PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
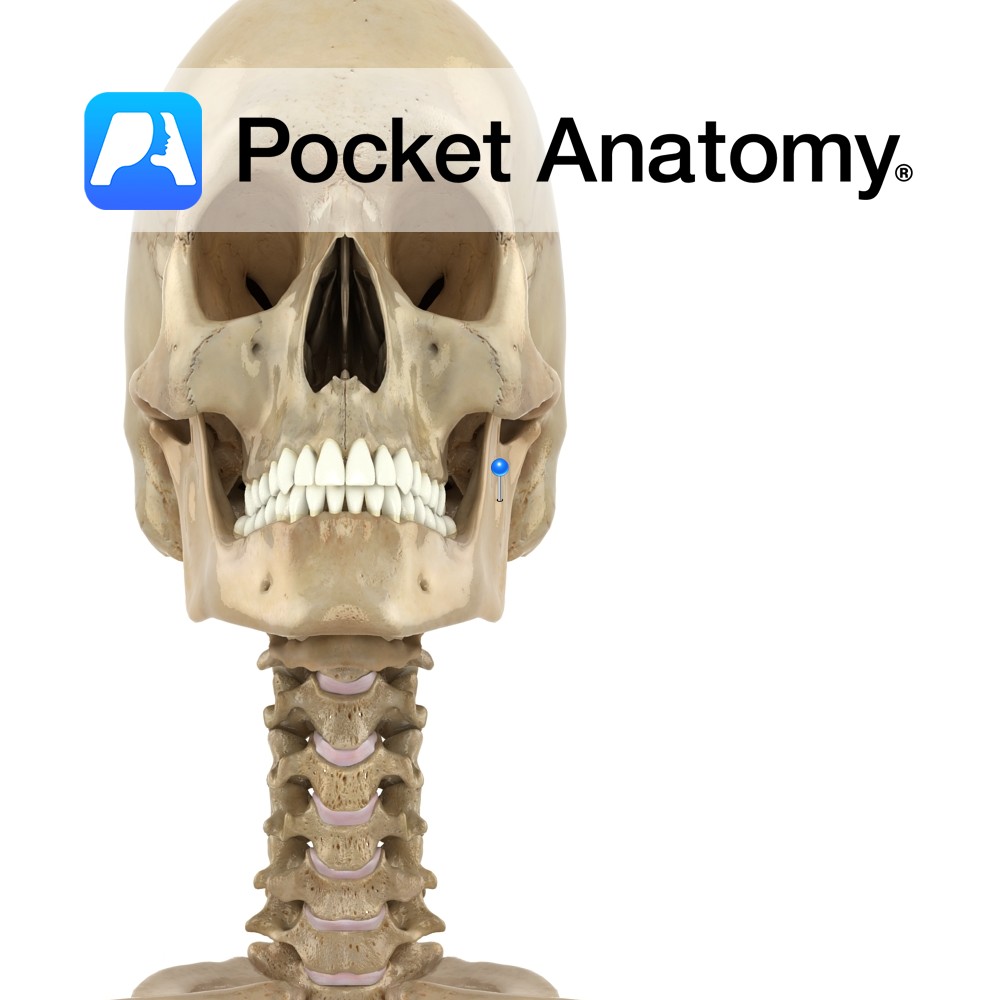
Anatomy The perpendicular part of the mandible, its upper extremities consisting of the coronoid and condylar processes, with the mandibular notch between. Laterally, almost fully covered by masseter; postero-medially, pterygoid. Clinical The mandible (jawbone) holds the lower teeth. Chews. involved in speech. Along with cranium, makes up skull. Four parts (each side): Anterior (left and
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
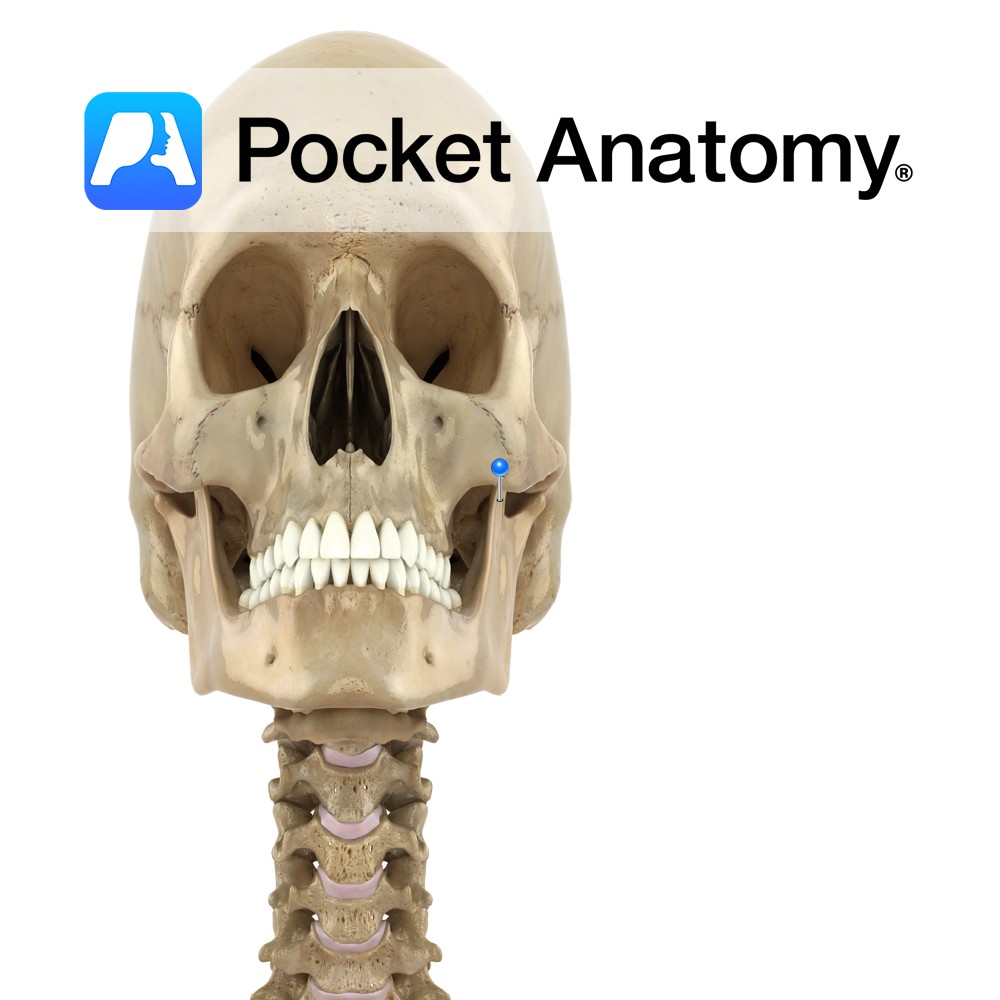
Anatomy Consists of a ridge. Begins faintly anteriorly where it begins at mental tubercle (chin), more evident as it courses back and up to become continuous with anterior border ramus. Clinical Attachment for depressor anguli oris, quadratus labii inferioris. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
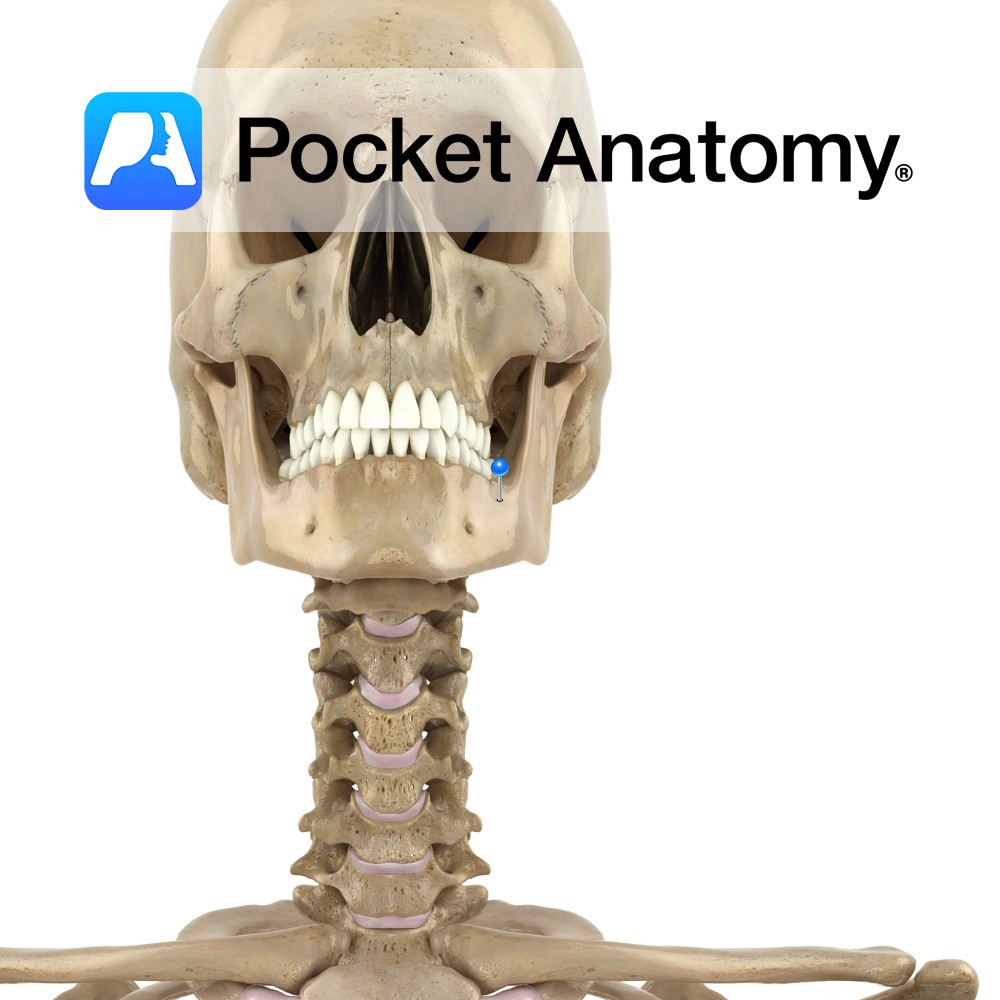
Anatomy At front of top of ramus, separated by mandibular notch from condylar process behind. Laterally, temporalis and masseter attached, medially temporalis and some of buccinator. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
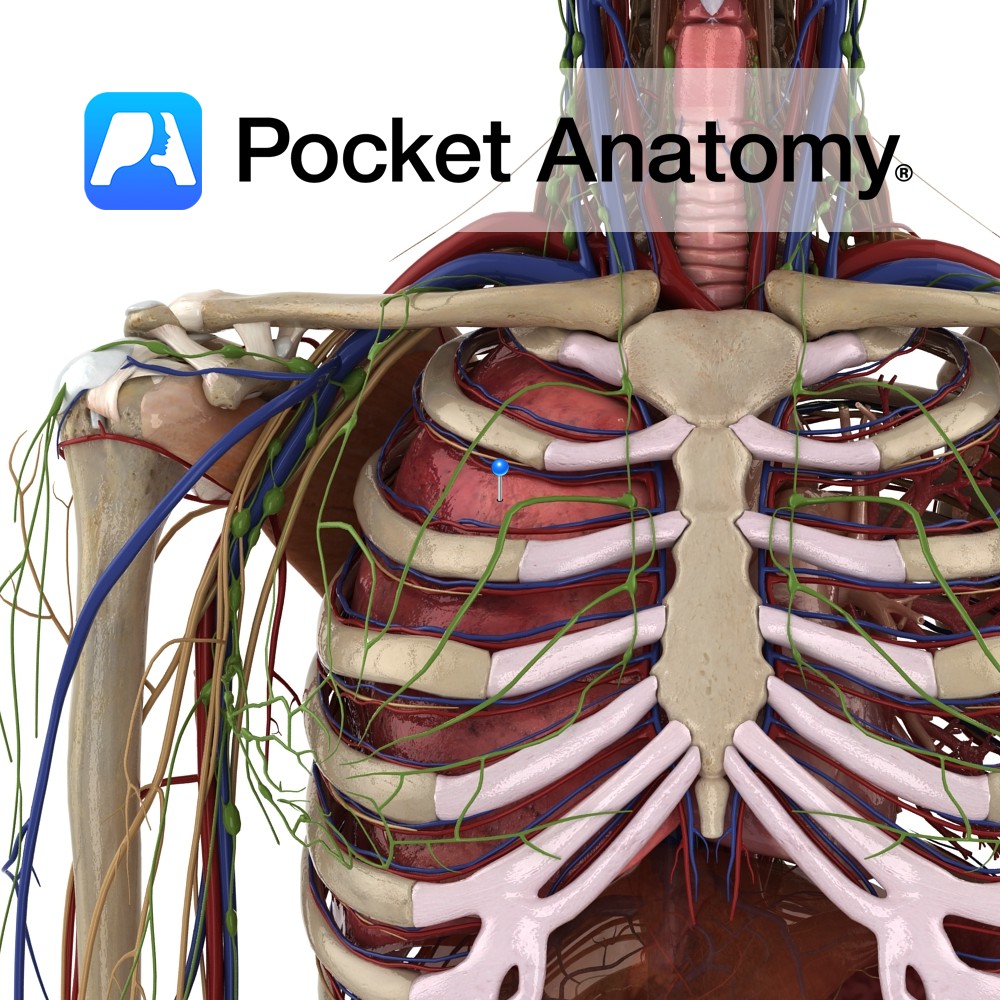
Anatomy Paired thoracic respiratory organs, right 3 lobes, left 2 (heart accommodated), in closed pleural cavities, separated by mediastinum, diaphragm below, thoracic inlet (T1, 1st ribs, manubrium) above, surrounded by thoracic cage (T1-12, ribs, costal cartilages, sternum). Hilum; artery, vein, bronchus. Trachea divides left and right bronchi, continues in lung: main bronchus – lobar (3R,
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
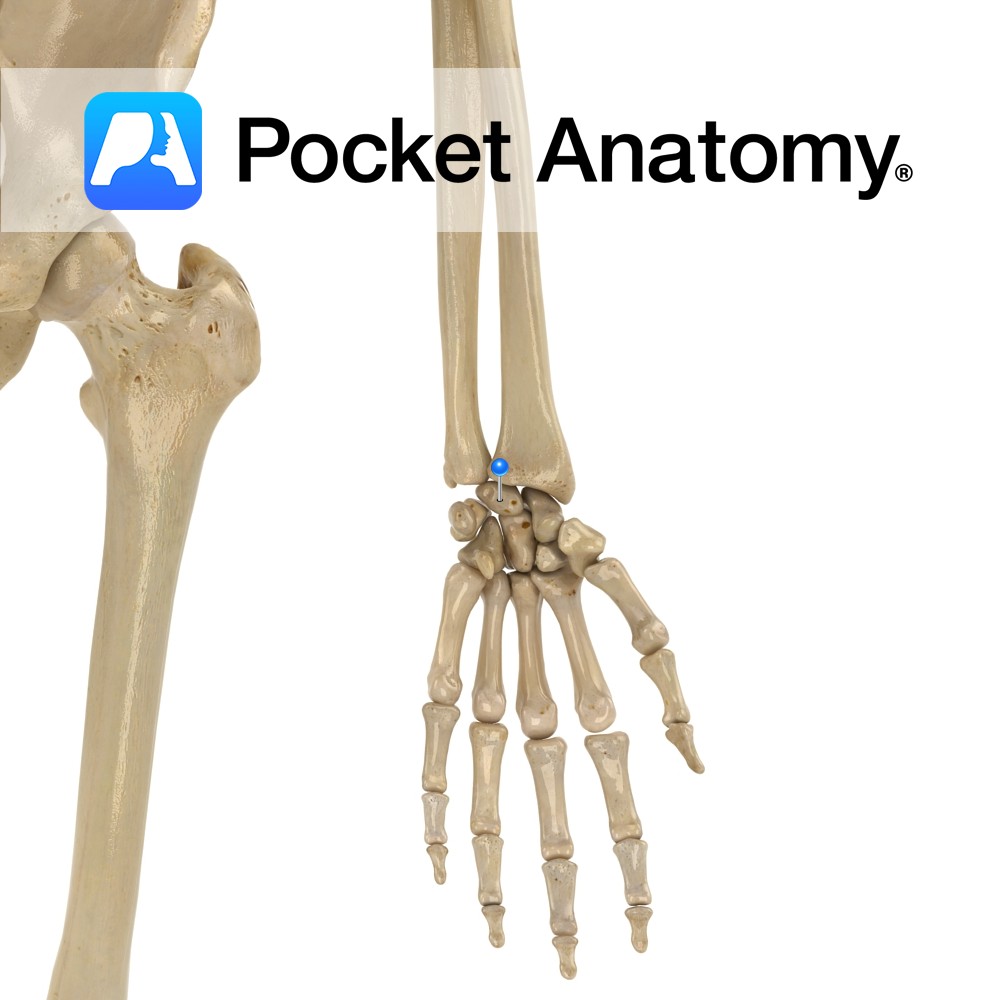
Anatomy Centre of nearer row of carpal bones, crescent-shaped. Articulates up with radius, down with capitate and hamate, in with triquetral, out with scaphoid (scaphoid is other carpal that articulates with radius). Clinical Most frequently dislocated carpal bone. Kienbock’s disease; avascular necrosis, cause unclear, rare. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Radial and palmar aspects of the flexor digitorum profundus tendons. Insertion: Lateral aspect of extensor apparatus of index, middle, ring and little fingers. Functions Extension of interphalangeal joints while flexing metacarpophanalgeal joint. Supply Nerve Supply: -Medial two: Deep branch of the ulnar nerve (C8, T1) -Lateral two: Digital branches of the median nerve
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
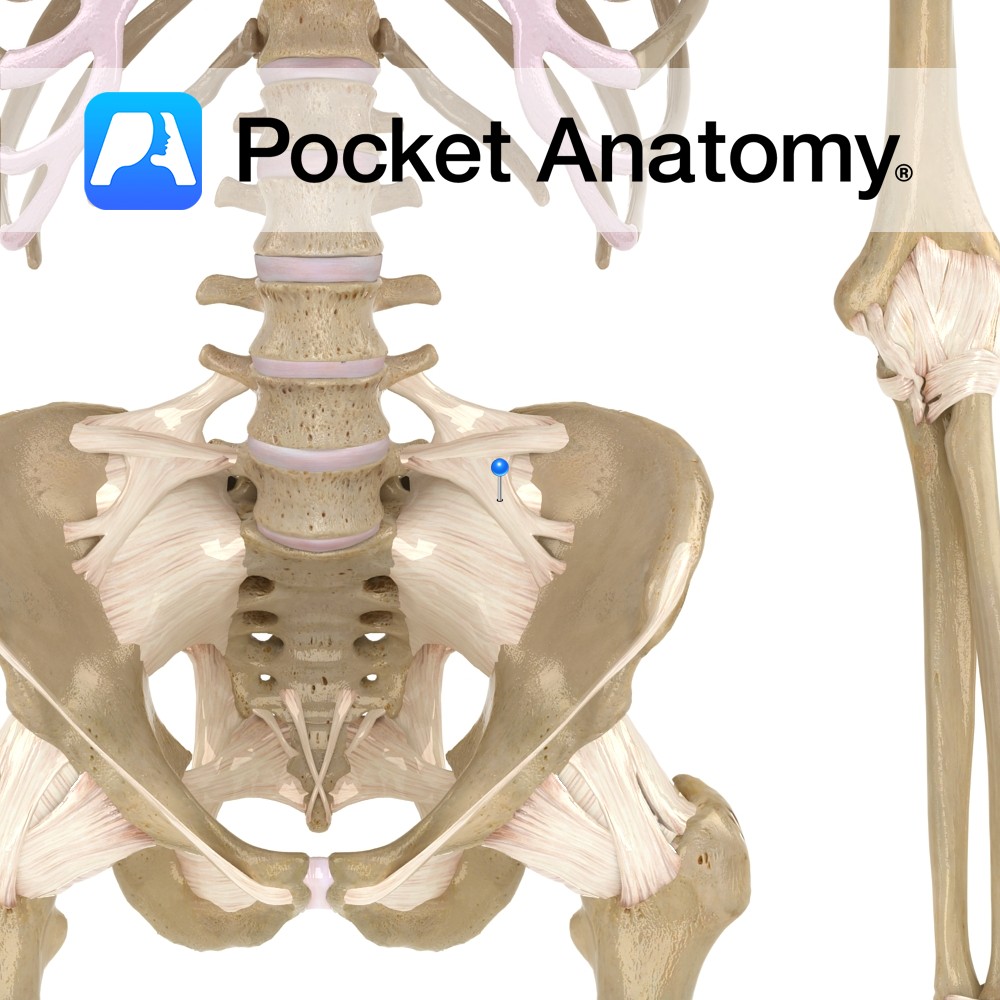
Anatomy The lumbrosacral ligament attaches bilaterally from the transverse process of lumbar vertebra five to the ala of the sacrum. Functions Provides static stability to the lumbrosacral joint and lumbar region of the back. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
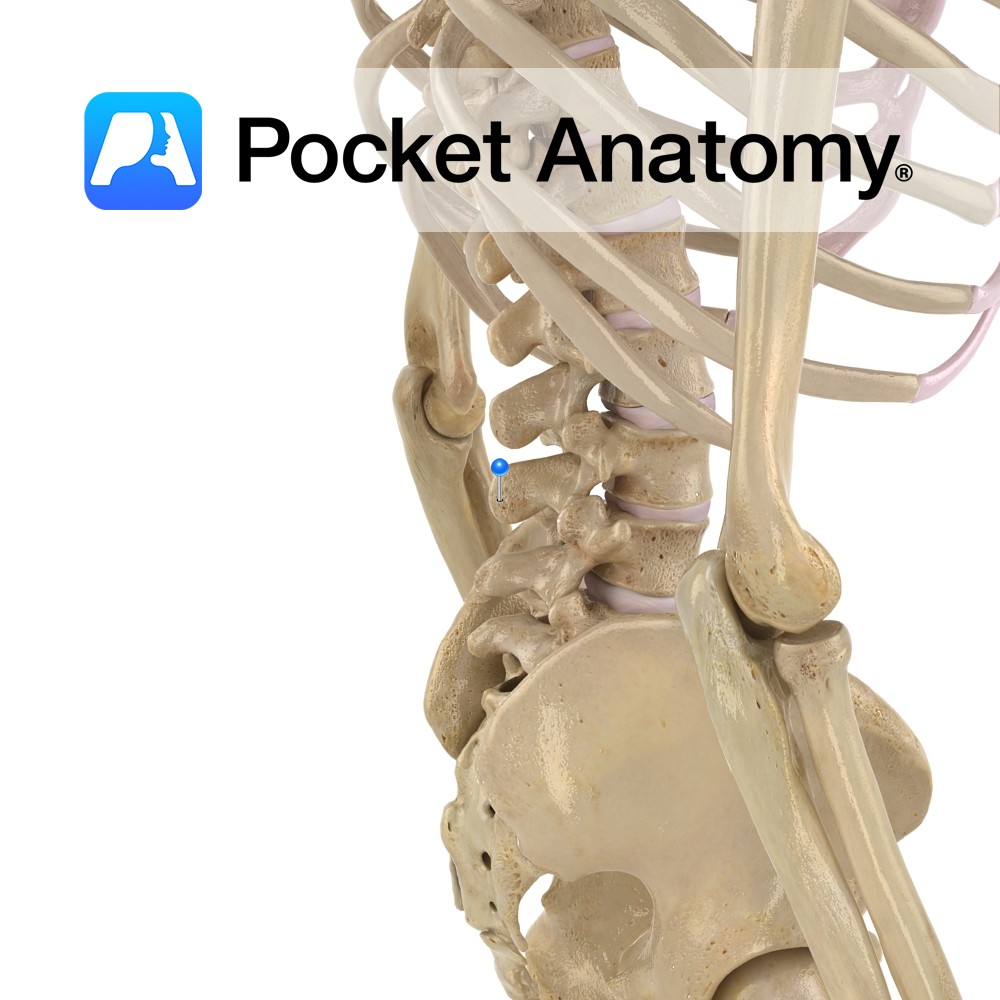
Anatomy Strong pedicles project posteriorly from either side of the back of the vertebral body, joining strong laminae which themselves meet at the midline (from where a spinous process projects back and down) to complete the neural arch (enclosing the vertebral foramen). Where pedicle meets lamina each side, a long thin transverse process, to which
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
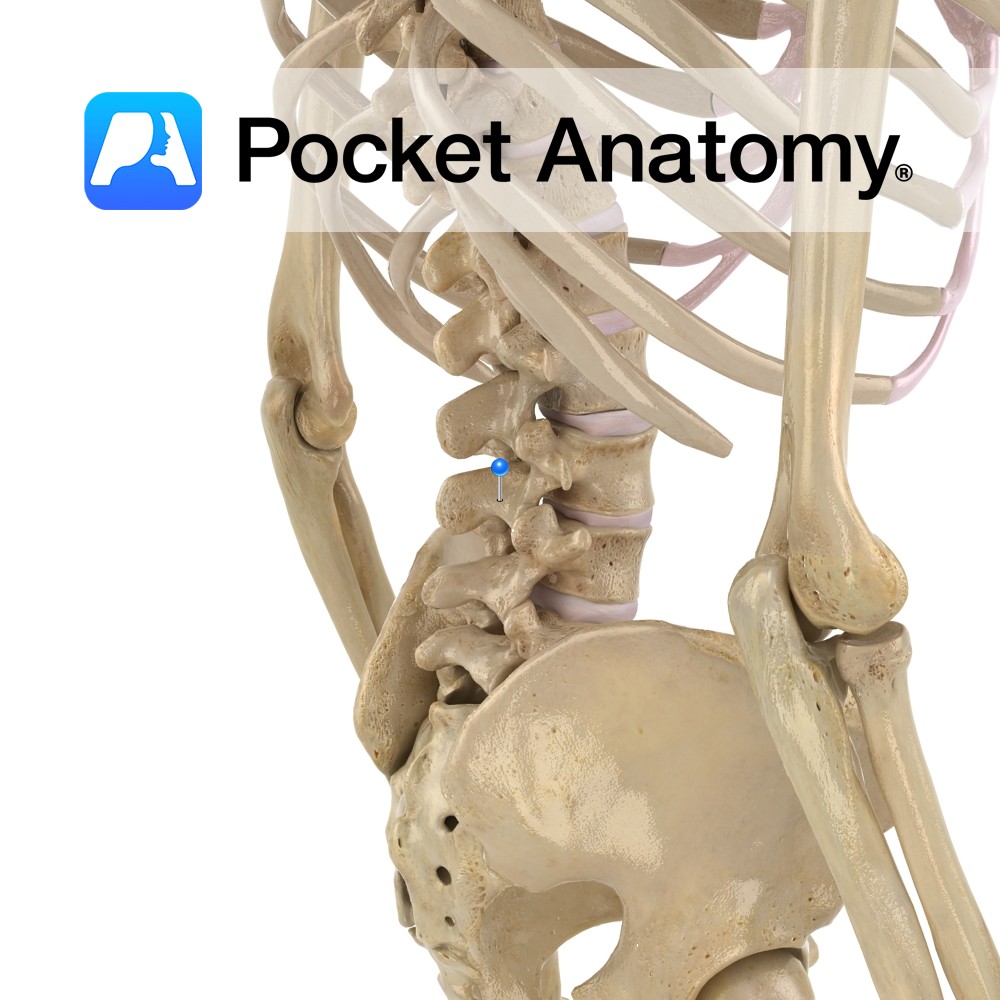
Anatomy Strong pedicles project posteriorly from either side of the back of the vertebral body, joining strong laminae which themselves meet at the midline (from where a broad, thick spinous process projects back and down) to complete the neural arch (enclosing the vertebral foramen, bigger than thoracic, smaller than cervical). Interested in taking our award-winning
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
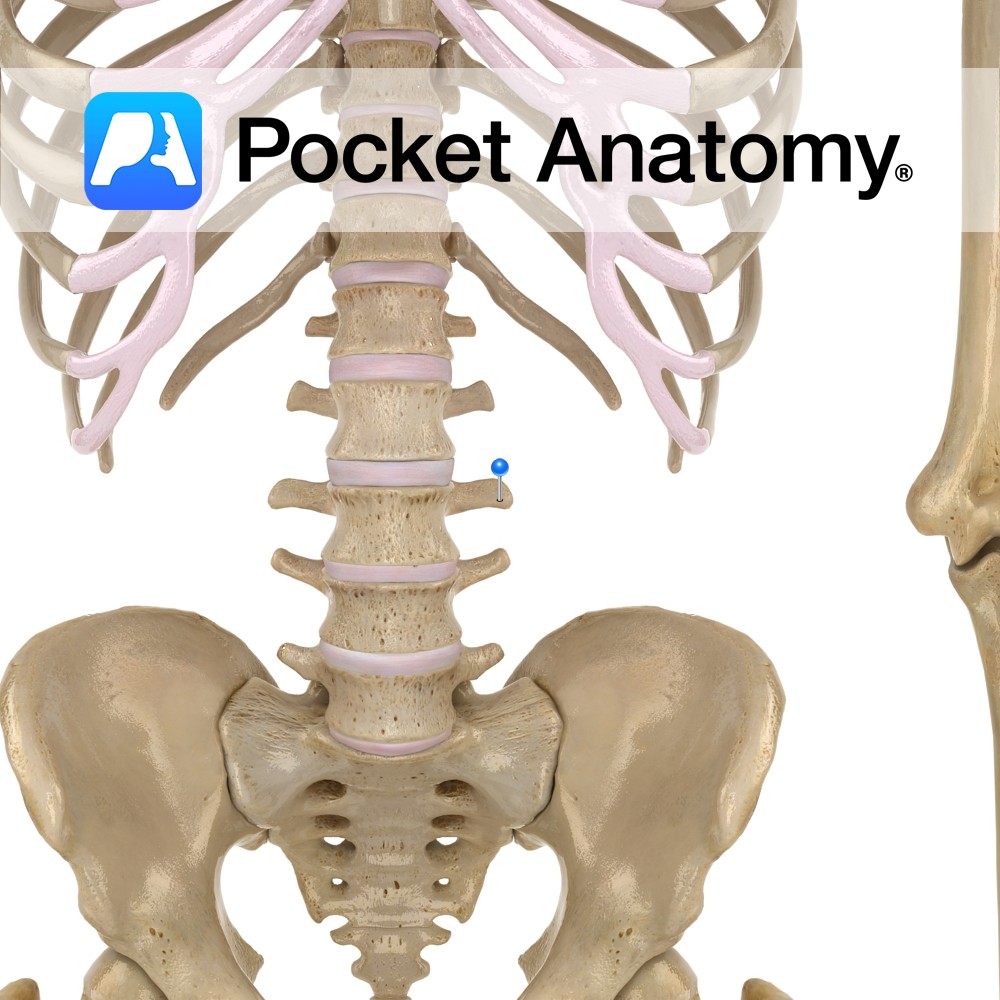
Anatomy Strong pedicles project posteriorly from either side of the back of the vertebral body, joining strong laminae which themselves meet at the midline (from where a spinous process projects back and down) to complete the neural arch (enclosing the vertebral foramen, bigger than thoracic, smaller than cervical). Where pedicle meets lamina each side, a
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins

.jpg)