PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
Anatomy Articulates up with capitate, out with index metacarpal, in with ring metacarpal (1st thumb, 2nd index, 3rd middle, 4th ring, 5th little), down with proximal phalanx (3rd MCP). Clinical MCP is a knuckle (4 each hand, as thumb MCP not ordinarily included). Common sites for fractures and other fist injuries. Interested in taking our
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
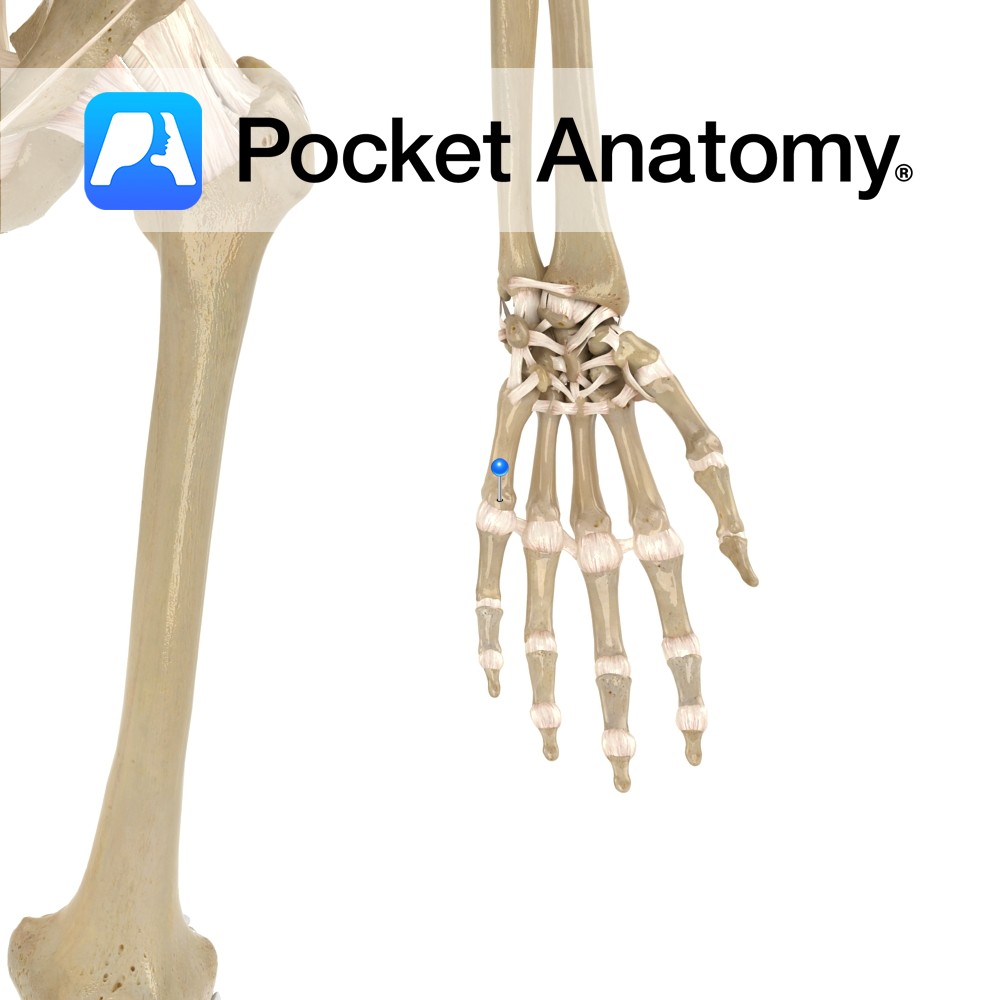
Anatomy Articulates up with hamate, out/laterally with 4th metacarpal, down with proximal phalanx (5th MCP). Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Motion These are the joints lying between the distal heads of the metacarpals and the proximal phalanges of the digits. They are synovial condylar joints. They have a wide range of motion, including: flexion, extension, abduction and adduction. The flexion component of these is the most extensive, commonly terminated by a grasped object. Stability Articular
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
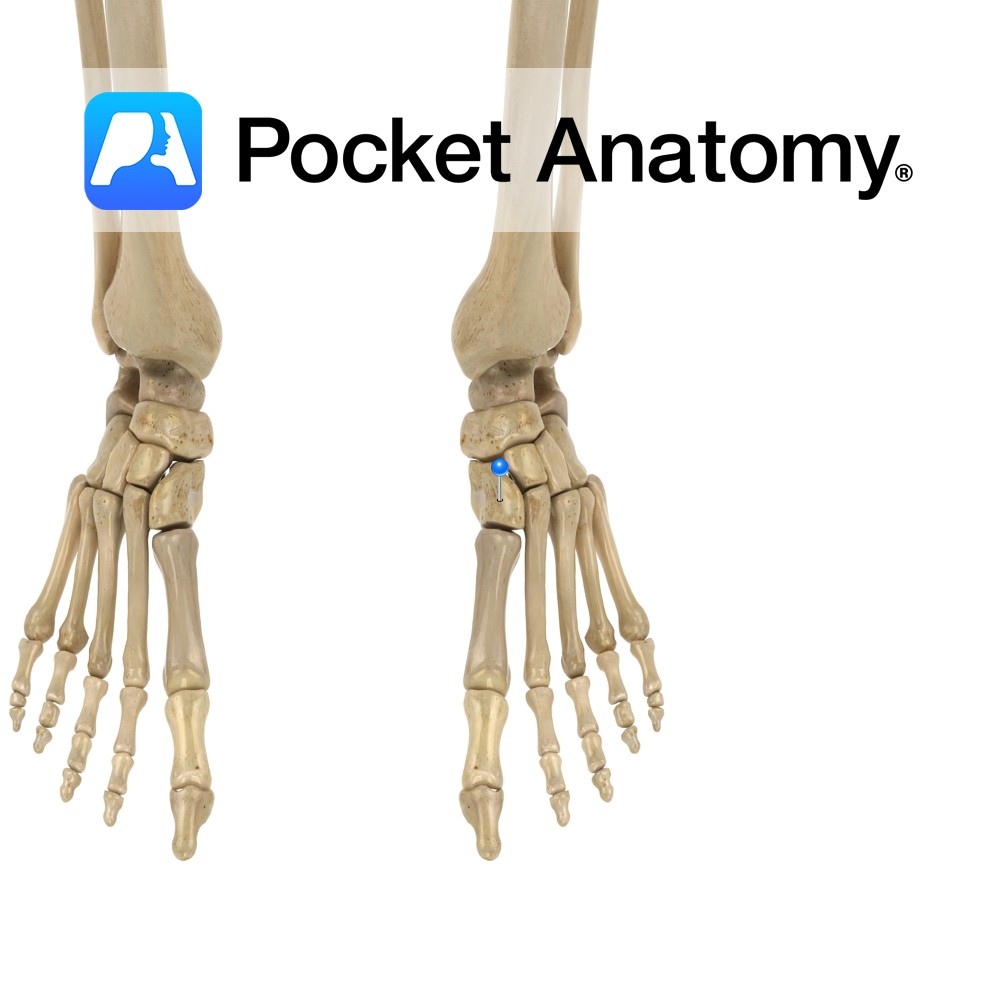
Anatomy Thickest shortest metatarsal, on medial edge foot behind/proximal to big toe, articulates proximally with medial (1st) cuneiform, sometimes out (from base) with 2nd metatarsal, distally with 1st proximal phalanx and below (from head) with sesamoid bones. Tibialis anterior, peroneus longus attached. Vignette Metatarsal bones are prismoid, thicker at proximal end (base/ posterior extremity/tarsal end),
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Articulates proximally with lateral (3rd) cuneiform, out with 4th and in with 2nd metatarsals (from base), distally with 2nd proximal phalanx. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
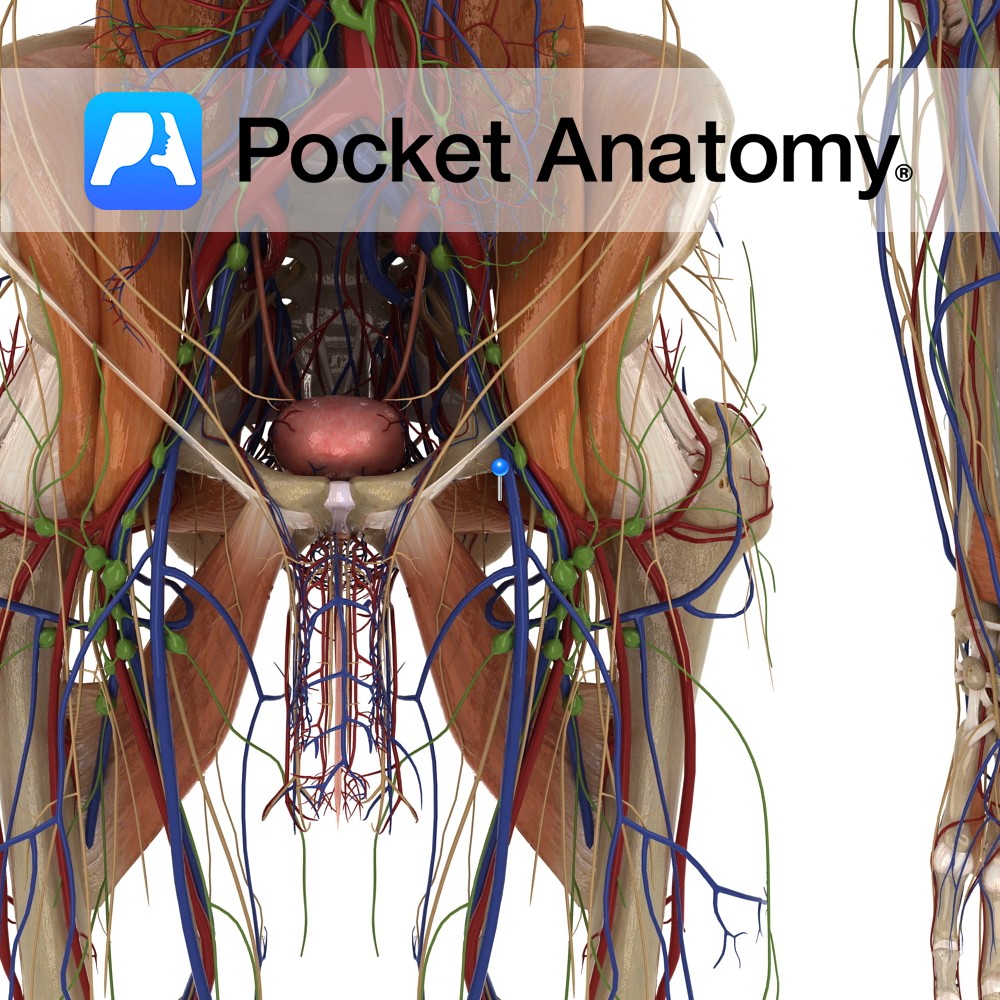
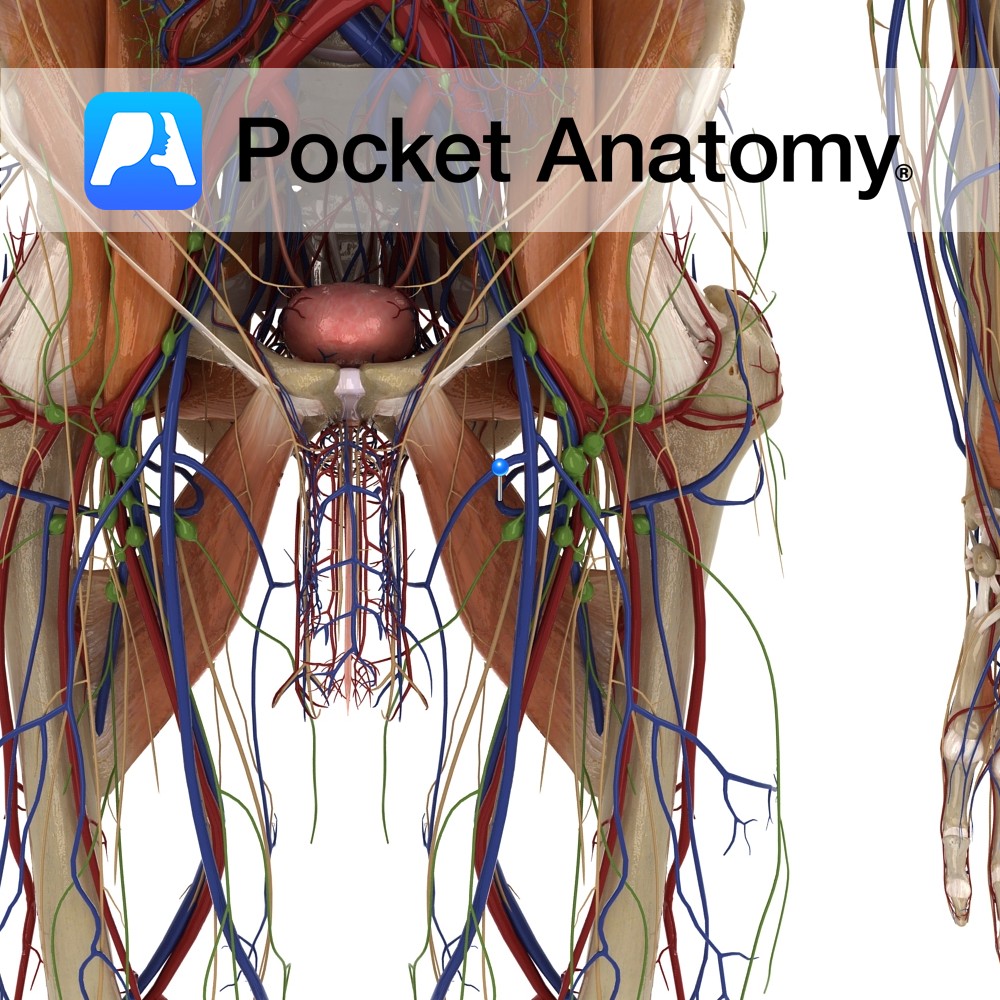
Anatomy Course Originates from the deep femoral artery. It first passes between the iliopsoas and pectineus muscles, and then passes between the obturator externus and adductor brevis muscles. Finally, it passes above the margin of the adductor magnus to travel medially around the neck of the femur. It then divides into two major branches deep
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Begins at the neck of the femur and medially travels above the margin of the adductor magnus. It passes between the obturator externus and adductor brevis muscles, and then between the iliopsoas and pectineus muscle. It drains into the deep femoral vein. Drain Drains the head and neck of the femur. Interested in
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Tarsal bone, wedge-shaped, largest of the cuneiforms, articulates forward with 1st (big toe) and 2nd metatarsals, laterally/out with middle/intermediate cuneiform, proximally with navicular. Vignette Hindfoot; talus, calcaneus. Midfoot; cuboid, navicular, cuneiforms (medial, intermediate, lateral). Forefoot; metatarsals, phalanges. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
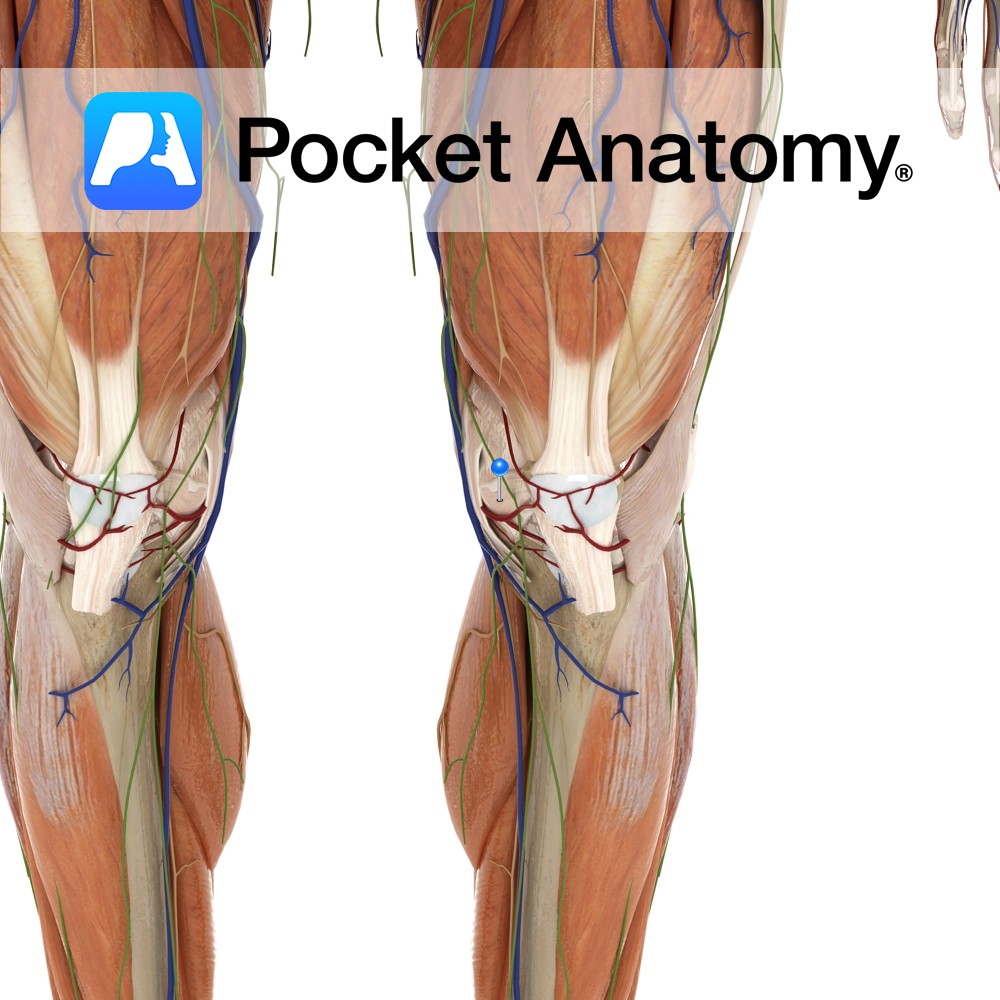
Anatomy Attaches from the inferior medial margins of the patella to the inferior margin of the medial tibial condyle. It also blends with the patella ligament. Functions Provides static stability to the patella. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
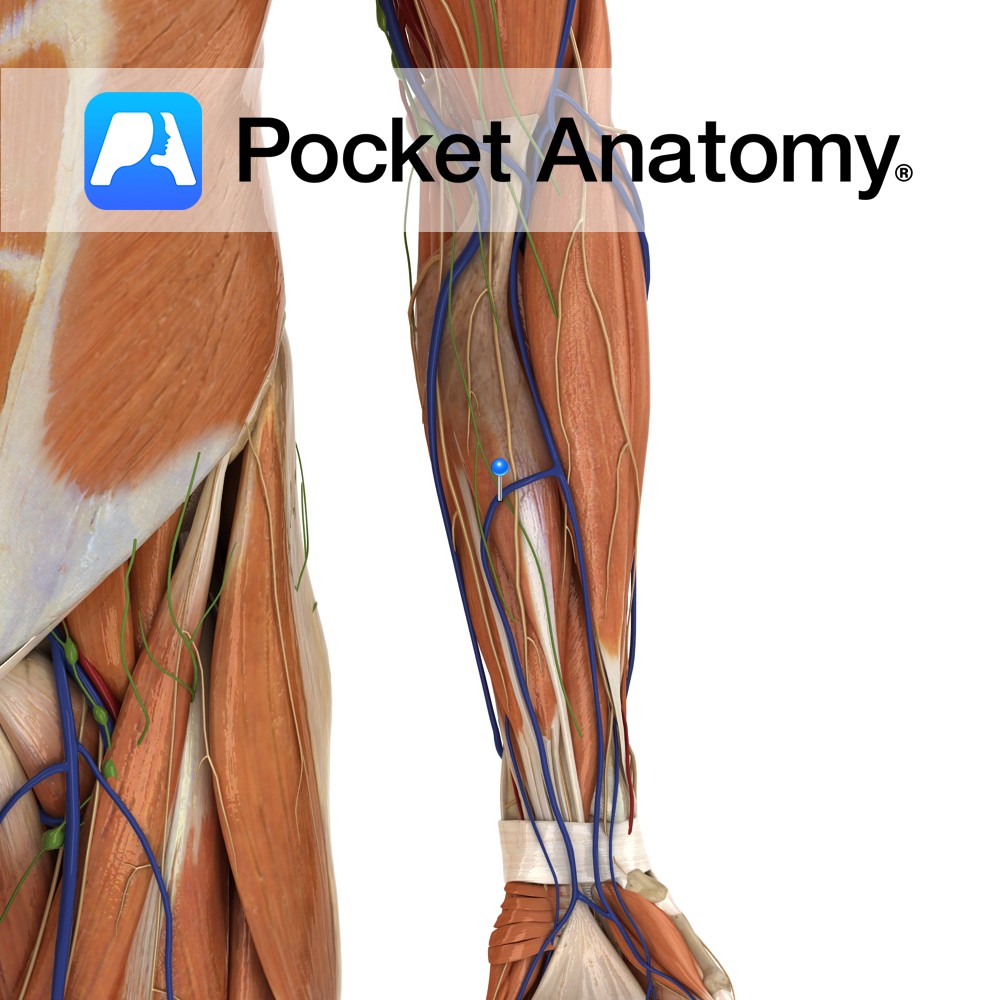
Anatomy Course A superficial vein that drains the palmar network of the hand. It ascends on the ulnar side of the forearm to drain into the median cubital vein. Drain Drains the palmar surface of the hand. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)