PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
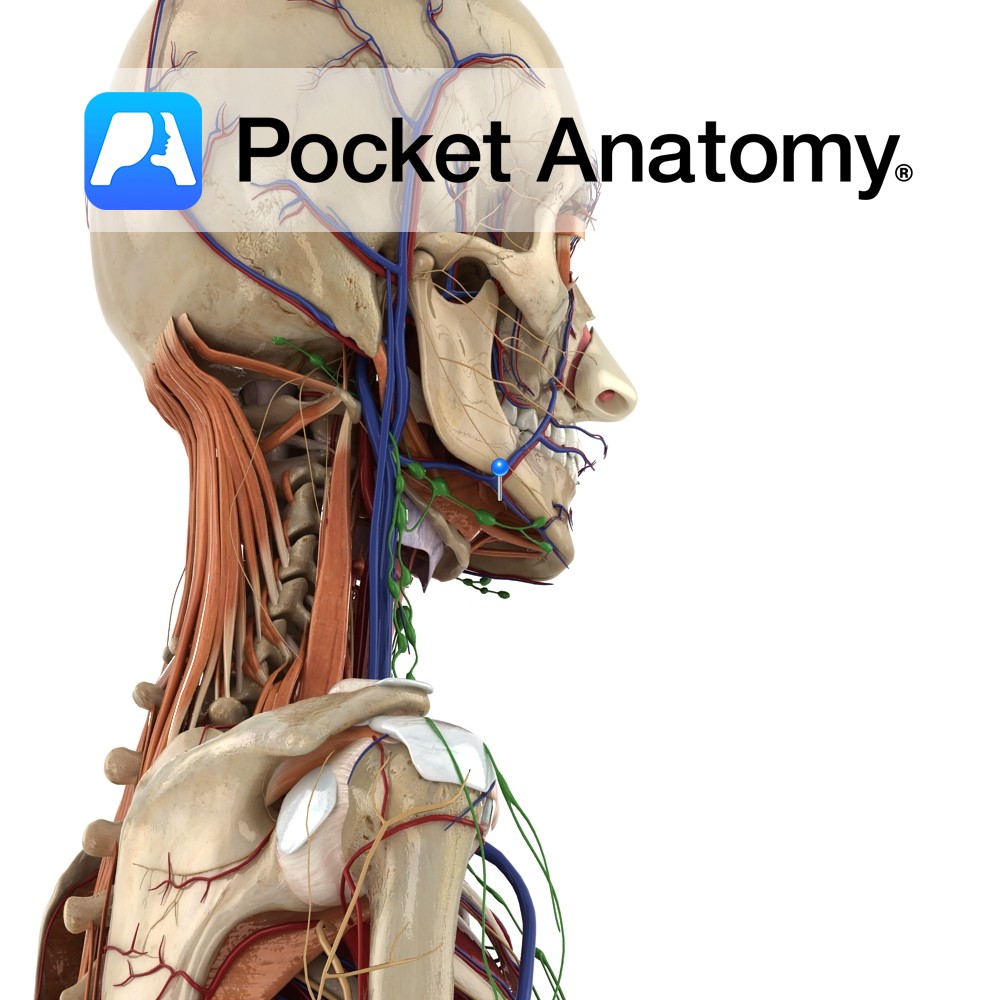
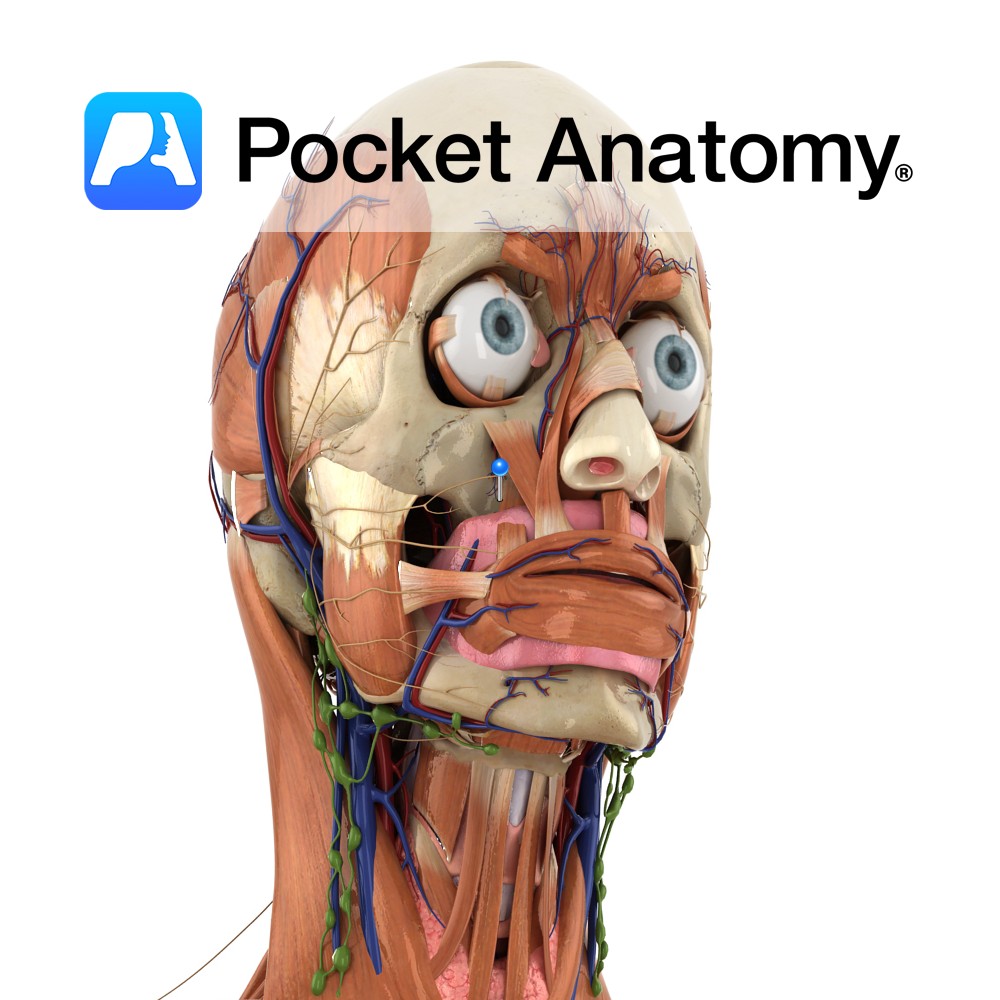
Anatomy Course Arises from the posterior trunk of the mandibular nerve (V3), and also carries fibres from the facial nerve (VII). The lingual nerve first arises between the lateral pterygoid muscle and the tensor palatine muscle. It is then joined by the branches from the facial nerve (VII) via the chorda tympani nerve, while it
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
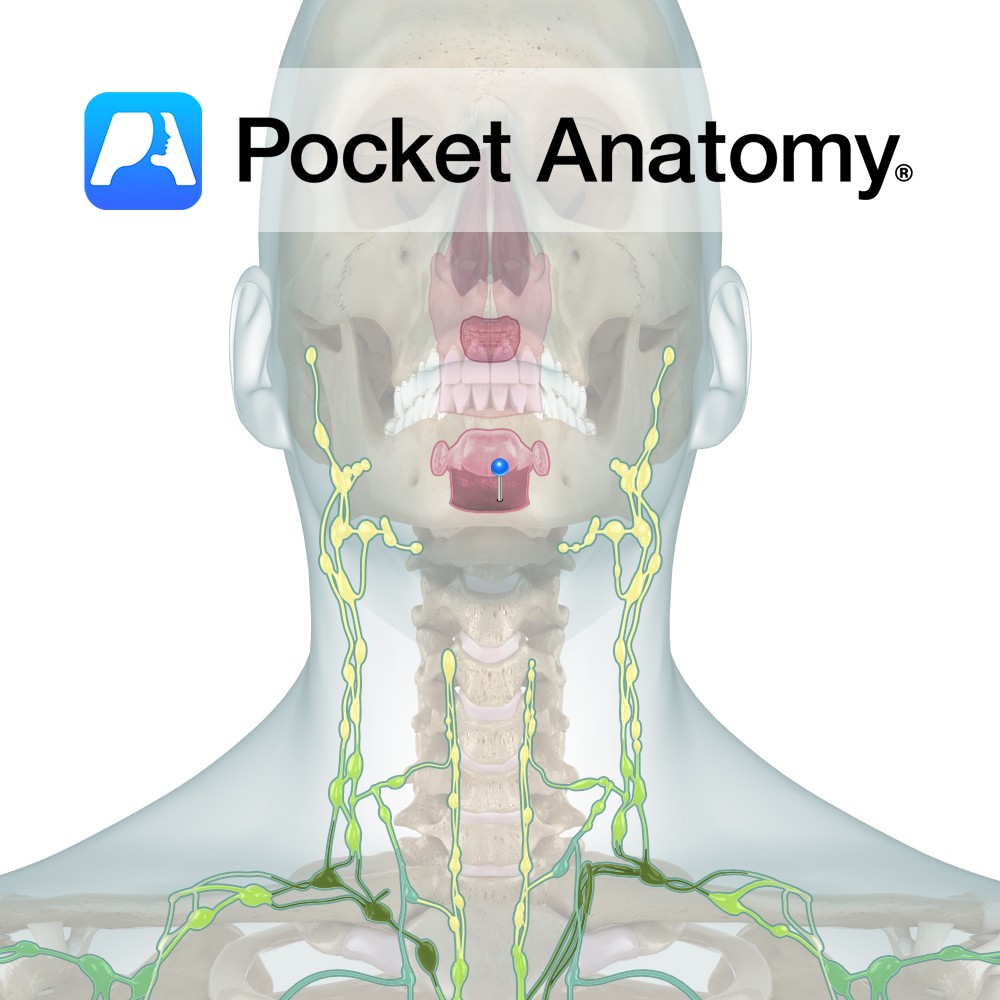
