PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
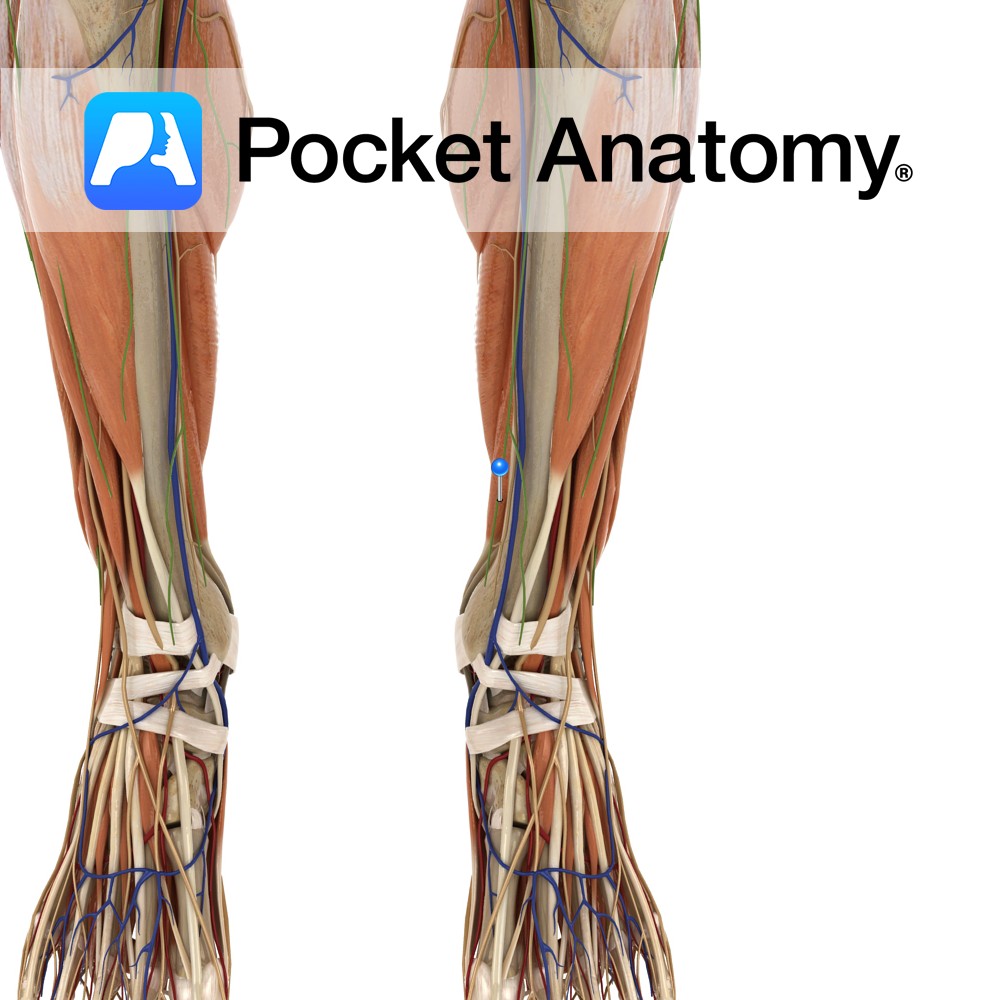
Anatomy Origin: Medial side of the posterior surface of the tibia inferior to the soleal line. Insertion: Plantar surface of the base of the distal phalanges of the lateral four toes. Key Relations: -One of the four muscles of the deep posterior compartment of the leg. -The flexor digitorum longus tendon passes posterior to the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
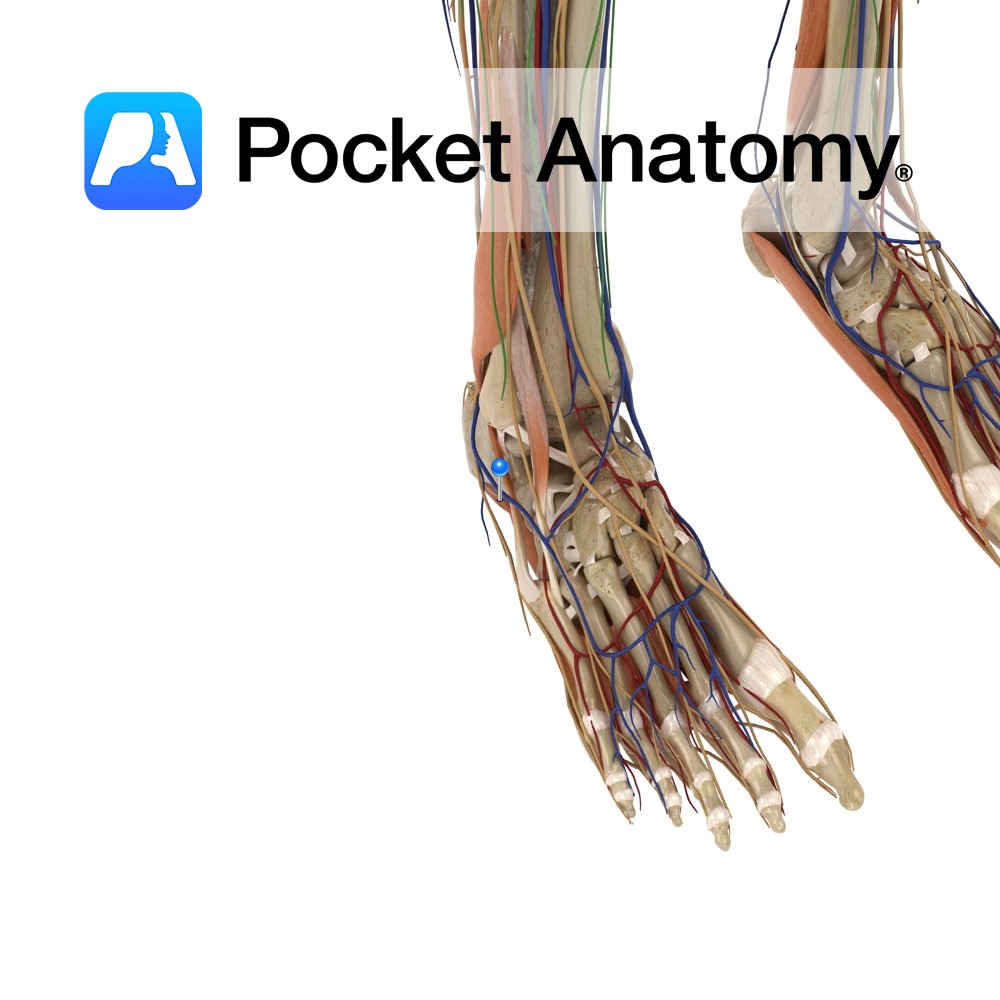
Anatomy Origin: Medial process of the calcaneal tuberosity and plantar aponeurosis. Insertion: Sides of the plantar surface of the middle phalanges of the lateral 4 toes. Key relations: -Lies superior to the plantar aponeurosis. -Gives rise to 4 tendons that lie superficial to the flexor digitorum longus tendons. See plantar view of flexor digitorum brevis.
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
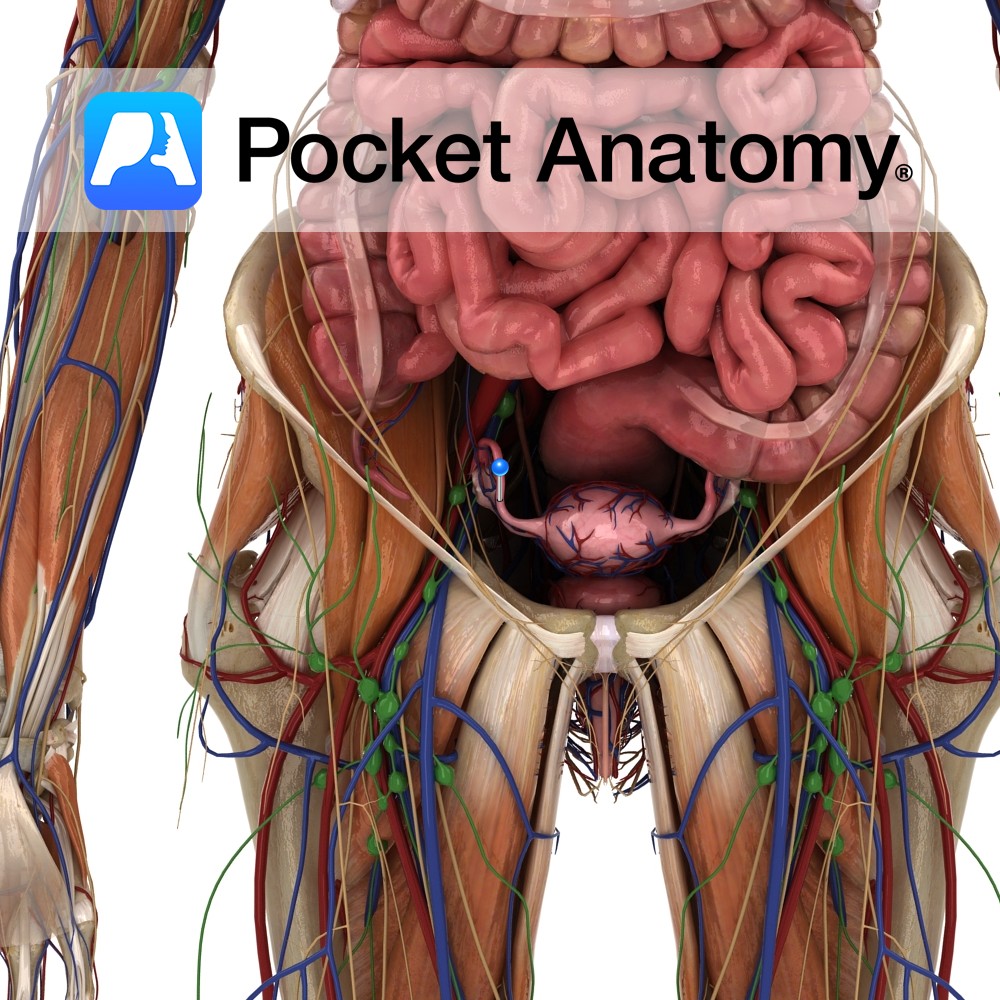
Anatomy Paired narrow muscular tubes (also known as uterine tubes, oviducts, salpinges), continuous with uterus medially, expanded laterally to envelop/overlay much of the ovary. Lateral to medial sections; wide infundibulum with fimbriae and ostium, ampulla, isthmus, intramural/interstitial part, uterotubal junction with ostium. The ends of the fallopian tube are termed ostia. The pinhead-sized proximal/medial/inner ostium
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
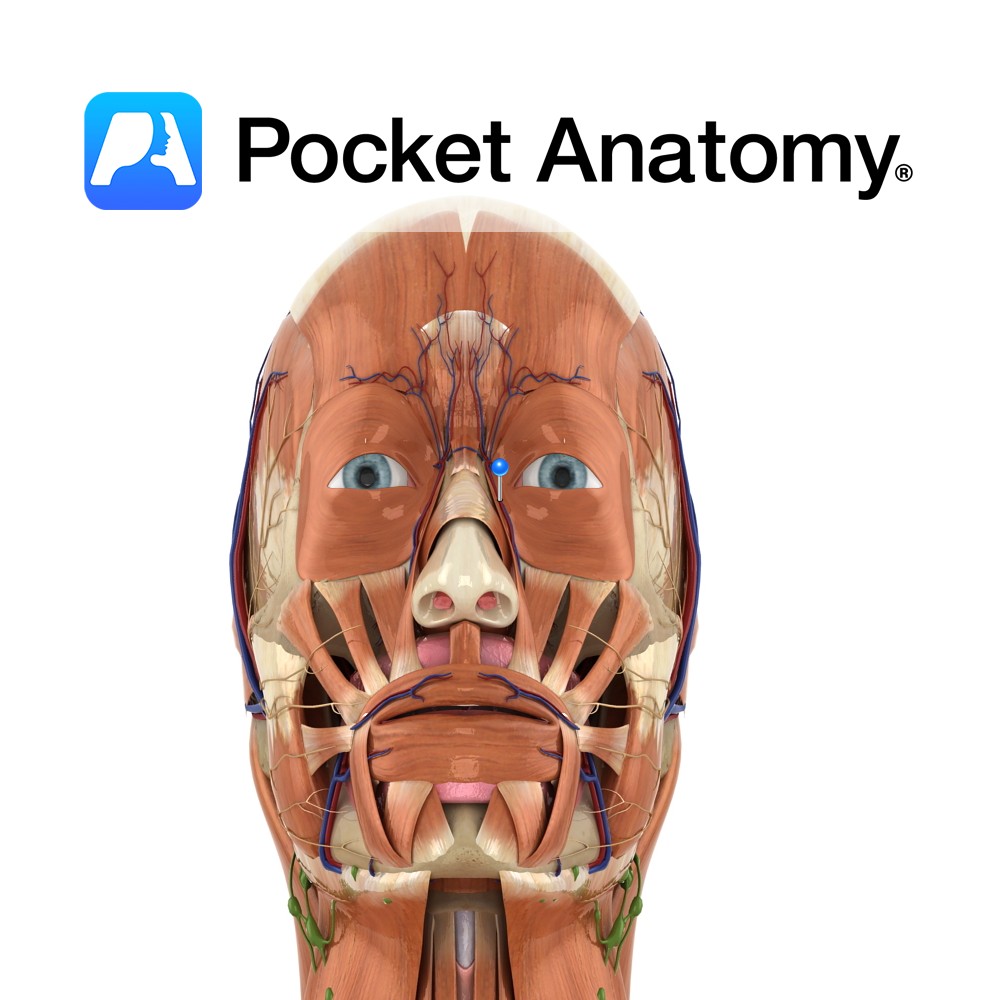
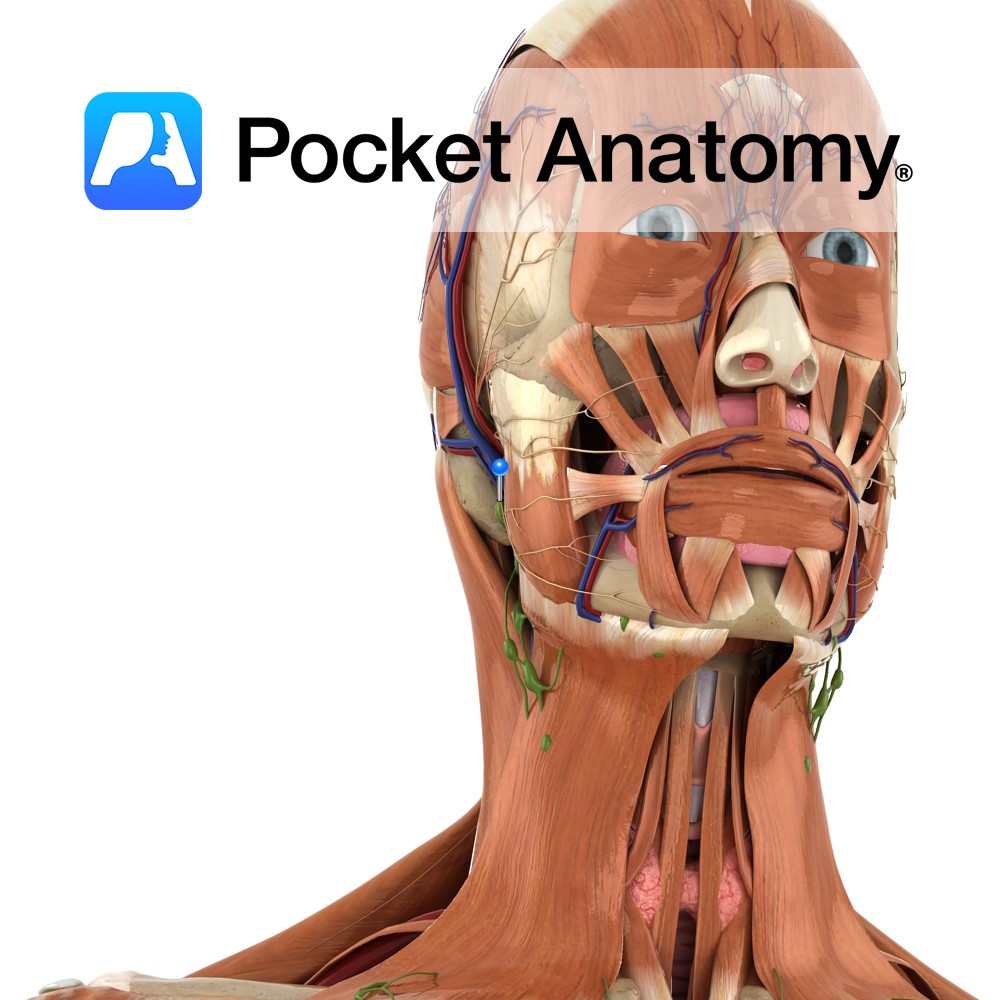
Anatomy Course Continuation of the angular vein at the base of the nose. It travels with the facial artery, but is considerably less tortuous. It can either empty directly into internal jugular vein or it can join with the retromandibular vein to form the common facial vein. Drain Drains the superficial veins of the face.
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Also known as the seventh cranial nerve. Has a motor and sensory origin that join together to form the nerve. It passes through the internal auditory meatus through the facial canal and finally exits from the stylomastoid foramen, and into the parotid gland where it divides into its terminal branches (temporal, zygomatic, buccal,
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
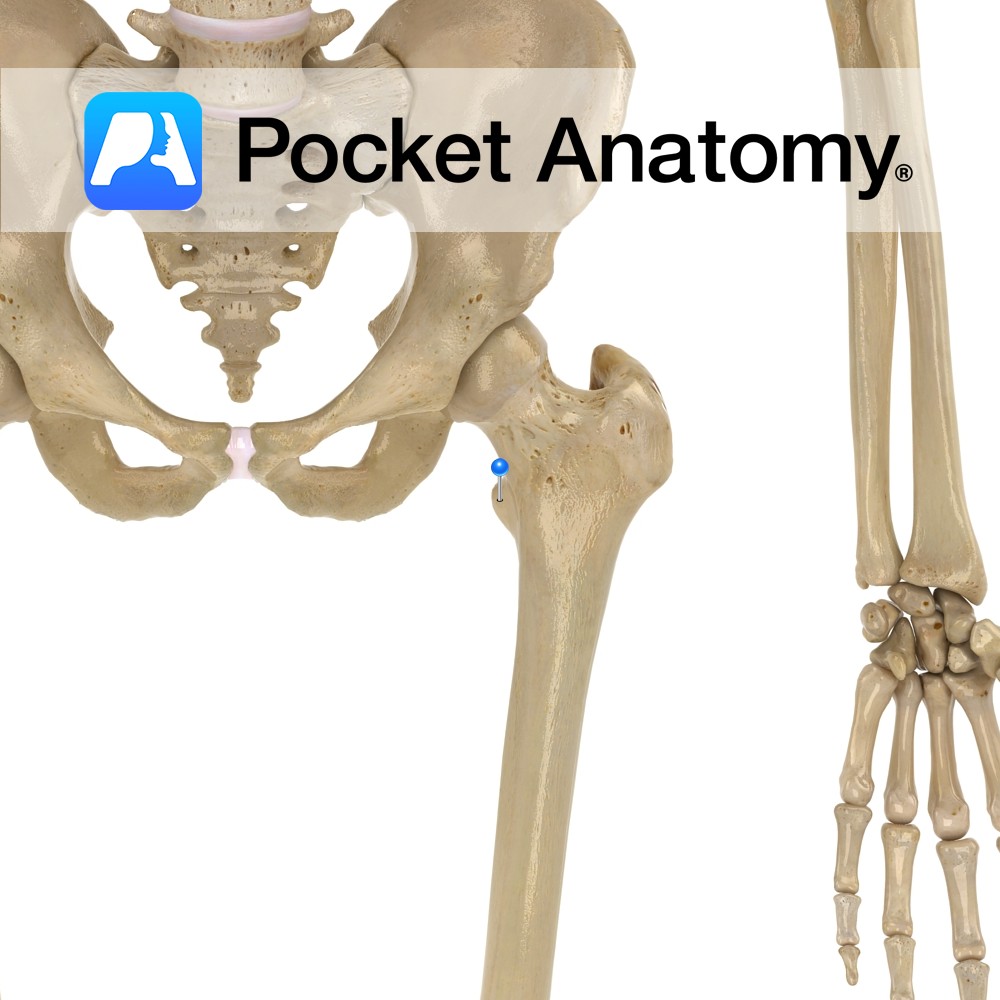
Anatomy Small bulge back from lower part of neck of femur, attachment tendon psoas major. Clinical Isolated fracture rare; ordinarily associated with intertrochanteric fracture. Vignette Trochanter; from the Greek for runner. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Convex eminence at lateral aspect of lower end of femur; fibular (lateral) collateral ligament (LCL) attached, running down to head of fibula. Clinical 4 major knee ligaments; MCL (medial/tibial collateral ligament, medial epicondyle femur to medial condyle tibia), LCL (lateral/fibular epicondyle femur to head fibula), ACL (anterior cruciate ligament, from inside of lateral femoral
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Oblong eminence at lateral/outer aspect of lower femur, separated in the front from medial condyle by trochlear groove, at back by intercondyloid fossa. Articulates at front with patella, bottom and back with tibia. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
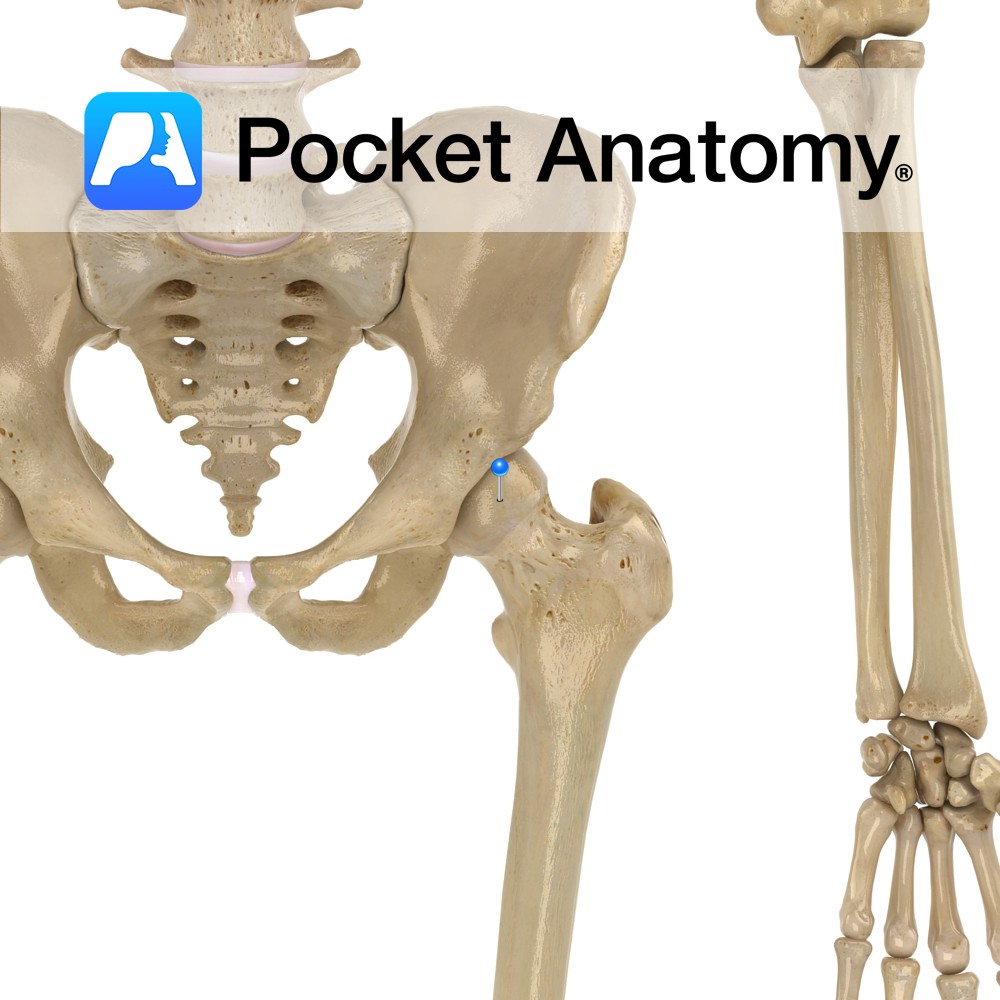
Anatomy Most superior/proximal part femur, the ball of the ball-and-socket hip joint (acetabulum the socket), connected by neck to shaft, globular, points up in and forward, coated with cartilage (other than fovea which gives attachment to ligament of head of femur). Clinical Fracture of femoral head is usually due to significant (high force) trauma, and
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
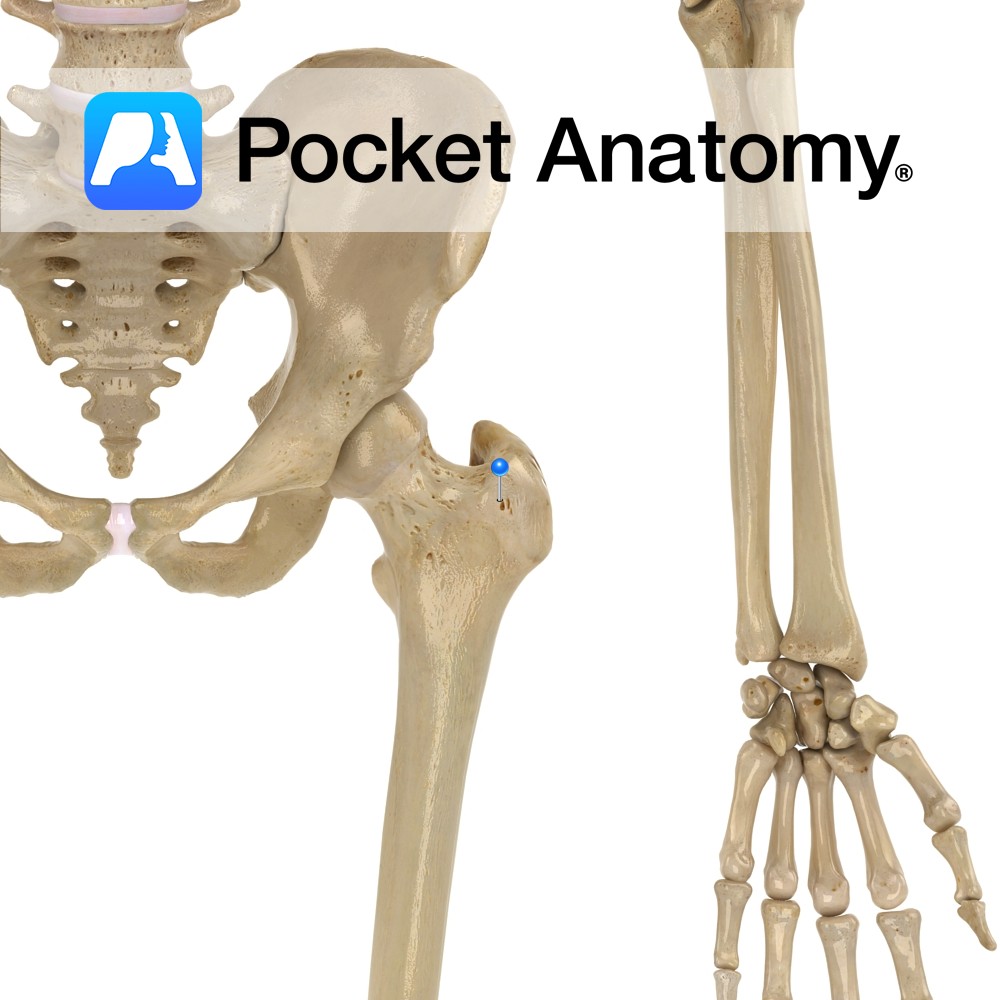
Anatomy Large bulge back and out from junction neck and shaft, main attachment of many muscles involved in complex hip movement (including rotation) manifested eg as postural gait; including vastus lateralis, obturator internus/externus, superior/inferior gemellus, piriformis, gluteus medius/minimus. The greater and lesser trochanters bulge out from top of femur and give leverage to muscles that
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins