PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
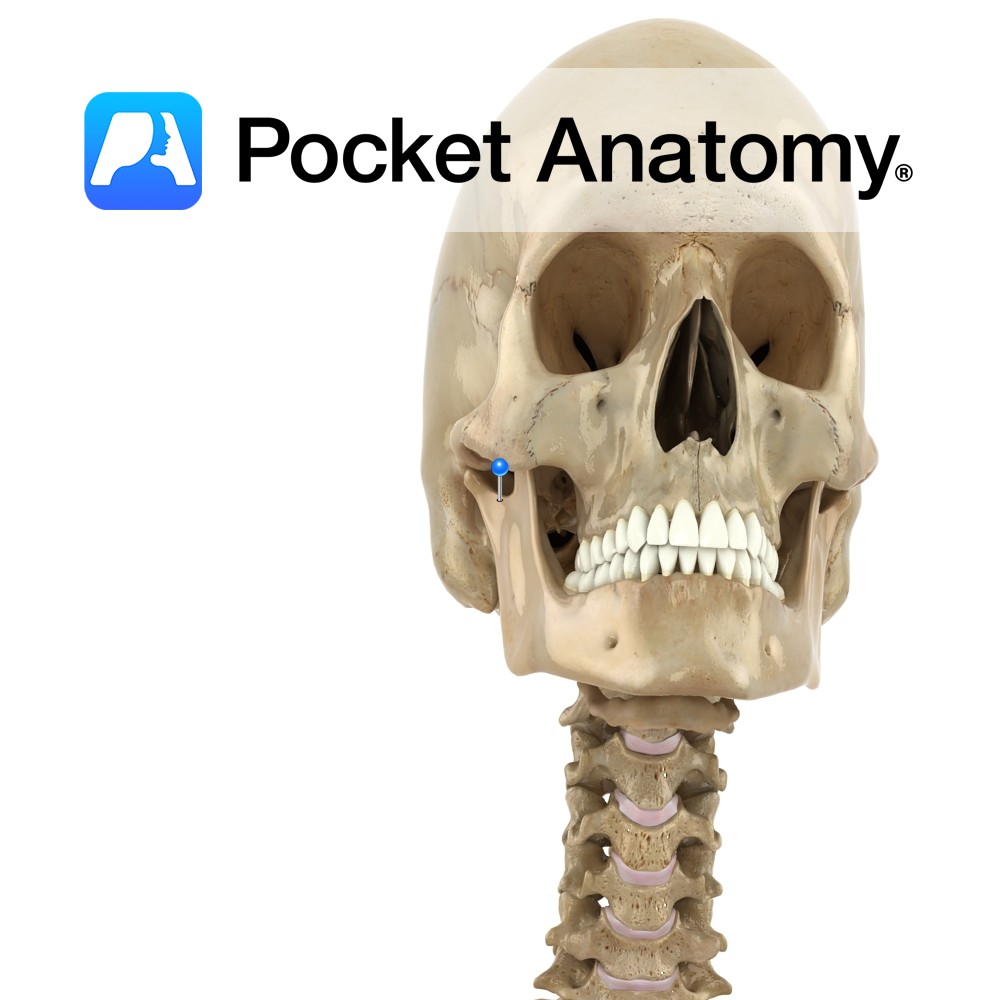
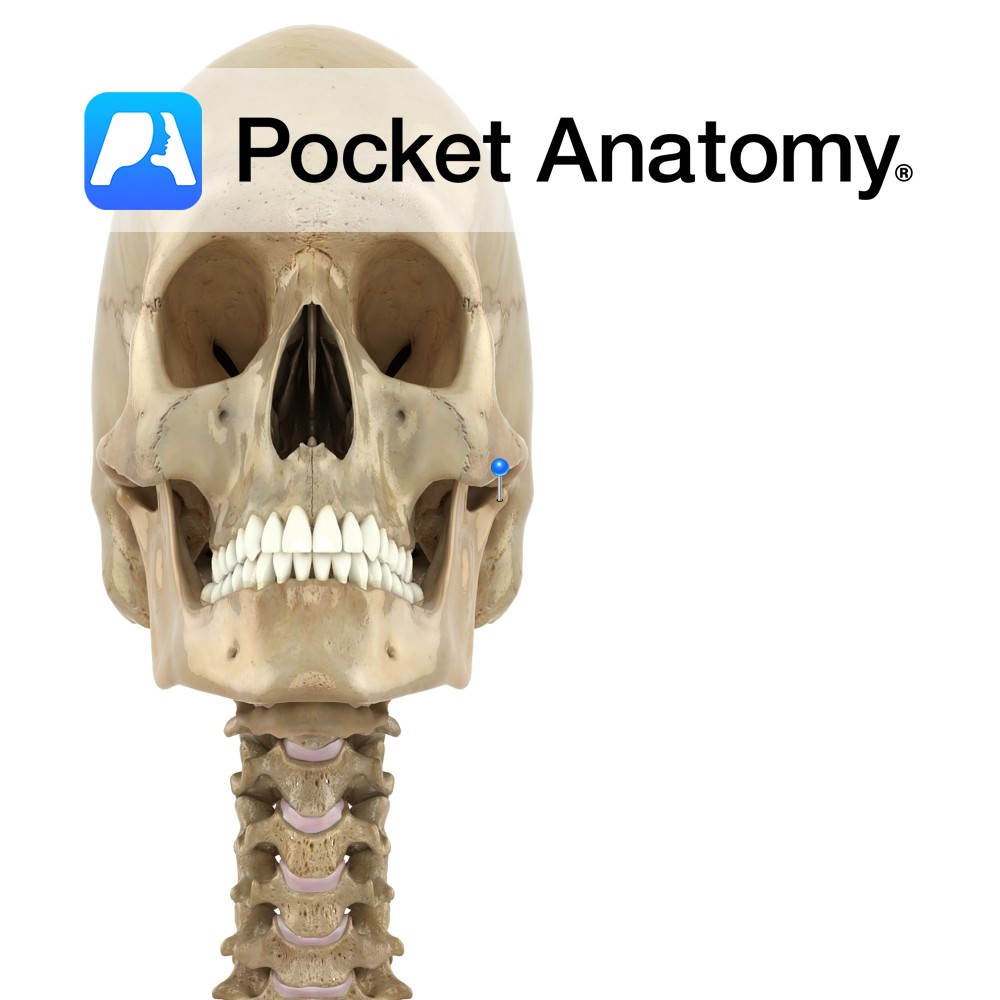
Anatomy Frontal bulge that articulates with frontal process zygoma (cheekbone). Vignette Can felt as bony prominences lateral to edges of mouth, down from the eyes. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
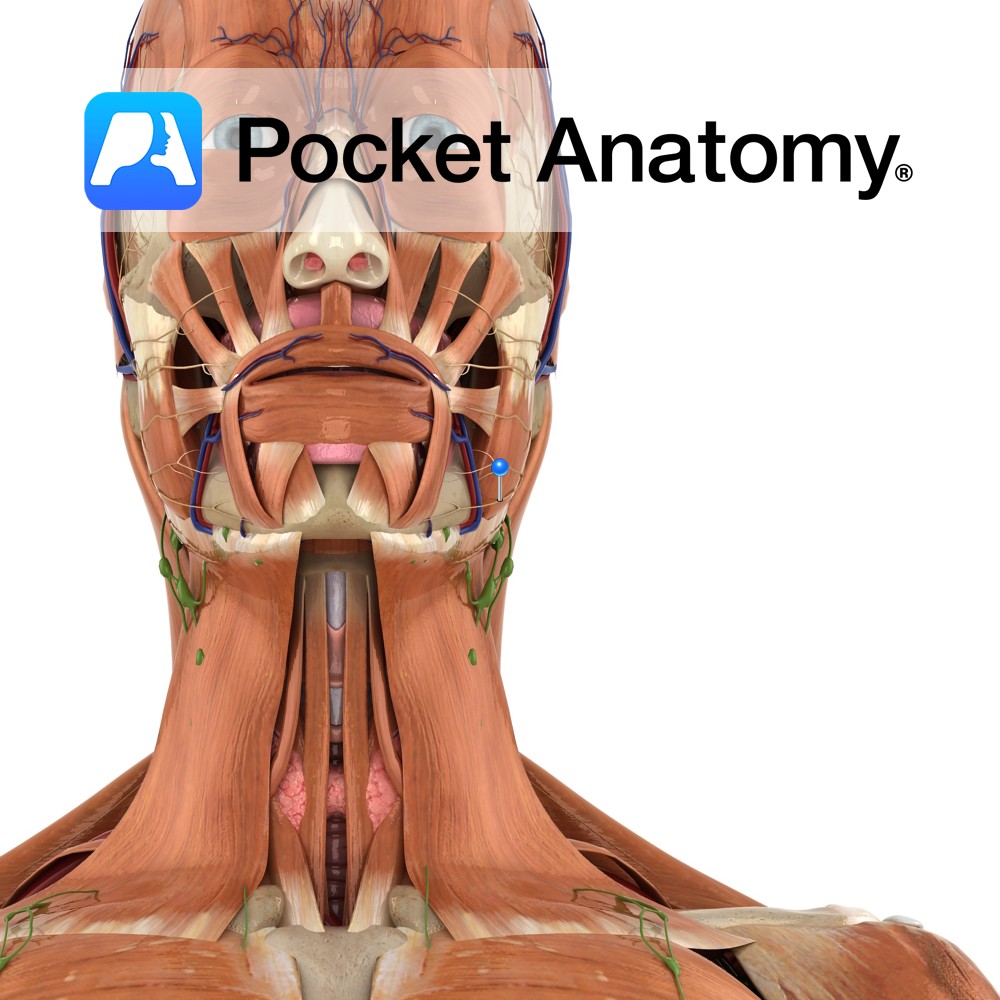
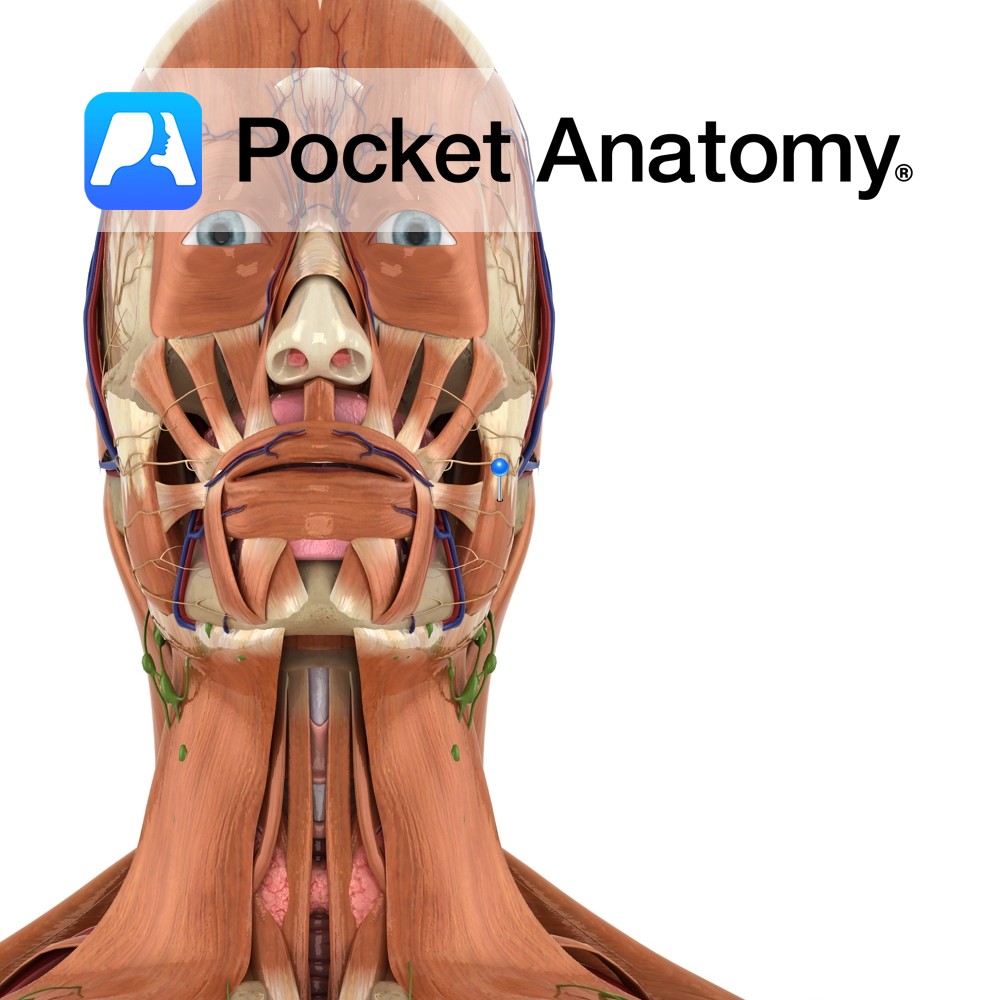
Anatomy Origin: Superficial and Deep portion: Inferior border and medial surface of zygomatic arch. Insertion: Superficial and Deep portion: Outer aspect of angle of jaw and lower half of ramus of mandible. Key Relations: -The superficial portion is larger and thicker whereas the deep portion is much smaller. -The muscle is crossed superficially by the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy A strong band, four centimetres wide by twelve centimetres long. It attaches from the medial epicondyle, below the abductor tubercle, to the subcutaneous surface of the tibia, a hand’s breadth below the joint line. It has deep and superficial fibres with the deep fibres binding with the joint capsule. Functions Provides static stability to
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
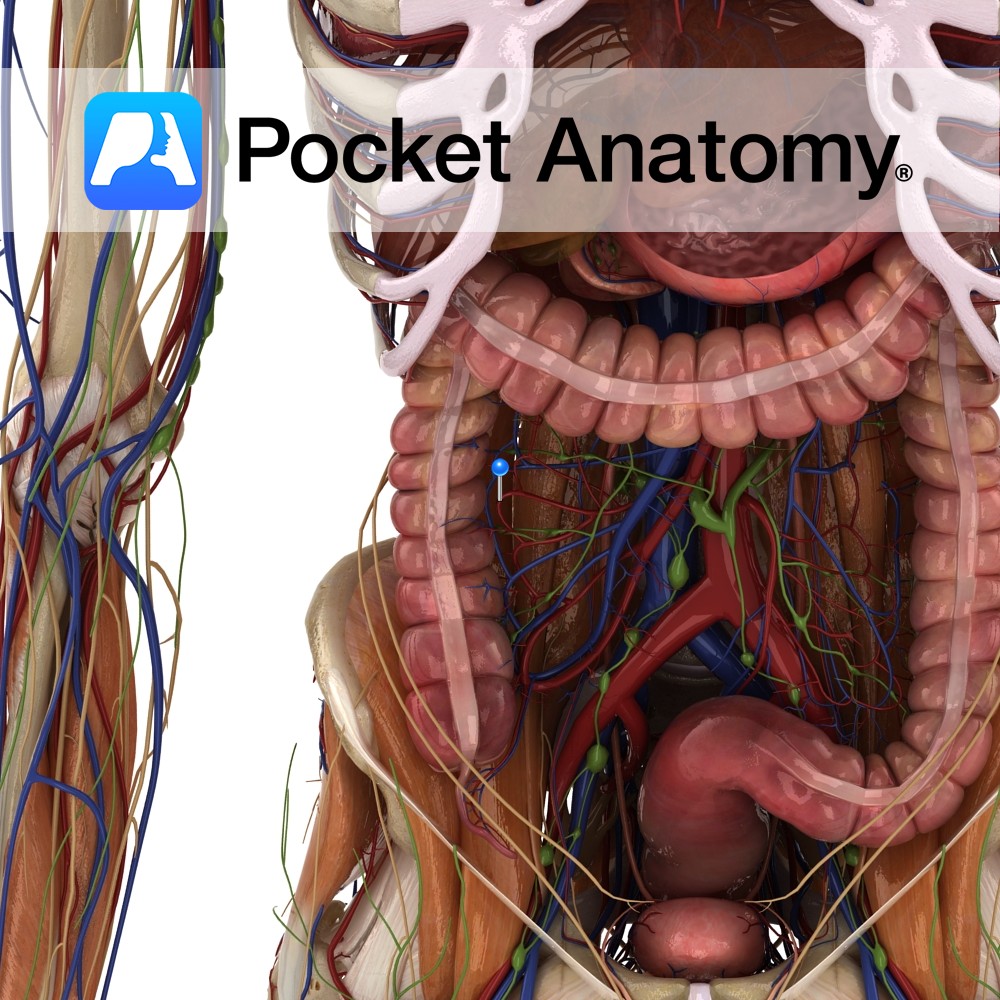
Anatomy Course Connects the superior and inferior mesenteric arteries in the gut. Formed when an anastomosis forms between the right, middle and left colic arteries, as well as the ileocolic artery. It runs in the mesentery with the other vessels of the bowel. Supply Supplies the bowel with blood, in conjunction with the other branches
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Superficial and Deep portion: Inferior border and medial surface of zygomatic arch. Insertion: Superficial and Deep portion: Outer aspect of angle of jaw and lower half of ramus of mandible. Key Relations: -The superficial portion is larger and thicker whereas the deep portion is much smaller. -The muscle is crossed superficially by the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
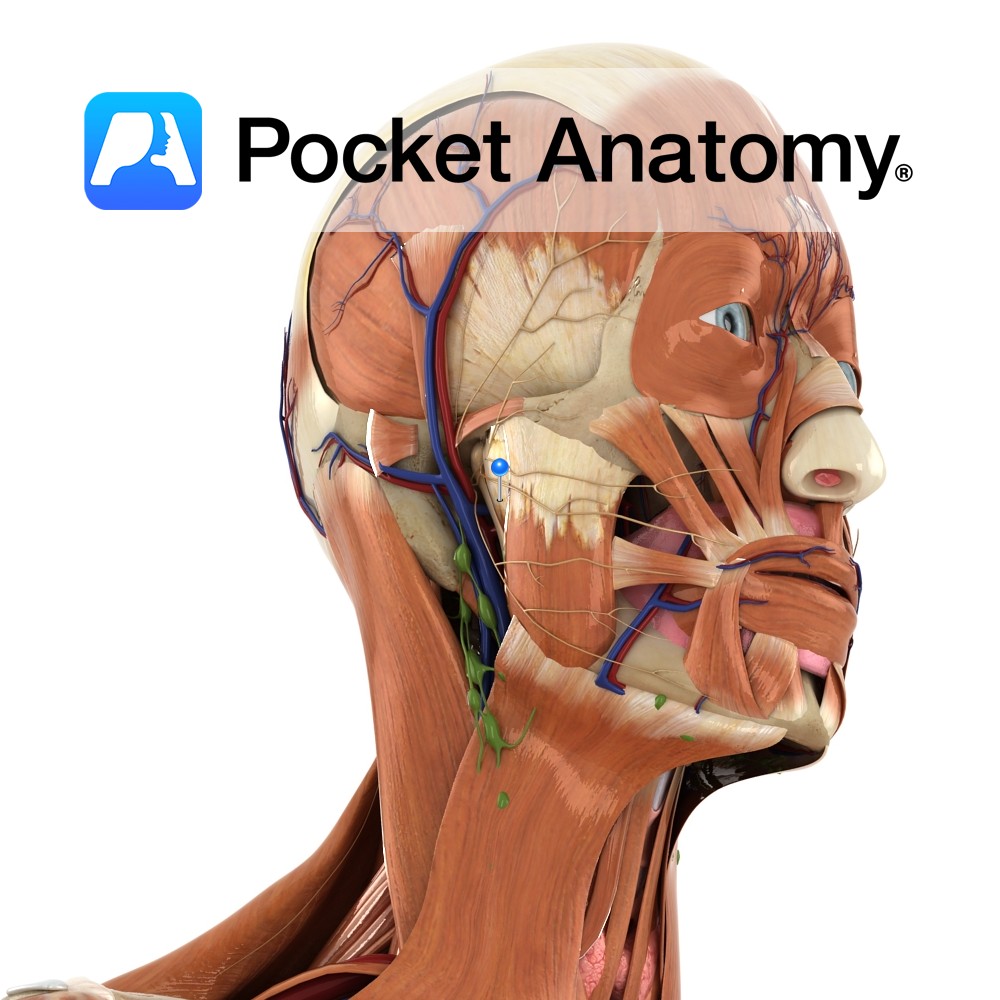
Anatomy Branch of the facial nerve (also known as the seventh cranial nerve). Facial nerve: Has a motor and sensory origin that join together to form the nerve. It passes through the internal auditory meatus through the facial canal and finally exits from the stylomastoid foramen, and into the parotid gland where it divides into
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Concavely curved upper border of ramus, with coronoid process at front end and condylar at back. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
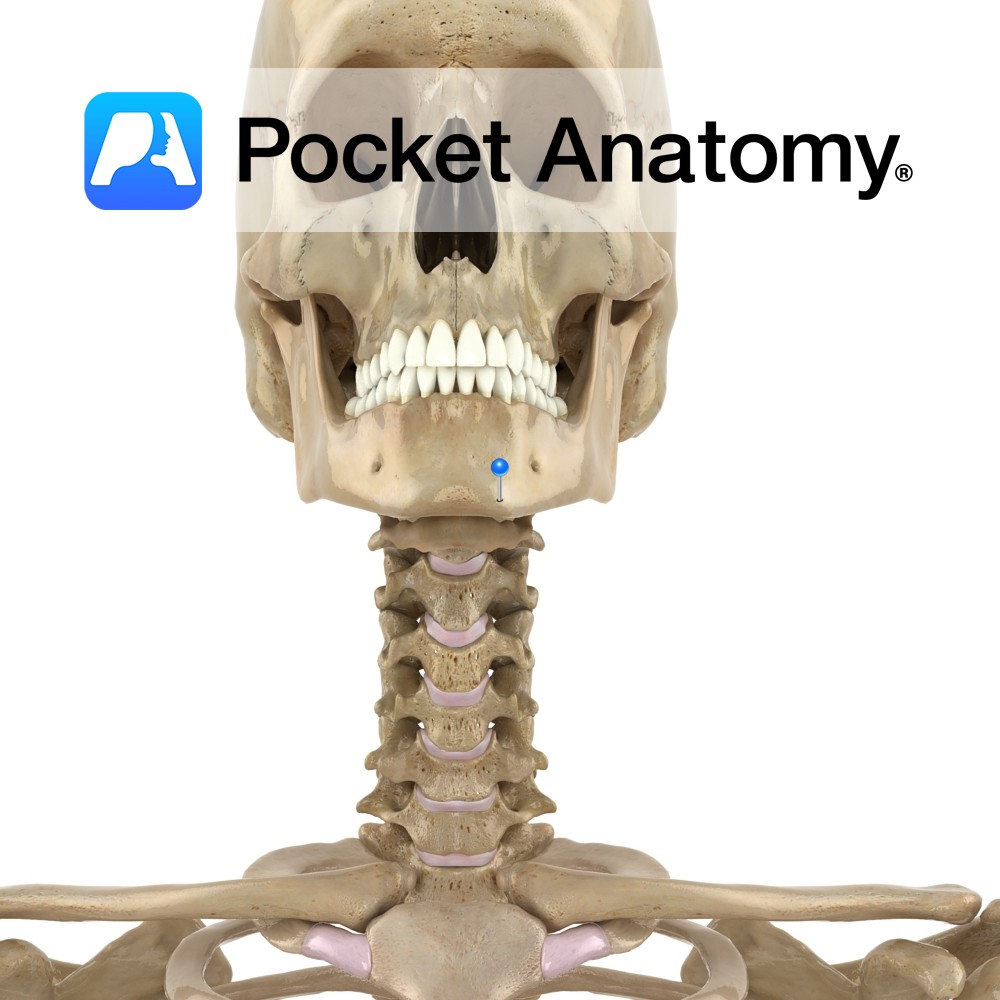
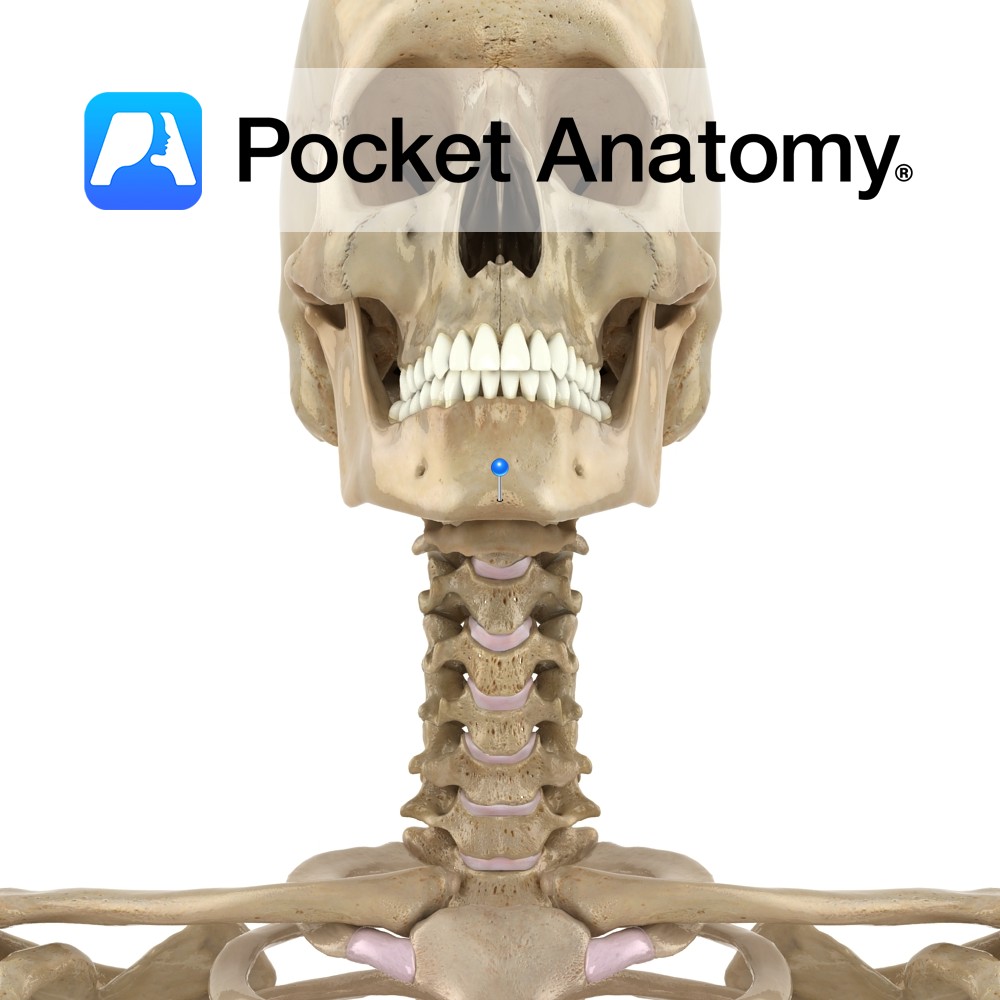
Anatomy The midline symphysis menti marks the fusion of left and right parts of body of mandible. It spreads at its inferior end, forming a forward mental protuberance and on each side, a small mental tubercle. Oblique line ends here. Vignette Chin dimple when there is incomplete fusion of right and left parts of body
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy The midline symphysis menti marks the fusion of left and right parts of body of mandible. It spreads at its inferior end, forming a forward mental protuberance and on each side, a small mental tubercle. Vignette Chin dimple when incomplete fusion of right and left parts of body of mandible (or of muscle). Inherited
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy At back of top of ramus, separated from coronoid process by the mandibular notch. Process consists of neck and head. Articulates with glenoid fossa of temporal bone at the TMJ (tempero-mandibular joint), a synovial joint with an articular disc. Tempero-mandibular ligament attached at lateral extremity of condyle. Vignette TMJ pain common in muscles of
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins


-collateral-ligament.jpg)