Anatomy Round areas of lymphoid tissue on dorsal surface of root/back of the tongue. Clinical Tonsils (Lingual, Palatine, Pharyngeal) are masses of Lymphoid tissue with 10-20 crypts, constituting the first defences met by inhaled, eaten and drunk pathogens/antigens. Component of MALT (Mucosa Associated Lymphoid Tissue). Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
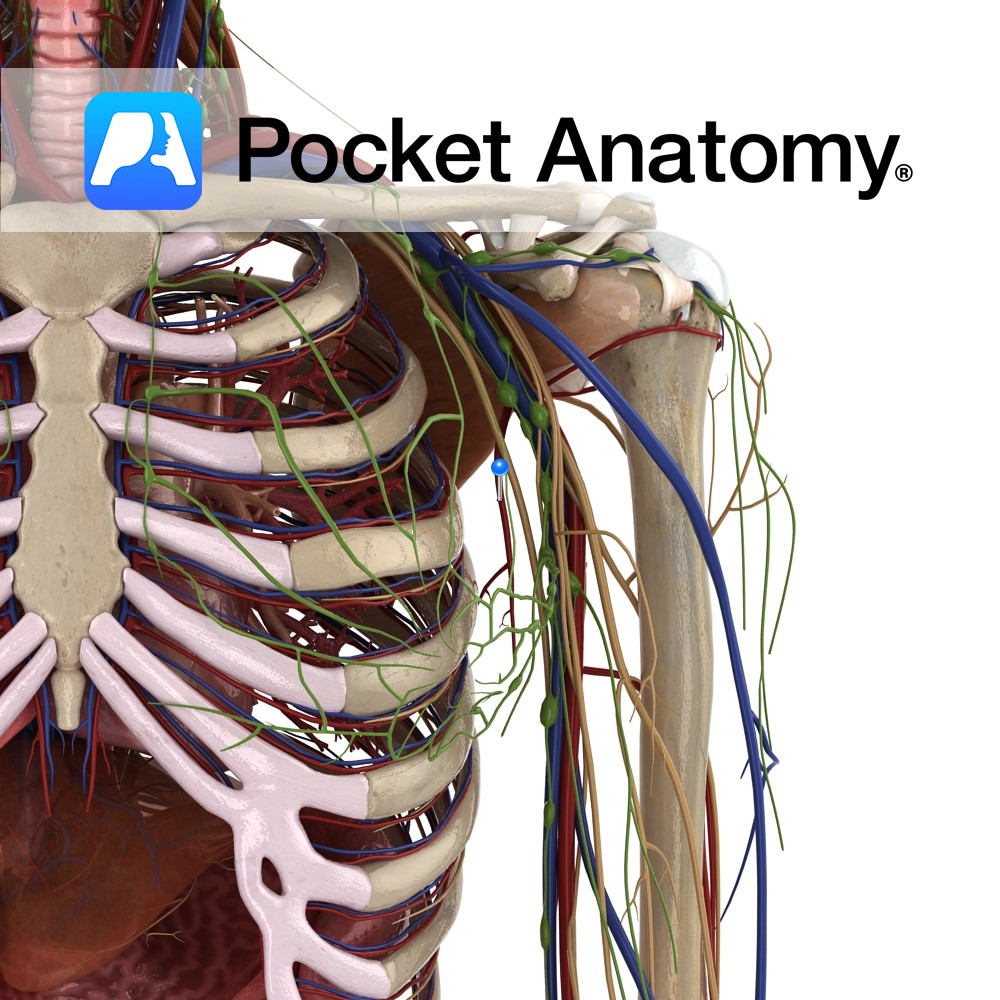
Anatomy Course Branches from the axillary artery, beyond the lateral margin of pectoralis minor. It then travels inferomedially on the thoracic wall, following the pectoralis minor muscle. It terminates here, anastomosing with intercostal vessels, internal thoracic arteries and the subscapular artery. Supply Contributes to the blood supply of the front wall of the axilla, the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
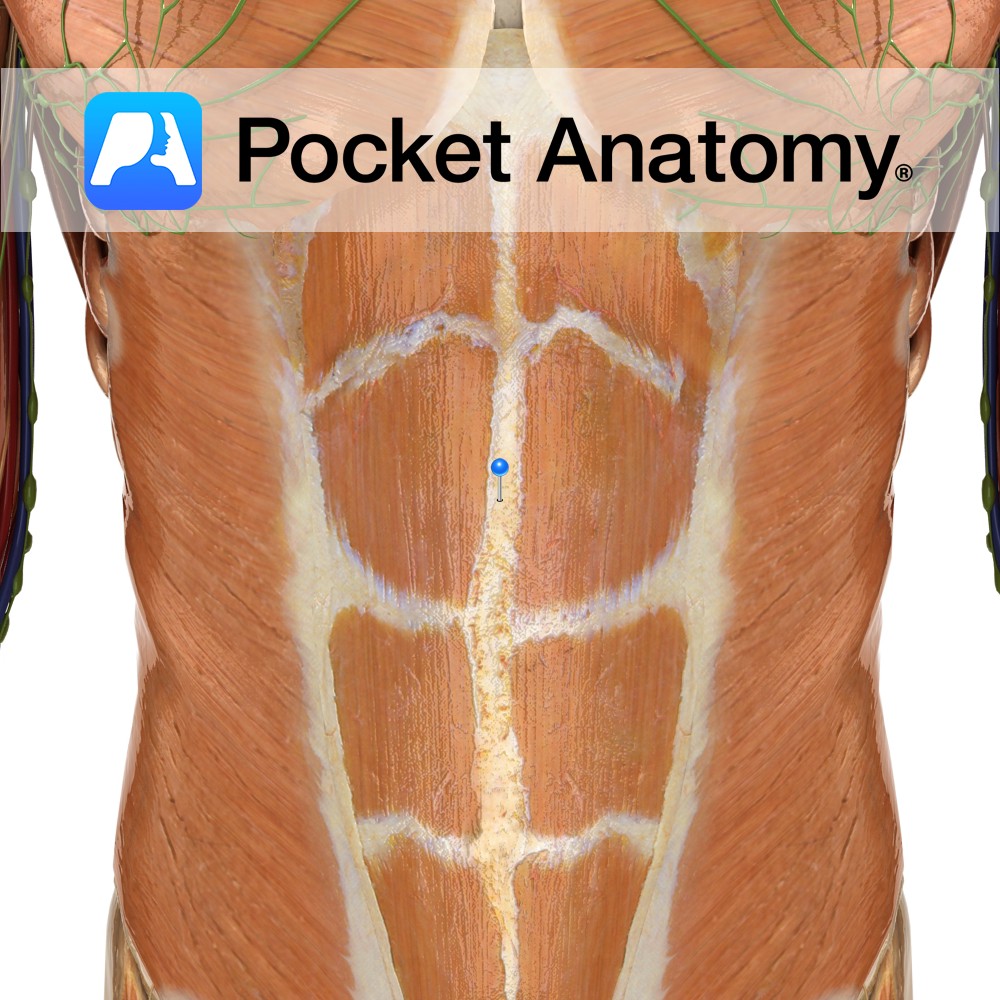
Anatomy Formed from the fusion of the aponeuroses of the abdominal muscles. It forms the midline of the abdomen. It extends from the xiphoid process superiorly to the pubic symphysis inferiorly. Functions The attachment point for the vertical and anterolateral abdominal muscles. Clinical Surgeons tend to make incisions along this line during abdominal surgery due
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
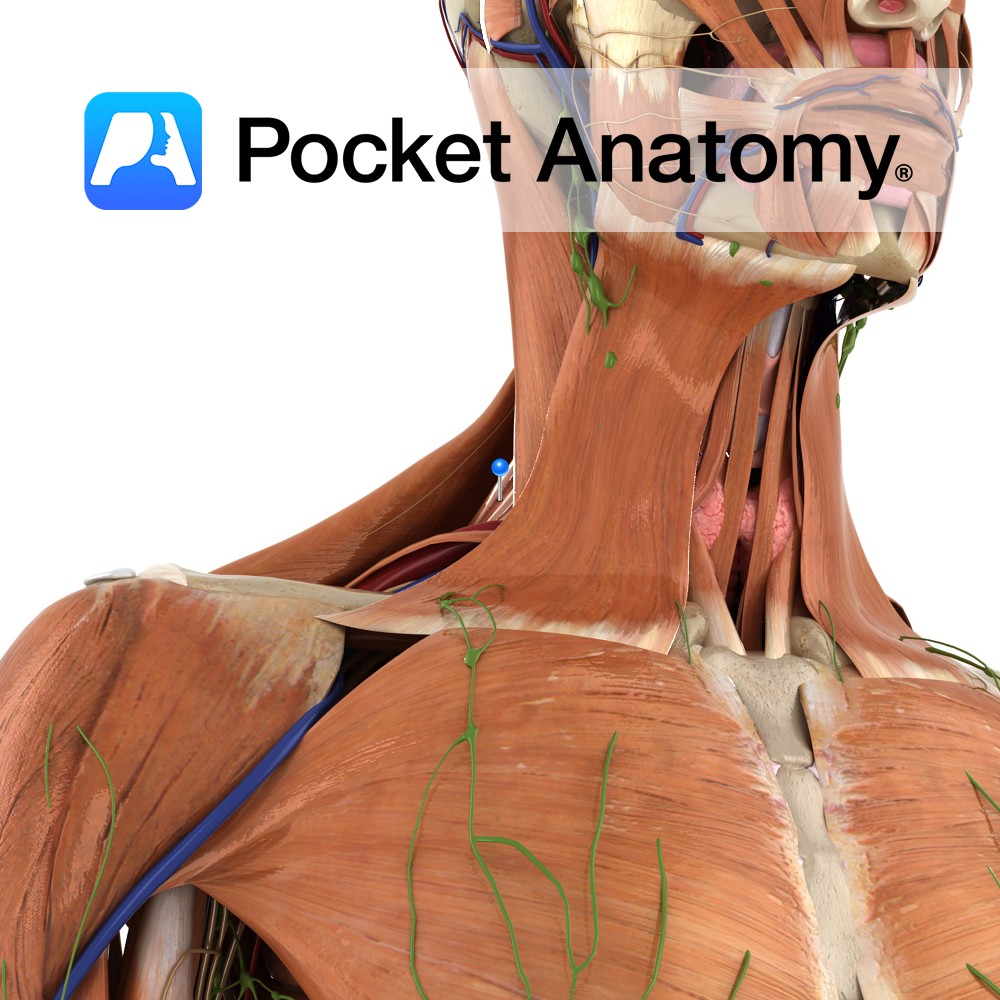
Anatomy Origin: Posterior tubercles of the transverse processes of the upper four cervical vertebrae (C1 to C4). Insertion: Medial border of the scapula between the superior angle and the spine, opposite the supraspinous fossa. Key Relations: Lies within the floor of the posterior triangle of the neck. Functions -Working with various other muscles of the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
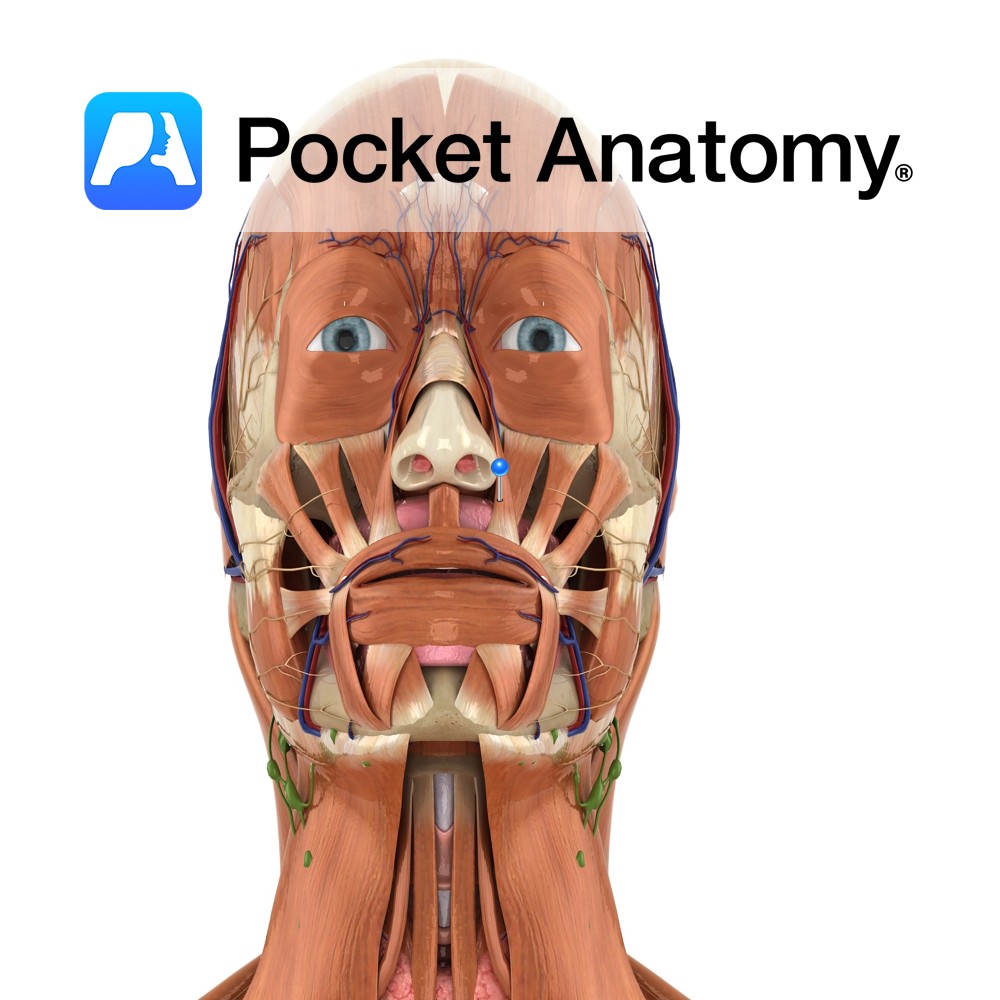
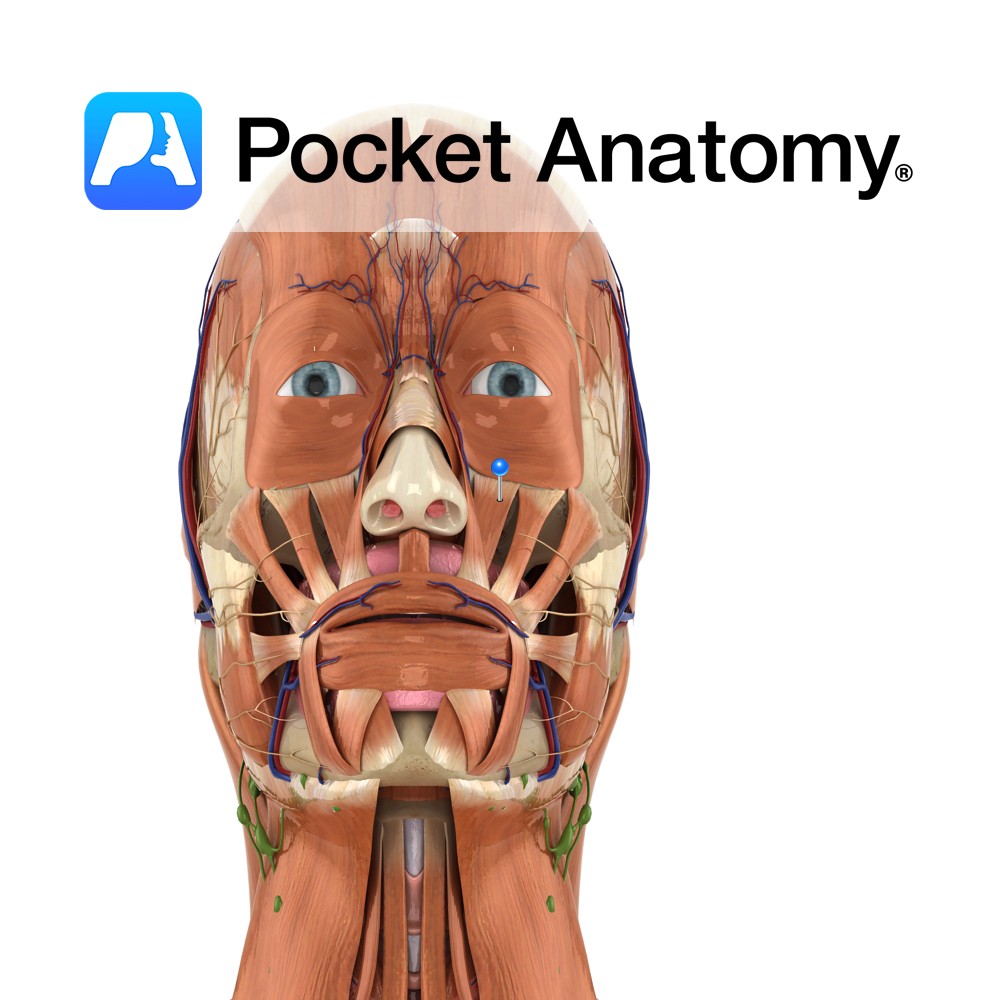
Anatomy Origin: Frontal process of maxilla. Insertion: Alar cartilage of nose and upper lip. Key Relations: Lies medial to levator labii superioris. Functions Raises upper lip and opens the nostrils. Supply Nerve Supply: Buccal branch of the facial nerve (CN 7). Blood Supply: Lateral nasal artery. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Infra-orbital margin of maxilla. Insertion: Skin of upper lateral half of upper lip. Key Relations: Fibres run inferomedially and merge with orbicularis oris. Functions Raises upper lip and forms the nasolabial furrow. e.g. during sadness.. Supply Nerve Supply: Buccal branch of the facial nerve (CN 7). Blood Supply: Superior labial branch of the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
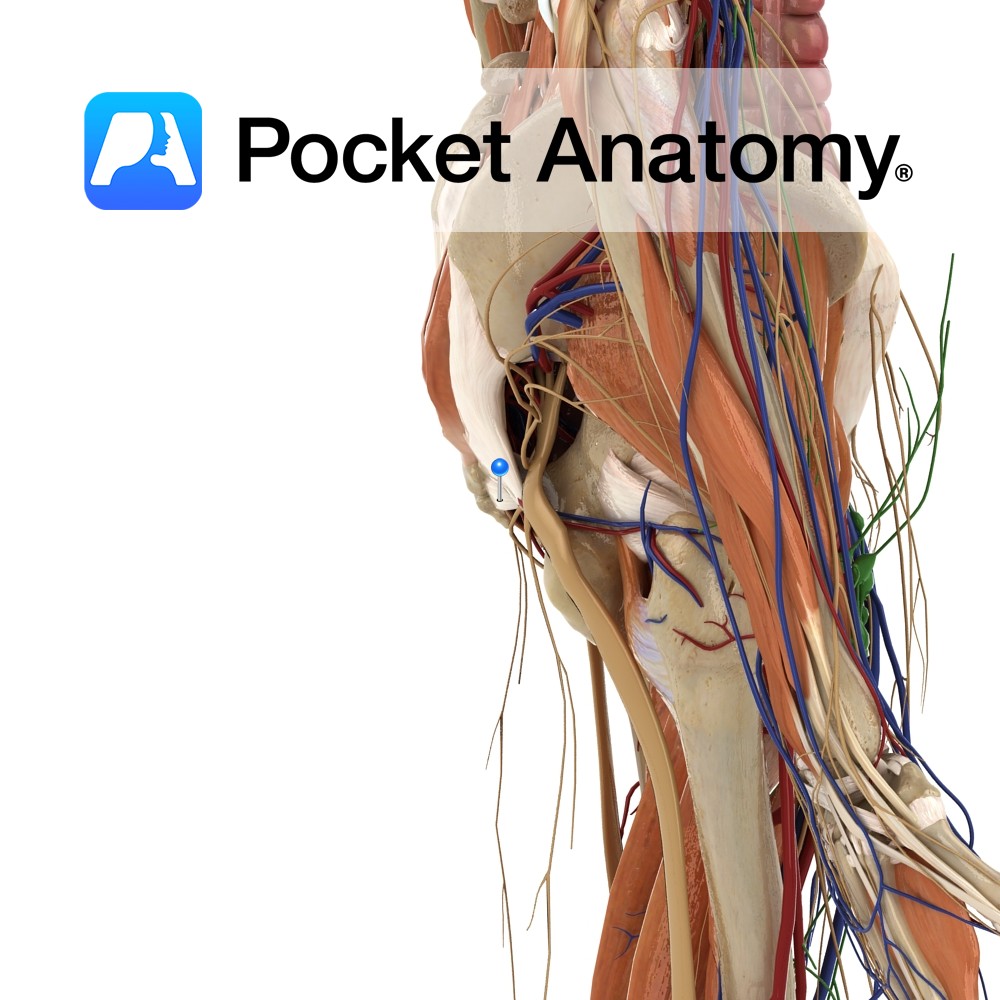
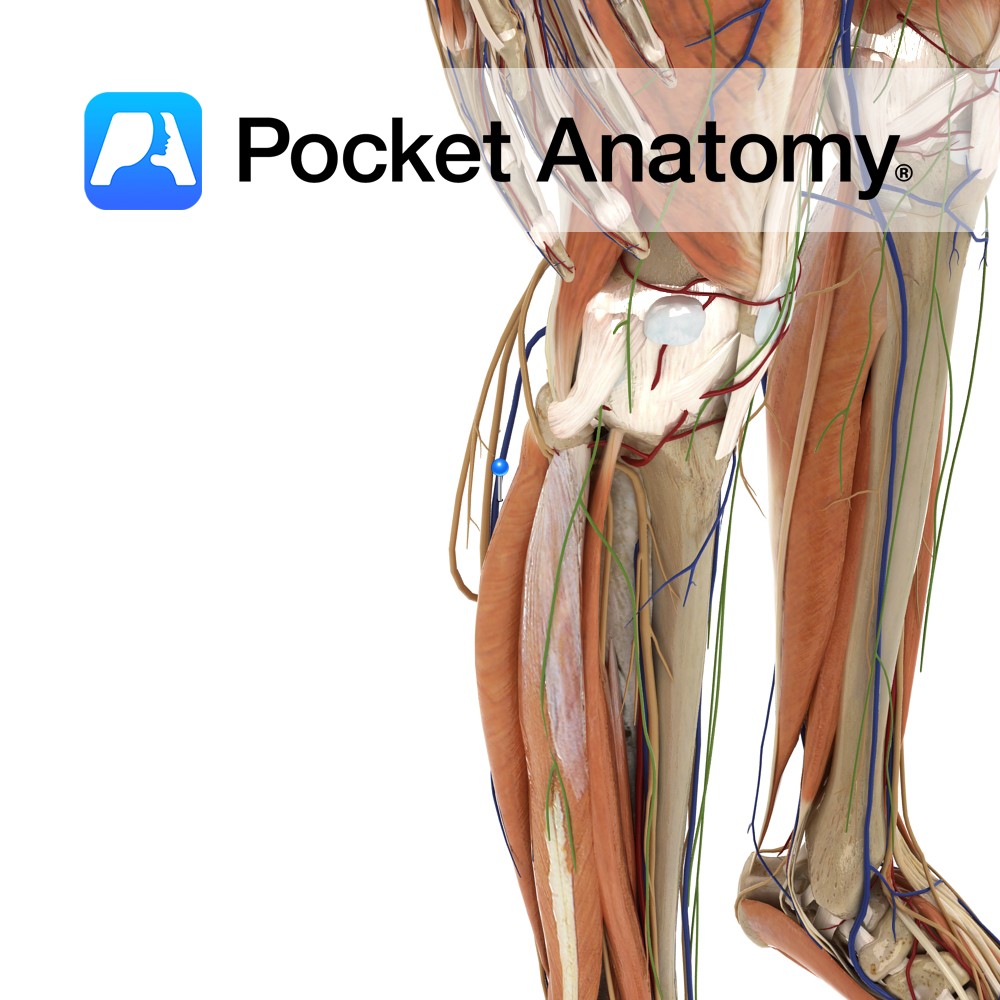
Anatomy Origin: Body of the pubis, tendinous arch of obturator fascia and pelvic surface of ischial spine. Insertion: Coccyx, around the anal canal and the anococcygeal ligament. Key Relations: -Forms posterior part of the levator ani muscle. -Contributes to formation of the pelvic diaphragm in association with coccygeus (for more information see the above layer)
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Maxilla inferior to the infra-orbital foramen. Insertion: Skin at the corner of the mouth. Key Relations: Lies posterior to levator labii superioris, levator labii superioris alaeque nasi and zygomaticus major and minor. Functions Raises corner of the mouth and forms the nasolabial furrow e.g. during sadness.. Supply Nerve Supply: Buccal branch of the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Originates laterally from the dorsal venous arch of the foot. It ascends superficially on the posterior aspect of the leg until it pierces the deep fascia and joins the popliteal vein. Drain The lesser saphenous vein drains the superficial leg and foot. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins