PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
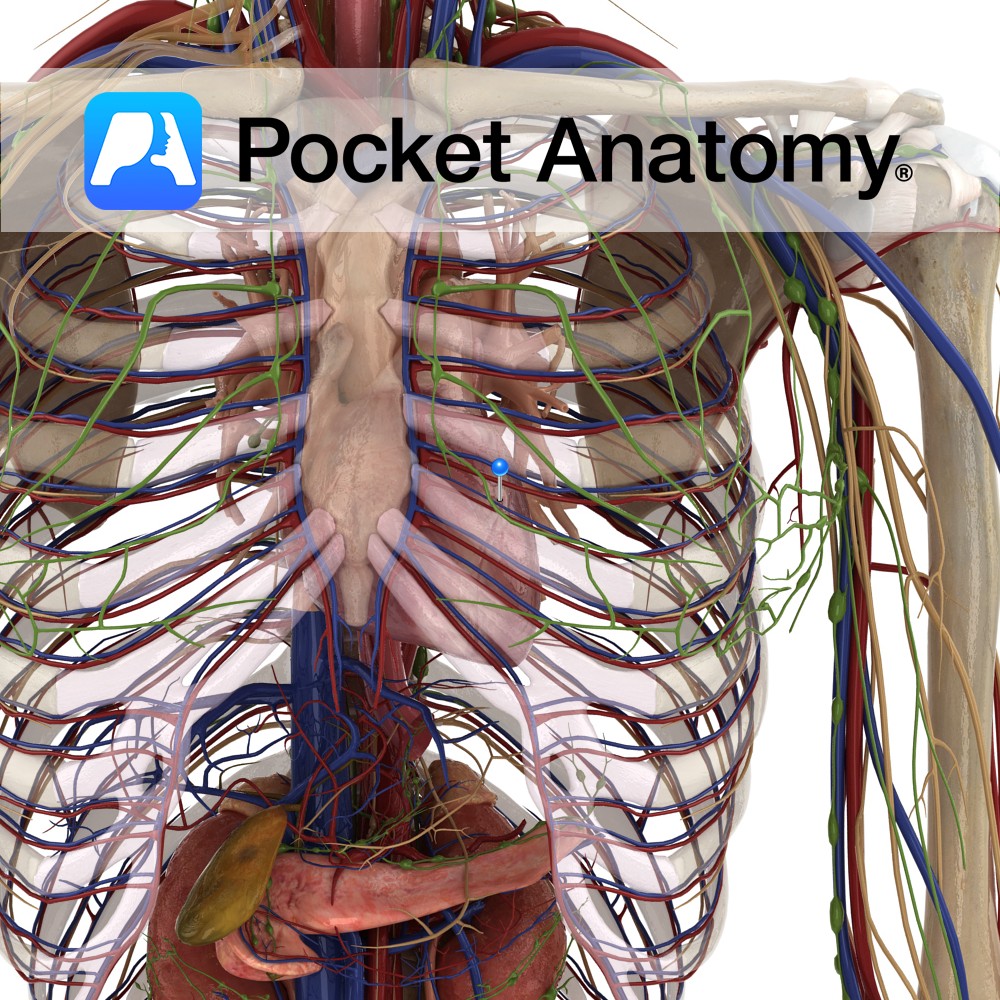
Anatomy Fist-sized blood- pumping muscular (involuntary striated) organ, left of centre in thorax. A double pump with separating septum, each part/side (right and left) comprising 2 chambers – an atrium (into which a vein delivers blood) and a ventricle (from which blood is pumped to an artery) and 2 valves (cuspid between atrium and ventricle,
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
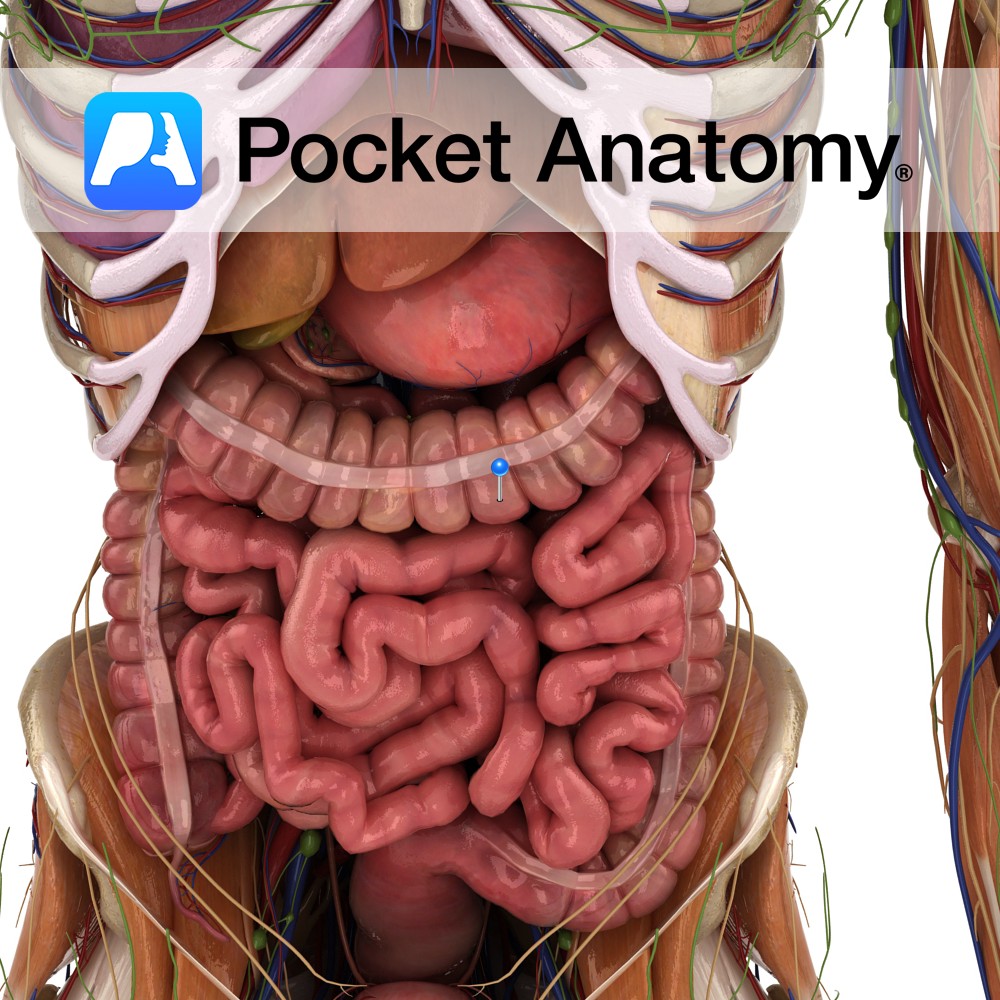
Anatomy Peristalsis (gut movement – churning, mixing, kneading, moving contents on) is caused by smooth muscles, internal layer circular and outer longitudinal. In SI, outer layer (muscularis externa) surrounds gut, whereas in LI, there are 3 separate longitudinal bands (taenia coli). These are shorter (more so when contracted) than the rest of the circumference of
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
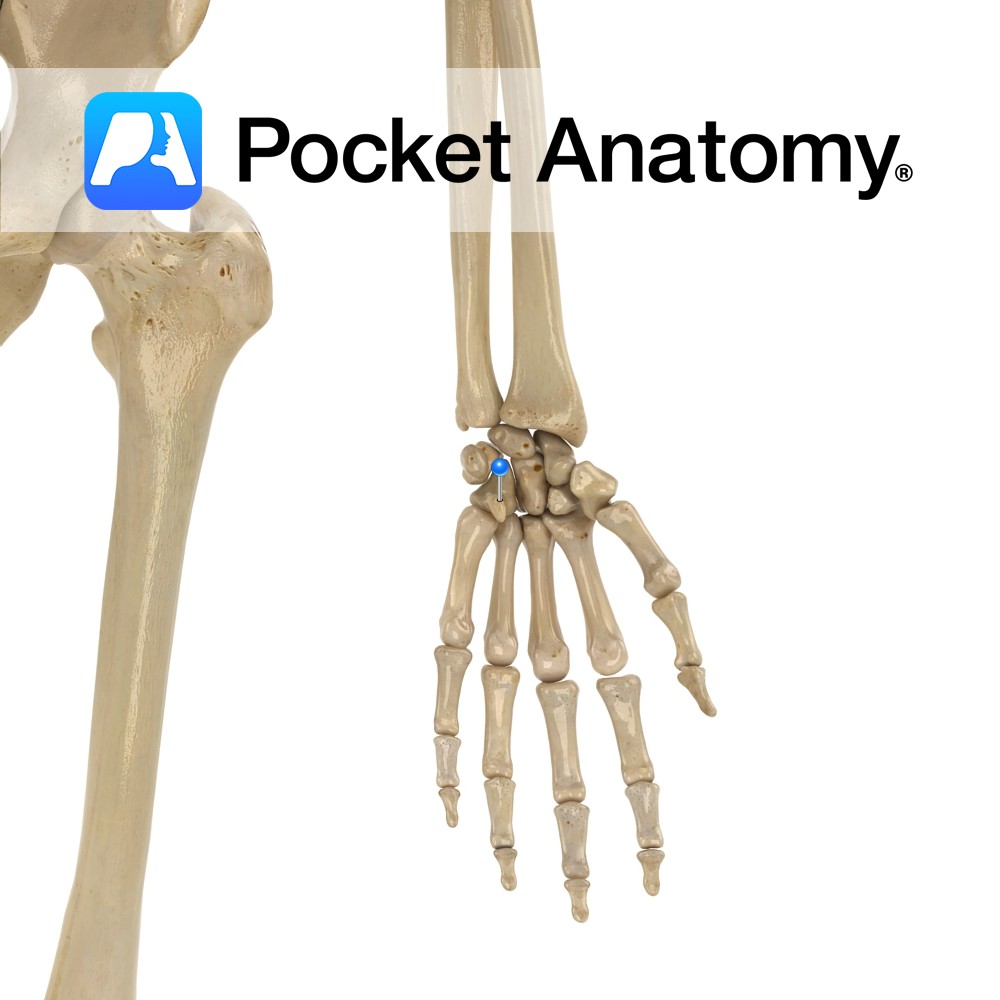
Anatomy Small finger side of further row of carpal bones, wedge-shaped with hook-like palmar projection. Articulates up with lunate, down with 4th, 5th meta-carpals, out with capitate, in with triquetral. Clinical Golf duffer’s fracture, also common in baseball (can lead to surgical removal) and hockey (slapshot). Vignette Hamatus (Latin); hooked. Interested in taking our award-winning
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Medial head: Popliteal surface above the medial condyle of the femur. Lateral head: Lateral aspect of the lateral condyle of the femur. Insertion: Middle part of the posterior surface of the calcaneus by the tendo calcaneus (Achilles tendon). Key Relations: -One of the three muscles of the superficial posterior compartment of the leg.
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
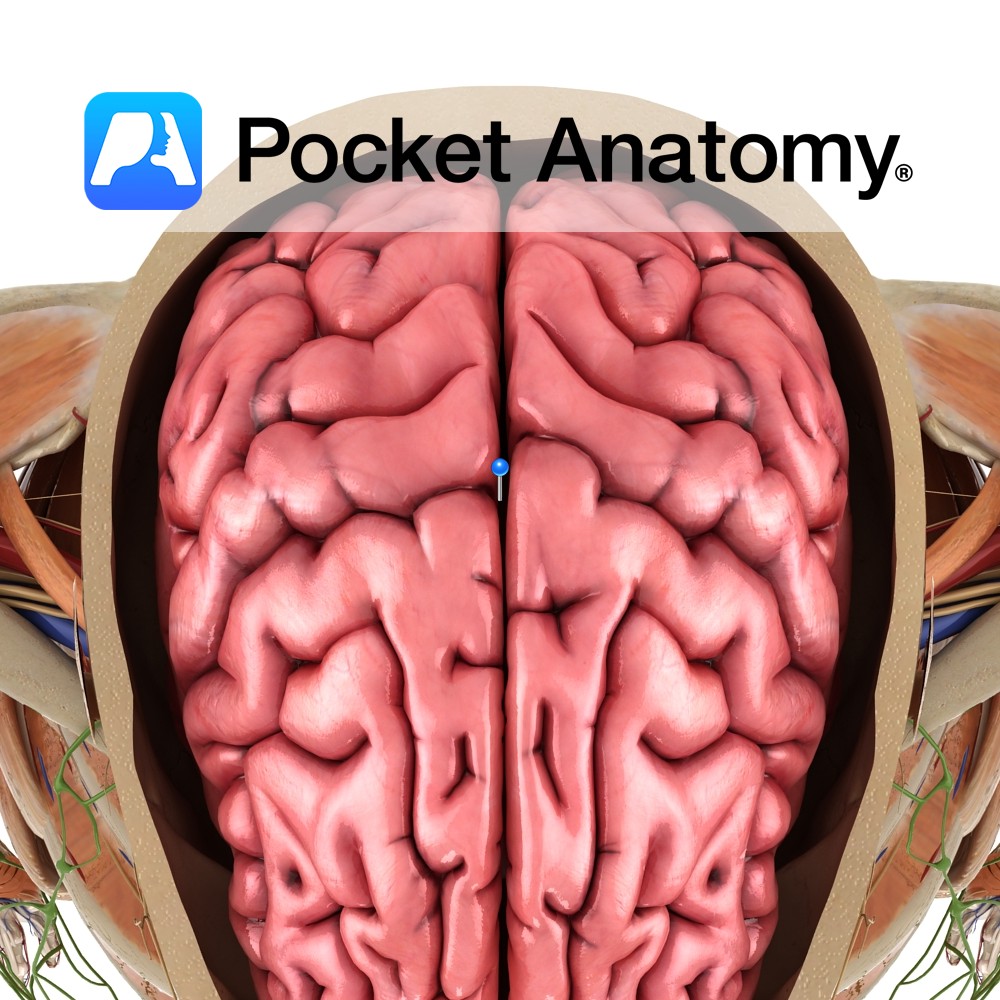
Anatomy A deep midline sagittal fissure located separating the two cerebral hemispheres. The floor is formed by the corpus callosum, and the falx cerebri of the dura mater extends deep within the fissure. Functions Separates the two cerebral hemispheres. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
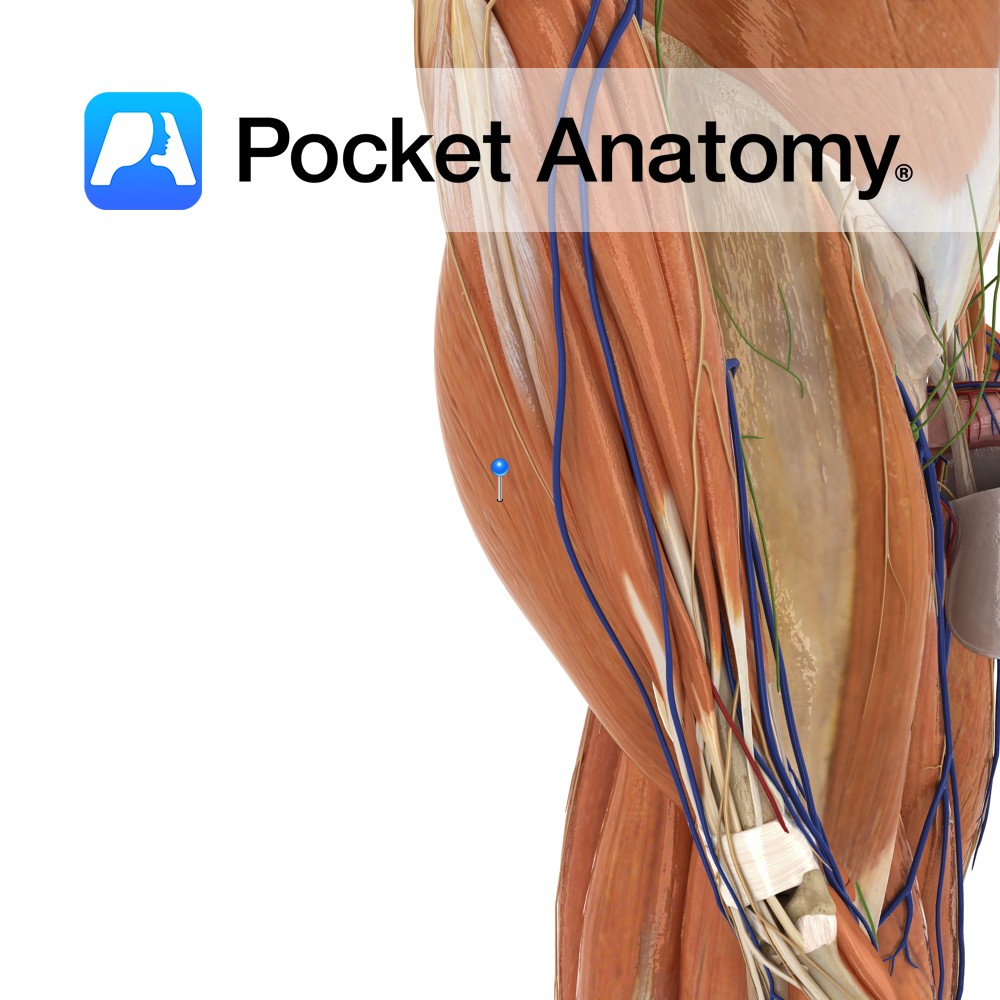
Anatomy Origin: Body and inferior ramus of pubis. Insertion: Superomedial surface of tibia. Key Relations: -One of the six muscles of the medial compartment of the thigh. -At its insertion to the tibia, the tendon of gracilis is located between the tendons of sartorius and semitendinosus. This 3 pronged arrangement is known as pes anserinus
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Outer surface of the ilium between the anterior and inferior gluteal lines. Insertion: The fibres converge to form a tendon that inserts on the anterior border of the greater trochanter of the femur. Key Relations: -Gluteus minimus lies posterior to gluteus medius. -The deep branches of the superior gluteal vessels and the superior
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Outer surface of the ilium with the iliac crest and posterior gluteal line above and the anterior gluteal line below. Insertion: The fibres converge to form a strong, flat tendon that inserts on the lateral surface of the greater trochanter of the femur. Key Relations: -The posterior third of gluteus medius lies posterior
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Posterior gluteal line of the ilium, posterior aponeurosis of erector spinae, posterior surface of the sacrum , lateral aspect of the coccyx and the sacrotuberous ligament. Insertion: Iliotibial tract of the fascia lata and gluteal tuberosity of the femur. Key Relations: The upper border of gluteus maximus lies anterior to the inferior third
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
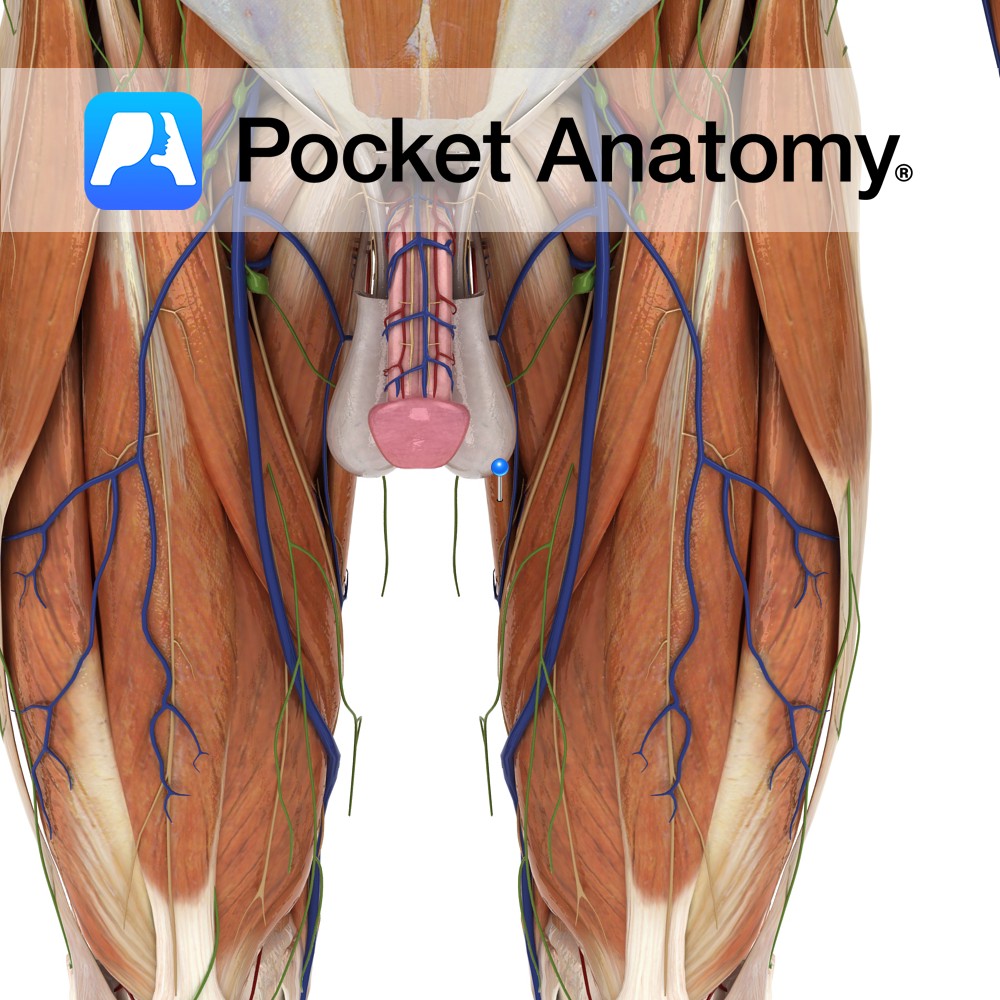
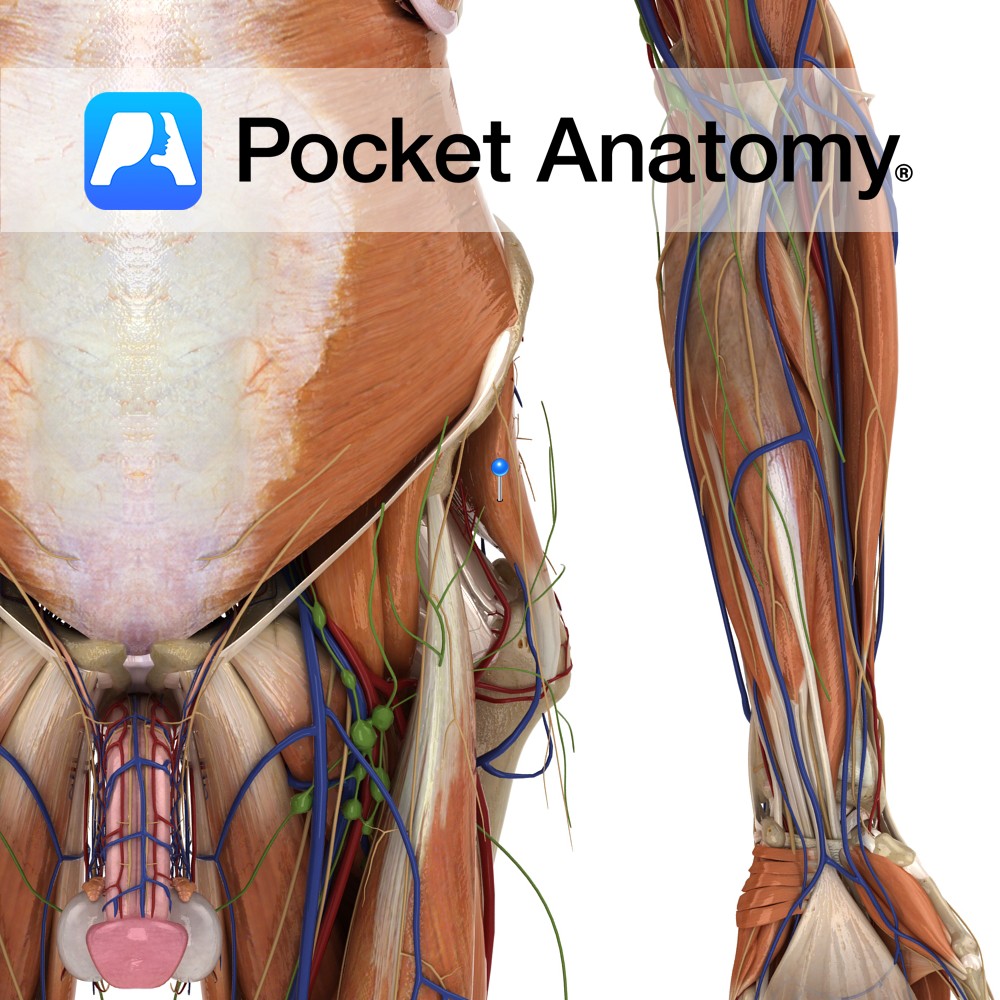
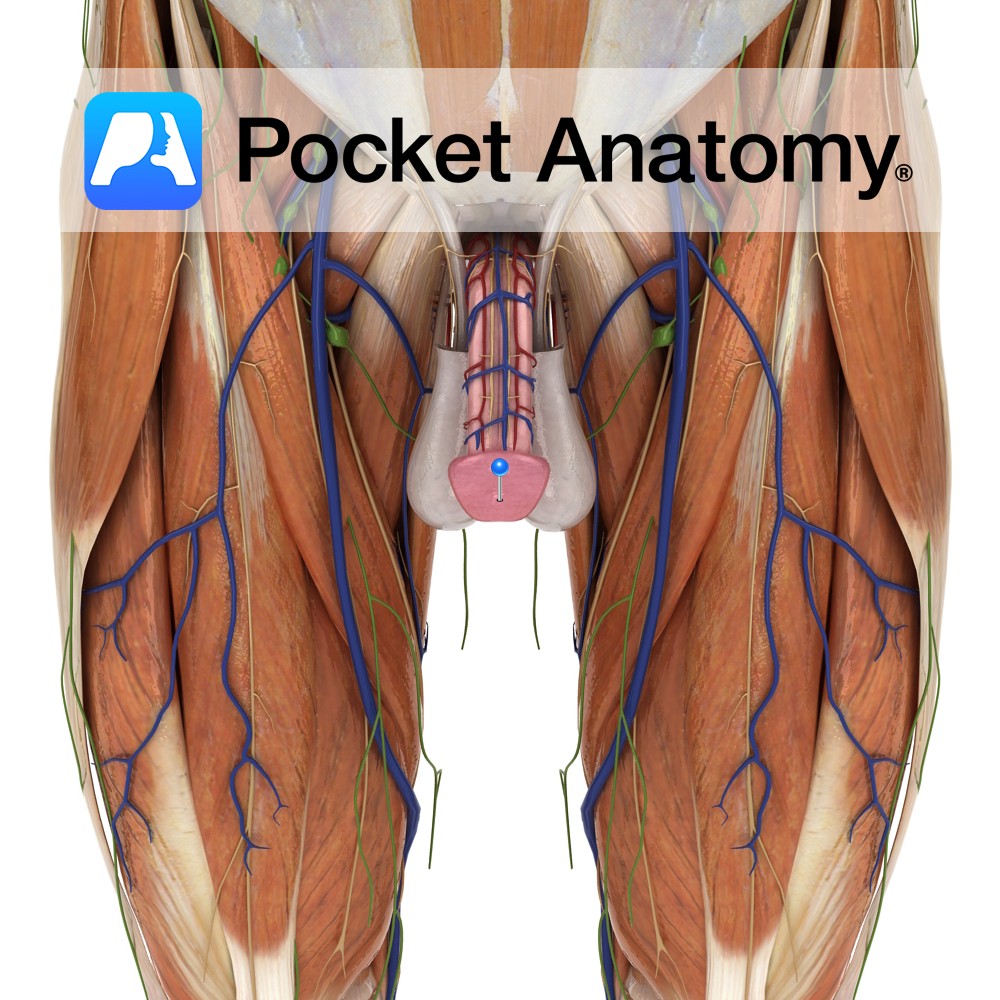
Anatomy Conical distal end of penis, with slit opening (meatus or external urethral orifice), sensitive homologue of clitoris, ordinarily covered partially/fully in flaccid state by retractable foreskin/prepuce (removed in circumcision), is the expanded end of corpus spongiosum molded around joined ends of corpora cavernosa, its base bulging as a corona distal to a sulcus at
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins

.jpg)