PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
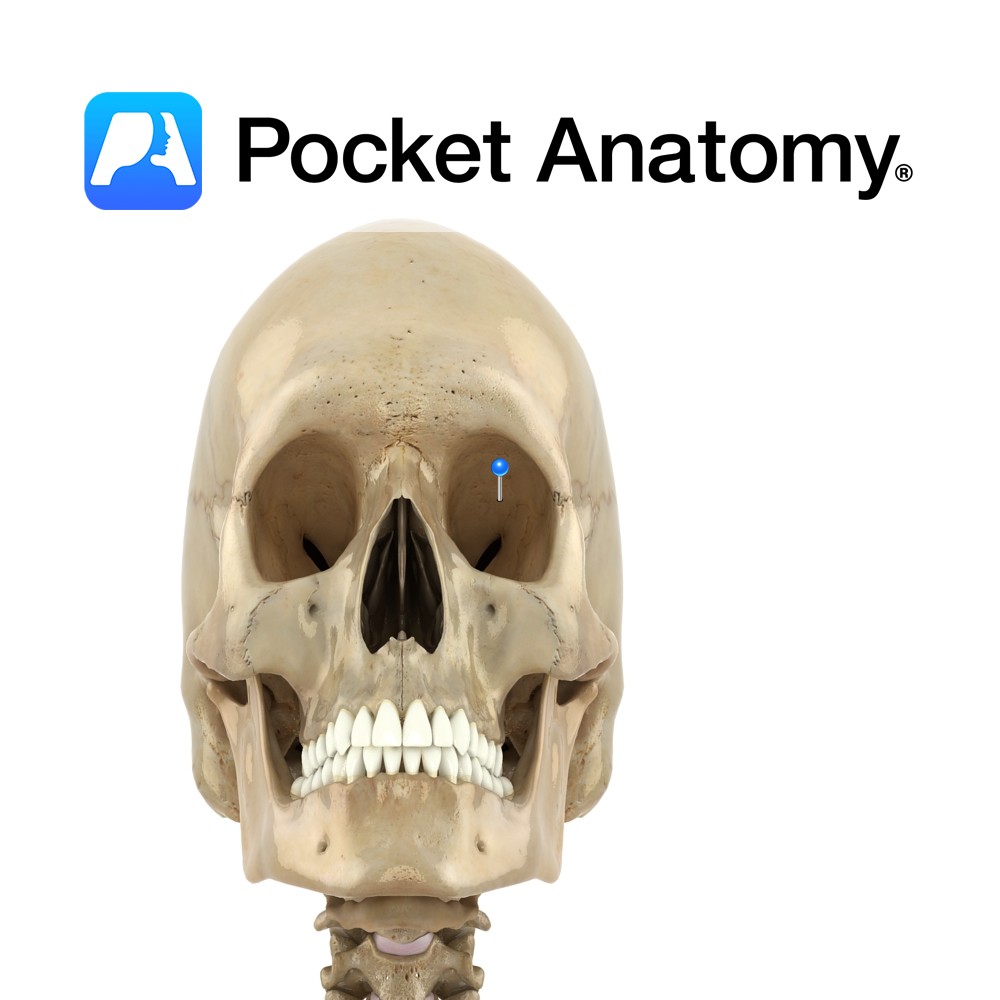
Anatomy Section of frontal bone which forms part of eye sockets/orbits. Frontal bone curves in at bottom, as thin triangular orbital plates. Left and right plate are separated by a gap – the ethmoid notch. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
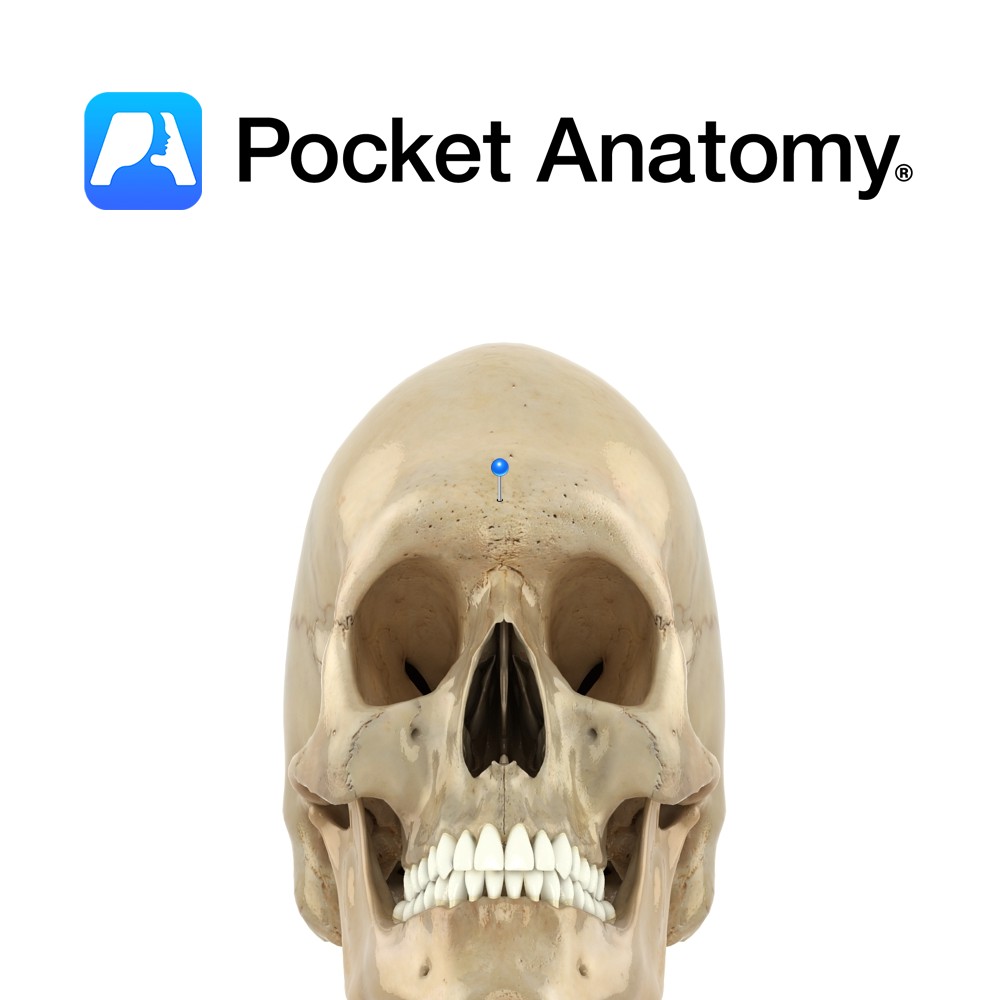
Anatomy Slightly raised flat area where the superciliary arches meet (ie between eyebrows); the most forward part of the forehead. Clinical Glabellus (Latin); smooth. Usually hairless. Vignette Site for testing the Glabellar reflex; tapping on glabella causes blinking, which stops after several repetitions. However, often persists in Parkinson’s (Myerson’s sign). Interested in taking our award-winning
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
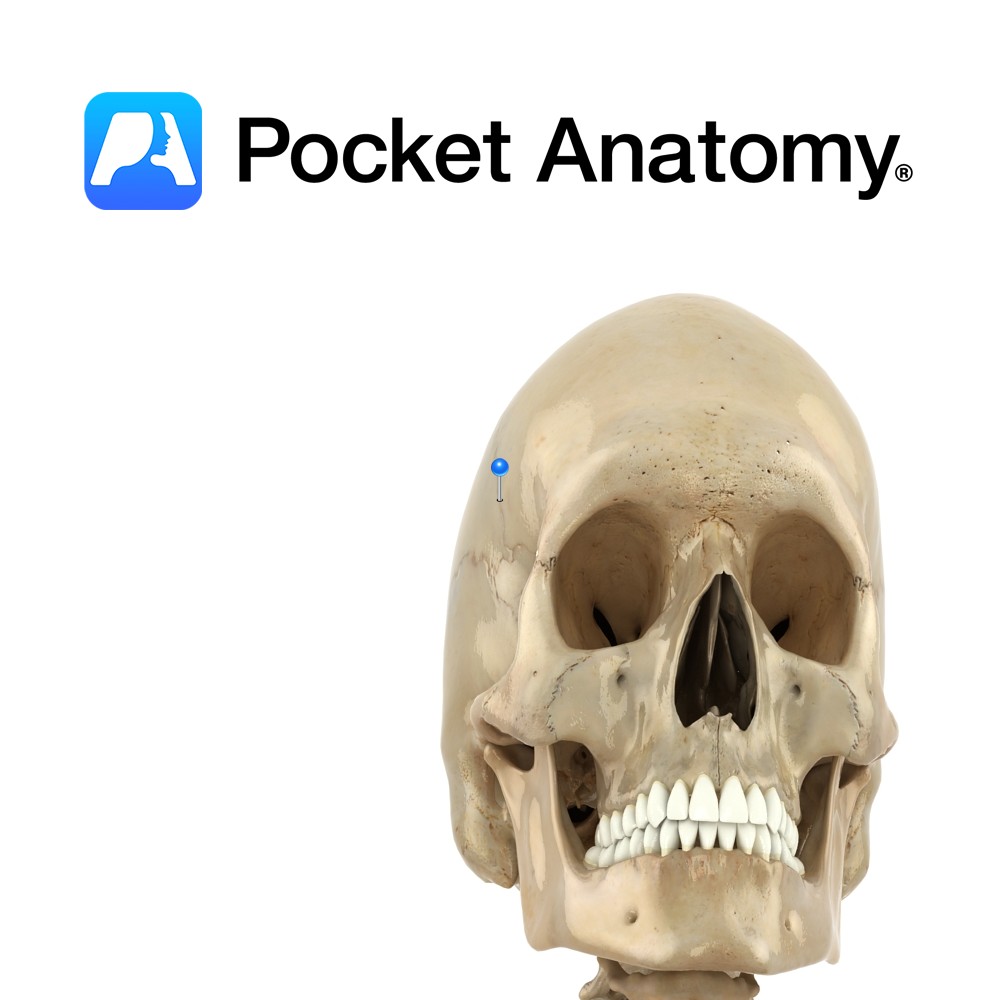
Anatomy Rigid midline joint or seam between frontal bone and paired parietal bones behind. Ends at side of skull at junction of frontal, parietal and sphenoid bones. Vignette Korone (Greek); garland, wreath. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
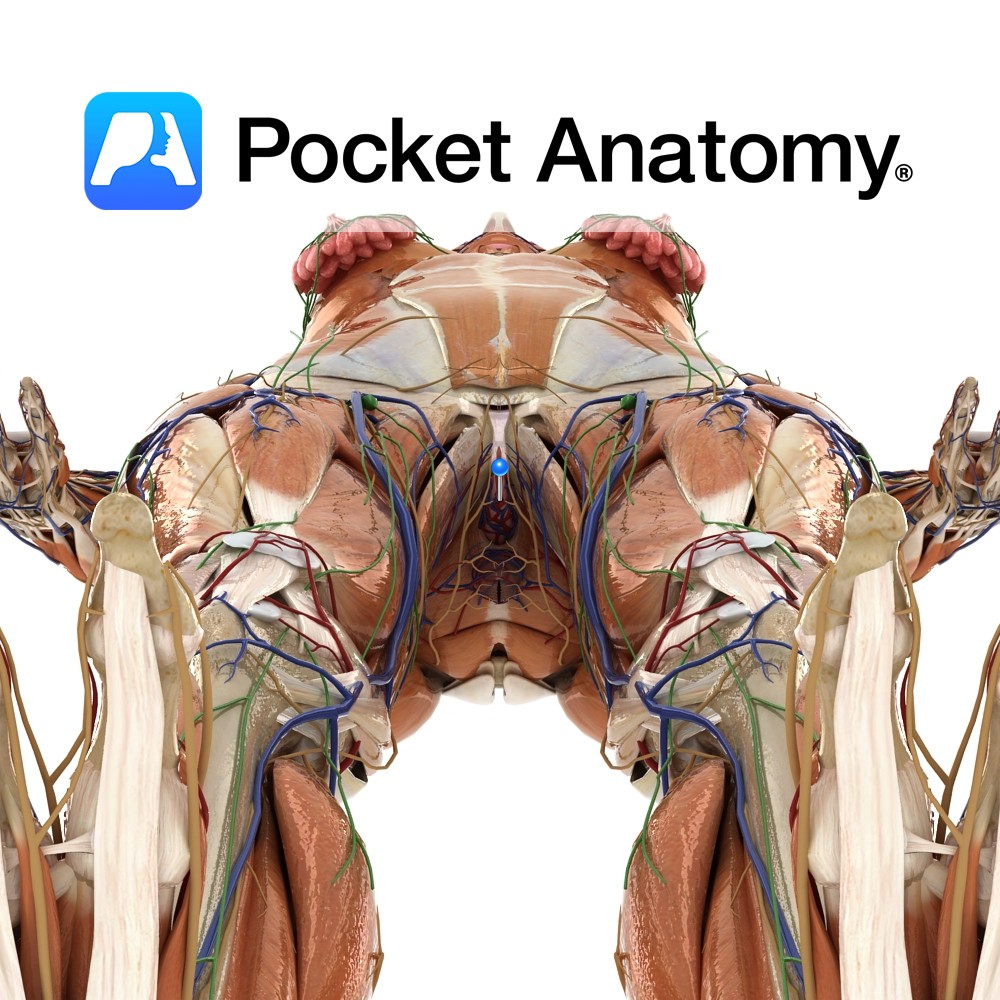
Anatomy Otherwise referred to as the fourchette, this is the meeting of the labia minora behind the vagina, in front of the anus (their anterior meeting/junction swaddles the clitoris as prepuce and frenulum). It is part of the vulva (external genital organs – including mons, clitoris, urethra/vaginal orifices, labia majora/minora), itself part of the perineum
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
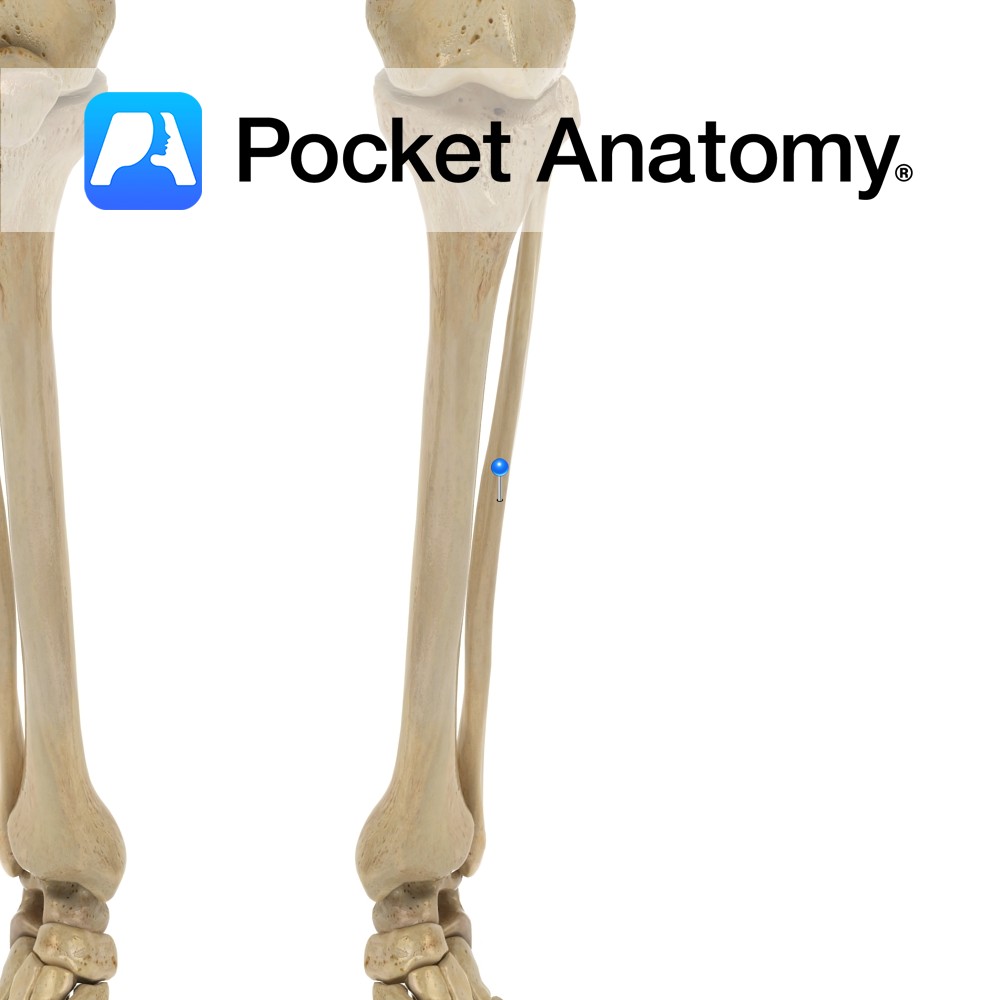
Anatomy The shaft is connected to that of tibia along its length by an interossous membrane, separating anterior and posterior muscles. The membrane is 1 of 3 articulations between tibia and fibula, along with the proximal tibiofibular joint above and the tibiofibular syndesmosis below. Clinical Fracture of tibia usually associated with fracture fibula, as interosseous
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
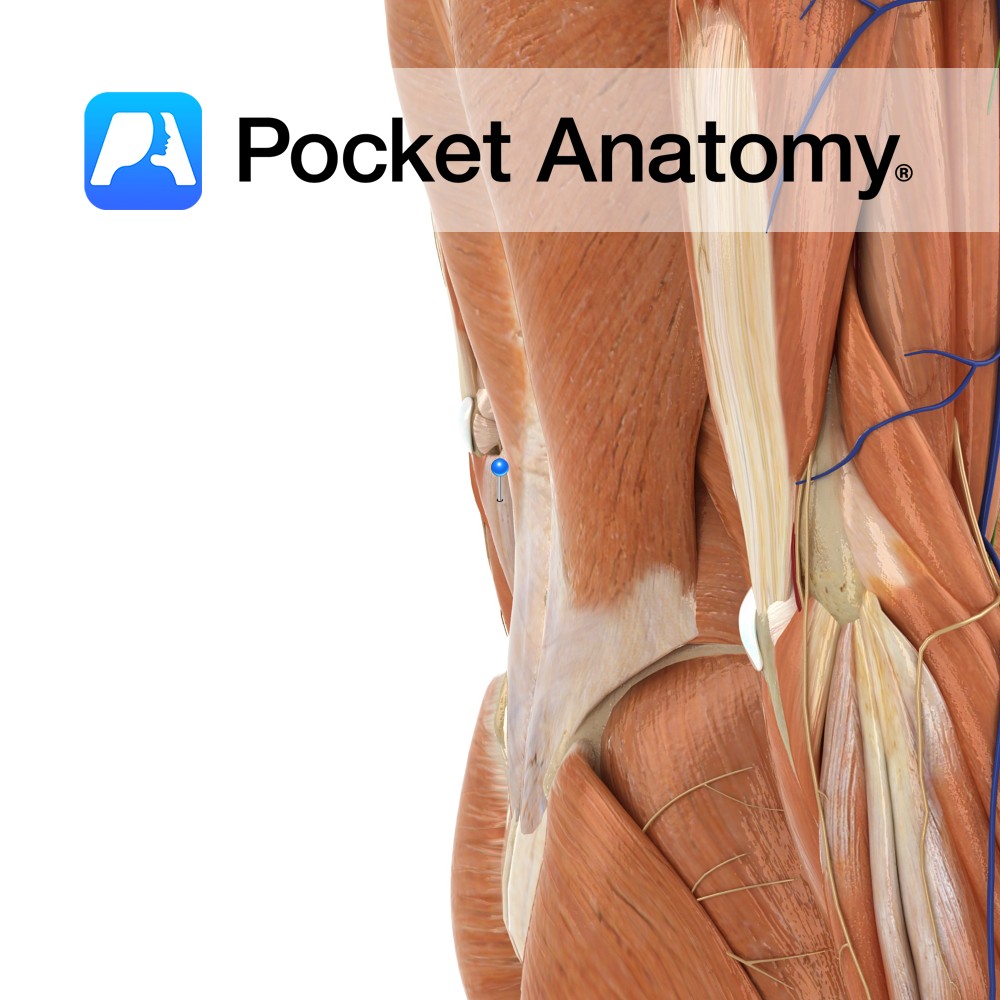
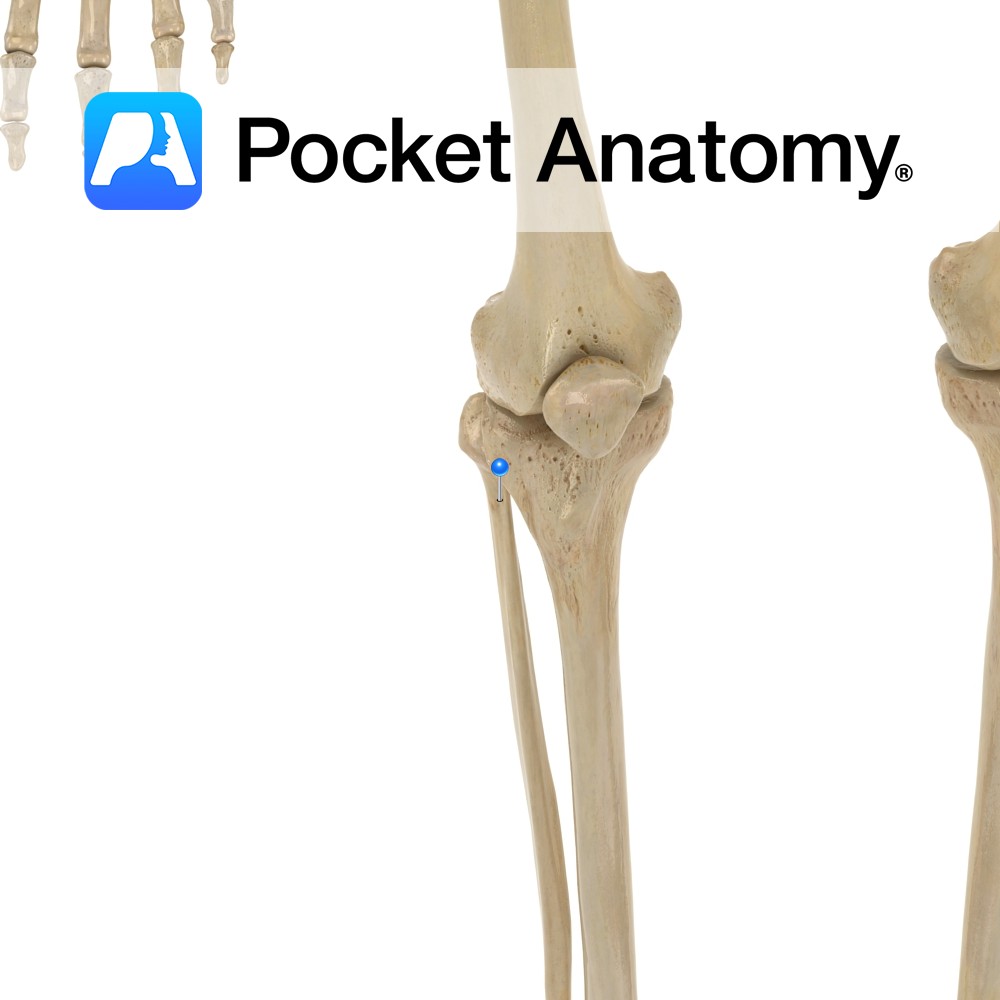
Anatomy Slight narrowing between head and shaft, over which the peroneal nerve runs. Clinical Peroneal nerve can be felt and rolled, cord-like, to produce tingling in leg and foot. Damage to peroneal nerve can lead to foot drop; the foot drags during walking, as dorsiflexion is impaired. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
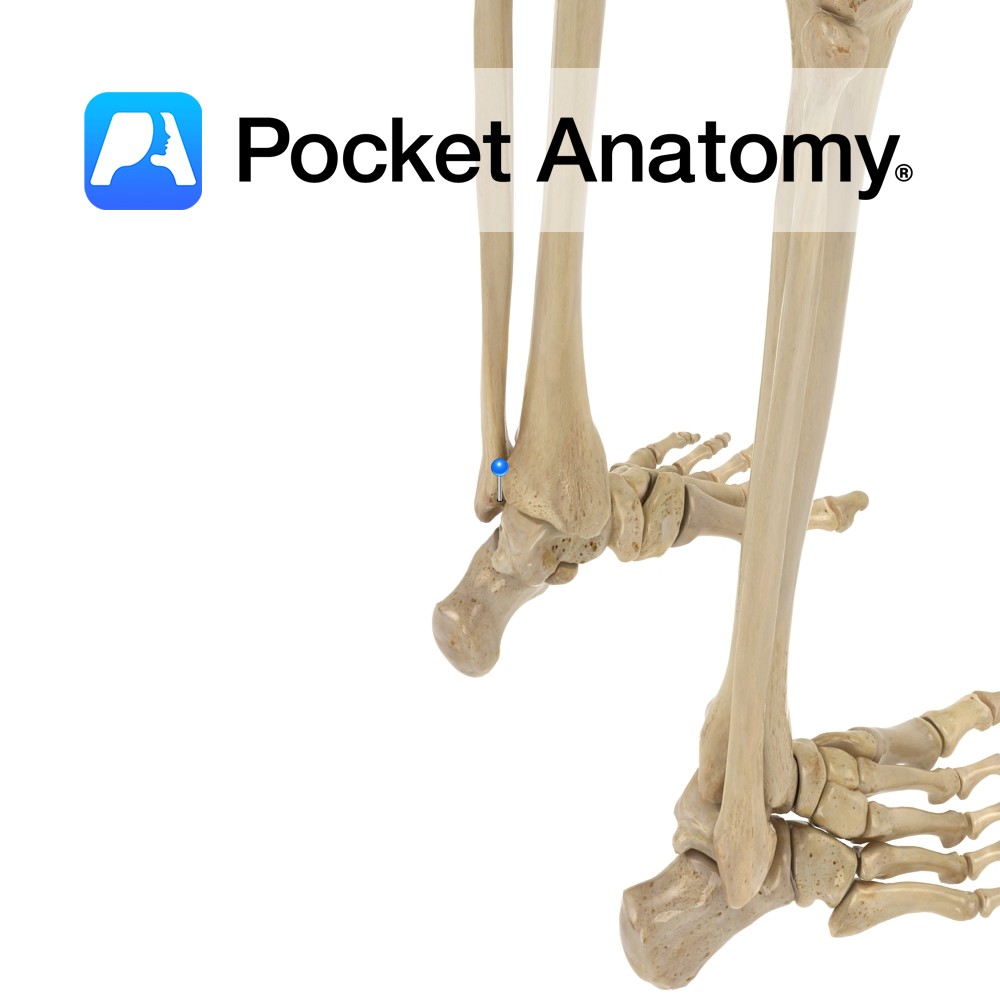
Anatomy Pyramidal lower extremity of fibula, runs down lateral to and articulates (medially/in) with the talus, behind and in front of which joint there are posterior and anterior talofibular ligaments, and below which, from the point/summit is the calcaneofibular ligament (down and slightly back). The visible outer knob of the ankle. Clinical Ankle injuries most
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Plantar surface of the base of the 5th metatarsal and sheath of adjacent fibularis longus tendon. Insertion: Base of the 5th proximal phalanx. Key Relations: Runs along the lateral aspect of the foot. See plantar view of flexor digiti minimi brevis of foot.. Functions Flexes the 5th toe at metatarsophalangeal joint. Supply Nerve
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
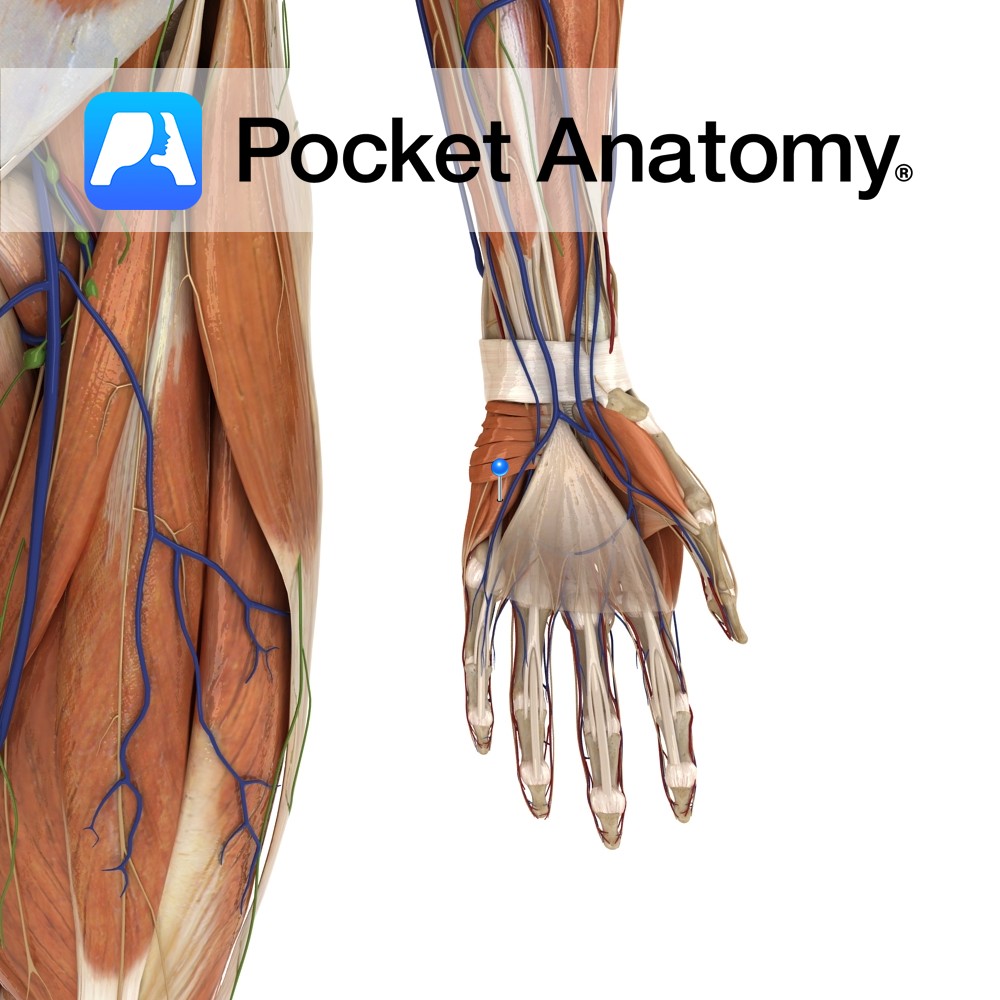
Anatomy Origin: Hook of the hamate and the ulnar border of the flexor retinaculum. Insertion: Ulnar aspect of the base of the proximal phalanx of the little finger. Key Relations: -Is one of the muscles of the hypothenar eminence of the hand. -Abductor digiti minimi lies on its lateral side and the two muscels are
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Humeral head: Medial epicondyle of humerus via the common flexor tendon. Ulnar head: Medial margin of olecranon and upper two thirds of dorsal border of ulna by an aponeurosis. Insertion: Pisiform bone, then via pisohamate and pisometacarpal ligaments into the hook of the hamate and the fifth metacarpal. Key Relations: -The ulnar nerve
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins

.jpg)