PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
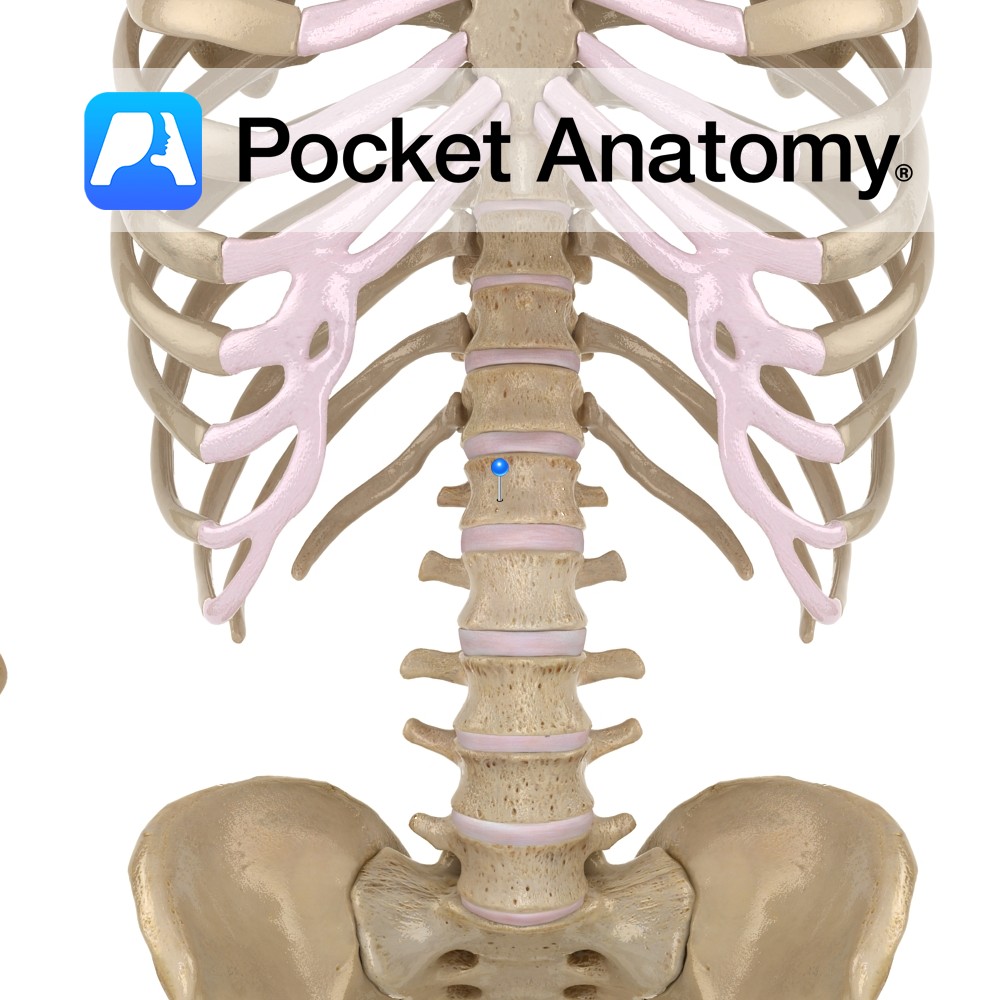
Anatomy Big, wide vertebra (bodies progressively bigger C1 – L5), cylindrical, upper and lower surfaces flat or somewhat concave. Articulates with vertebrae above and below through fibrocartilaginous discs that allow some vertebral movement and provide shock absorption. No articular facets (unlike those on thoracic for articulation with ribs). No transverse foramina (unlike cervical). Clinical Significant
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
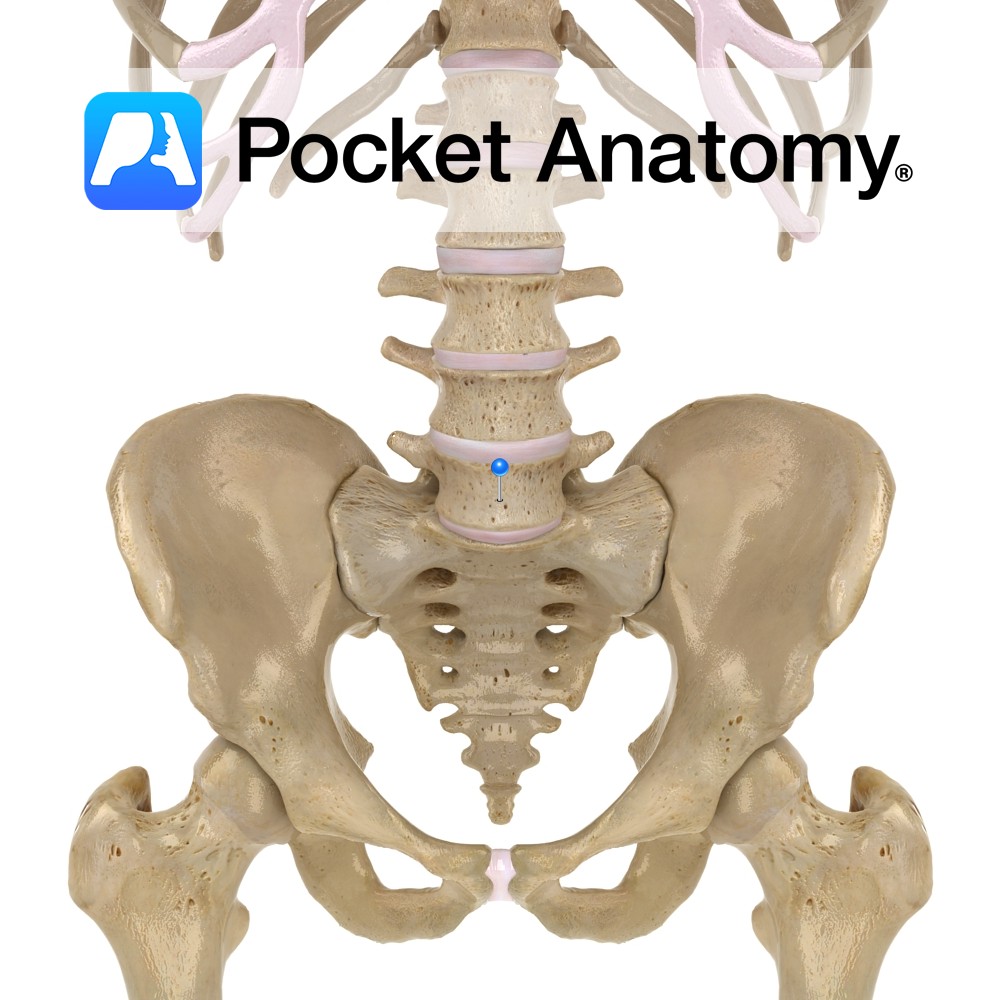
Anatomy Completes the progression, through L4, of change in where transverse process arises, from junction pedicle and lamina, to arising from junction pedicle and body, homologous with rib. Transverse processes are strong. Body is much thicker in front than behind (providing prominence to the lumbo-sacral junction). Superior articular process has a small mamillary process, and
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
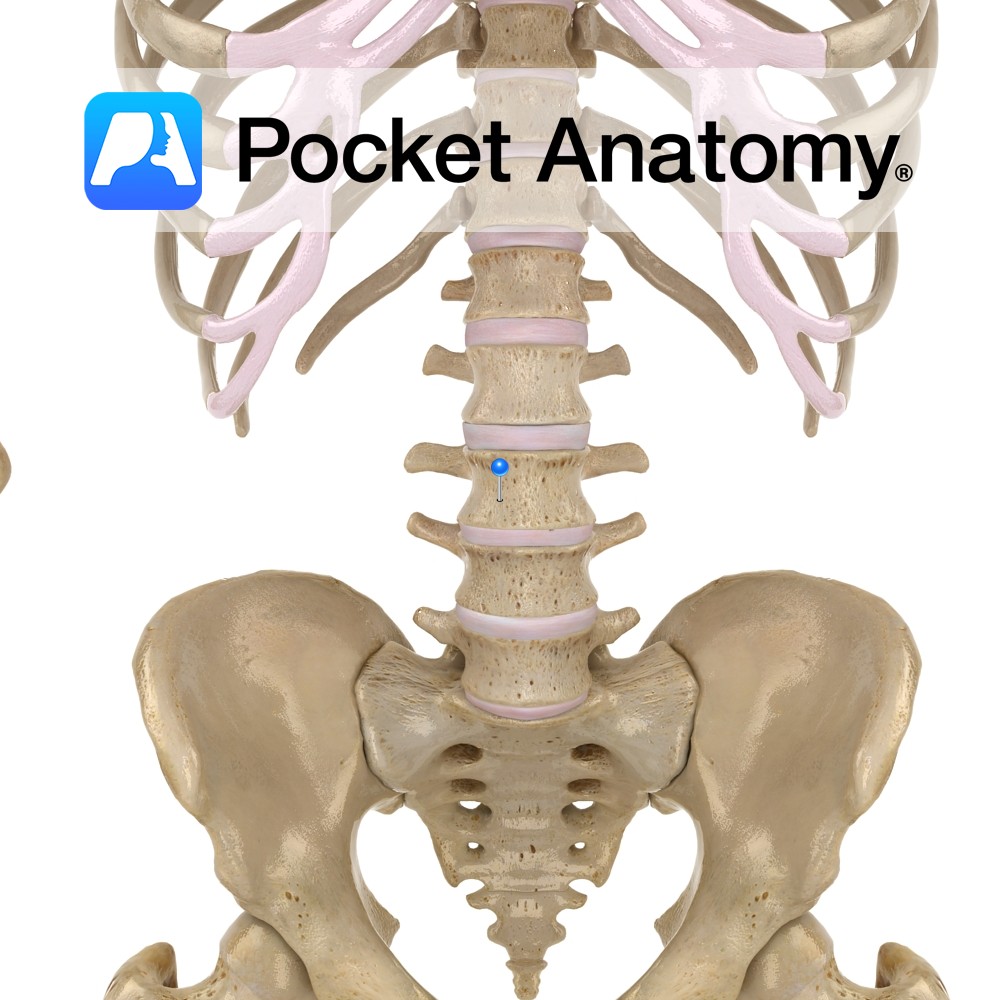
Anatomy 1st/highest lumbar vertebra. Body bigger than T12, smaller than L2-5 (progressively bigger, supporting more weight). No articular facets for ribs on body or transverse process (unlike thoracic), no transverse foramen (unlike cervical). Clinical Articulates above with T12, below with L2. L1-5 very strong spinal segment, exhibits flexion, extension, lateral flexion, rotation. Vignette Fracture commonly
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
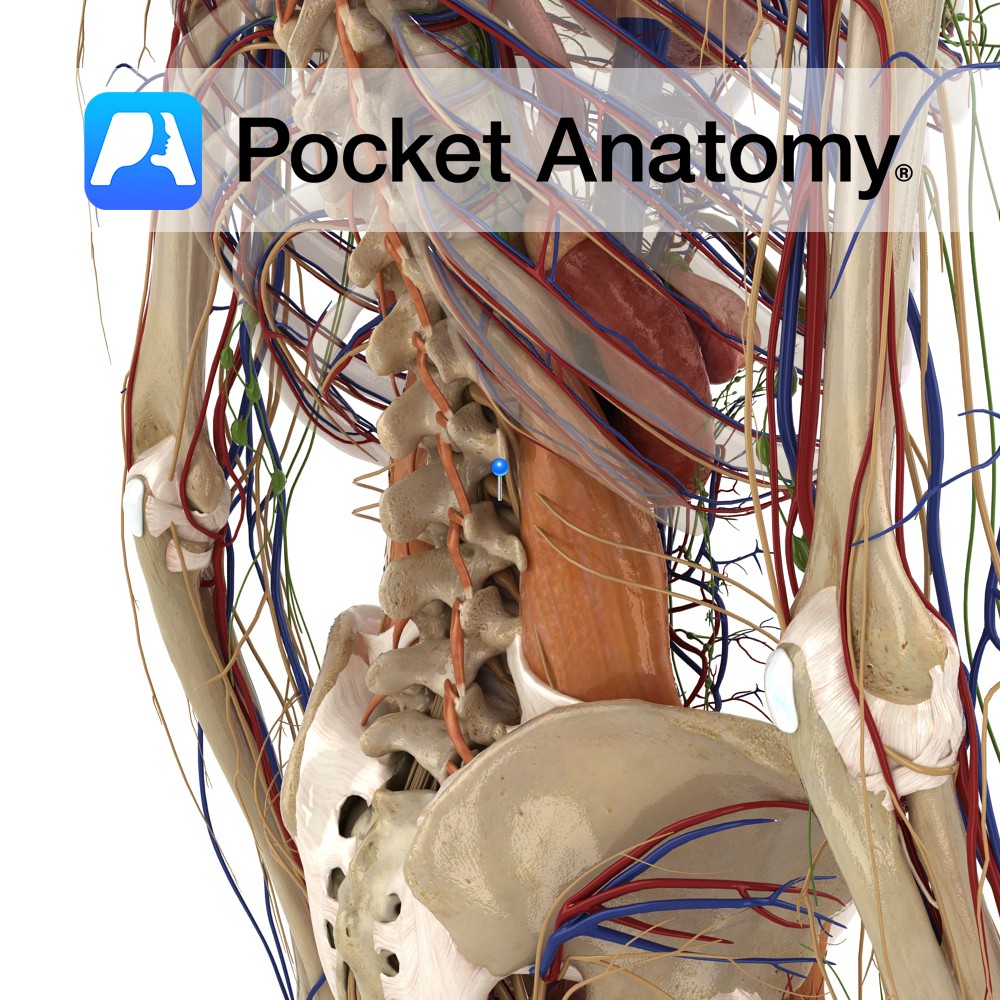
Anatomy Course Made up of the anterior rami of the spinal nerves L1 to L3, and some of L4 and T12, the subcostal nerve. The lumbar plexus is a part of the lumbosacral plexus. The nerves here all join together in different branching patterns to form a number of terminal branches, such as the iliohypogastric
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
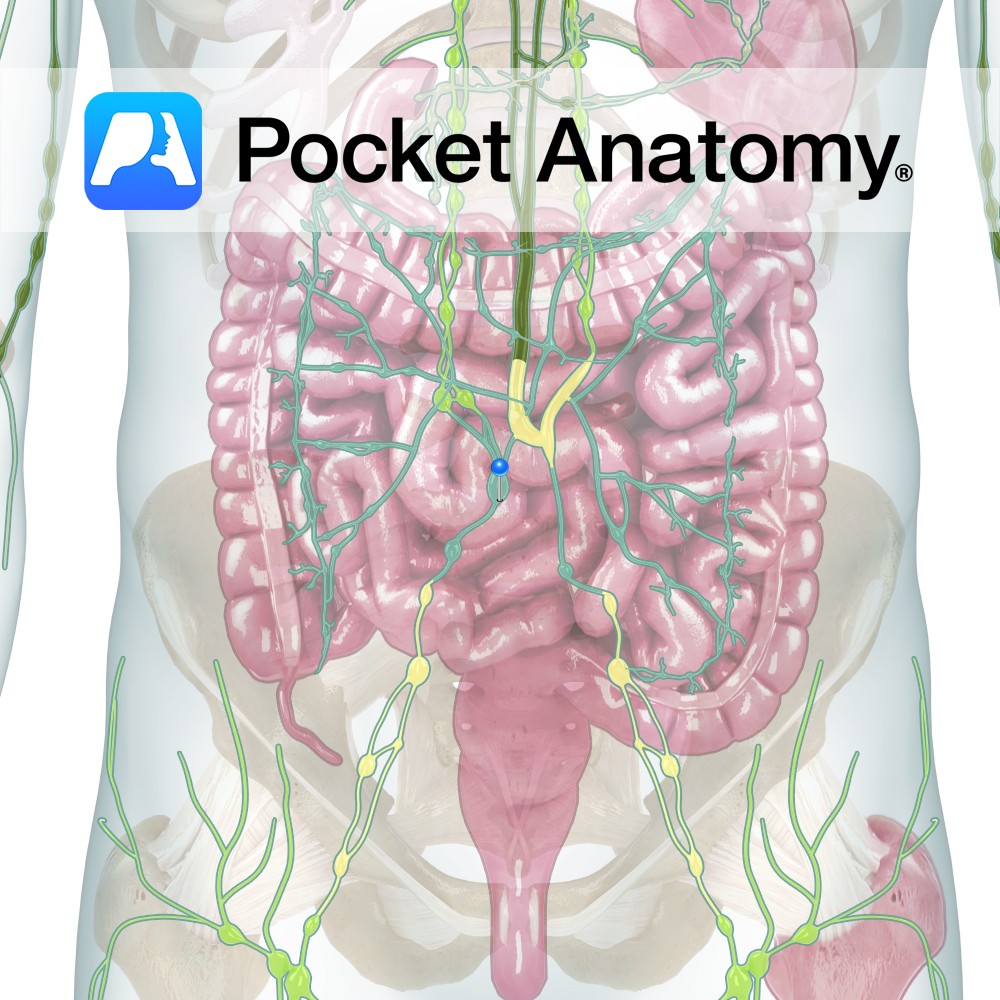
Anatomy One of the 5 lymphatic trunks (4 paired, 1 unpaired). Drains lymph from leg, lower abdominal wall, kidney and adrenal, pelvic wall and organs. Empties into Thoracic Duct. Vignette Lymph(atic) trunks are formed by the union of 2 or more efferent ducts and empty into either the Thoracic (Left Lymphatic) or Right Lymphatic Duct.
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Superior oblique part: Anterior tubercles of transverse processes of C3 to C5. Inferior oblique part: Anterior surface of bodies of T1 and T2. Vertical part: Anterior surface of bodies of T1 to T3 and C5 to C7. Insertion: Superior oblique part: Tubercle of anterior arch of the atlas (C1). Inferior oblique part: Anterior
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Transverse processes of C3 to C6. Insertion: Inferior surface of the basilar part of the occipital bone. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Posterior surface of transverse processes of T1 to T5 and the articular tubercle of C4 to C7. Insertion: Posterior margin of mastoid process and adjacent occipital bone. Functions Extends the head and rotates the head to the same side. Supply Innervation: Dorsal rami of cervical and thoracic spinal nerves (C6 to T4). Blood
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy The lower part of the posterior sacroiliac ligament. Derived from the third transverse tubercle of the posterior surface of the sacrum. It travels obliquely to attach to posterior superior iliac spine. Functions Provides static stability to the sacroiliac joint. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
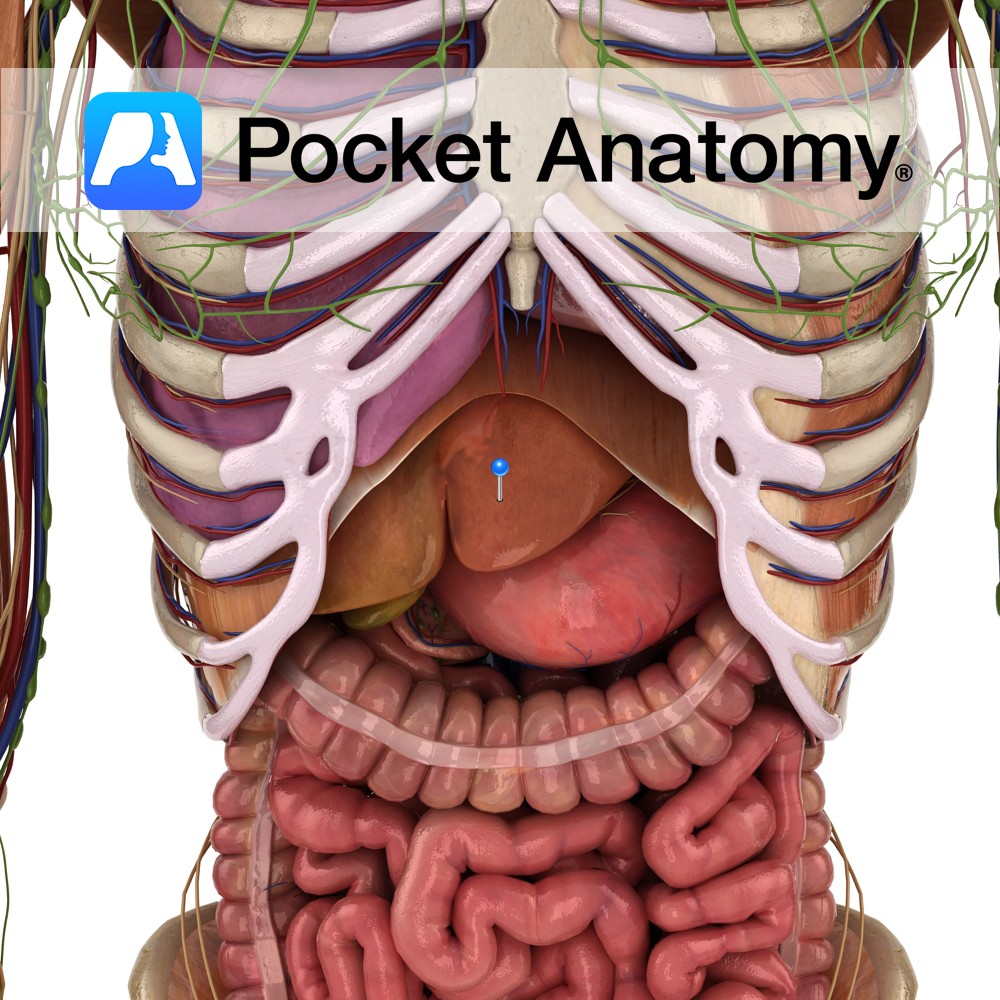
Anatomy Largest organ other than skin, largest gland, c. 1.5-3 kg, 4 lobes (left, right, caudate, quadrate), triangular, right upper quadrant abdomen under diaphragm. Hilum (or porta hepatis) is a fissure under left lobe, through which dual blood supply enters (hepatic portal vein from GI system, hepatic artery from celiac from aorta) and common bile
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins