PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
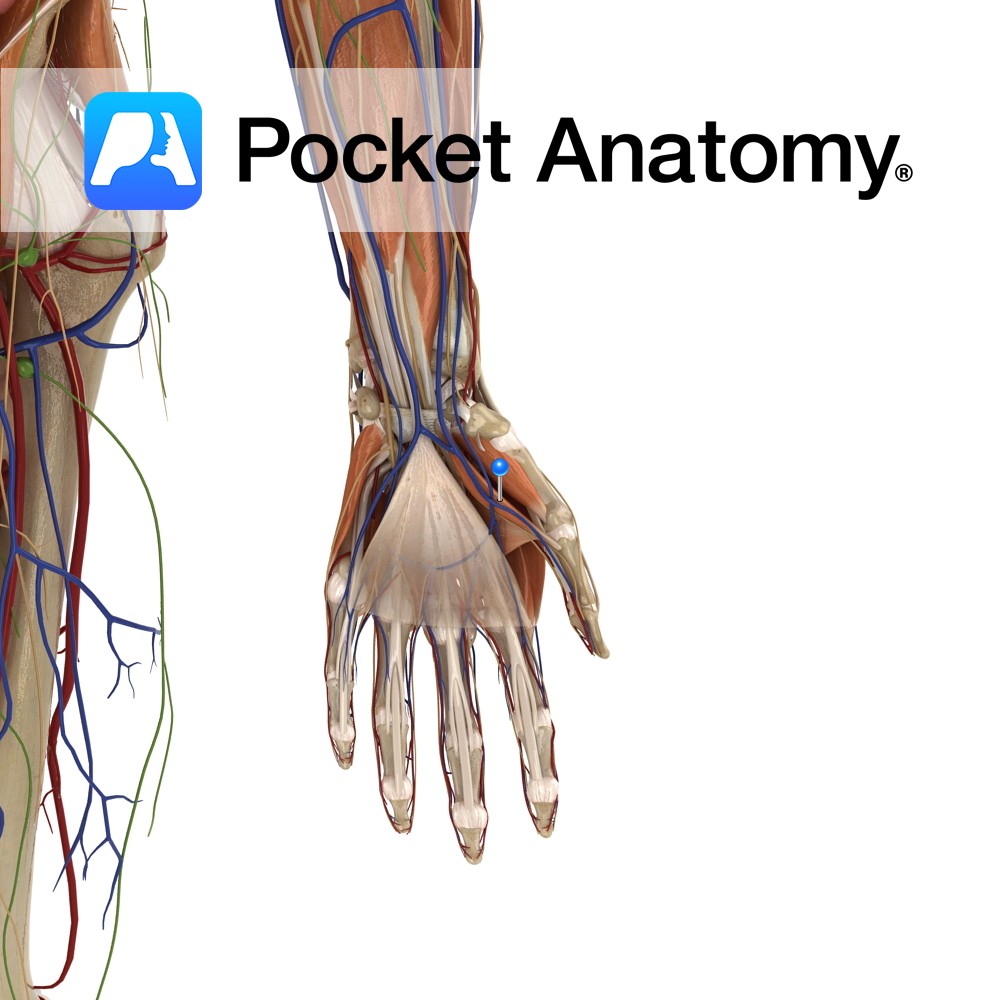
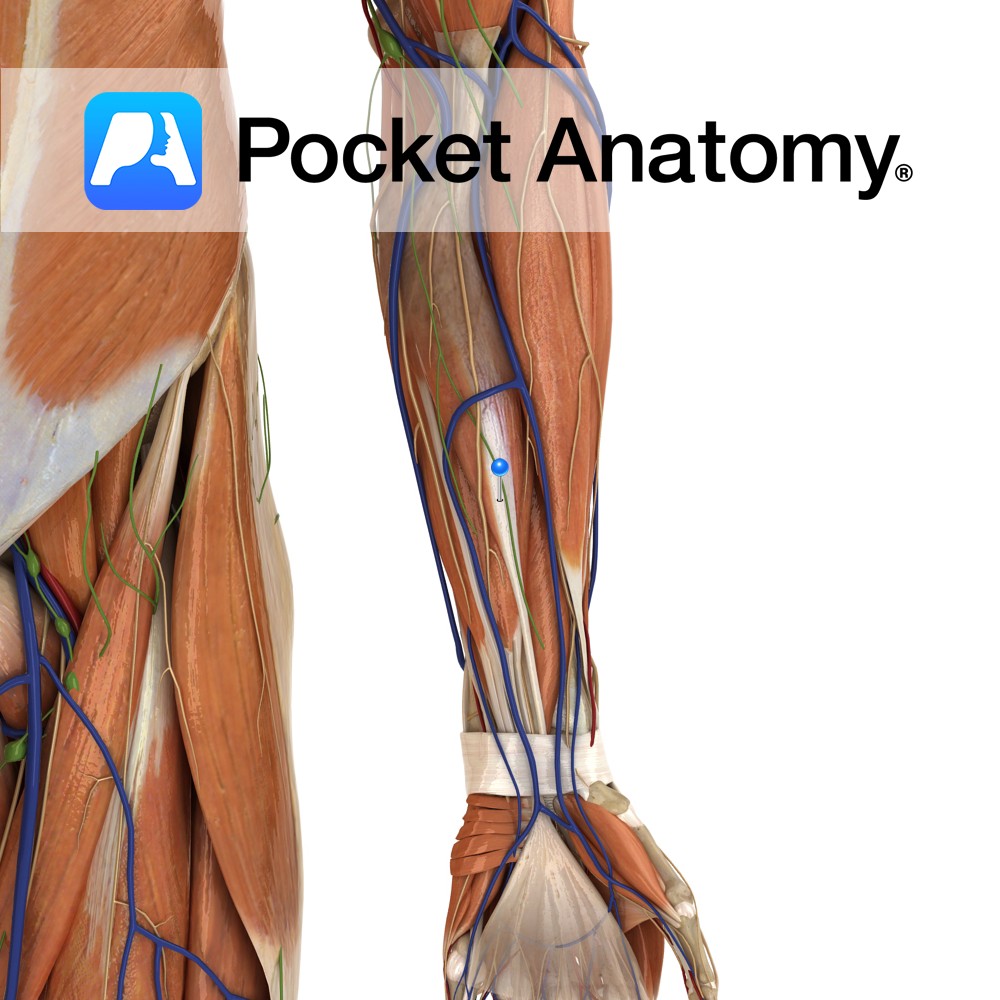
Anatomy Origin: Medial epicondyle of humerus via the common flexor tendon. Insertion: Plamar aspect of bases of second and third metacarpal bones (with a slip to the third). Key Relations: -The tendon of flexor carpi radialis is considered part of the carpal tunnel, although more accurately it passes through the flexor retinaculum, the cover of
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
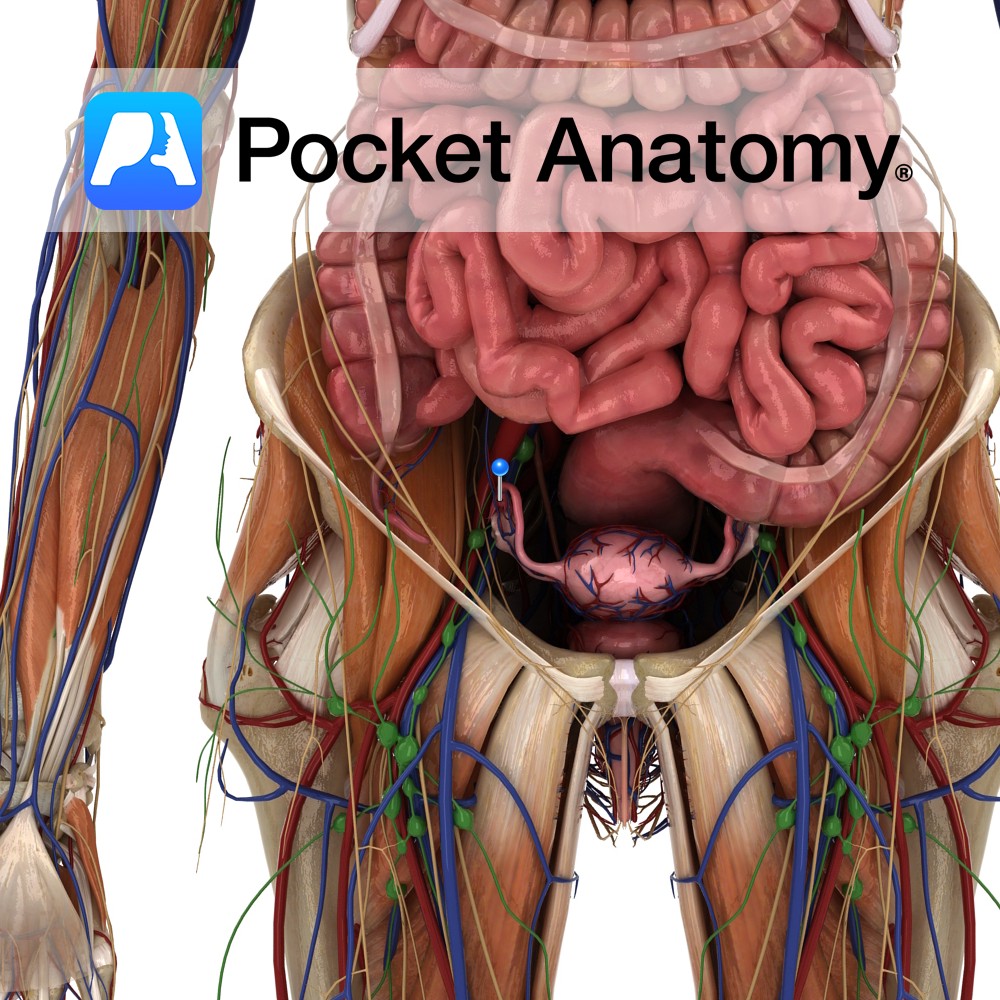
Anatomy Fringes/fingers projecting from widened lateral end (infundibulum) of fallopian tube, closely associated with ovary. One muscular fimbria – fimbria ovarica – is attached to the ovary. Fimbriae lined internally with millions of tiny hair-like cilia. Physiology Fimbria ovarica contracts at ovulation, pulling the tube more tightly towards the ovary. Cilia beat rapidly, creating current
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
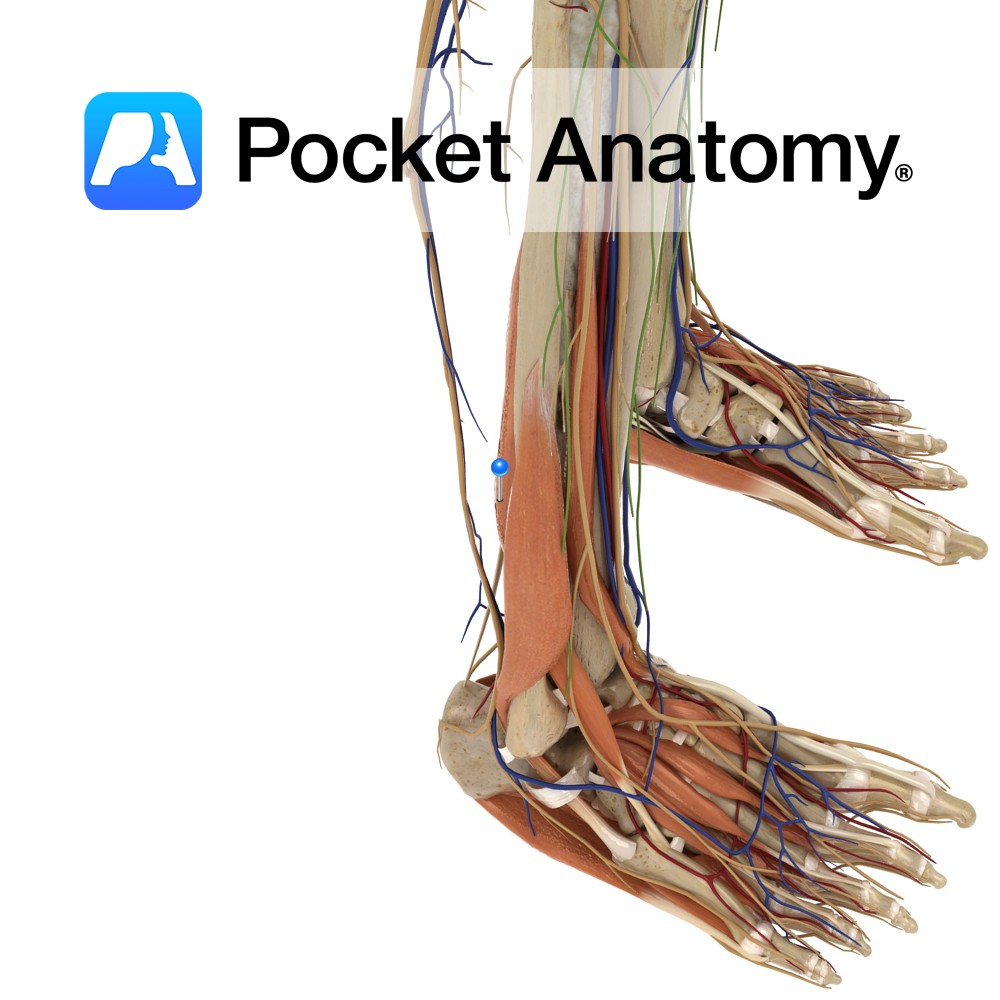
Anatomy Origin: Distal quarter of the anterior surface of the fibula and the interosseous membrane. Insertion: Dorsal surface of the base of the 5th metatarsal. Key relations: -One of the four muscles of the anterior compartment of the leg. -The fibularis tertius tendon passes posterior to the extensor retinaculae. It crosses anterior to the ankle
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Head and upper two-thirds of the lateral surface of fibula and the intermuscular septa. Insertion: Lateral surface of the medial cuneiform and the base of the 1st metatarsal. Key relations: -One of the two muscles of the lateral compartment of the leg. -The fibularis longus tendon passes posterior to the lateral malleolus along
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Distal two-thirds of the lateral surface of the fibula and the intermuscular septa. Insertion: Tuberosity on the lateral aspect of the base of the 5th metatarsal. Key Relations: -One of the two muscles of the lateral compartment of the leg. -The fibularis brevis tendon passes posterior to the lateral malleolus along the lateral
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Branch of the posterior tibial artery, which follows a parallel course to the tibial artery on the lateral side of the posterior fibula. Supply Supplies muscles and bones in the posterior compartment of the leg, but also the lateral compartment via its branches. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Superficial part: Flexor retinaculum and tubercle of the trapezium. Deep part: Trapezoid and capitates. Insertion: Base of the proximal phalanx of thumb. Key Relations: Is one of the muscles of the thenar eminence of the hand. Functions Flexion of the thumb at the metacarpophalangeal joint. Supply Nerve Supply: Superficial part: Recurrent branch of
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Lower two-thirds of the posterior surface of the fibula, the posterior intermuscular septum and the posterior surface of the distal part of the interosseous membrane. Insertion: Plantar surface of the base of the distal phalanx of the hallux (big toe). Key relations: -One of the four muscles of the deep posterior compartment of
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
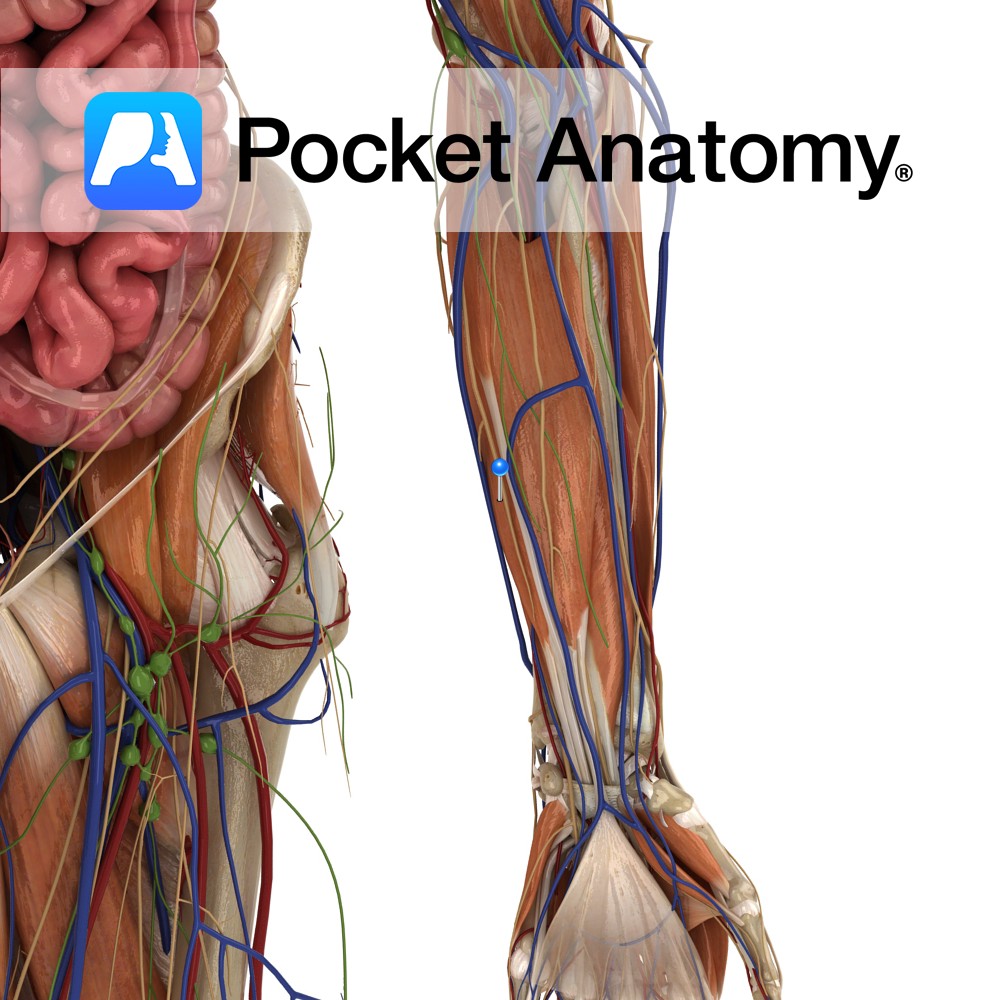
Anatomy Origin: Humeroulnar head: Medial epicondyle of humerus via the common flexor tendon, ulnar collateral ligament and coronoid process of ulna. Radial head: Superior half of anterior aspect of radius at anterior oblique line. Insertion: Four tendons of insertion attach to palmar surfaces of bodies of middle phalanges of the four fingers. Key Relations: -The
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
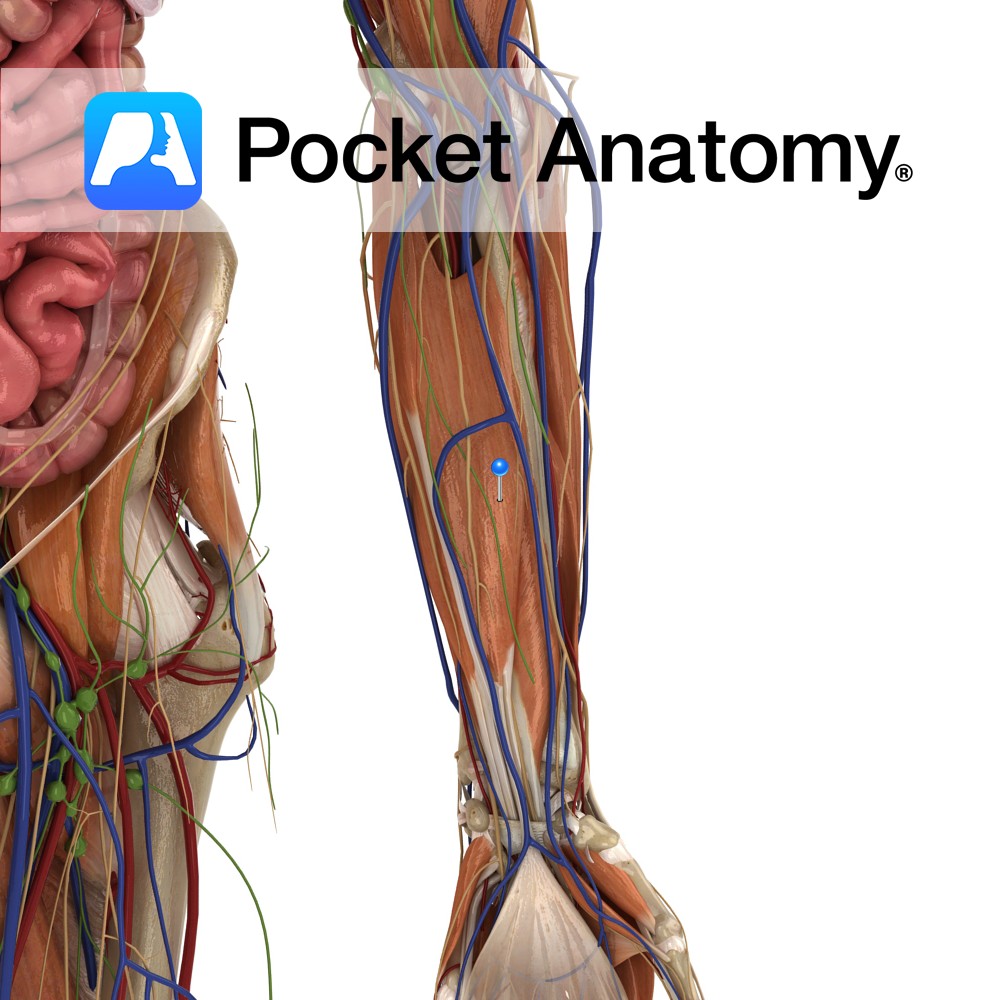
Anatomy Origin: Upper three quarters of medial and anterior aspects of ulna and from anterior aspect of interosseous membrane. Insertion: Four tendons attaching to palmar aspects of bases of the distal phalanges of each of the four fingers. Key Relations: -The lumbrical muscles arise in the palm from the tendons of flexor digitorum profundus. -The
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins

-tertius.jpg)
-longus.jpg)
-brevis.jpg)
-artery.jpg)