PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
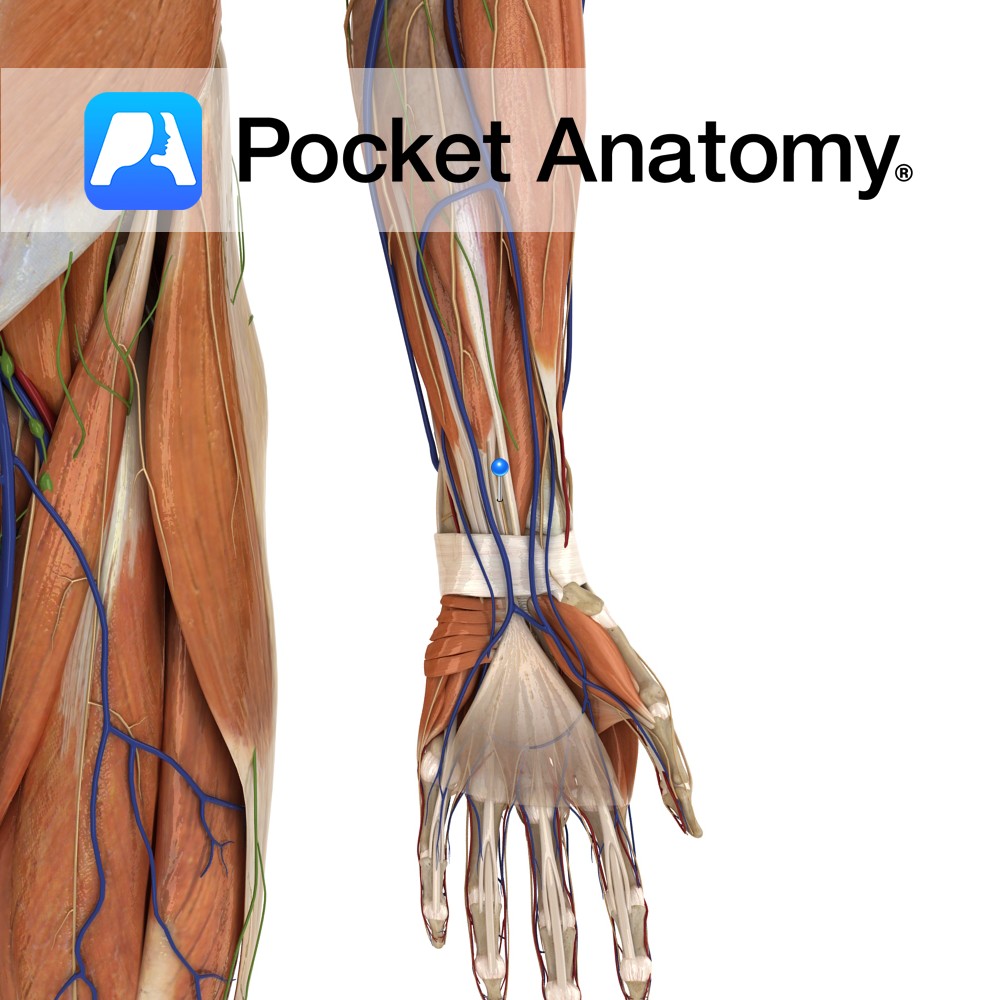
Anatomy Course Arises anterior to the axillary artery from the medial and lateral cords of the brachial plexus. It passes through the arm in the anterior compartment on the medial side between the biceps brachii and the brachialis muscle. It then crosses over the medial epicondyle of the humerus. It then enters the forearm from
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
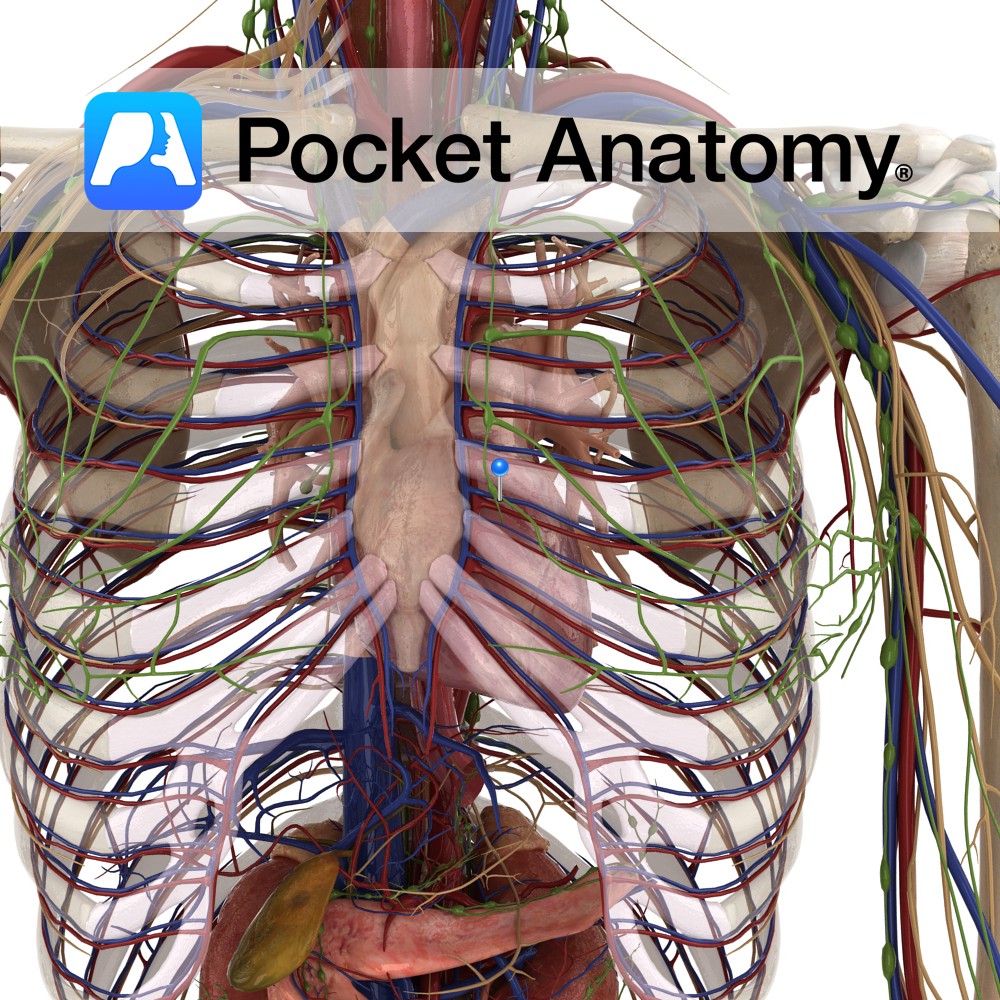
Anatomy Comprise Superior and Inferior Mediastinal Nodes. Superior drain from upper chest and neck next to esophagus and trachea, down to root/hilum lung. Inferior drain from level of hilum to lower lobes lungs. Superficial chest structures (skin, breast, shoulder muscles) drain to Axillary Nodes. Deep thorax structures drain to Mediastinal and Bronchopulmonary Nodes. Interested in
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
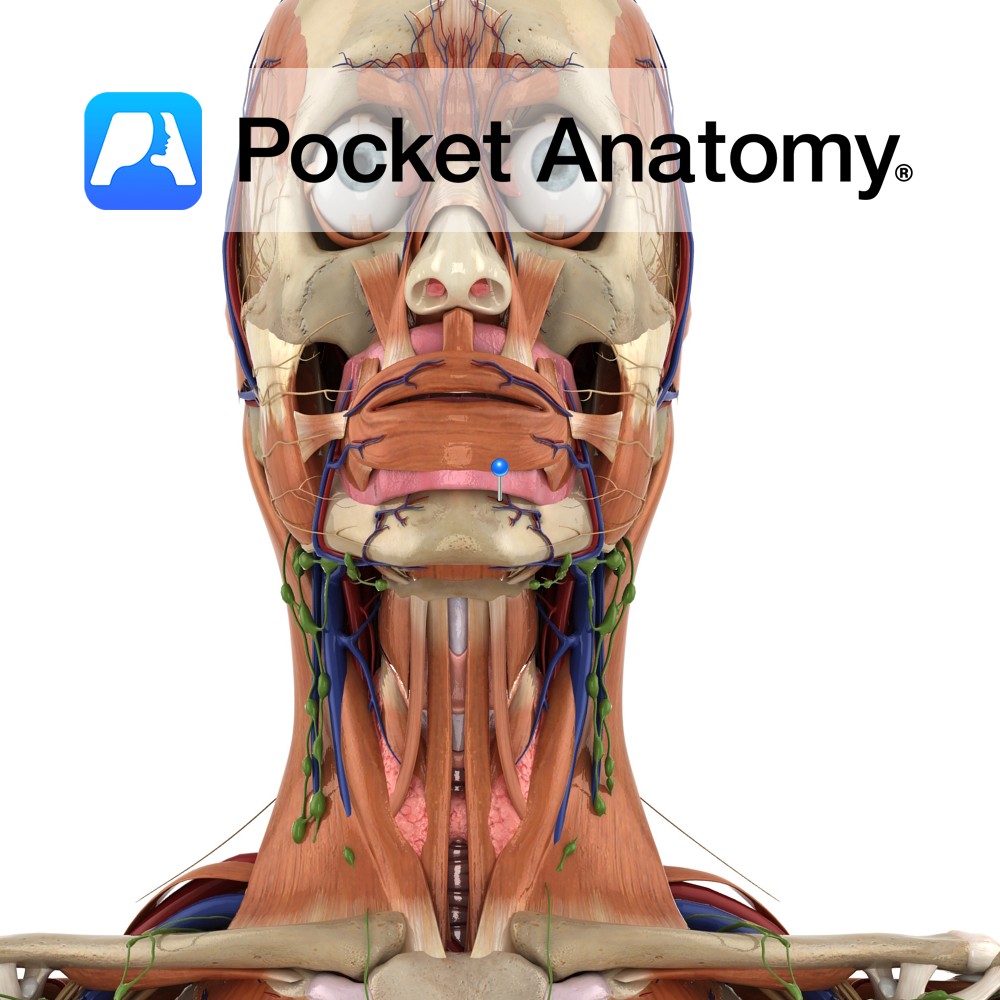
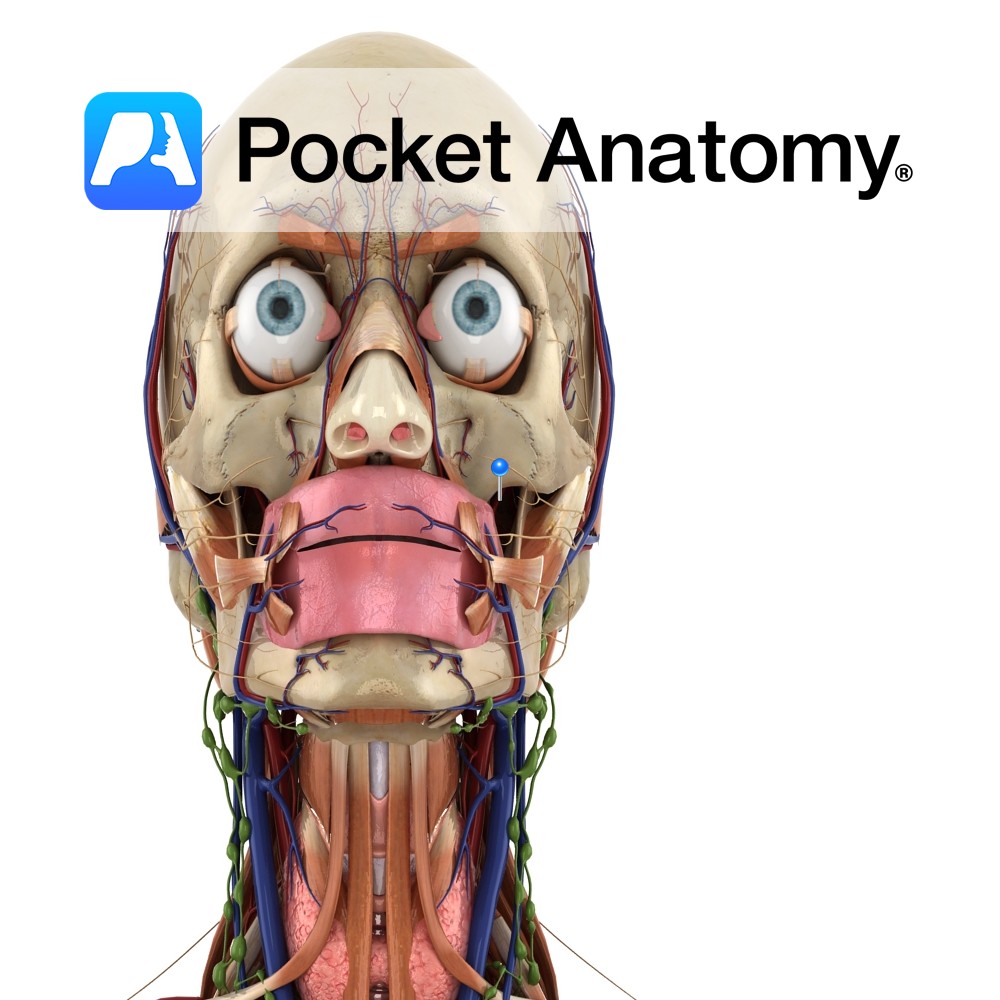
Anatomy Course Branch of the inferior alveolar artery which travels with the mental nerve and mental vein through the mental foramen of the mandible. Supply Branches supply both the molar and premolar teeth, as well as related gingiva. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
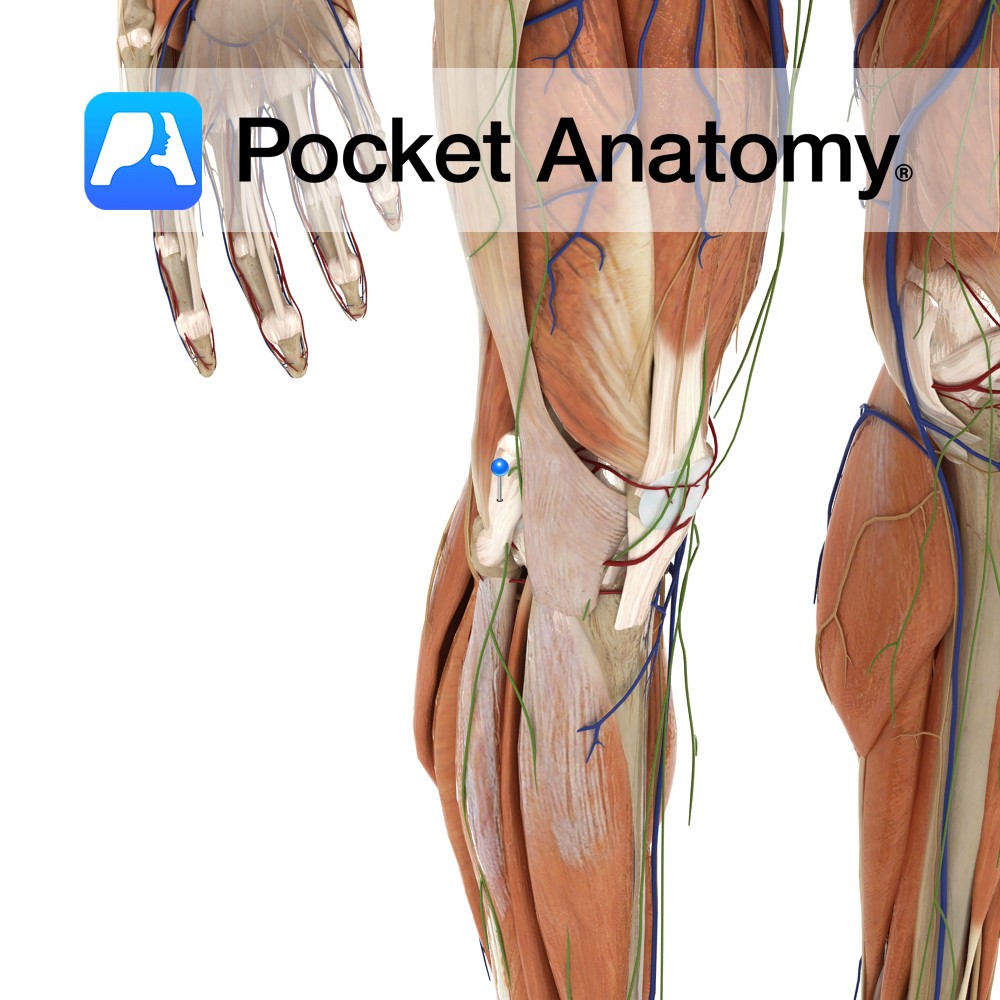
Supply Motor supply to the quadriceps femoris as well as many other muscles in the thigh. Cutaneous supply of the anterior and lateral thigh. Anatomy There are two anterior cutaneous branches of the femoral nerve: Intermediate femoral cutaneous nerve and Medial femoral cutaneous nerve. Course The femoral nerve is the largest branch of the lumbar
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course A branch of the common tibular nerve. It runs down the posteromedial aspect of the calf. Clinical Damage to the nerve will result in a loss of sensation in the skin on the anterior and posterior portions of the medial calf. Supply Provides sensory innervation to the skin on some of the anterior
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
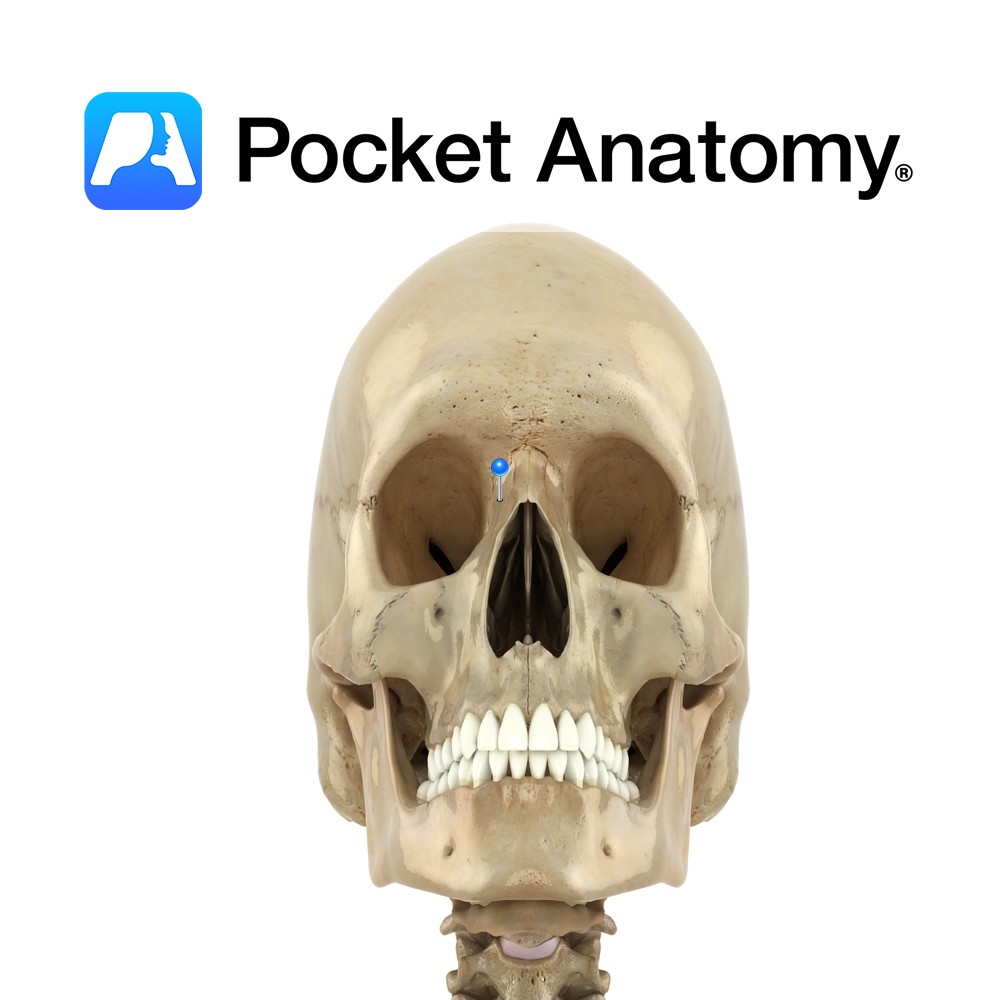
Anatomy Paired. One of the four processes of maxilla bone. Also called nasal process. Strong plate pointing up, in and back from body of maxilla; forms part of lateral wall of nasal cavity. Articulates above with frontal bone, and in front with nasal bone. Upper inner surface articulates with ethmoid bone. Interested in taking our
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
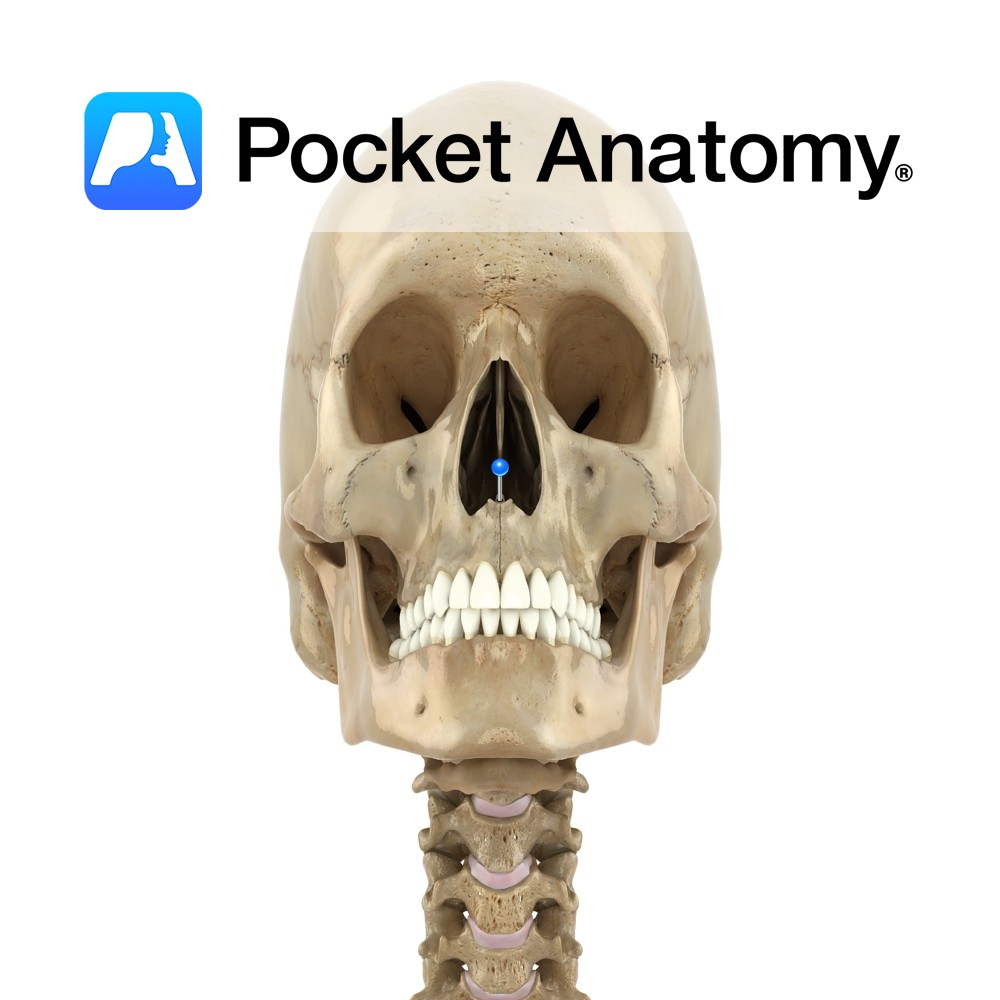
Anatomy The pointed lower ends (left and right) of the medial concave nasal notches of the frontal processes of the maxillae (4 processes; zygomatic, frontal, alveolar, palatine), meet and form this spine. Supports the lower back part of the septal cartilage. Vignette Can be palpated (felt) at junction of bottom of nose and philtrum (midline
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
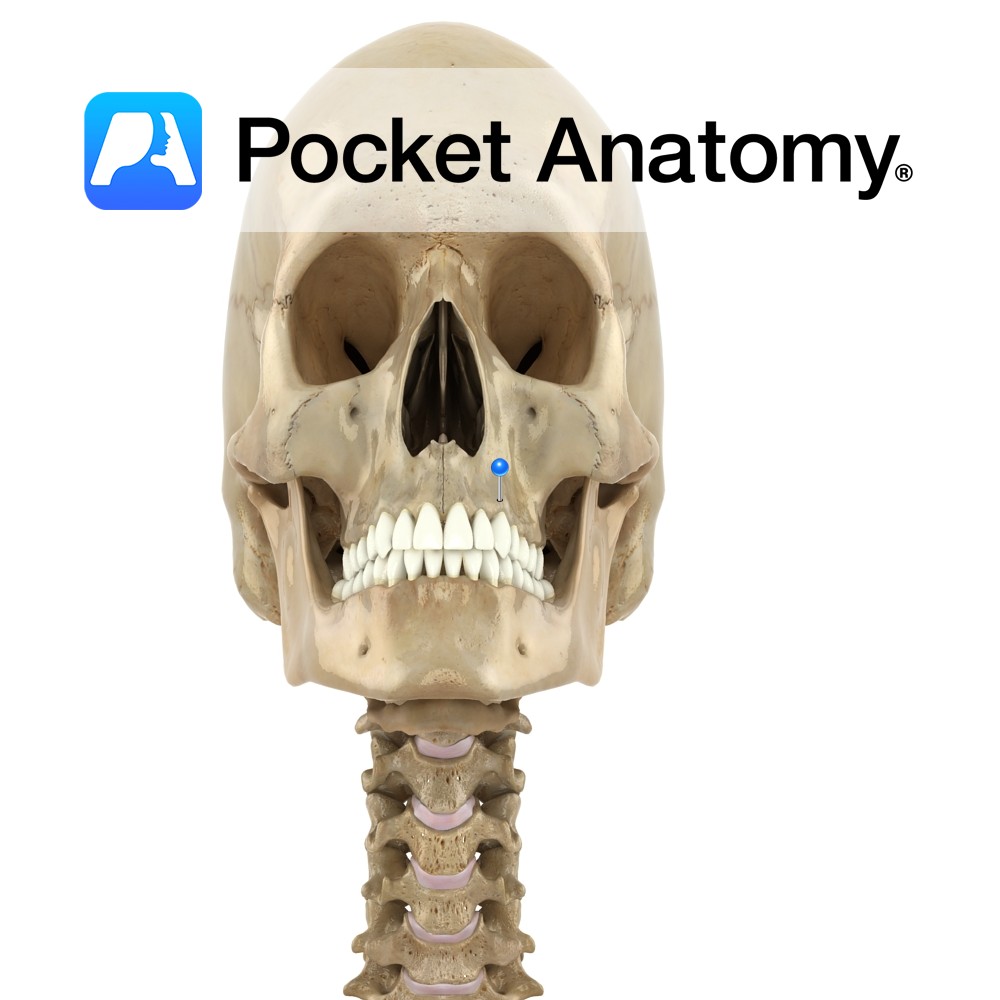
Anatomy Thick ridge of spongy bone, with cavities (tooth sockets) for 16 upper teeth (8×2). Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
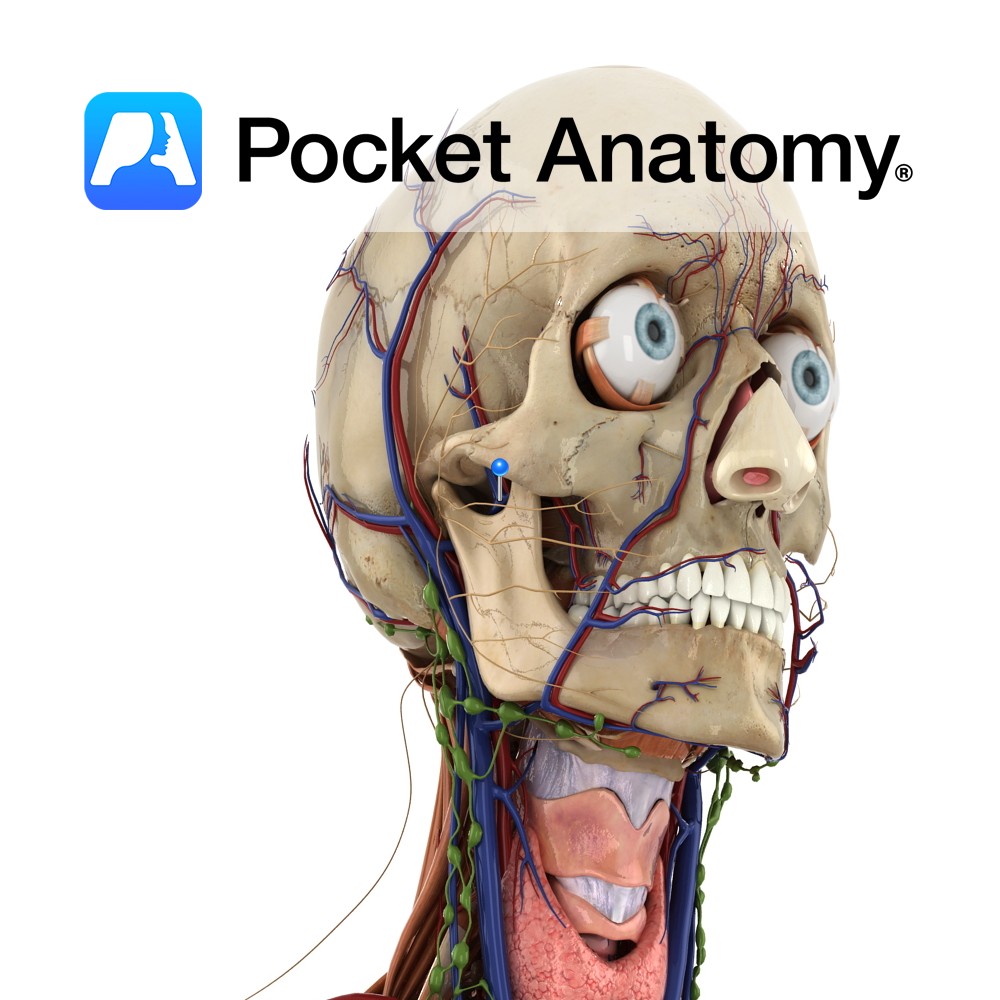
Anatomy Course The final vein of the pterygoid plexus. It is a short vein and it flows into the retromandibular vein. Eventually it flows into the external carotid vein. Drain Drains the deep structures of the face. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course A branch of the external carotid artery. It begins just behind the neck of the mandible, and passes forward just beneath the bone and then through the infratemporal fossa. The artery then enters the pterygopalatine fossa by passing through the pterygomaxillary fissure. Once in the pterygopalatine fossa it splits into several terminal branches.
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins