PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
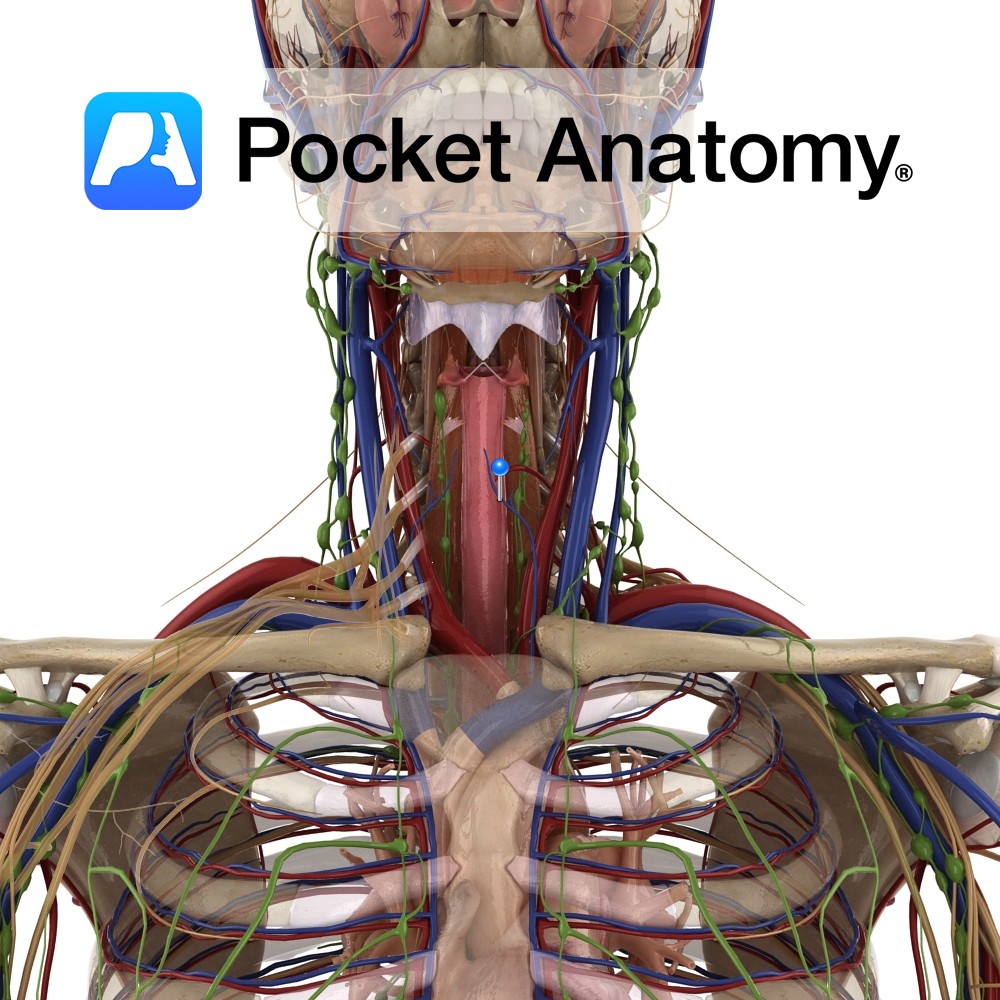
Anatomy Course Commences in the thyroid venous plexus that is located in front of the trachea. Usually divides into several veins. The right veins descend across the innominate artery and drain into the right innominate artery. The left veins empty into the left innominate trunk. Drain Drains structures of the neck such as the trachea,
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
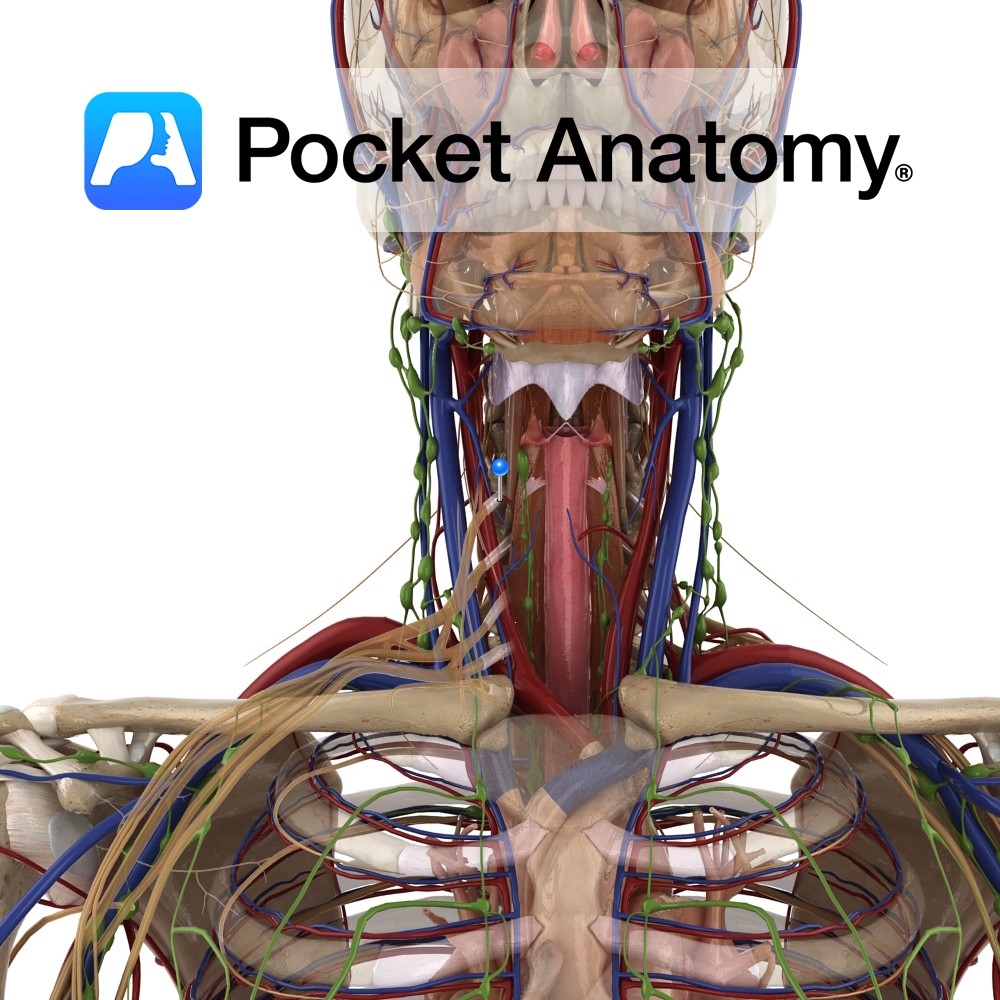
Anatomy Course Branch of the thyrocervical trunk of the subclavian artery. As it rises, it passes behind the carotid sheath and the sympathetic trunk. The middle cervical ganglion rests on the artery. Supply Supplies the lower part of the thyroid gland as well as the parathyroid glands. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Begins at the inferior border of the hemorrhoidal plexus where it travels shortly to empty into the internal pudendal vein. Drain Drains the inferior rectum. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
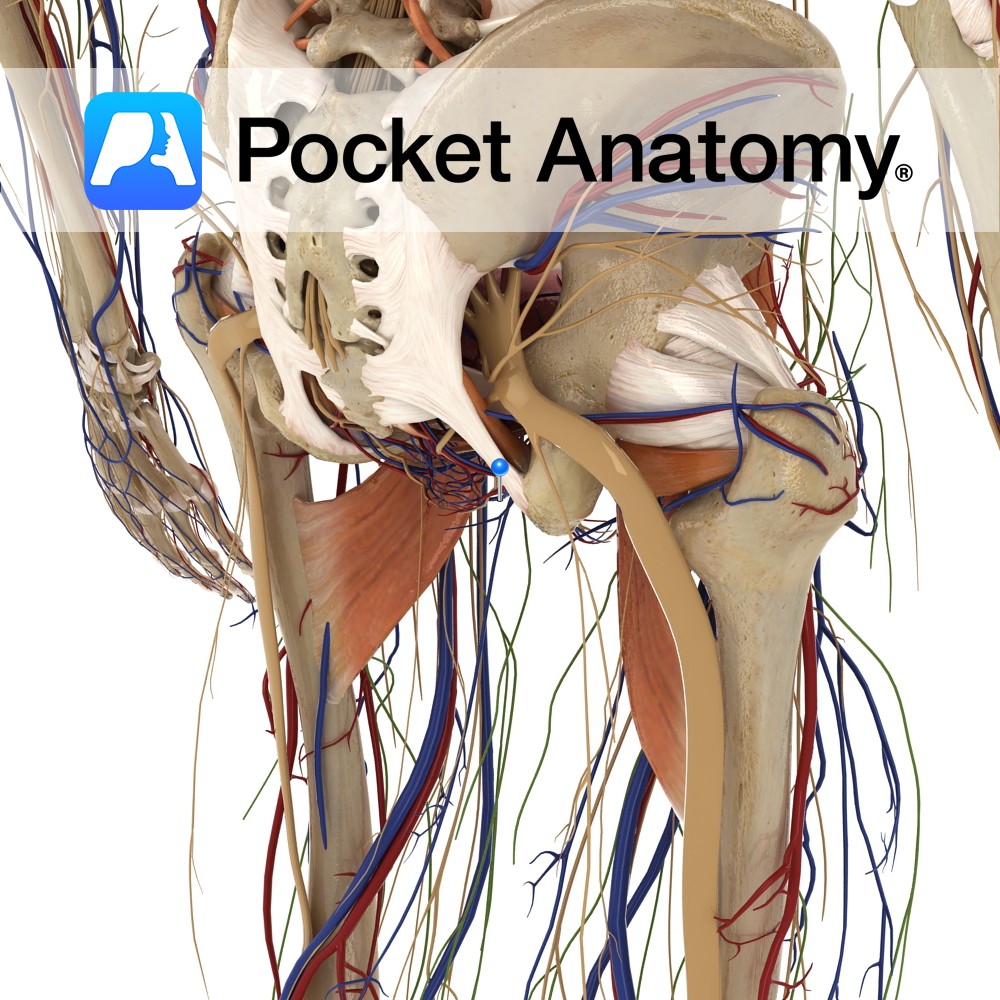
Anatomy Course Branches off the internal pudendal artery as it crosses the ischial tuberosity. It promptly pierces the pudendal cavity and gives off its branches. Supply Responsible for supplying the lower half of the rectum as well as some branches to the superficial gluteal region. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
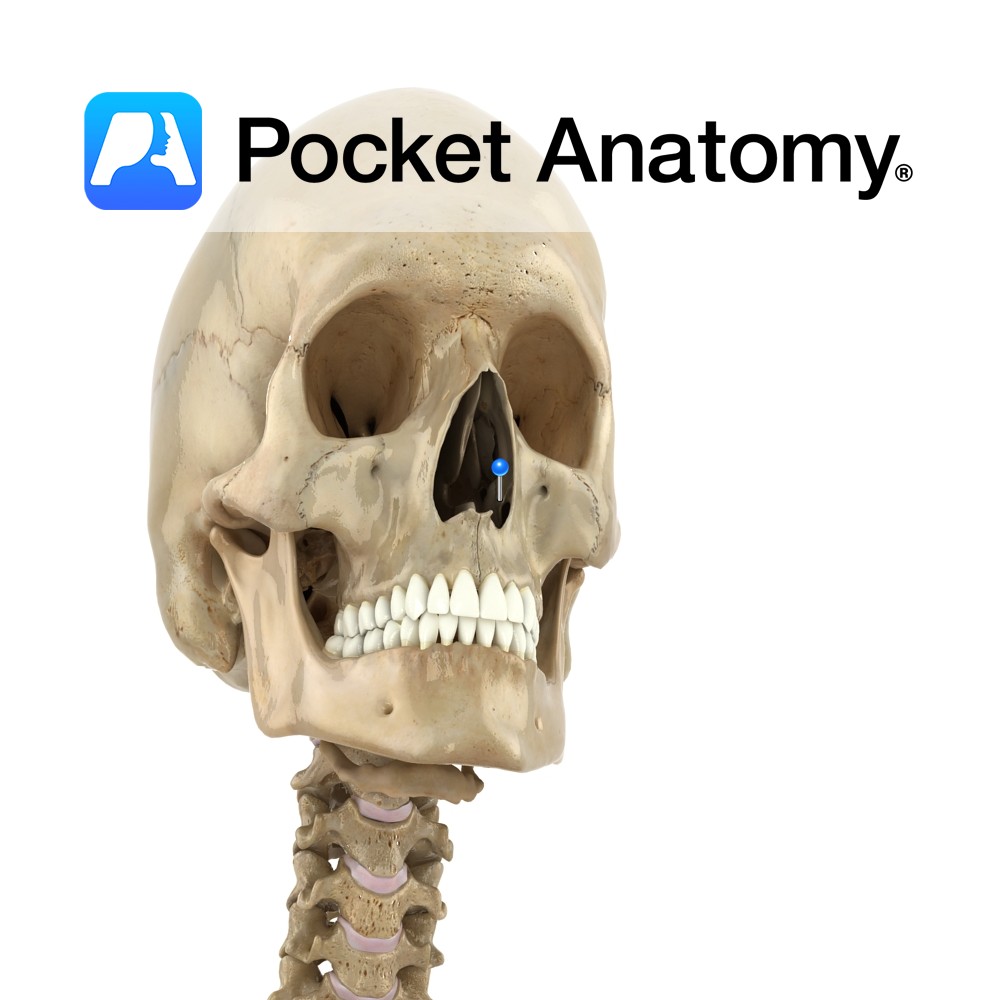
Anatomy Paired. Turbinated. Forms inferior meatus at lower part of lateral wall of nasal cavity, presents big surface area for air-conditioning (filter, warm, moisten). Is covered by mucous membrane and perforated by nasolacrimal duct. Articulates with ethmoid, maxilla, lacrimal and palatine. Clinical Superior nasal concha not a separate bone; part of ethmoid. Vignette Concha (Spanish);
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
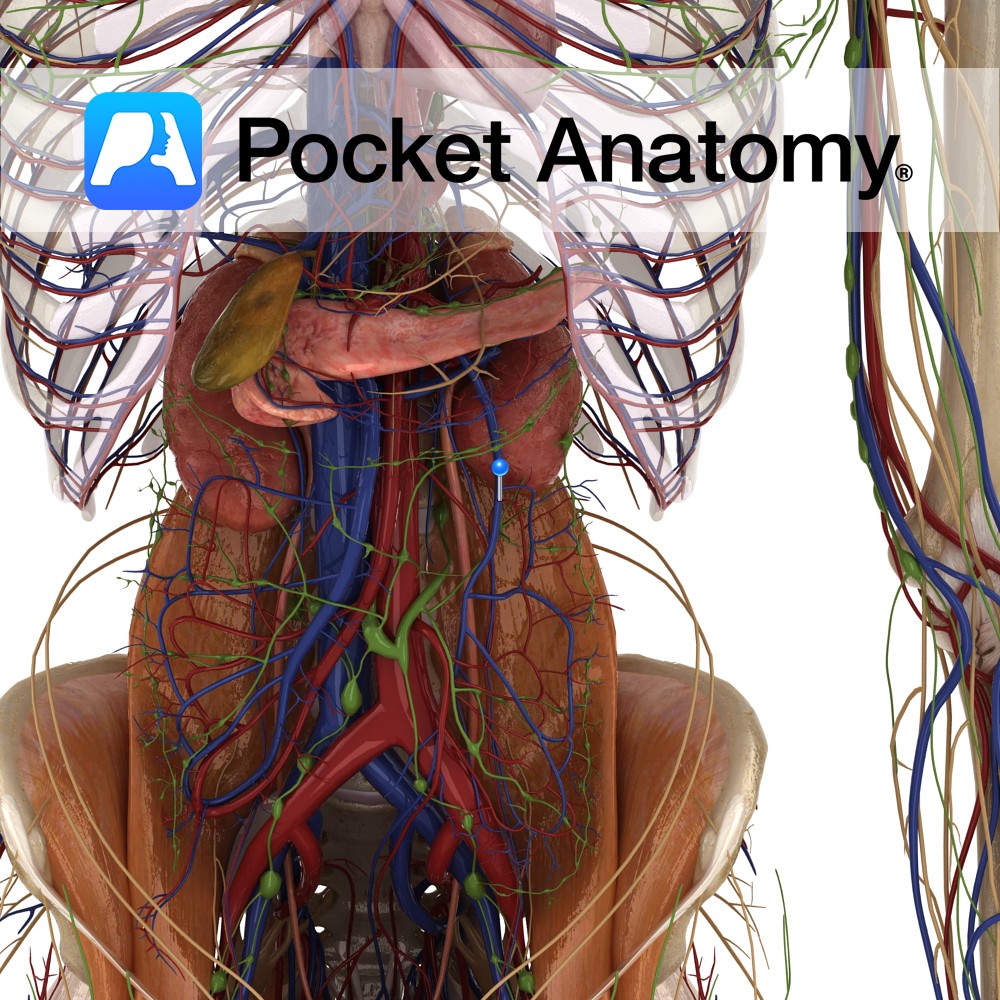
Anatomy Course Receives blood rich in nutrients from the large intestine via its tributaries and then terminates by joining with the splenic vein to form the portal vein. Drain Drains the large intestine, sigmoid colon and the rectum. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy A thickening of the lower border of the abdominal oblique muscles, attaching from the anterior superior iliac spine to the pubic tubercle medially. Functions Forms the inguinal canal and part of the tendon of the external obliques. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
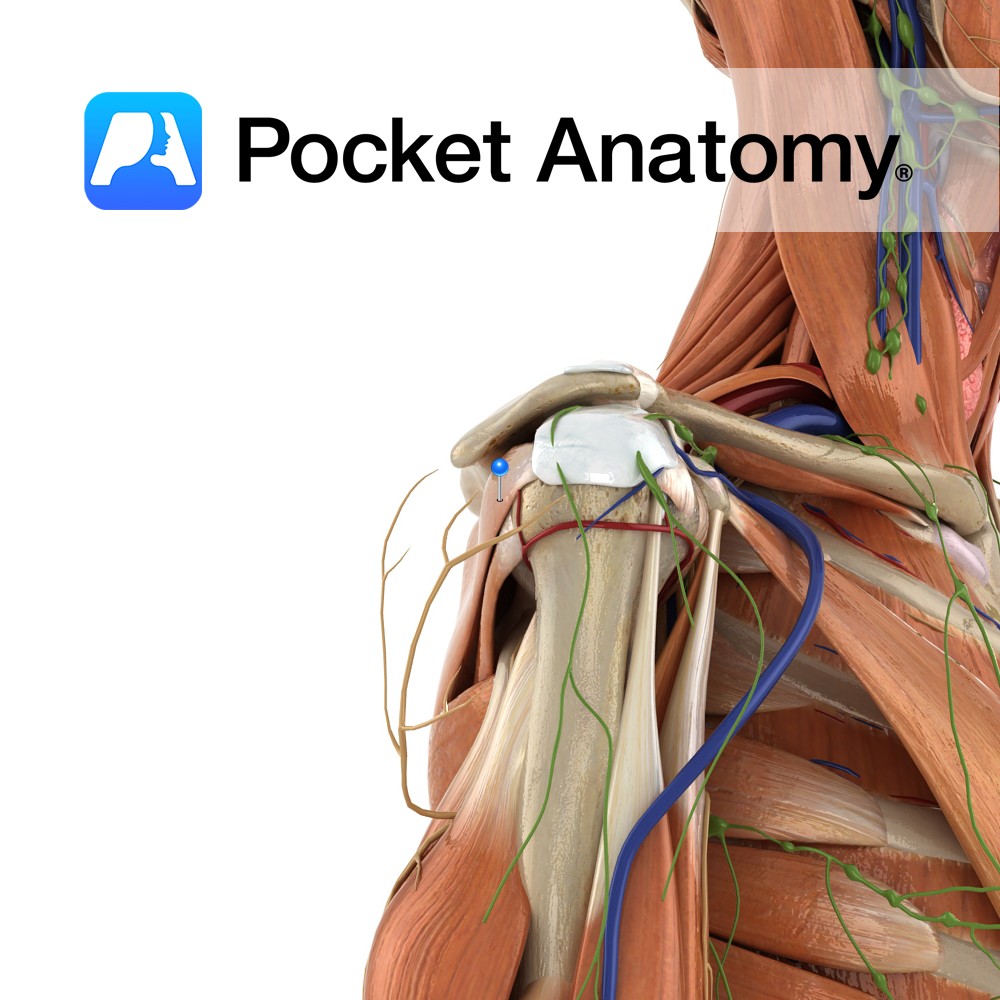
Anatomy Origin: Medial two-thirds of infraspinous fossa of scapula and infraspinous fascia that covers the muscle. Insertion: Middle facet of greater tubercle of humerus. Key Relations: -The tendon of infraspinatus is sometimes separated from the capsule of the shoulder joint by a bursa, which may communicate with the joint cavity. -One of the four muscles
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
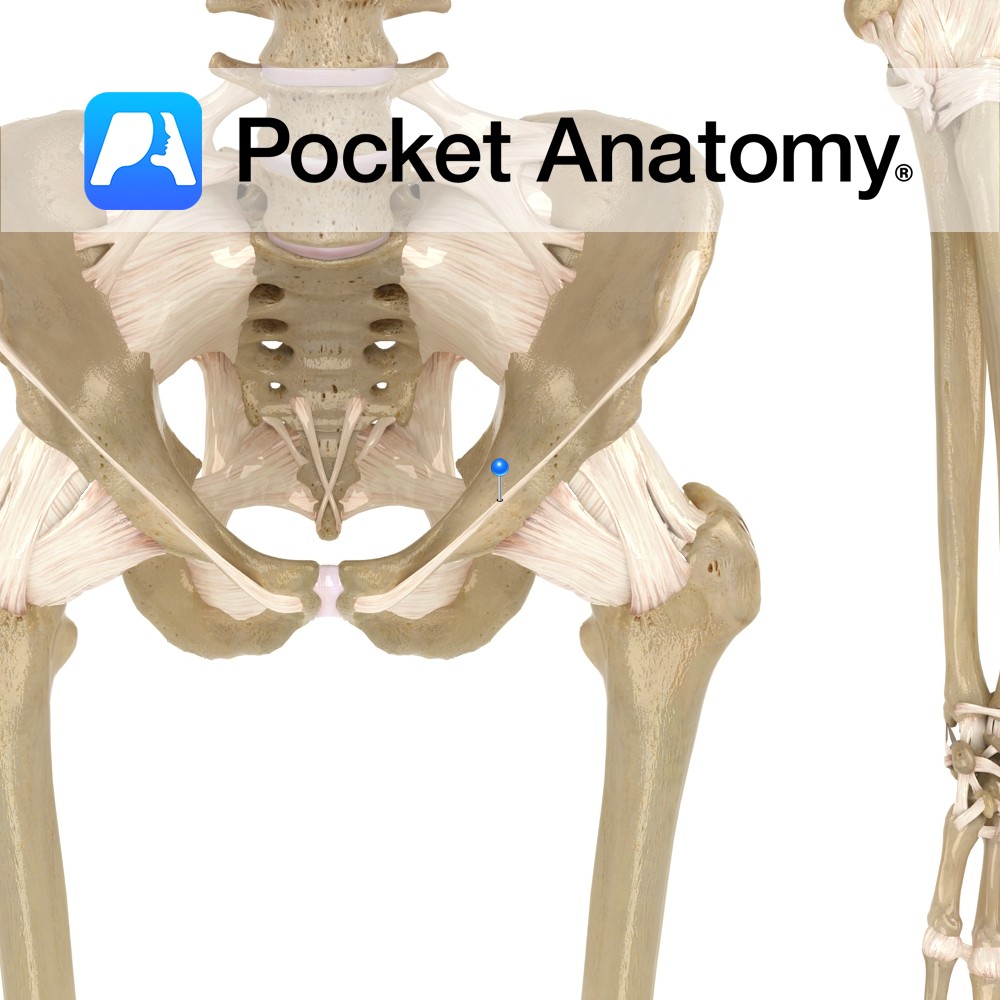
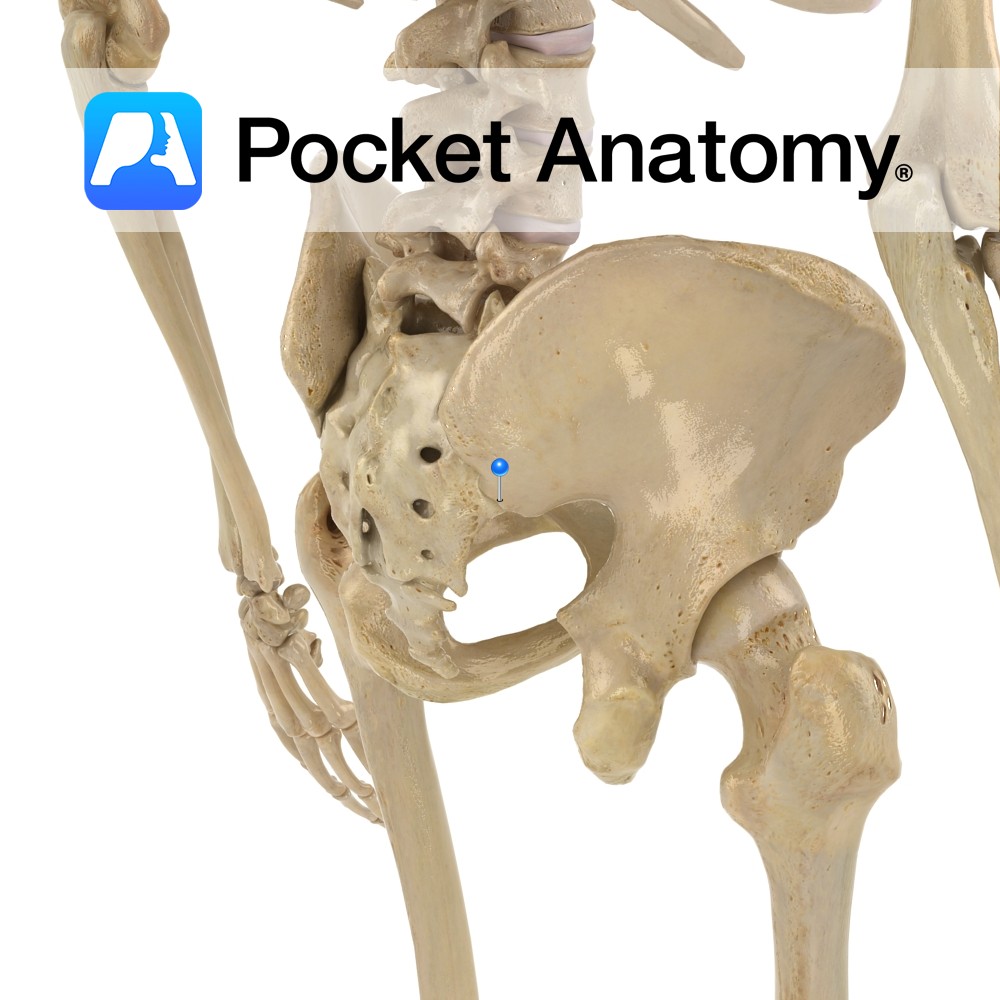
Anatomy Bulge on the lower back border of the ala of the ilium, separated by a notch above from the posterior superior iliac spine, and by the greater sciatic notch below from the spine of the ischium. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
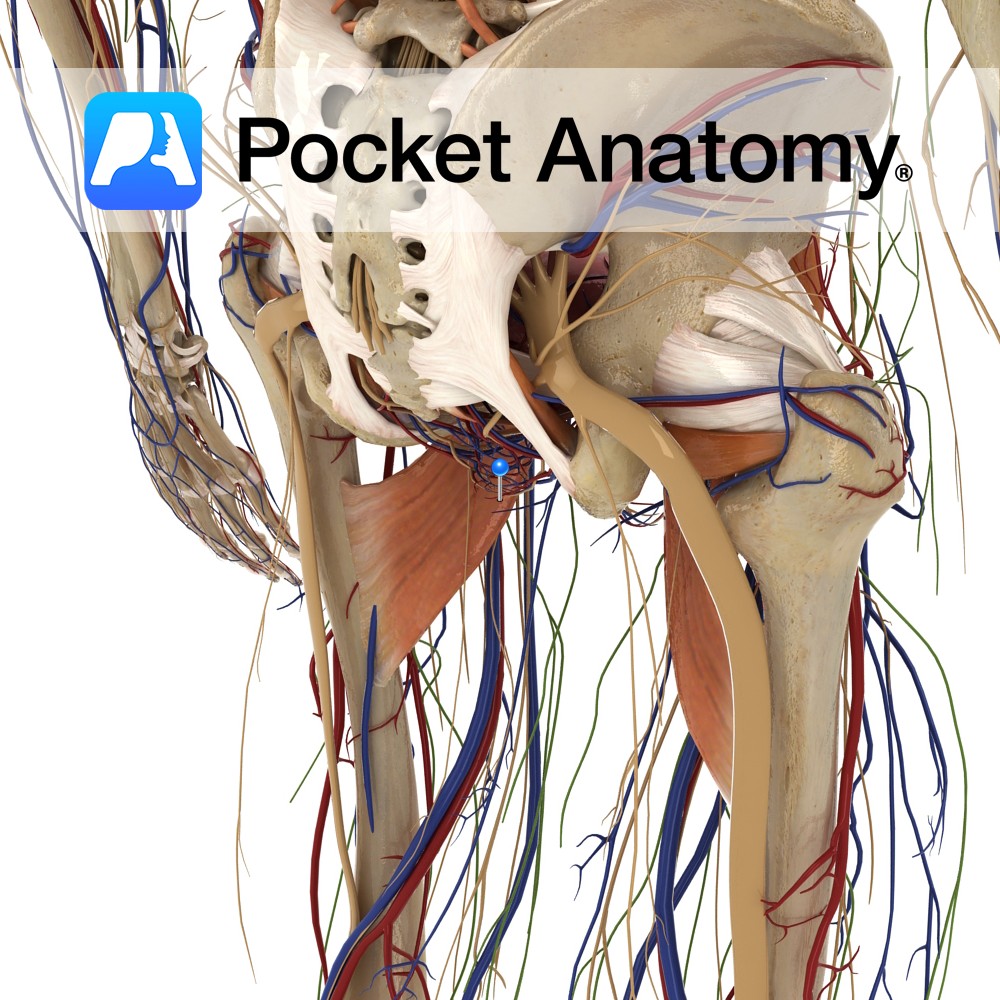
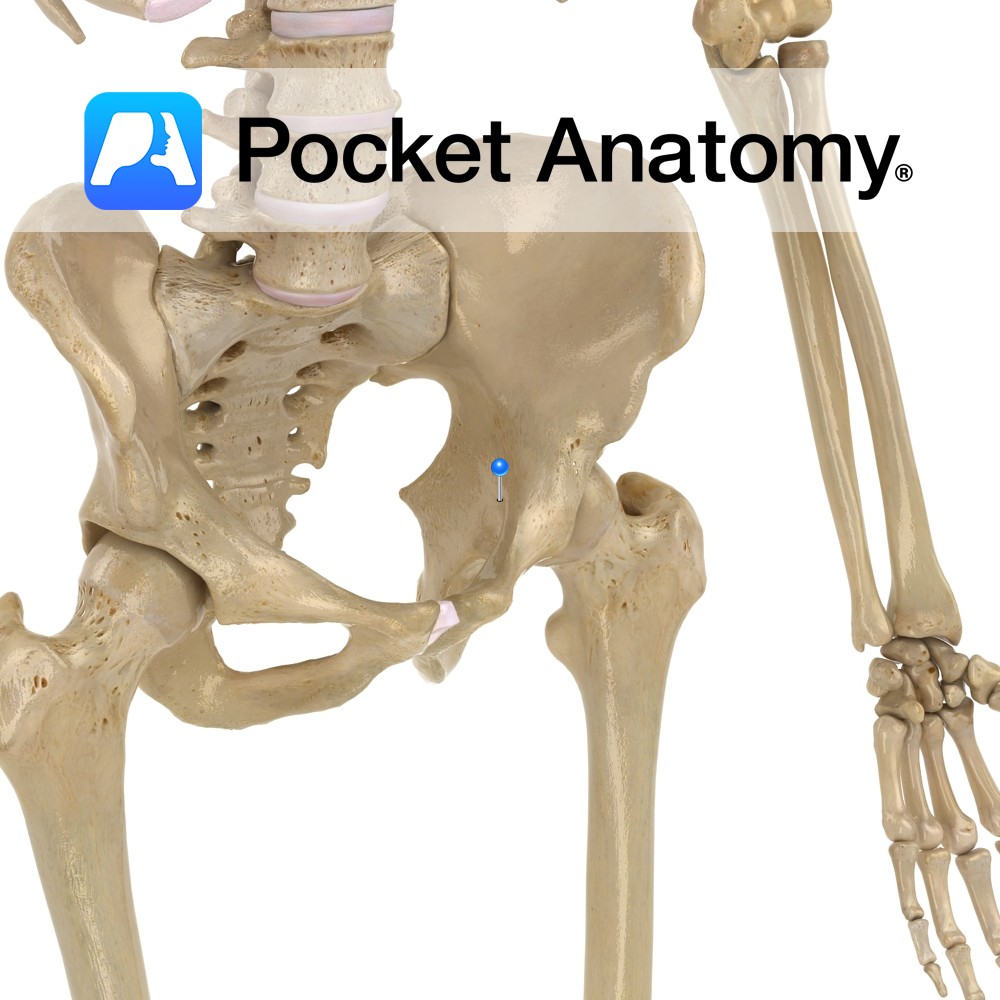
Anatomy Also called iliopectineal eminence. Triangular area on medial surface where ilium and ischium unite (hip bone is union of ilium, ischium and pubis). Corresponding lateral surface is part of acetabulum. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins