PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
Anatomy Course Right gastroepiploic artery originates from the gastroduodenal artery and travels along the greater curvature of the stomach from right to left until it meets the left gastroepiploic artery which originates from the splenic artery. Supply Together the gastroepiploic arteries supply the stomach and the greater omentum. Clinical The right gastroepiploic artery has been
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
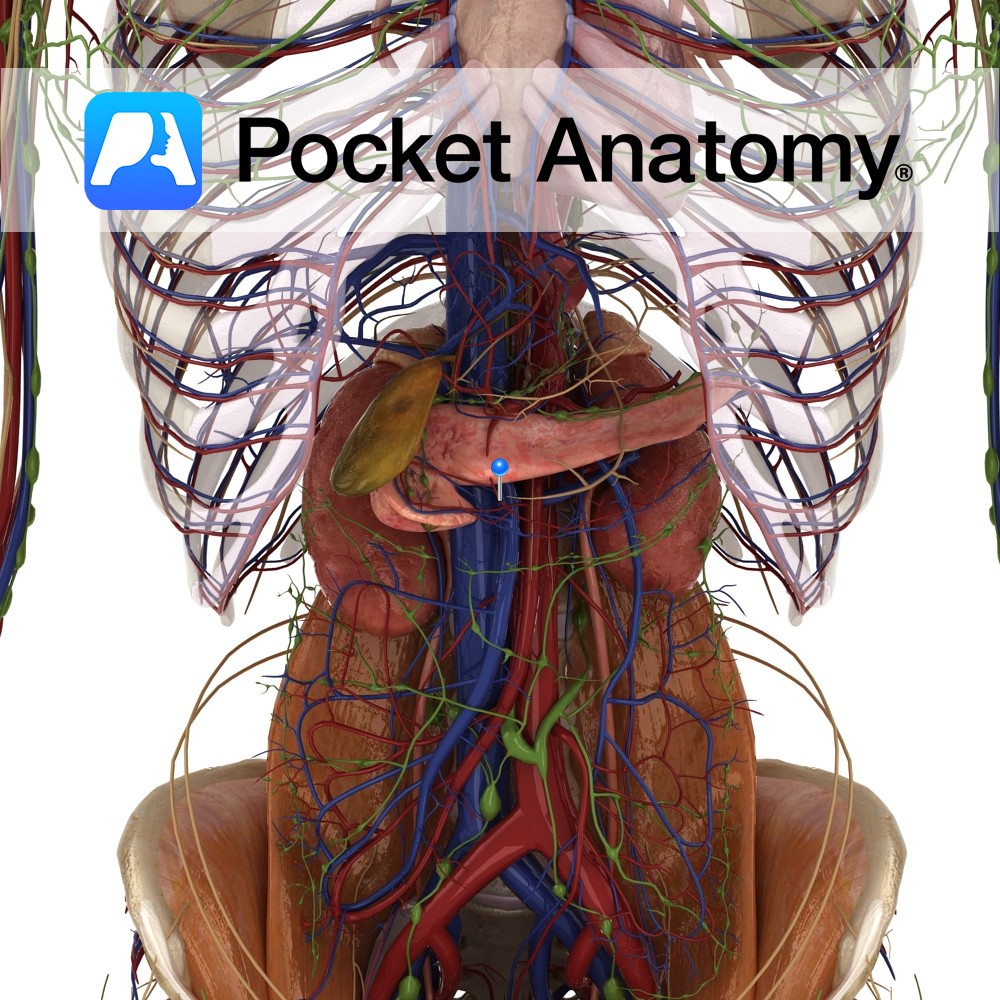
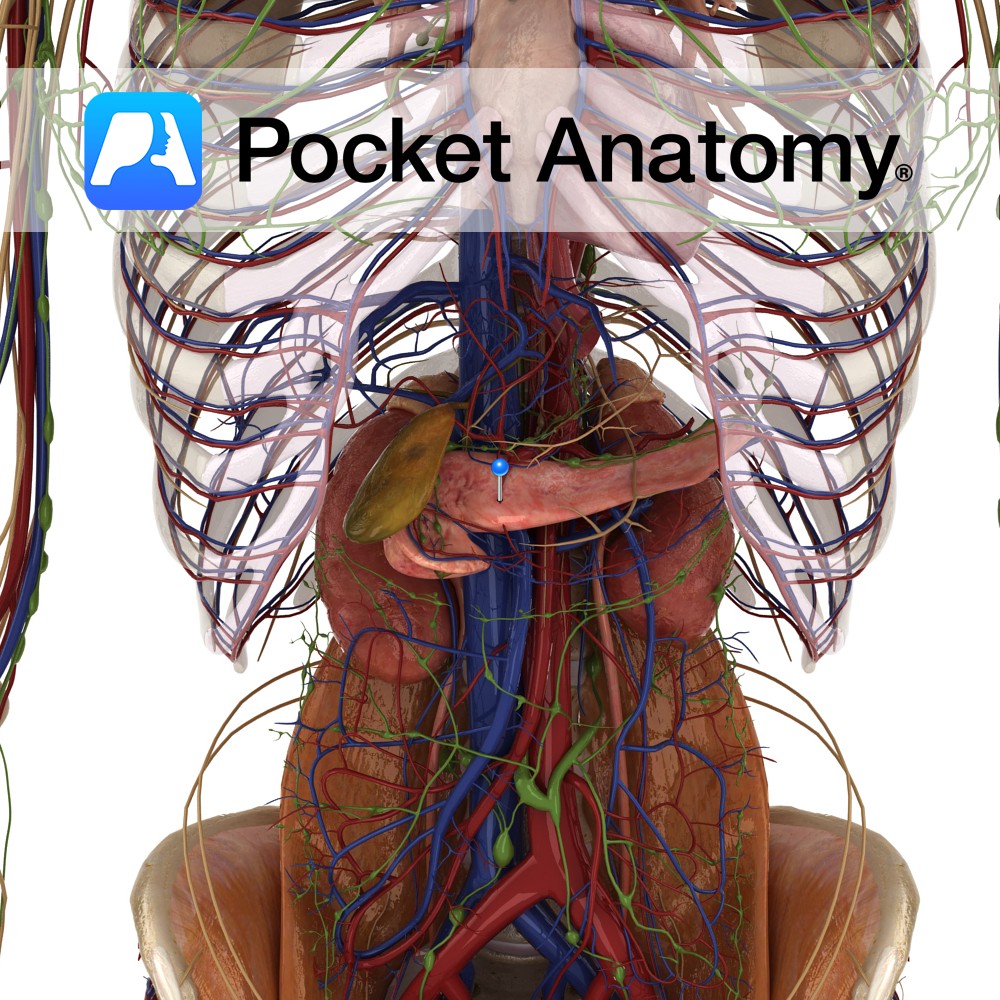
Anatomy Course Branch of the hepatic artery that descends posterior to the duodenum until it reaches its inferior border and gives off its terminal branches. Supply Supplies the pylorus of the stomach and the proximal duodenum. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
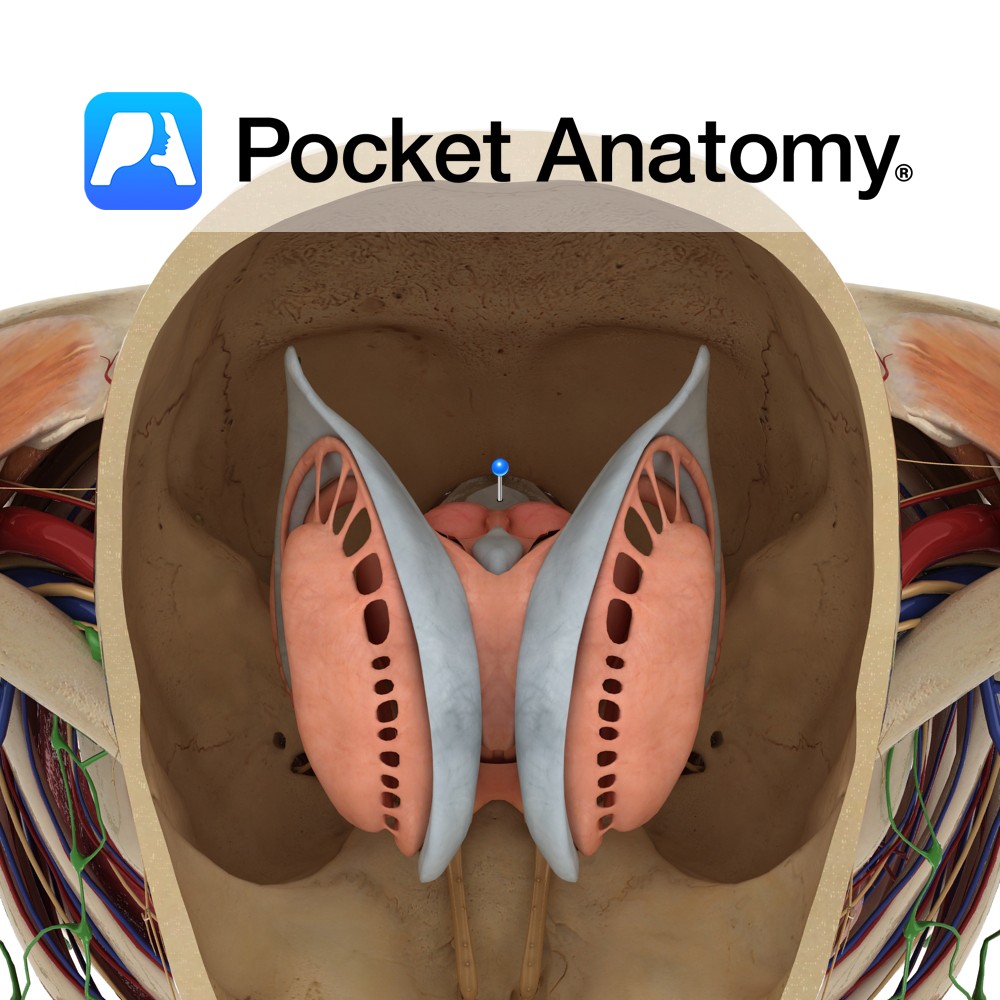
Anatomy Is a rhomboid or diamond shaped cavity lined with ependymal cells part of the series of fluid-filled cavities, which make up the ventricular system. It is located anterior to the cerebellum and posterior to the pons and superior half of the medulla. It is connected superiorly to the third ventricle via the cerebral aqueduct
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Motion There are two radioulnar joints: the proximal radioulnar joint and distalradioulnar joint. Both are synovial pivot joints. They permit pronation and supination only. Proximal radioulnar joint: The circumference of the radial head articulates with the fibro-osseous ring made by the ulnar radial notch and annular ligament. Distal radioulnar joint: The distal head of the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
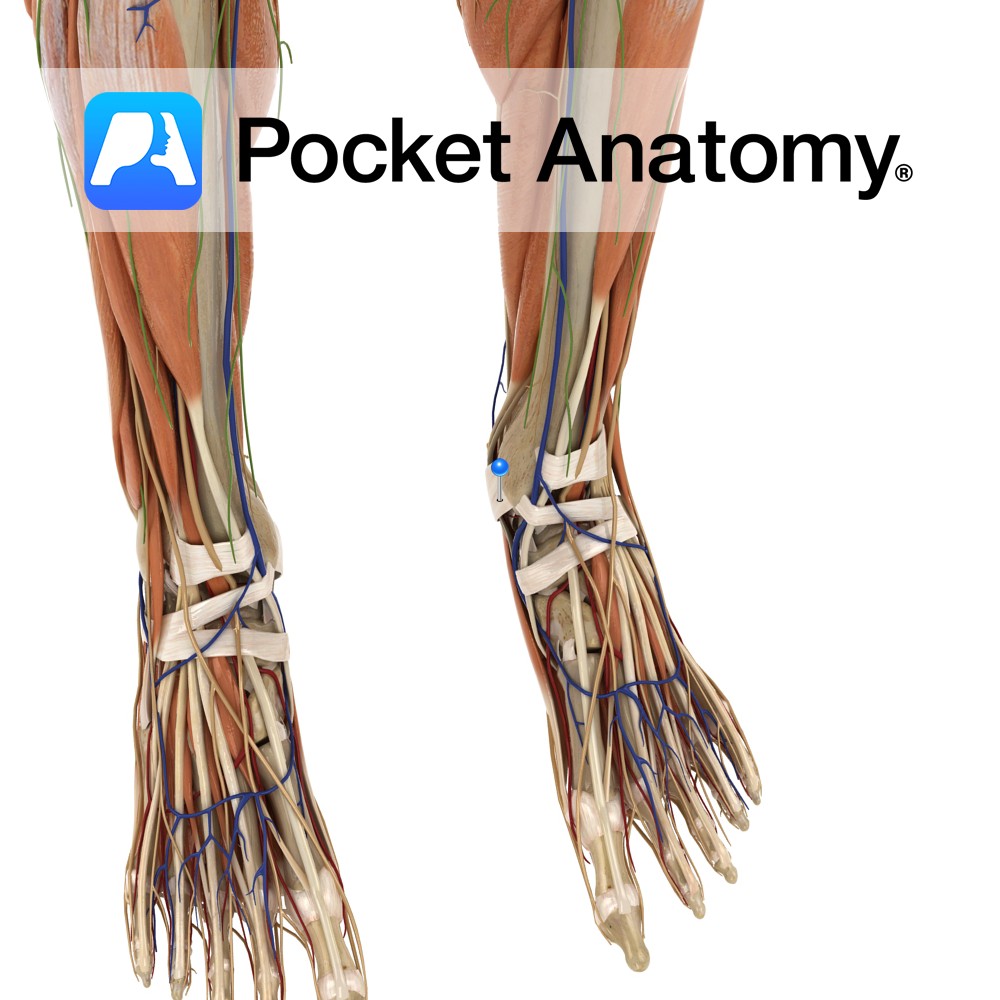
Anatomy Attaches from the posterior surface of the medial malleolus, pacing obliquely backwards to the inferiomedial margin of the calcaneus. Functions Provides static stability to the medial ankle joint. Acts as a pulley for the flexor halluces longus, flexor digitorum longus and tibials posterior tendons. Vessels of the foot pass under the flexor retinaculum. Clinical
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
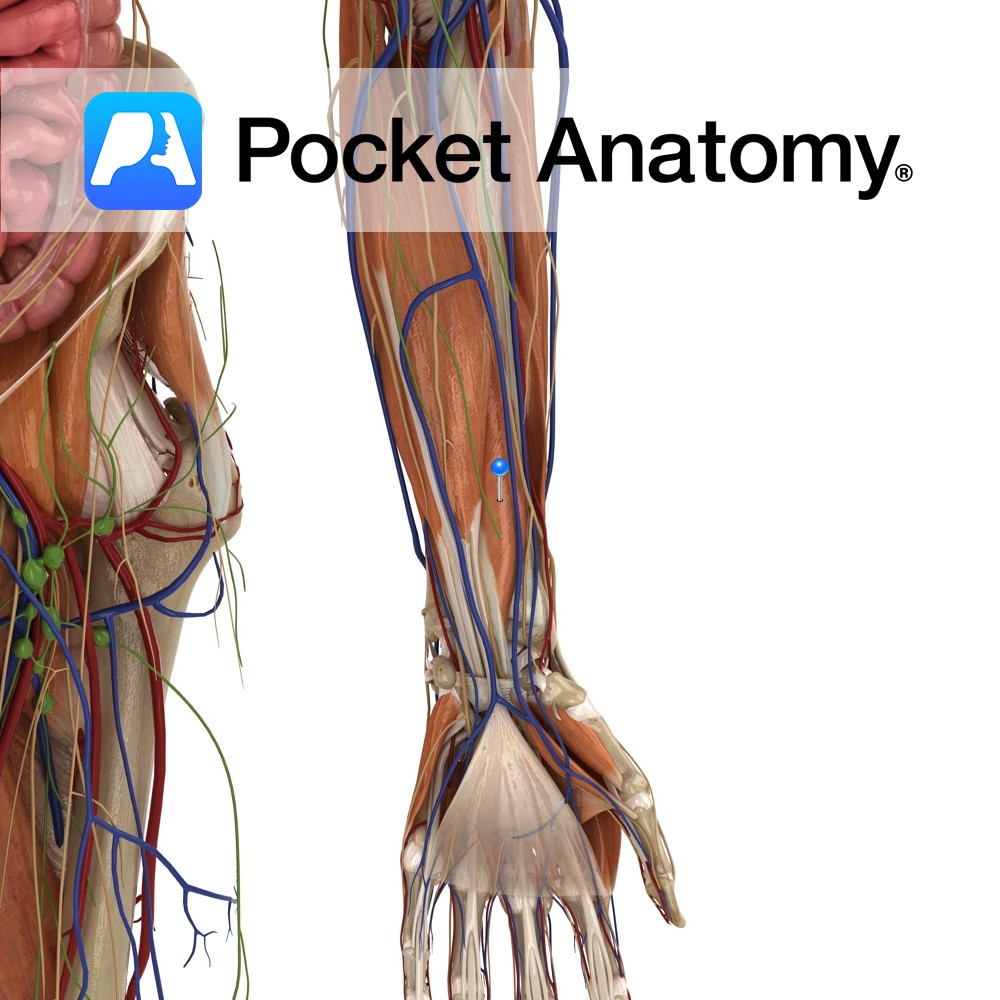
Anatomy Origin: Anterior surface of middle third of radius and adjacent interosseous membrane. Insertion: Base of the distal phalanx of thumb. Key Relations: -The tendons of flexor pollicis longus passes through the carpal tunnel as it enter the palm of the hand. -One of the three muscles in the deep anterior compartment of the forearm.
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Lateral head: Lateral aspect of the lateral condyle of the femur. Medial head: Popliteal surface above the medial condyle of the femur. Insertion: Middle part of the posterior surface of the calcaneus by the tendo calcaneus (Achilles tendon). Key Relations: -One of the three muscles of the superficial posterior compartment of the leg.
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Hollow, muscular, very distensible, pear-shaped organ under liver; receives bile through common hepatic, cystic ducts; concentrates (strengthens) and reserves; releases into cystic duct, on to common bile duct, ampulla of Vater, duodenum through papilla; c. 3″ long, 4″ diameter full; fundus, body, neck (sometimes with saccular Hartman’s pouch), tapering to duct; inferior covered by
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
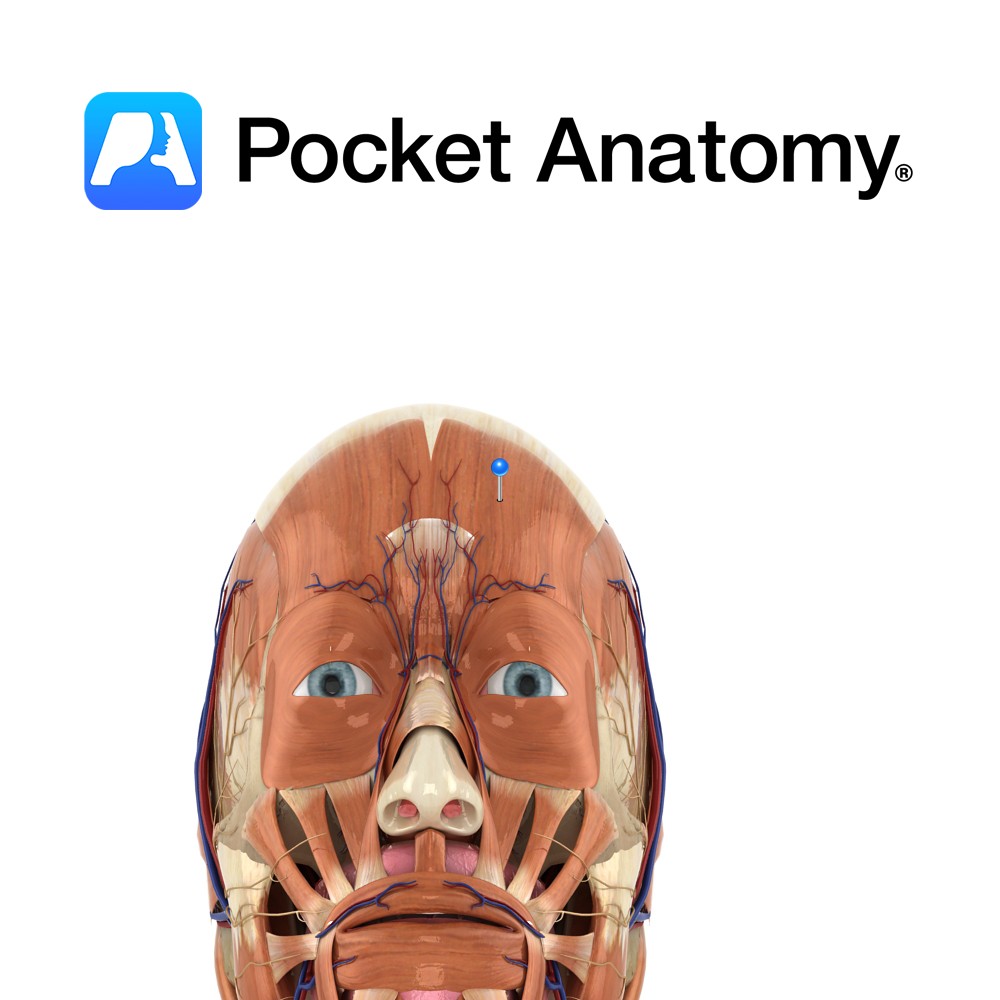
Anatomy Origin: Frontalis has no bony origin. Its fibres are continuous with those of the muscles procerus and corrgator supercilii. Insertion: Fibres join the galea aponeurotica (epicranial aponeurosis) below the coronal suture. Key Relations: Many consider frontalis and occipitalis as one muscle (called occipitofrontalis) with an aponeurotic tendon between two bellies- a frontal belly and
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
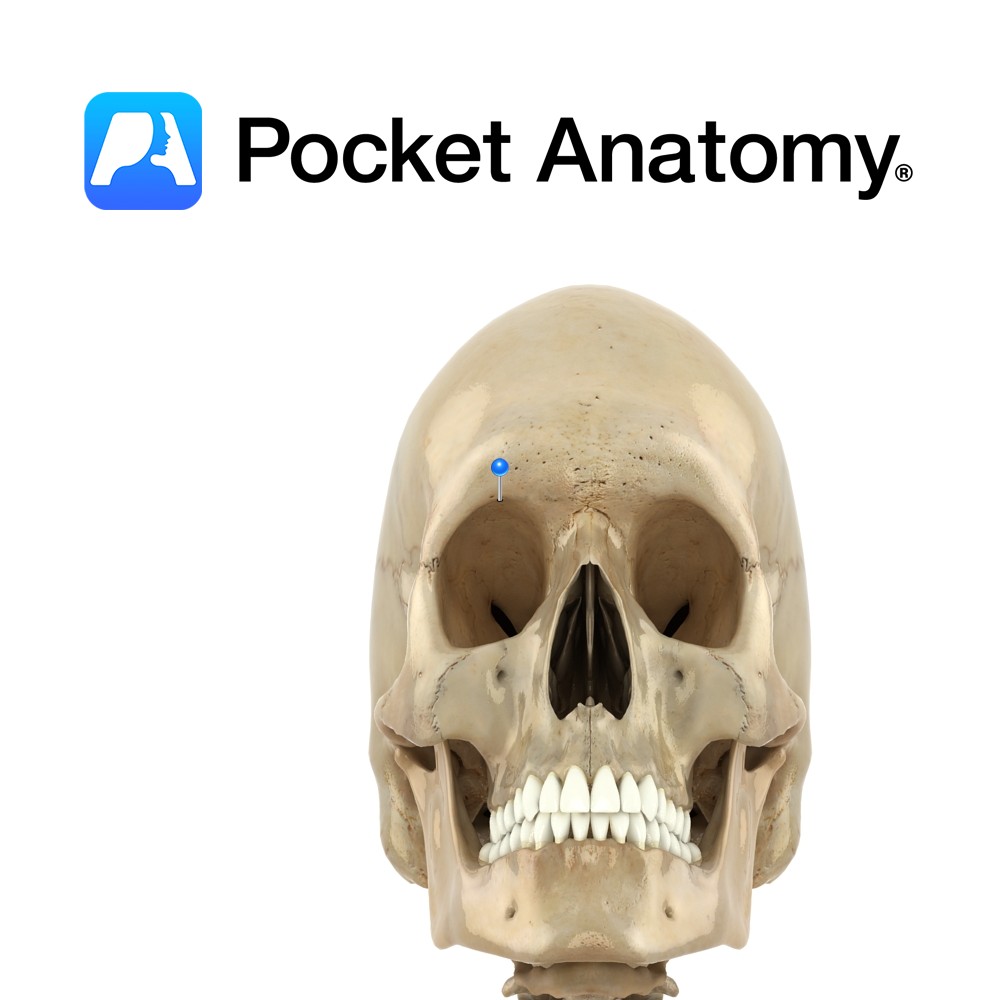
Anatomy Small notch at medial margin on top of each eye socket, through which supra-orbital vessels and nerve pass through. Can be a foramen or a notch. Vignette Swimmer’s headache may be caused by tight goggles pressing on supraorbital nerve at (or near) notch. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins

.jpg)
.jpg)