PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
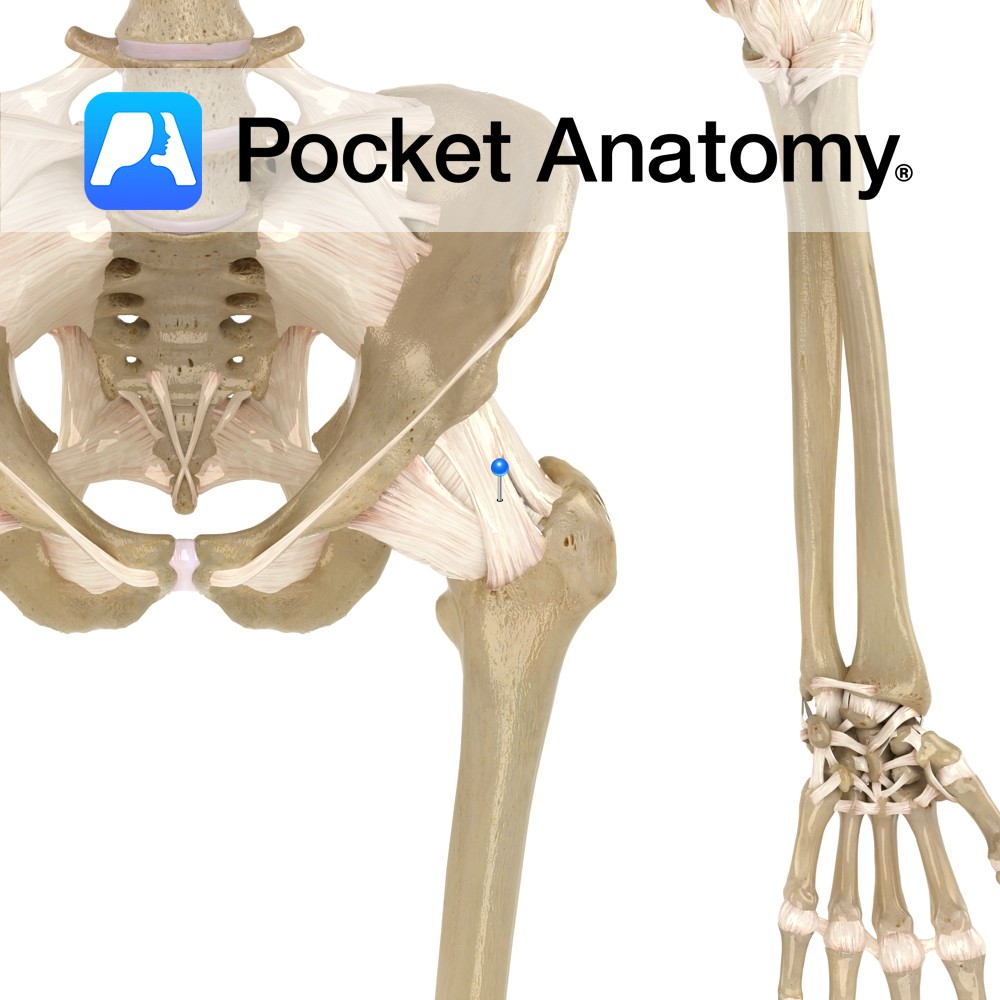
Anatomy A triangular or Y-shaped ligament. Its proximal attachment is to the ilium below the anterior inferior iliac spine along the margin of the acetabulum. Distally, it attaches along the intertrochanteric line of the femur. The ligament is thicker at either end, hence its Y-shape. Functions Provides static support to the hip joint. The ligament
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Inner lip of Iliac crest, upper two-thirds of iliac fossa, ala of sacrum and anterior sacroiliac and iliolumbar ligaments. Insertion: Psoas tendon and lesser trochanter of femur. Key Relations: -Iliacus fills the iliac fossa of the hip bone and, enters the thigh with psoas major passing under the inguinal ligament. -Forms the floor
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
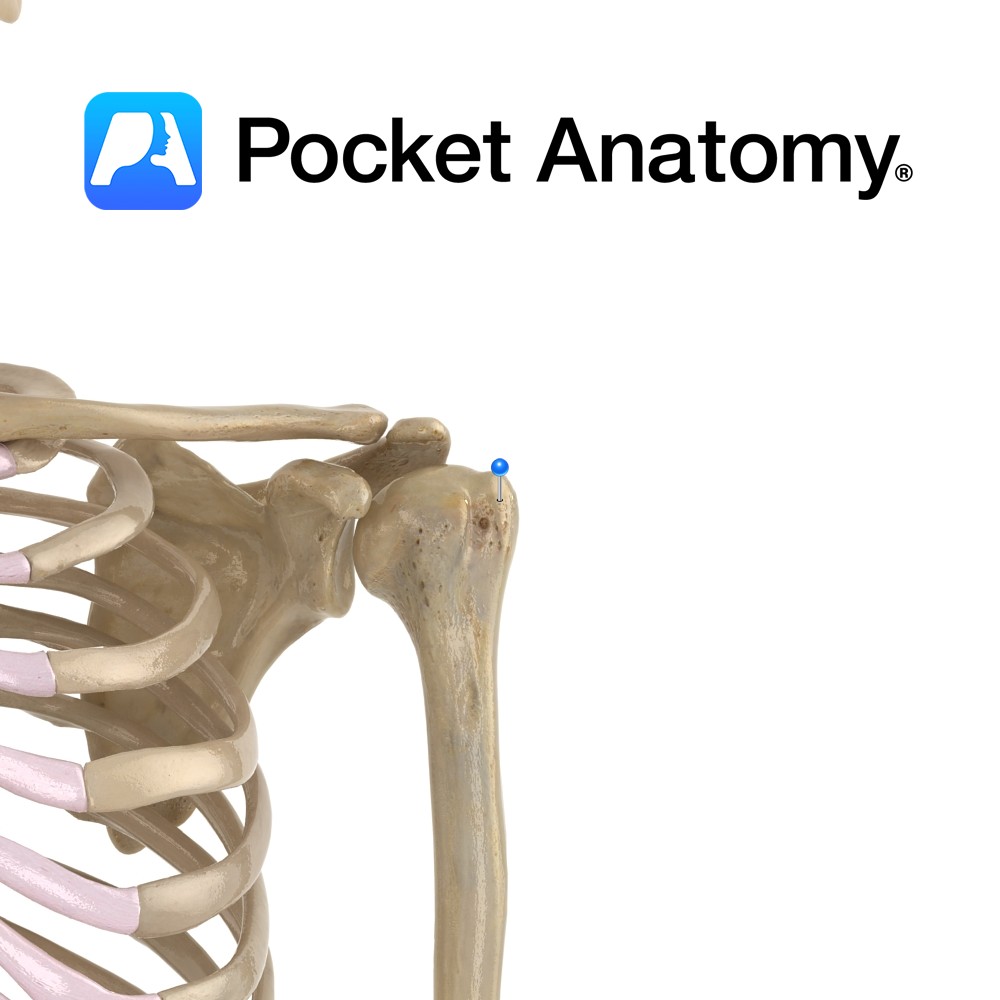
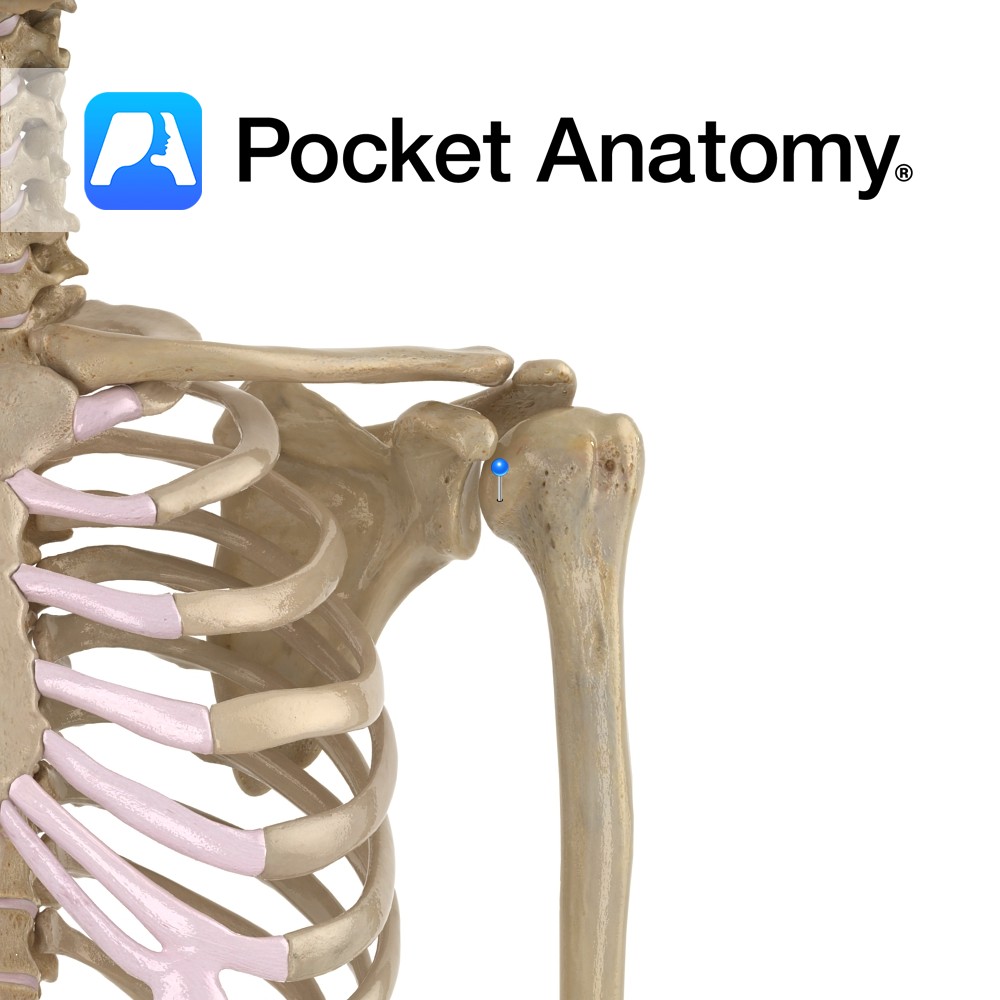
Anatomy Swelling lateral to humeral head, above and behind lesser tubercle. Attachments; supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
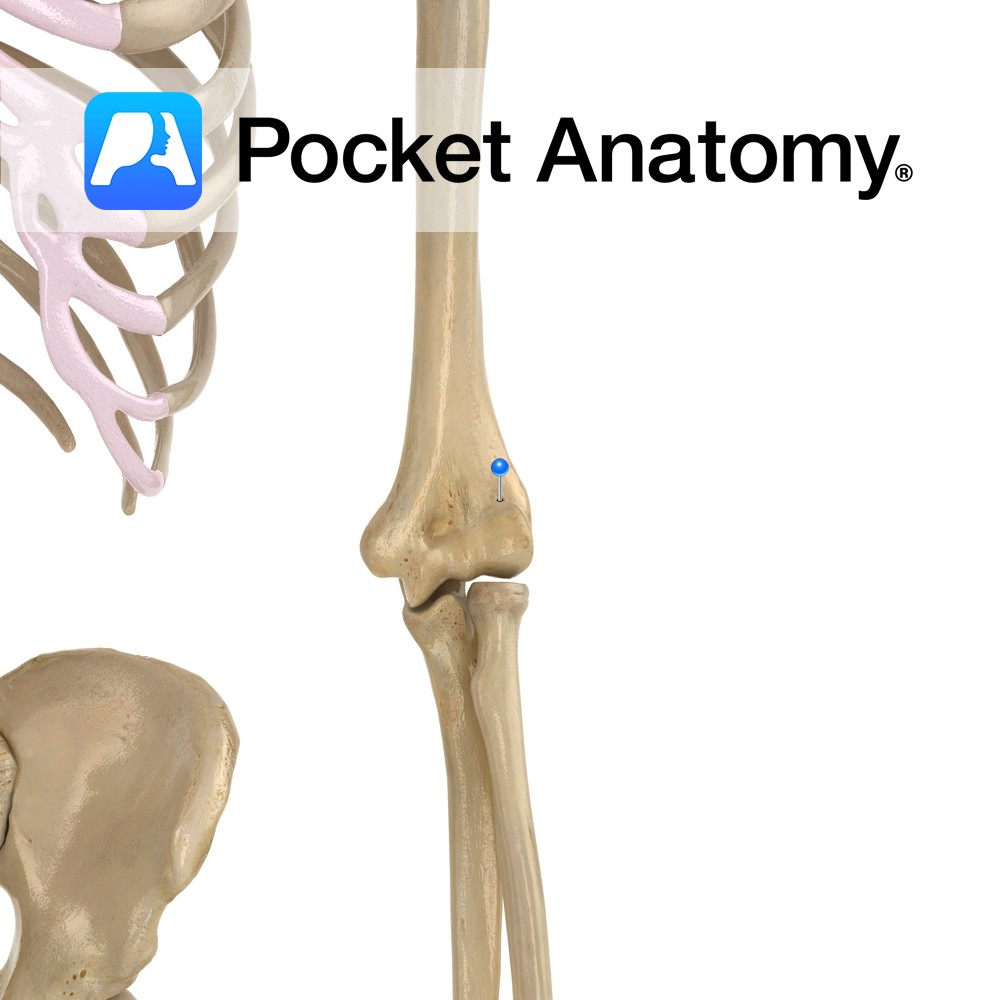
Anatomy Just above the trochlea (which articulates with head of ulna) at bottom of humerus medially. When the arm is bent (ie elbow hinge joint flexed), the coronoid process of ulna sits in the coronoid fossa (limiting further flexion). Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy The articular surface of the bottom of humerus is divided into trochlea medially (for trochlear notch of ulna, which is between coronoid process and olecranon) and capitulum laterally (for head of radius). Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
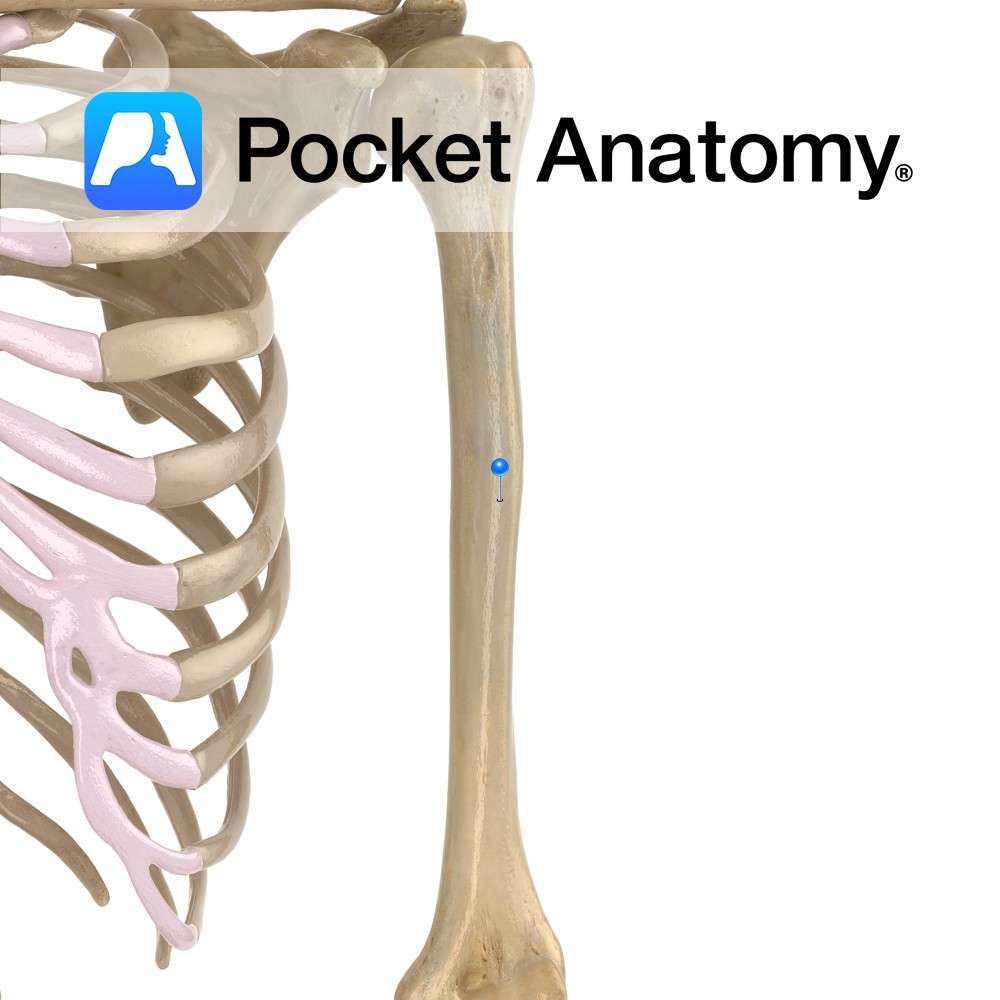
Anatomy Upper part cylindrical, lower prism-shaped. Deltoid tuberosity (for attachment of deltoid muscle) on antero-lateral aspect (to outside and front) at mid portion shaft. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
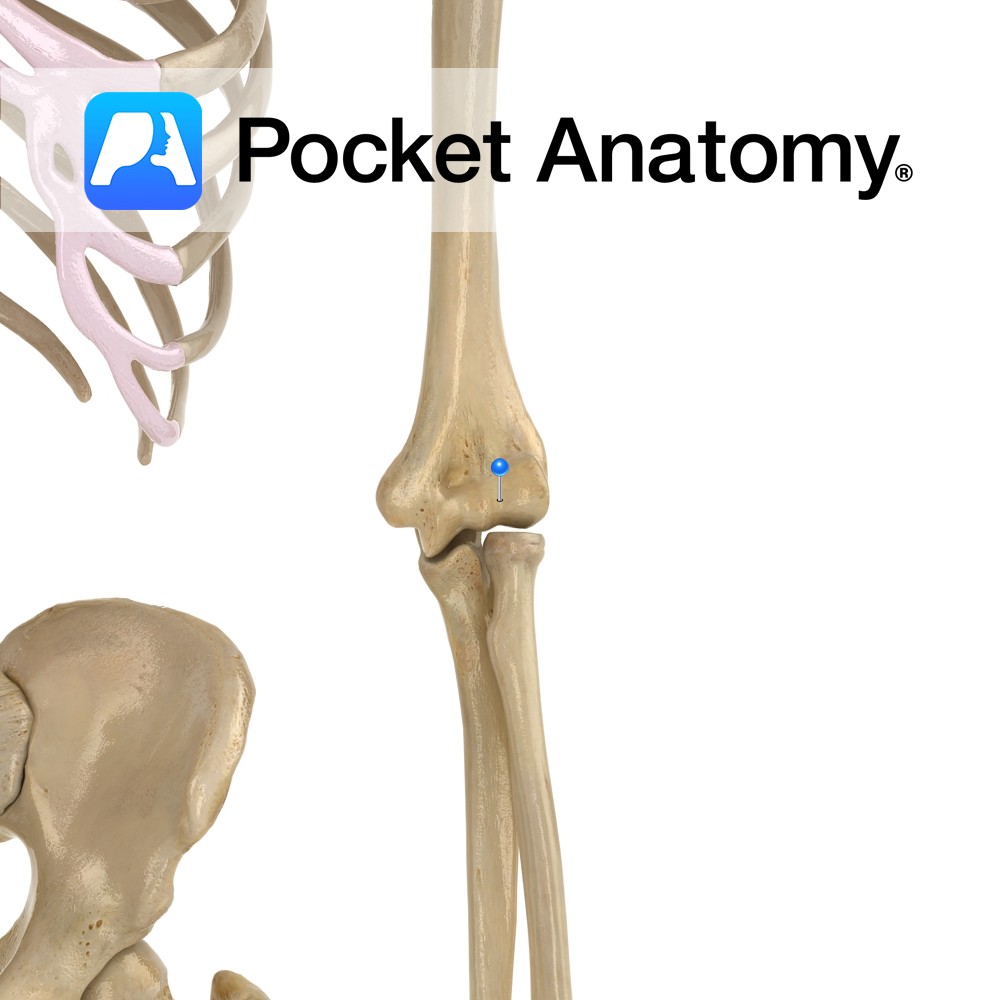
Anatomy Just above the capitulum (which articulates with head of radius) at bottom of humerus laterally. When the arm is bent (ie elbow hinge joint flexed), the front part of radial head sits in it (limiting further flexion). Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
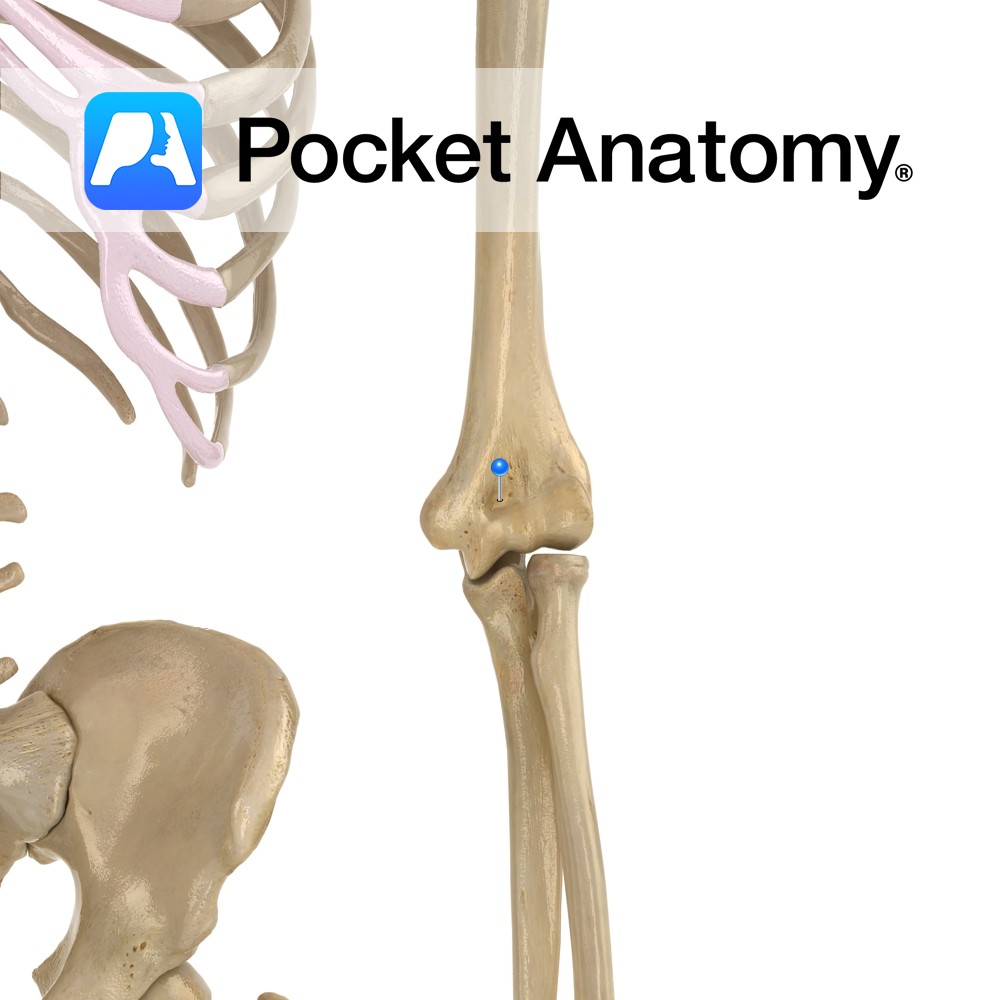
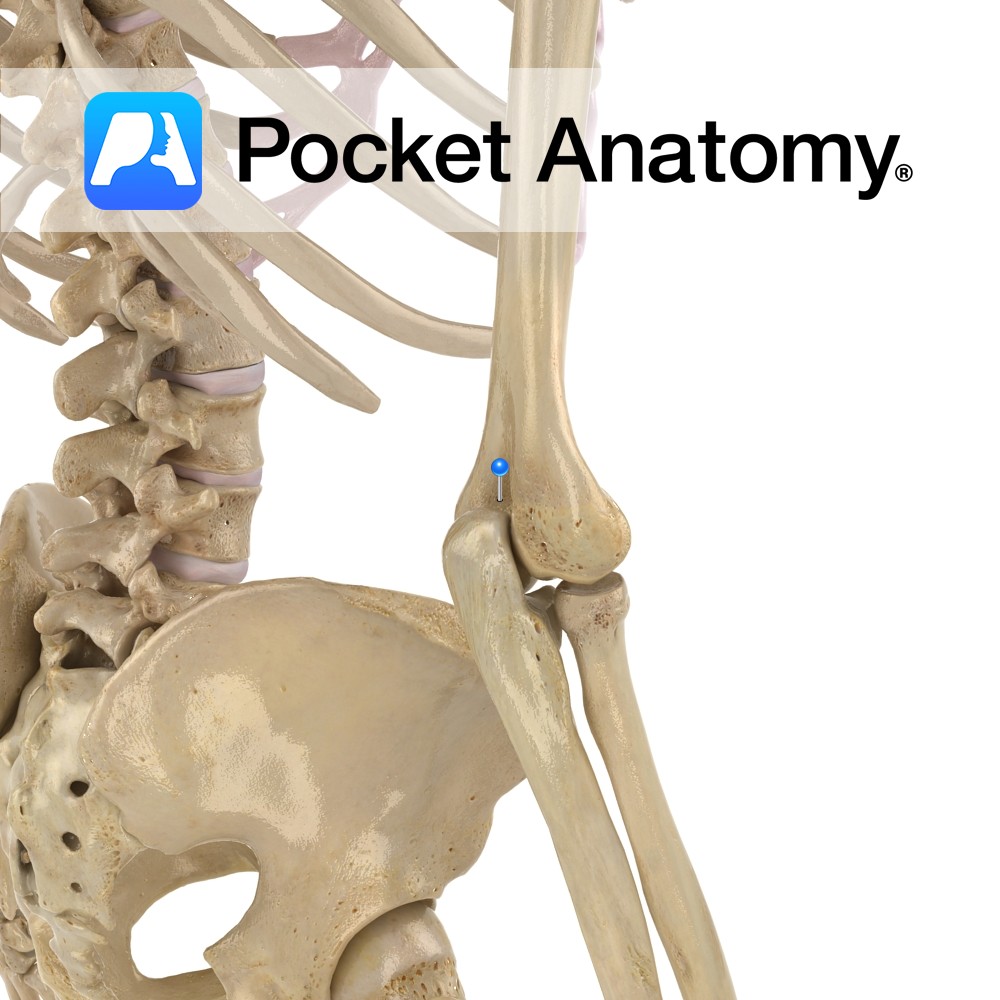
Anatomy When arm straightened (ie elbow hinge joint fully extended), the olecranon process of ulna sits in olecranon fossa at back of bottom of humerus, lending significant bony strength, stability and movement limitation (stopping hyperextension). Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Bump at bottom of humerus, medially (when hand pronated, ie palm forward). Attached; ulnar collateral ligament of elbow (significant in stabilizing the joint against valgus – lateral flexion), pronator teres, common flexor tendon. Bigger than lateral epicondyle. Clinical “Funny bone”; ulnar nerve runs just behind it (and can be easily felt – cordlike), with
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Swelling below and medial to humeral head, below and in front of greater tubercle. Attachment; subscapularis. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins