . Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Swelling on inside of upper extremity, to which MCL (tibial/medial collateral ligament, from medial epicondyle of femur above) is attached. Clinical Medial collateral ligament (MCL) injury common. MCL protects against varus angulation. Vignette Knee joint stability provided in part by shape of articular surfaces of femur and tibia, also by cruciate ligaments (anterior and
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Strong prong projecting down from medial/outer side of lower extremity, articulating laterally with the talus. Clinical Fractures can be isolated or more often, one of; bi-malleolar (with lateral malleolus -often requires surgery; tri-malleolar with lateral malleolus and posterior aspect of bottom of tibia – usually requires surgery; fracture often accompanied by ligamentous damage. Vignette
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
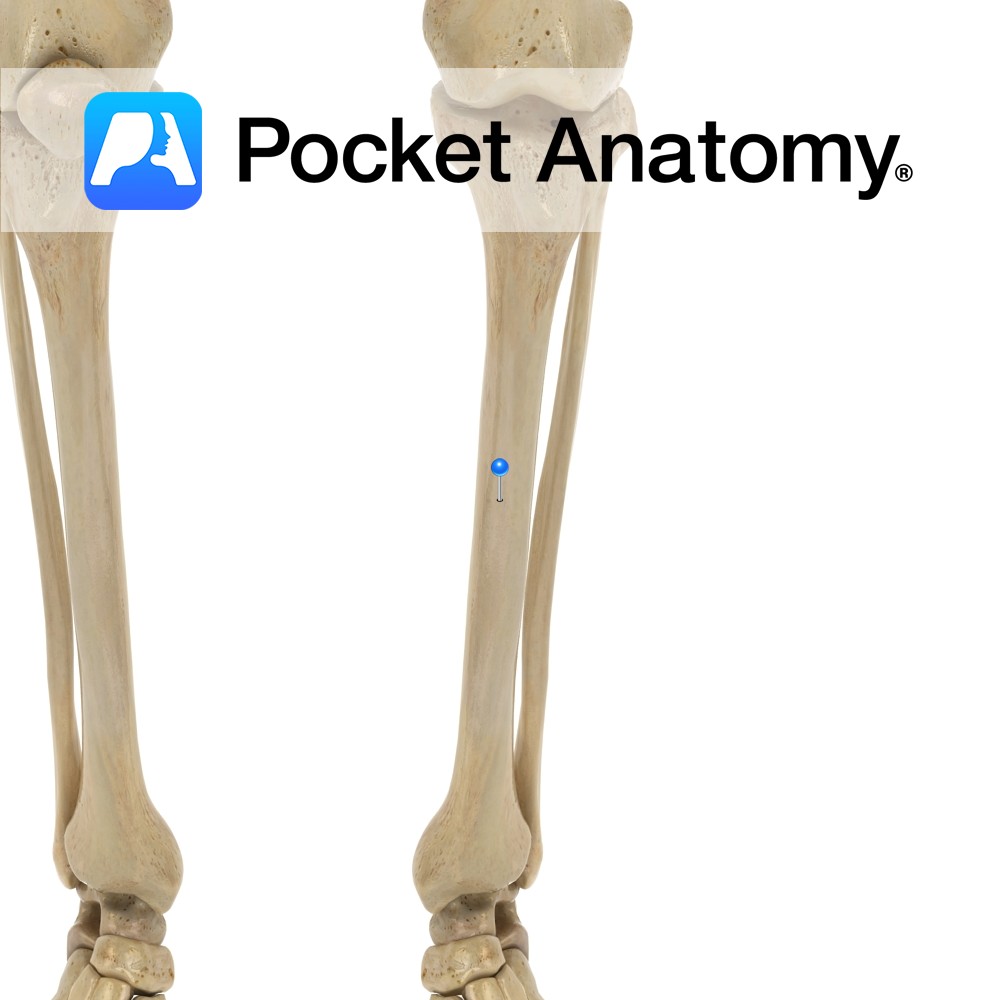
Anatomy Prismoid, broader at top than bottom, a little narrower in middle, runs down vertically (unlike femur which runs down and in). Clinical Skin and cubcutaneous covering of anterior and medial aspects of tibia very thin, so many fractures are open (ie skin broken, with increased risk bone infection – osteomyelitis) whereas fibula well padded.
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins