PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
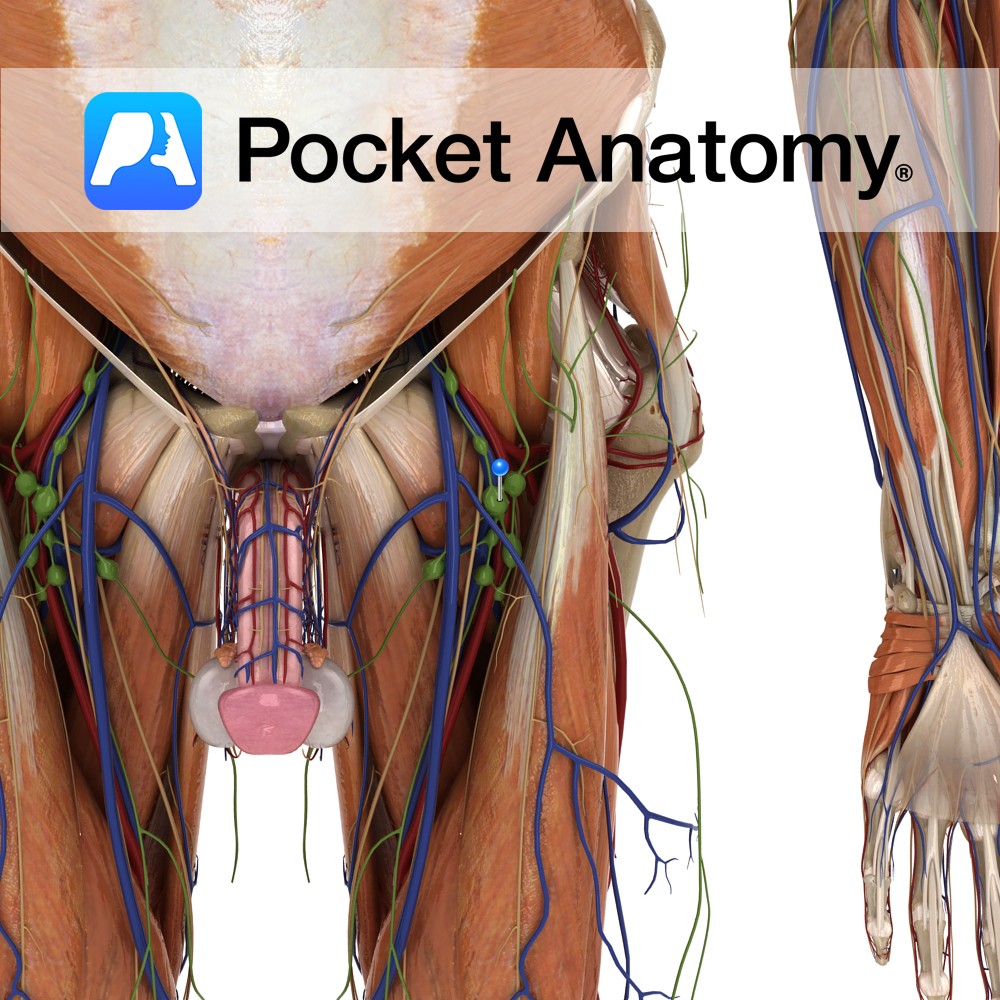
Anatomy Made up of External (around 8-10) and Internal (about 3) Iliac lymph nodes. External receive lymph from pelvis (including upper vagina and cervix or prostate, urethra, bladder) and from Inguinal Lymph Nodes. Internal receive from vagina, urethra, rectum, perineum, buttocks, back upper thigh. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
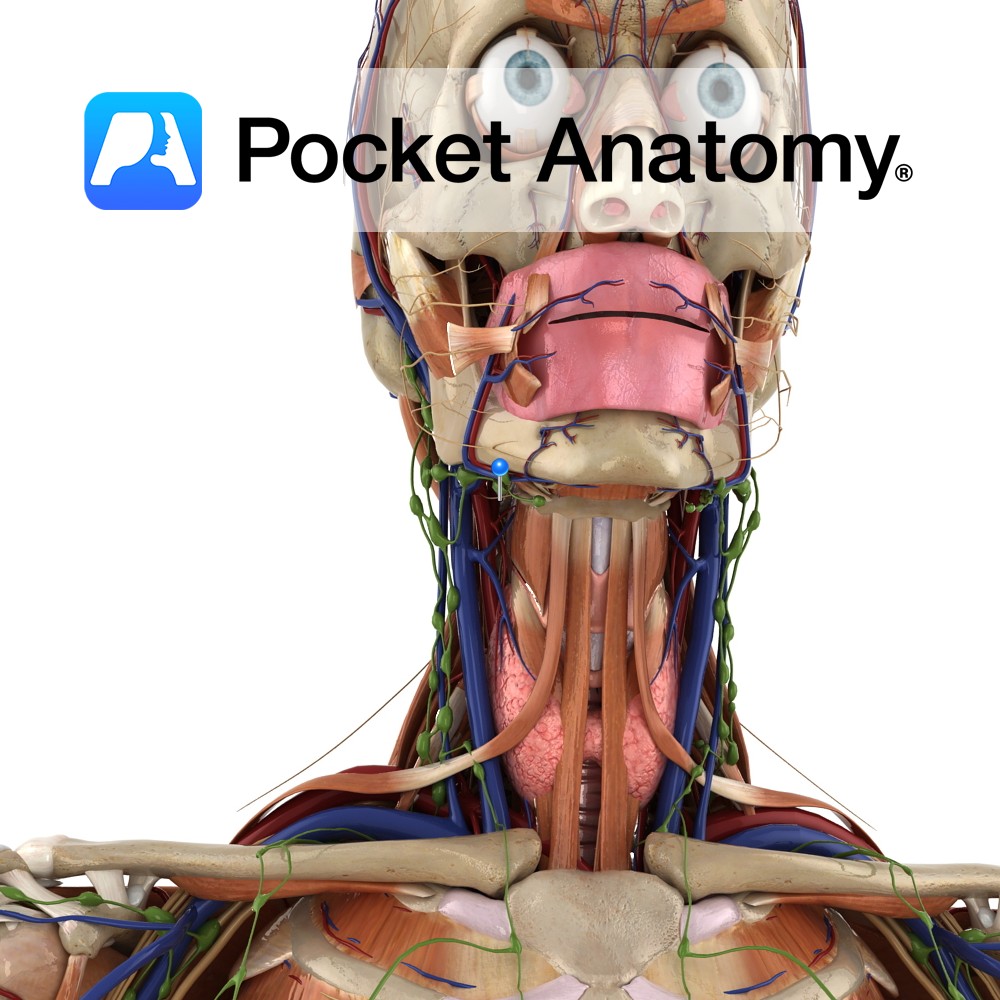
Anatomy Course Also known as the twelfth cranial nerve, it originates from the medulla. It passes through the hypoglossal canal and tucks in behind the vagus nerve and passes between the internal jugular vein and the internal carotid artery. It finally enters the submandibular region to reach the tongue. Supply Motor supply to the whole
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
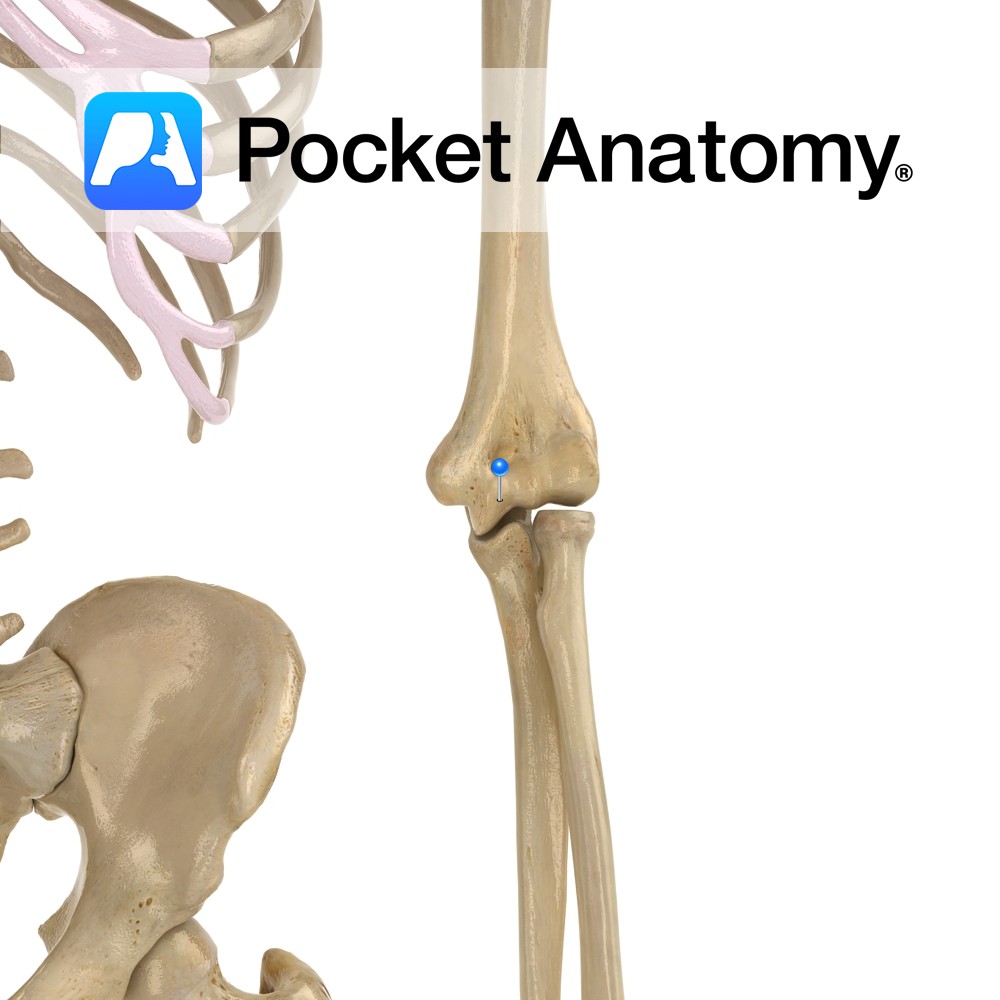
Anatomy The articular surface of the bottom of humerus is divided into trochlea medially (for trochlear notch of ulna, which is between coronoid process and olecranon) and capitulum laterally (for head of radius). Vignette Trochlea (Latin); pulley. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Common fracture site (much more so than anatomical neck), with risk of damage to adjacent axillary nerve. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
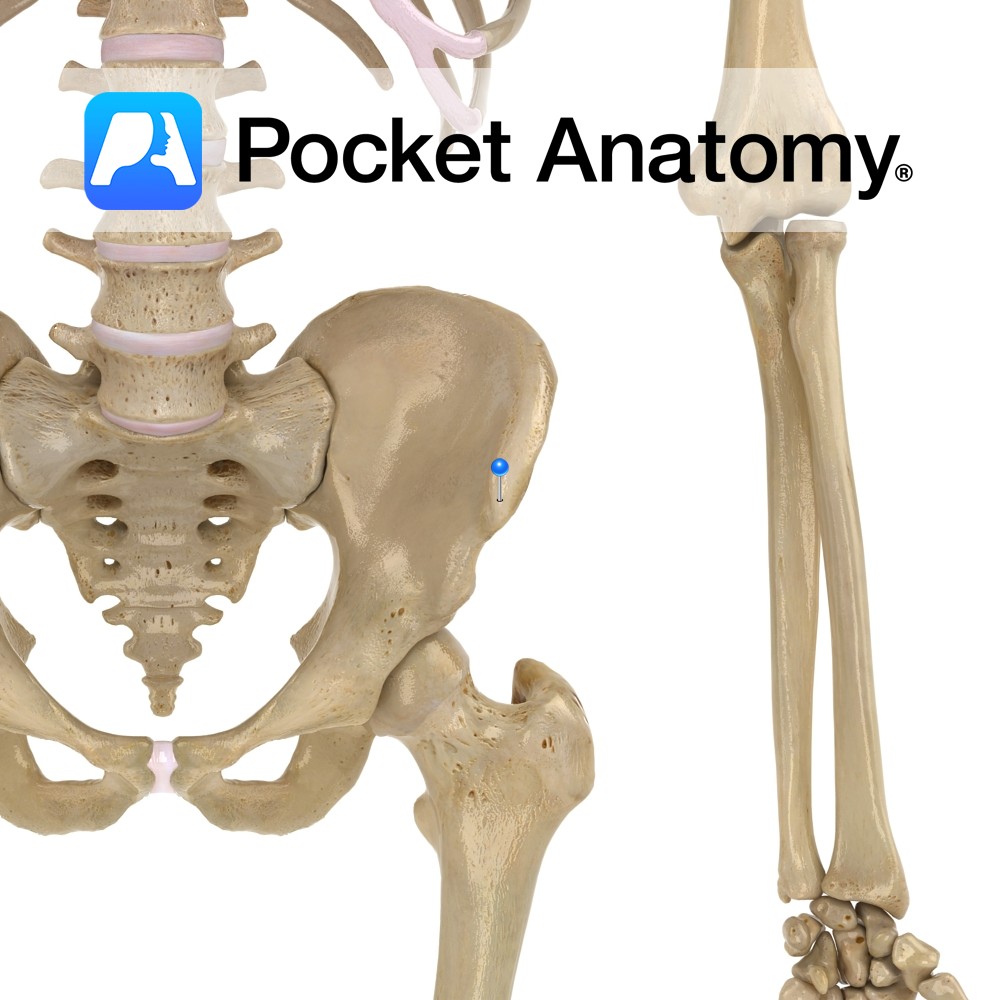
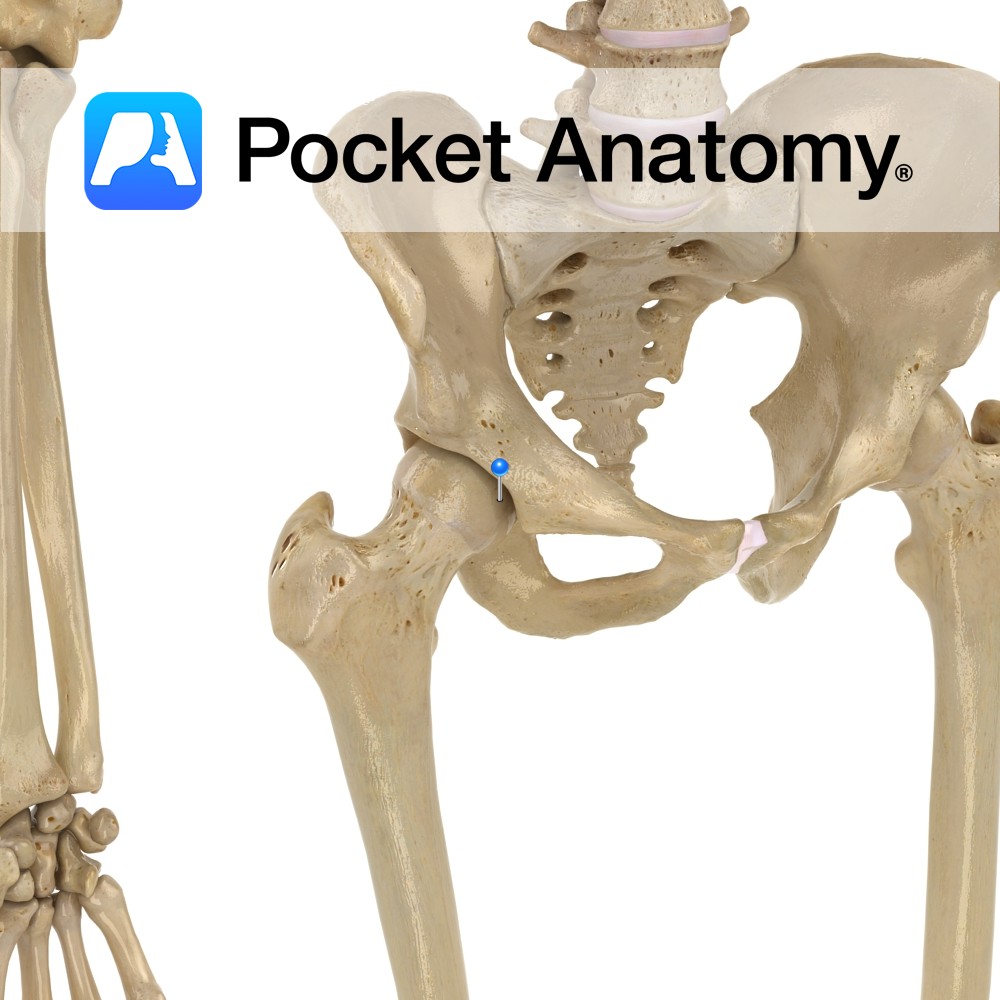
Anatomy The anterior limit of the Iliac crest of the ala of the ilium, separated by a notch from the anterior inferior iliac spine. Vignette Easily felt and located, useful surface anatomy landmark; McBurney’s point (where deep tenderness can indicate acute appendicitis) is 2/3 distance from umbilicus to anterior superior iliac spine. Interested in taking
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
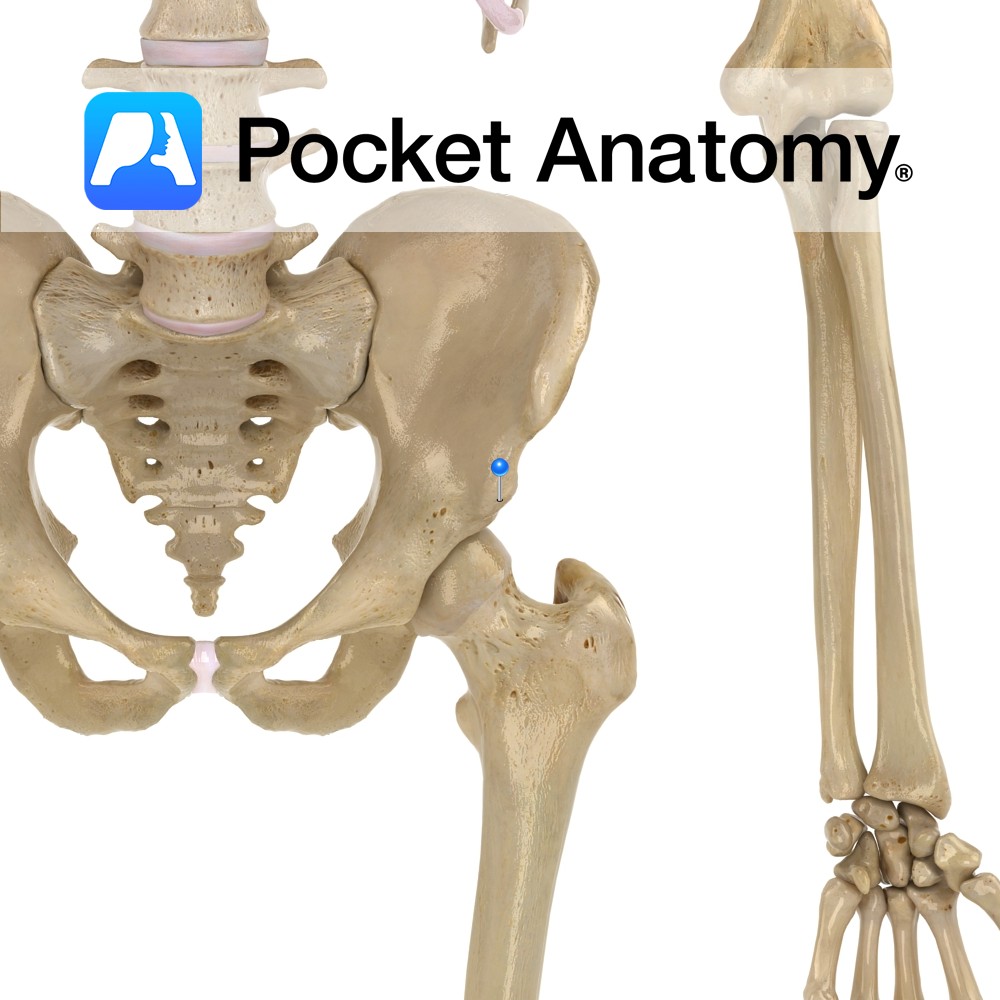
Anatomy Bulge on lower front border of the ala of ilium, separated by a notch from the anterior superior iliac spine. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy The hip bone (os oax) is made up (each side) of 3 bones (ilium, ischium and pubis), separated by hyaline cartilage at birth, fused and united by 25. The 3 bones meet and form (ilium 40%, ischium 40%, pubis 20%) the acetabulum, a deeply depressed articular cavity, the socket of the ball-and-socket hip joint,
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
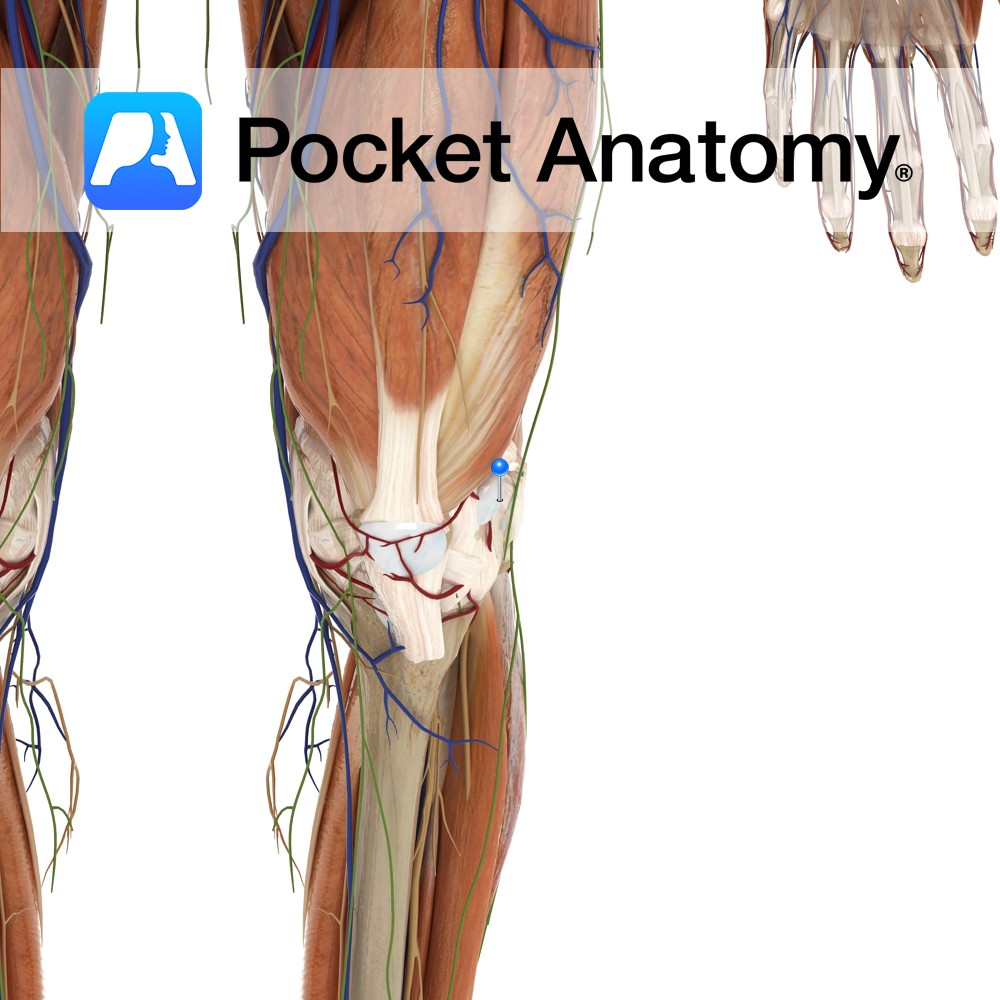
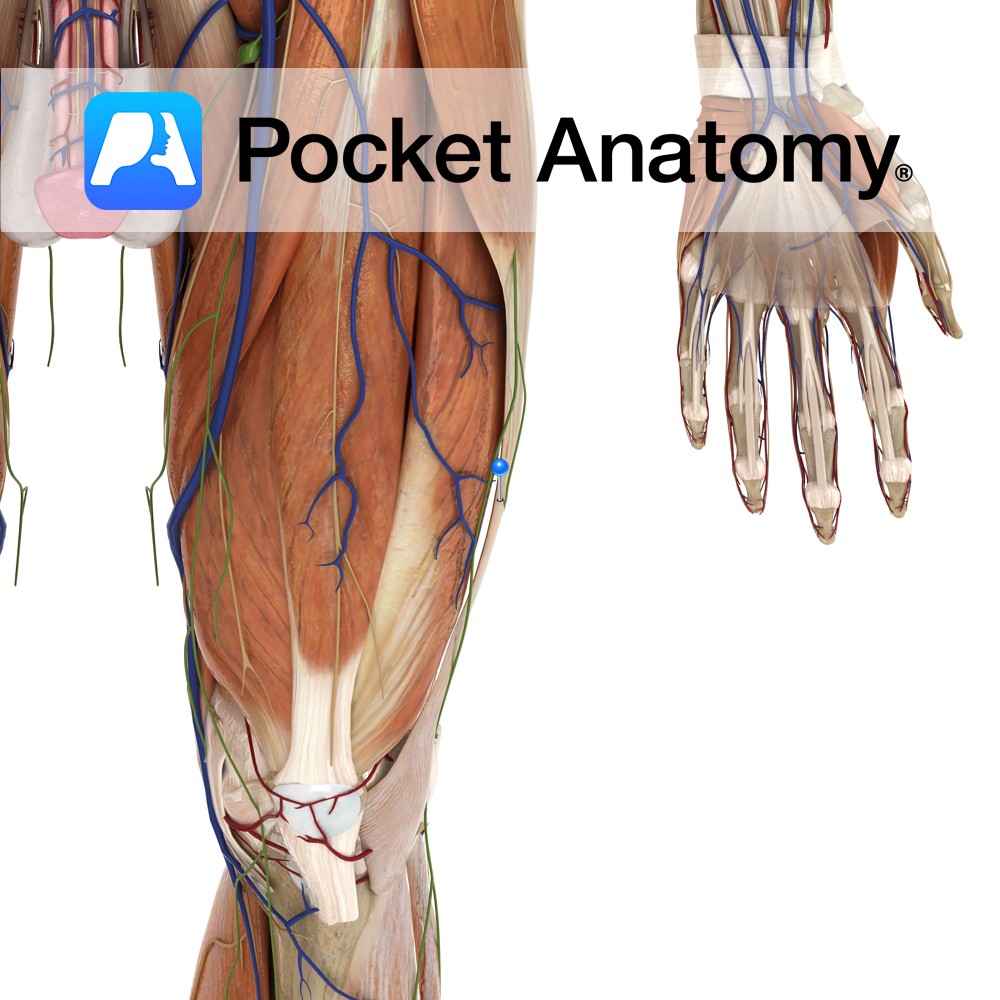
Anatomy Lies between the iliotibial tract and the lateral condyle of the femur. Functions It reduces friction to the tendon as it passes over the lateral condyle of the femur. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy A dense thickening of the deep fascia of the thigh. It attaches from the anterior aspect of the iliac crest to the lateral epicondyle of the femur and (Gerdy’s tubercle) anterolateral surface of the tibia. The gluteus maximus and the tensor fasciae latae muscle both insert into it and tension it. Functions The gluteus
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
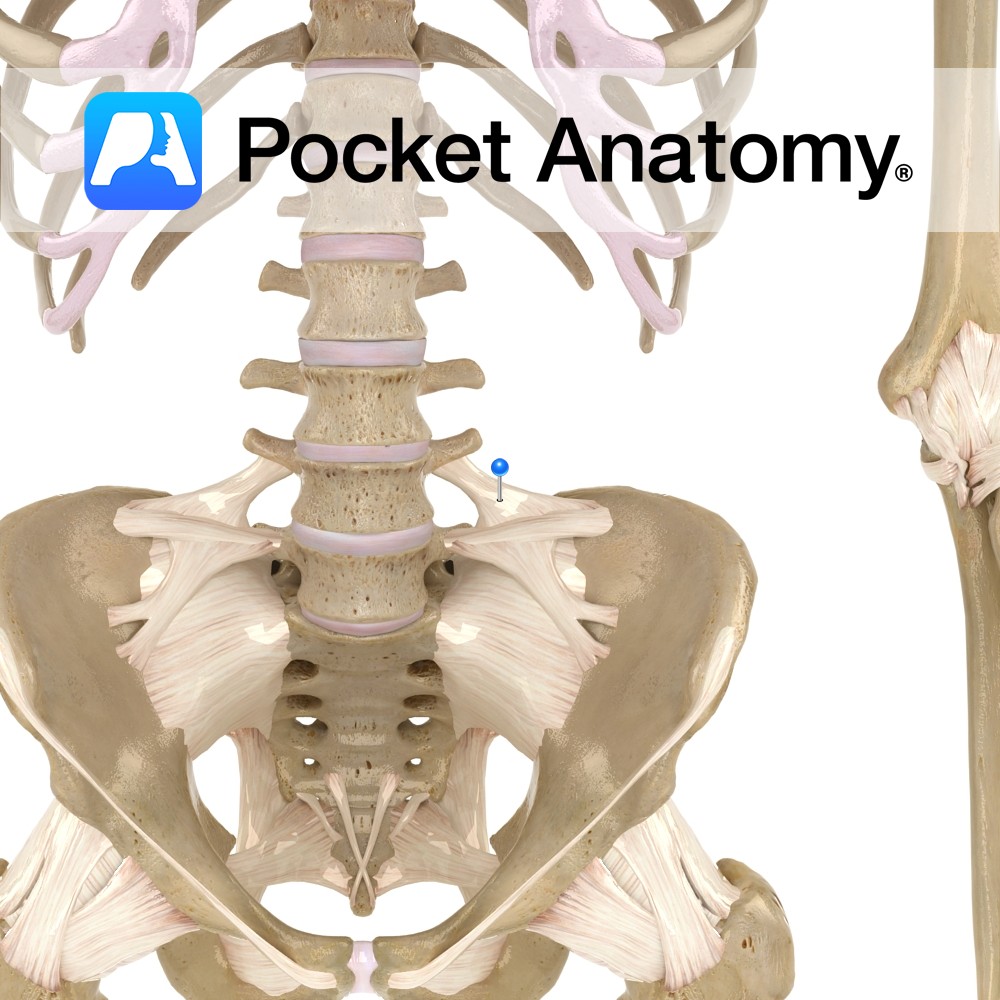
Anatomy Attaches from the transverse process of the lumbar vertebra to the posterior crest of the spine of the ilium. Functions Static stability to the lumbar region of the back and pelvic area. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins