PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
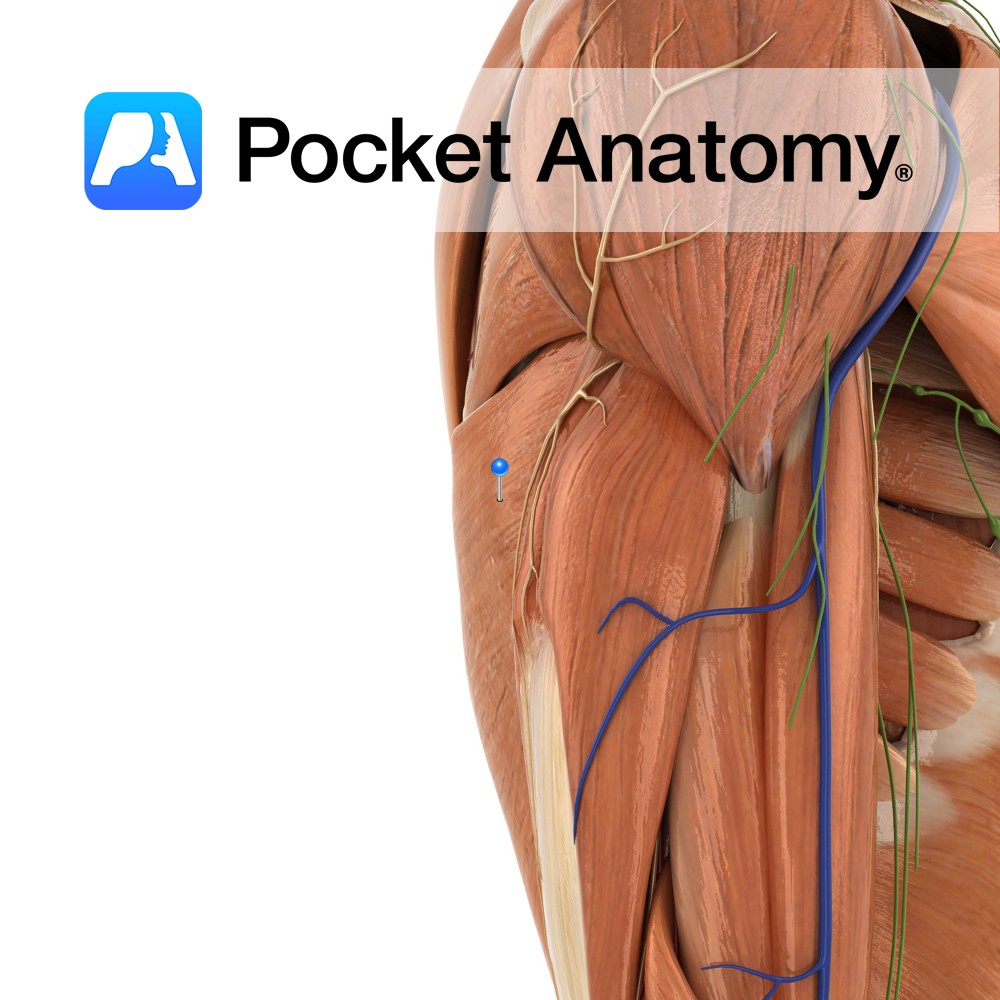
Anatomy Origin: Spinous processes of T7 to T12 and the thoracolumbar fascia, by which it is attached to the spines of all lumbar and sacral vertebrae. The posterior part of the iliac crest and the lower three to four ribs. Insertion: The fibres converge to form a flattened tendon and attaches to the floor of
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
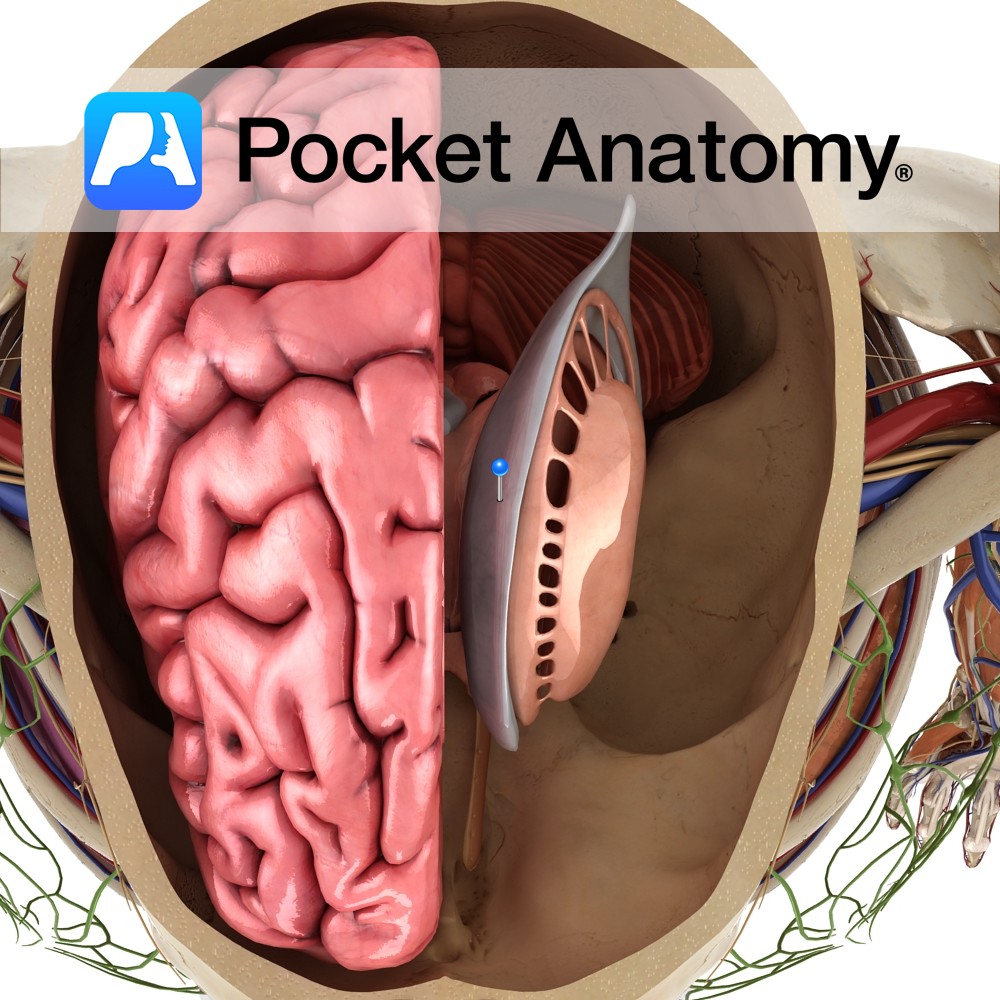
Anatomy This is a C-shaped cavity within each cerebral hemisphere lined with ependymal cells. They are part of the series of fluid-filled cavities, which make up the ventricular system. It is connected to the third ventricle via the interventricular foramen of Monro. It divides into a body, which occupies the parietal lobe and anterior, posterior
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Branches off from dorsalis pedis on the foot. It passes laterally over the tarsal bones and across the foot beneath the extensor digitorum brevis muscle to anastomose with arteries from the ankle. Supply Supplies the tarsal bones over which it crosses and the muscle extensor digitorum brevis. It also helps supply the ankle
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course A branch of the common fibular nerve. It runs down the posterolateral aspect of the calf. Supply Provides sensory innervation to the skin on some of the anterior and posterior portions of the lateral calf. Clinical Damage to the nerve will result in a loss of sensation in the skin on the anterior
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
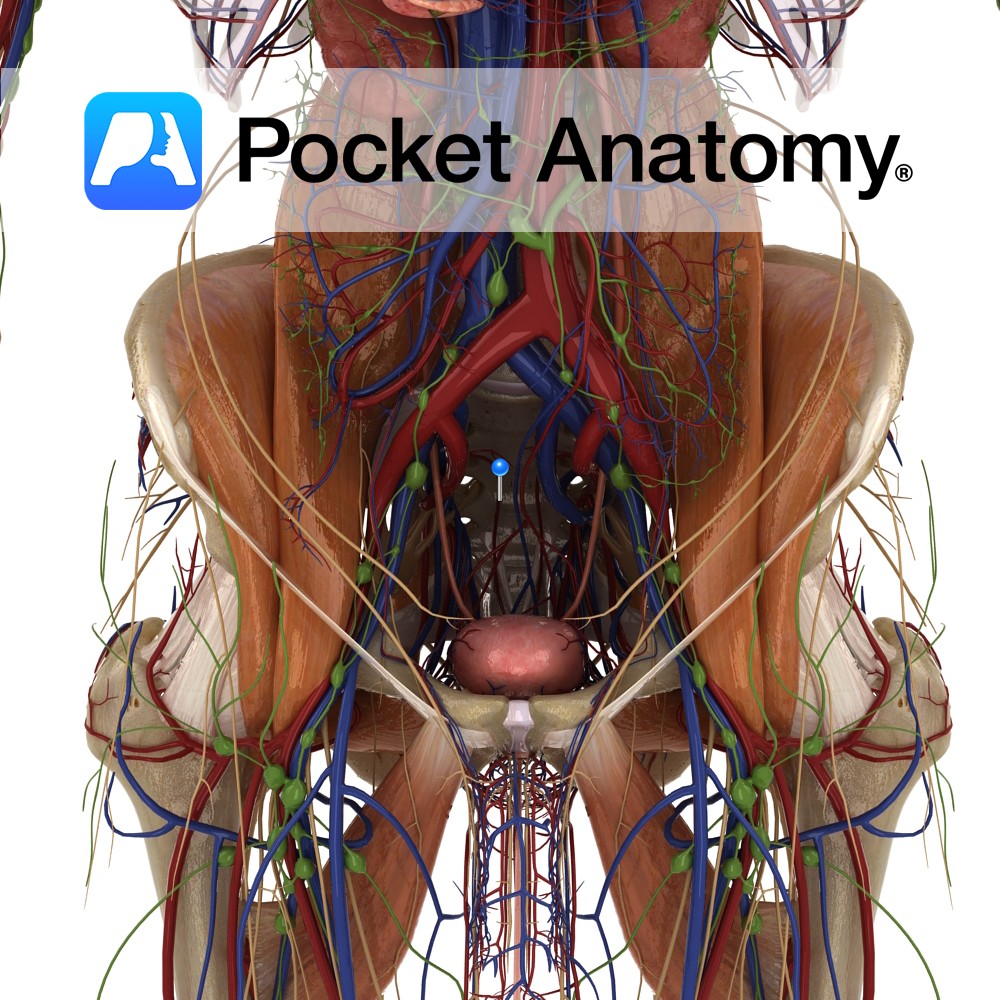
Anatomy Course A branch of the posterior trunk of the internal iliac artery. There are usually two that branch from the posterior trunk just before it exits the pelvic cavity, near the greater sciatic foramen. They remain medial and course inferiorly along the pelvic wall, giving off branches that pass through the anterior sacral foramina.
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
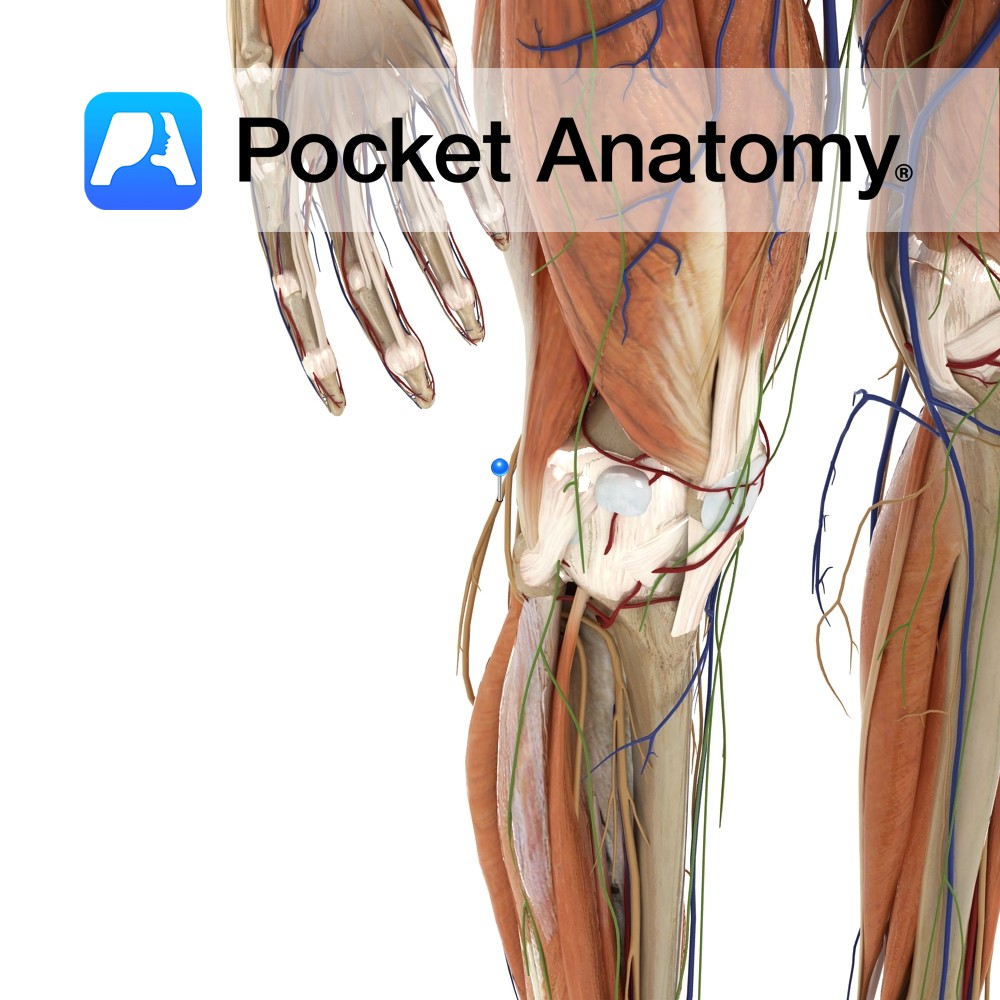
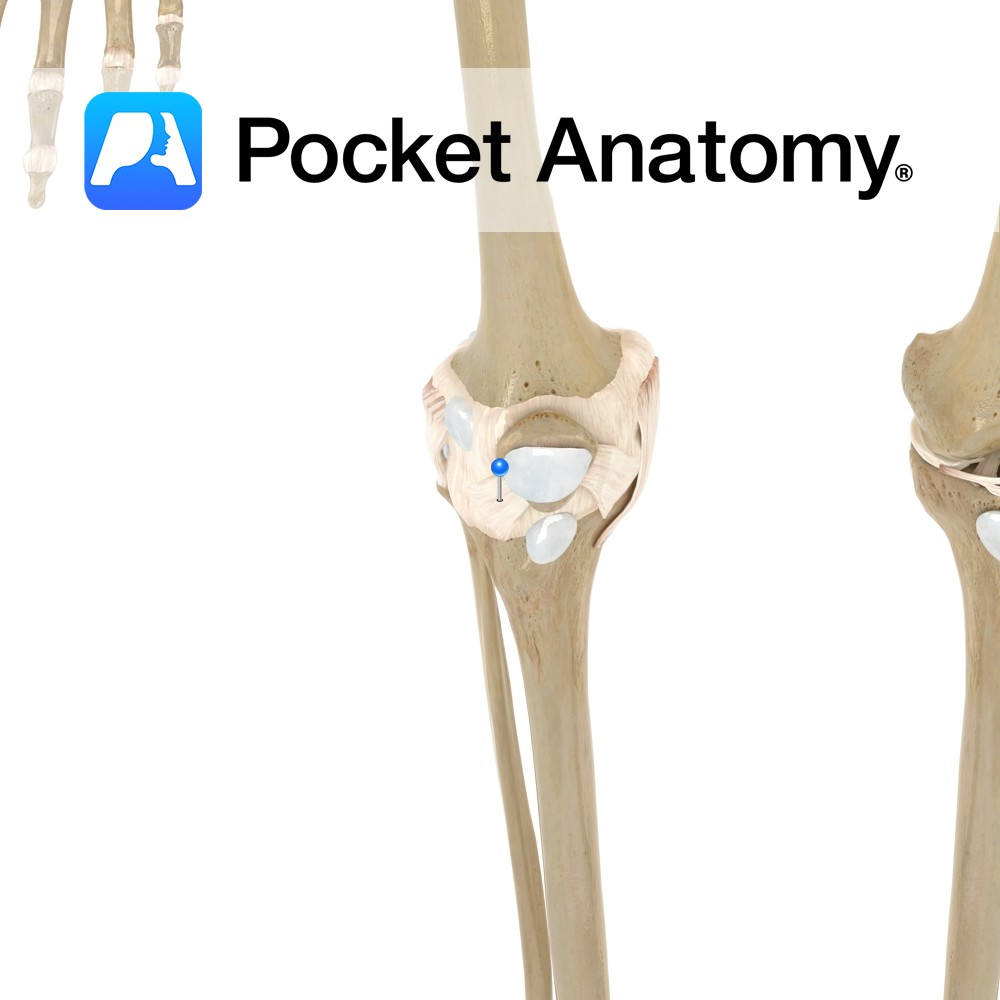
Anatomy Attaches from the inferior lateral margins of the patella to the inferior margin of the lateral tibial condyle. It also blends with the patella ligament. Functions Provides static stability to the patella. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
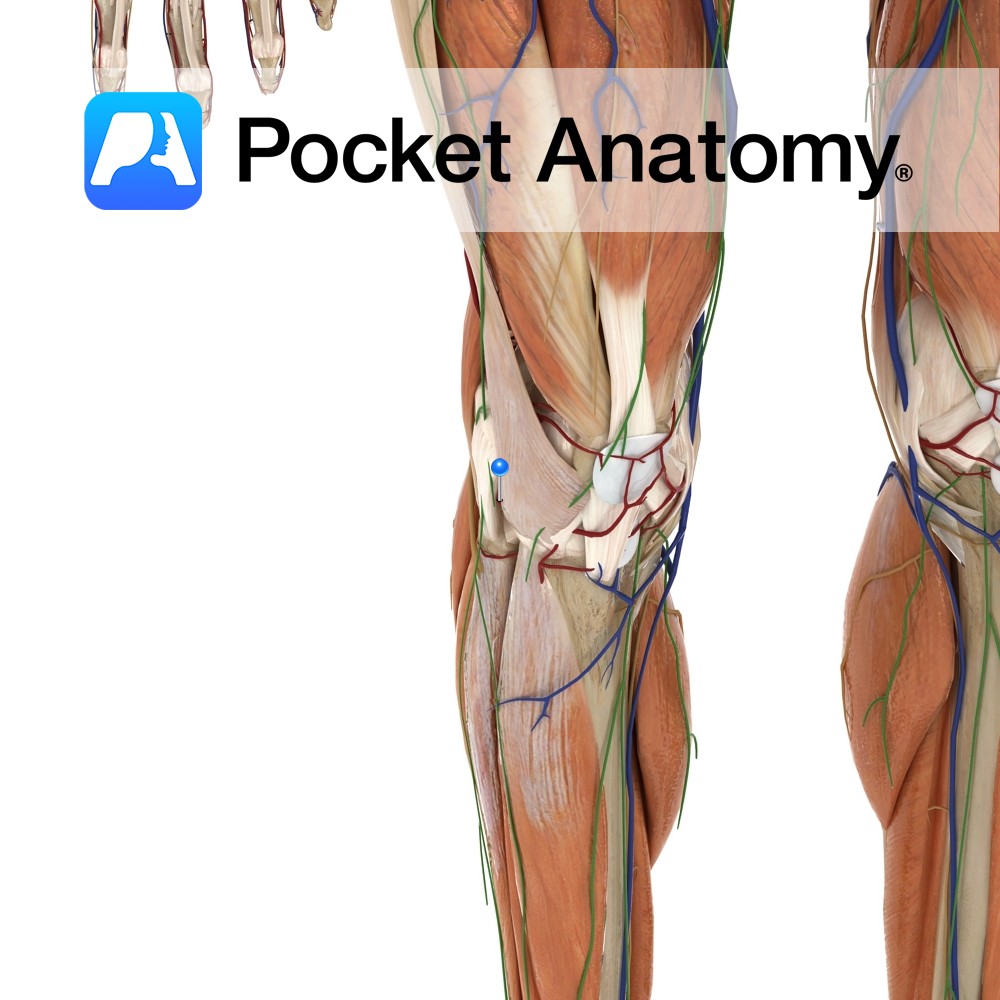
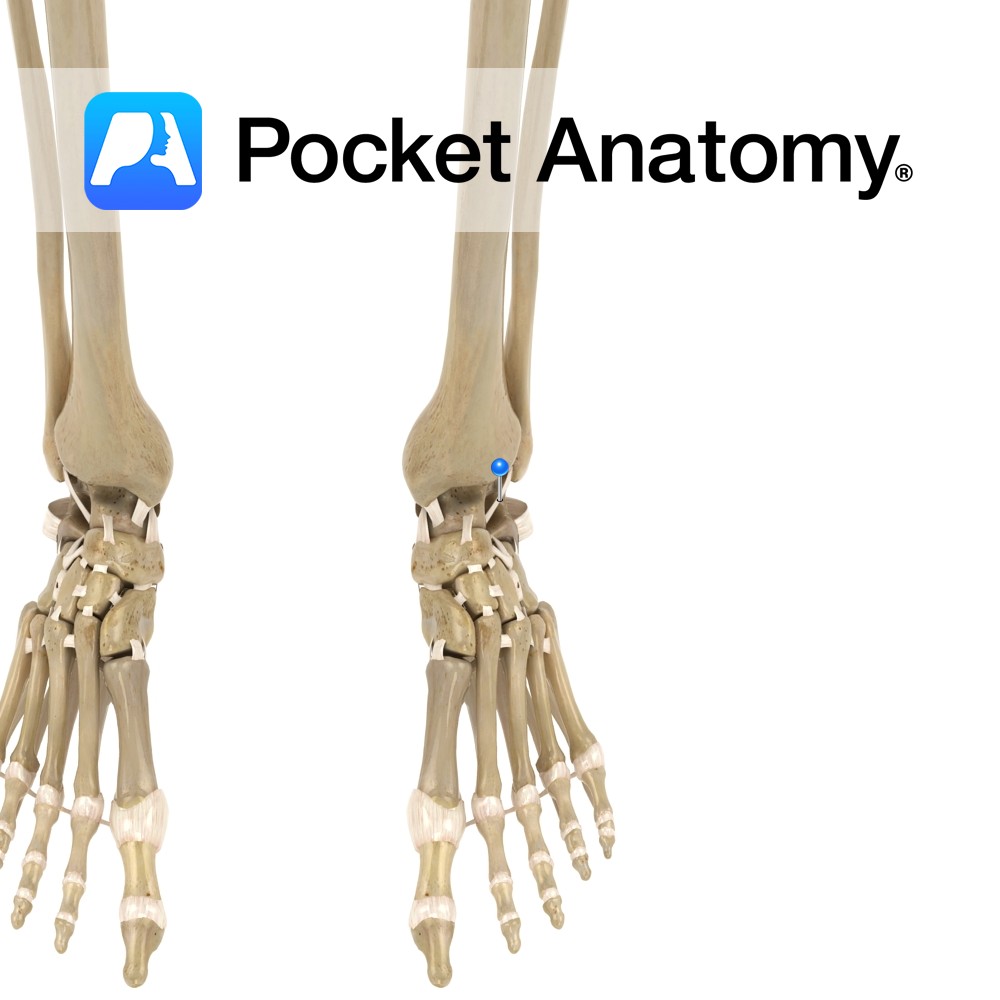
Anatomy Course A branch of the femoral artery, and part of the popliteal anastomosis at the knee. It runs around the head of the fibula, passing beneath the lateral head of the gastrocnemius muscle. The popliteal anastomosis receives blood from the femoral artery and the descending branch of the lateral circumflex femoral artery. Supply The
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
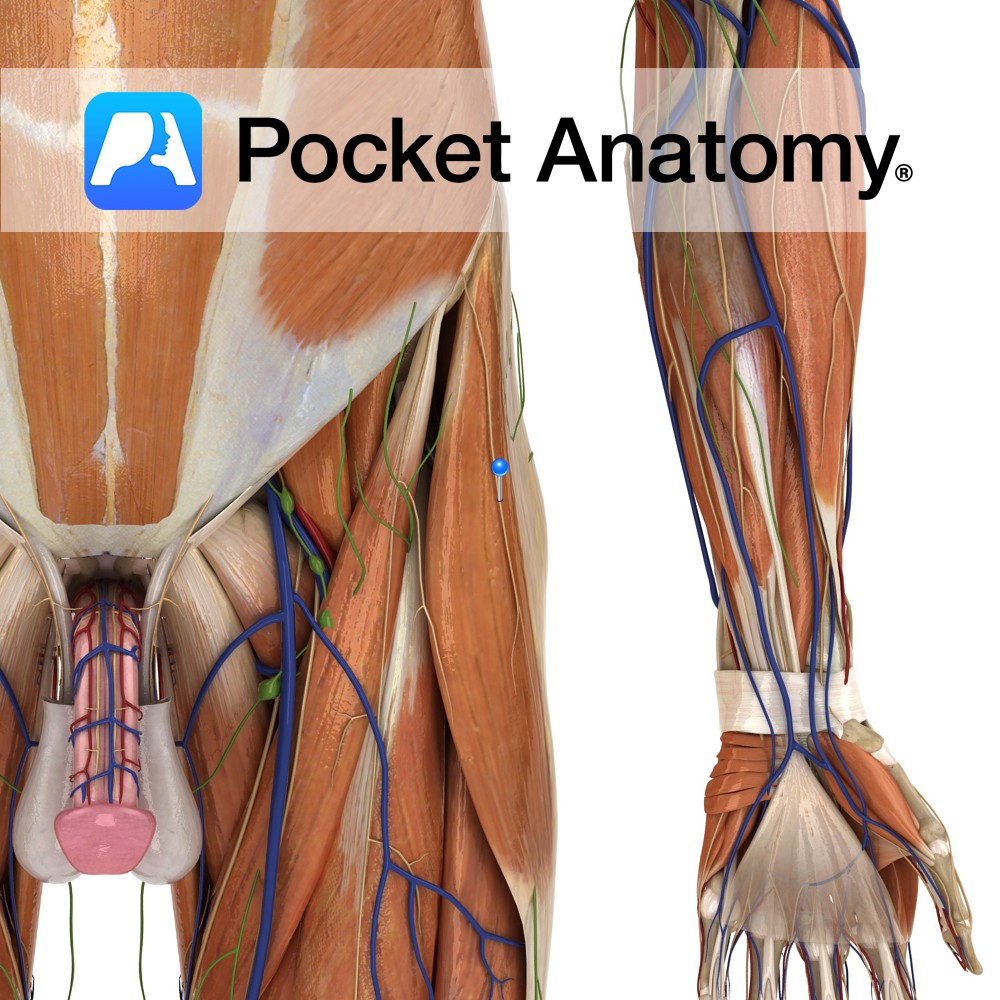
Anatomy Course Arises from the lumbosacral plexus, and is made up of fibres from the dorsal divisions of the spinal nerves L2 and L3. It leaves the abdomen by running along the iliacus muscle and exiting either beneath the inguinal ligament just anterior to the anterior superior iliac spine, or by piercing the inguinal ligament.
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
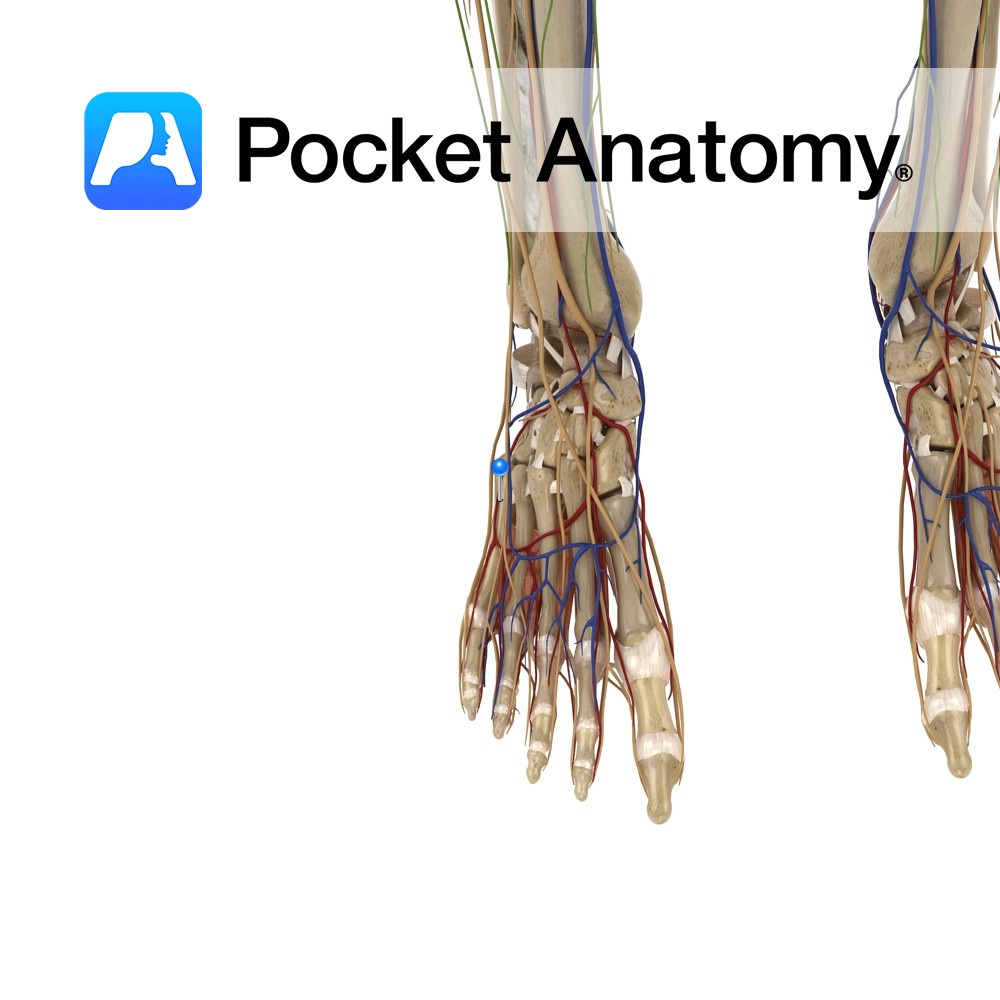
Anatomy Tarsal bone, wedge-shaped, articulates forward with 3rd metatarsal, in with intermediate/middle cuneiform, out with cuboid, up/proximally with navicular. Vignette The tarsal and metatarsal bones, with associated ligaments and muscles, form transverse and longitudinal arches (the medial longitudinal arch is the more elevated and elastic than lateral longitudinal, which is relatively rigid/locked), which act as
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy The anterior talofibular ligament attaches from anterior border of the lateral malleolus to the neck of the talus. Functions Part of the lateral collateral ligaments of the ankle. It provides static stability to the lateral and anterior aspect of the ankle joint. Clinical Most commonly injured ligament in the ankle. It tends to get
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins