PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
Anatomy Course Branch of the superficial iliac vein. Begins at the head of the femur, travelling medially, passing behind the sartorius and rectus femoris muscles, where it divides into terminal branches. It eventually drains into the femoral vein, just distal from the inguinal ligament. Drain Drains the head and neck of the femur. Interested in
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Arises from the deep femoral artery, just distal to the inguinal ligament. It travels laterally, passing behind the sartorius and rectus femoris muscles, where it divides into terminal branches. Supply The ascending branch of the lateral circumflex artery supplies the head and neck of the femur, as it anastomoses with the medial circumflex
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course One of the branches of the lateral circumflex artery. It branches from the main lateral circumflex after it passes deep to the sartorius and rectus femoris muscles. It descends deep to the rectus femoris along the thigh, piercing the vastus lateralis muscle. At the knee it connects with a branch of the superior
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course One of the terminal branches of the lateral circumflex artery. It branches from the main lateral circumflex after it passes deep to the sartorius and rectus femoris muscles. It ascends laterally, beneath the tensor fasciae latae muscle, and towards the hip joint. It joins with the medial circumflex femoral artery. Supply Supplies the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
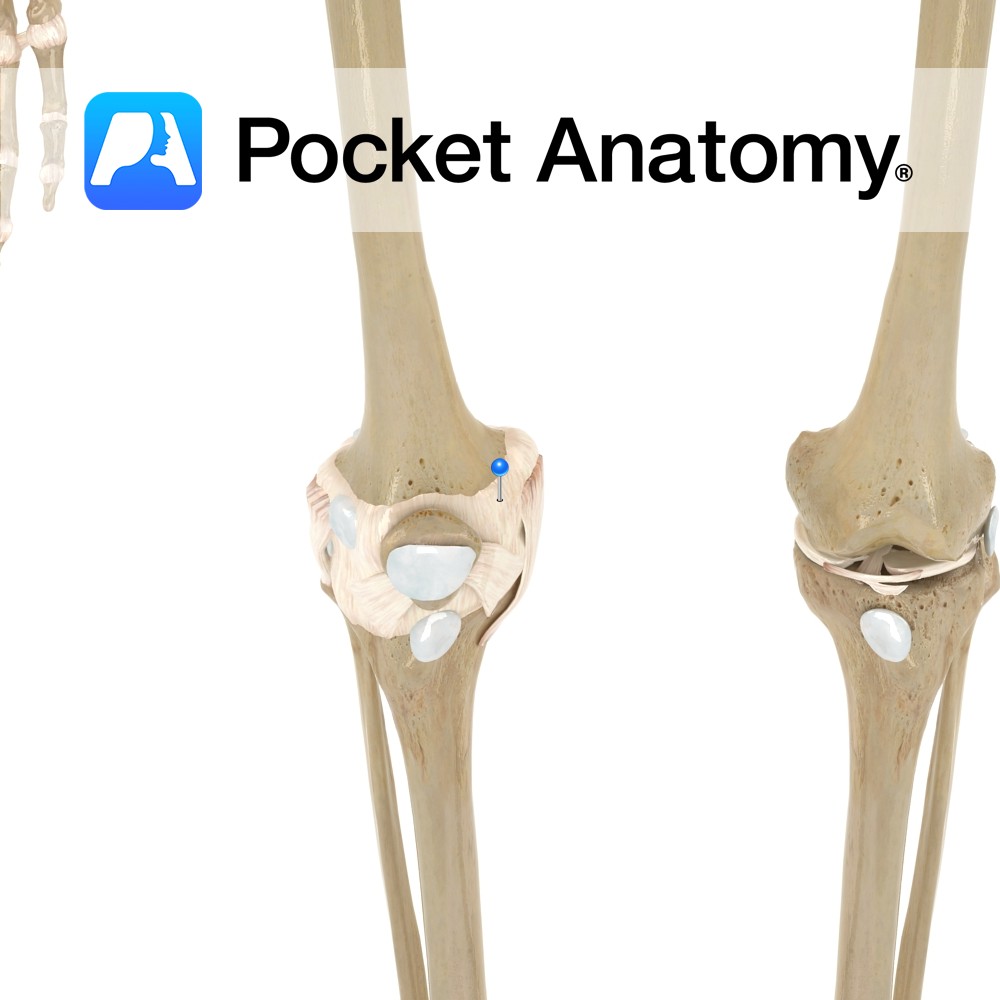
Anatomy A five centimetre long, extra-capsular cord. Its origin is on the lateral epicondyle of the femur, above the popliteal pit and attaches to head of the fibula. Functions Provides static stability to the lateral aspect of the knee joint. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Voice box, sound generator, in front of neck, level C3-6, between lower (hypo-) pharynx and trachea; extends from tip of epiglottis to inferior border cricoid; hyoid bone above not anatomically part but connected, intimately associated; skeleton of 9 cartilages (connected by muscles/ligaments); single – epiglottic, thyroid (rocks back and forth on cricoid, adjusts vocal
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Lactiferous/milk/mammary ducts which convey milk from acini/sacs (acinus is berry-like cluster of milk-producing cells) in breast lobules, to the nipple. Acinus – the cluster of cells, alveolus – the space they enclose, duct/ule – the tube carrying away the exocrine secretions ie milk). Ducts join and get bigger as they converge on nipple (branch
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy (inner labia, lesser/small lips, vaginal lips). Thin hairless skin flaps, 1-2″ long (considerable normal variability in length/width and degree of symmetry left/right), extending down/back from clitoris, either side of vulval vestibule (with urethral and vaginal orifice/introitus), medial to labia majora (separated from them by sulcus). Front ends divide and meet around clitoris (upper/front –
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy The capsule attaches to the margins of the articular surface of the femur. Posteriorly, the capsule attaches a finger’s breath above the intercondylar ridge of the femur. On the lateral condyle of the femur, it loops up to enclose the pit for the popliteus. Again, it attaches to the articulating surfaces of the tibia.
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Motion The knee joint is a uniaxial* synovial modified hinge joint. It is the largest synovial joint in the body. The knee joint consists of two articulations between the thigh and the leg, one between the condyles of the femur and the tibia and one between the patella and the patellar surface of the femur.
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins


.jpg)
.jpg)
-collateral-ligament.jpg)
.jpg)