PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
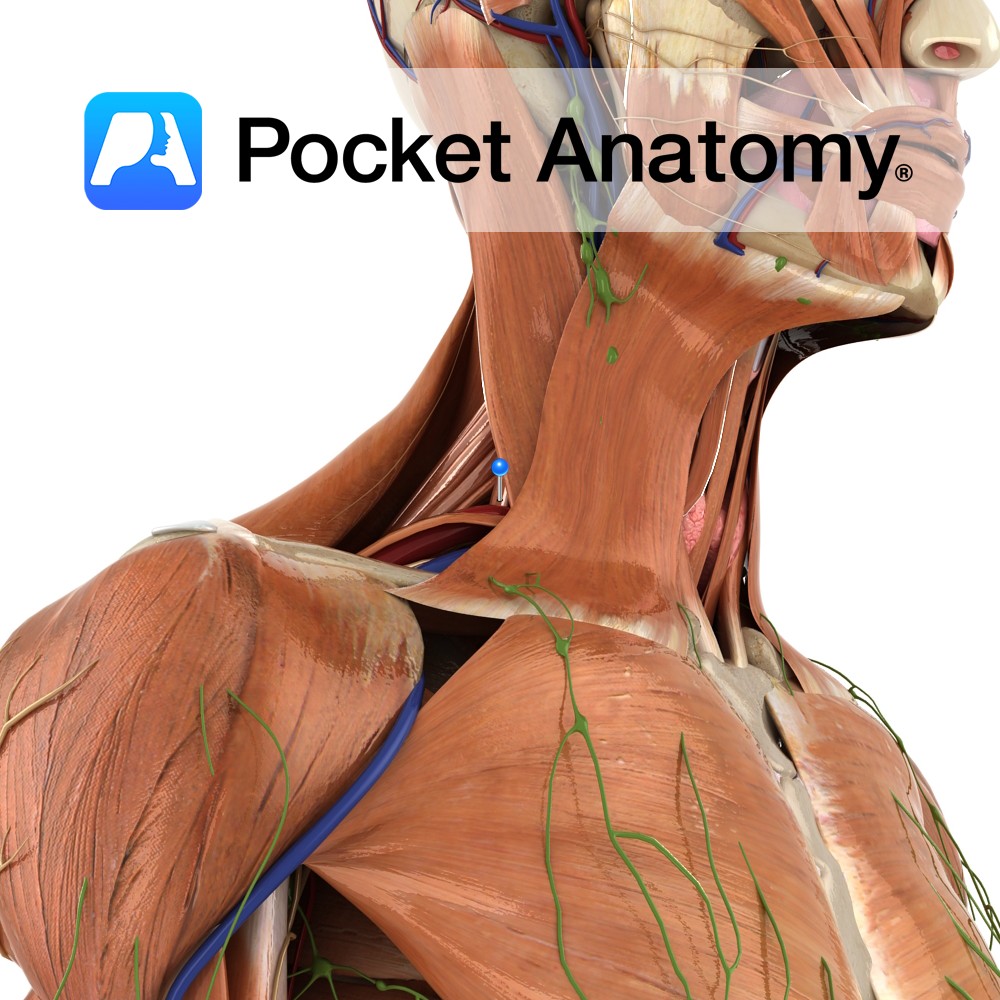
Anatomy Origin: Transverse processes of C2 to C7. Insertion: Upper surface of the 1st rib, posterior to the groove for the subclavian artery. Key Relations: -Largest and longest of the scalenes. -The brachial plexus and the subclavian artery pass between the anterior scalene and the middle scalene. Functions -Elevates the 1st rib. -Rotates the neck
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Entrance to alimentary tract, a mucomuscular tube from mouth to anus (sight, smell, hunger, anticipation have pre-ingestion roles); oval cavity lower part of head; anterior – lips, lateral – cheeks, inferior – tongue, floor of mouth, superior – hard palate, posterior – oropharynx (starts above at junction hard/soft palates, below behind circumvallate papillae tongue);
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
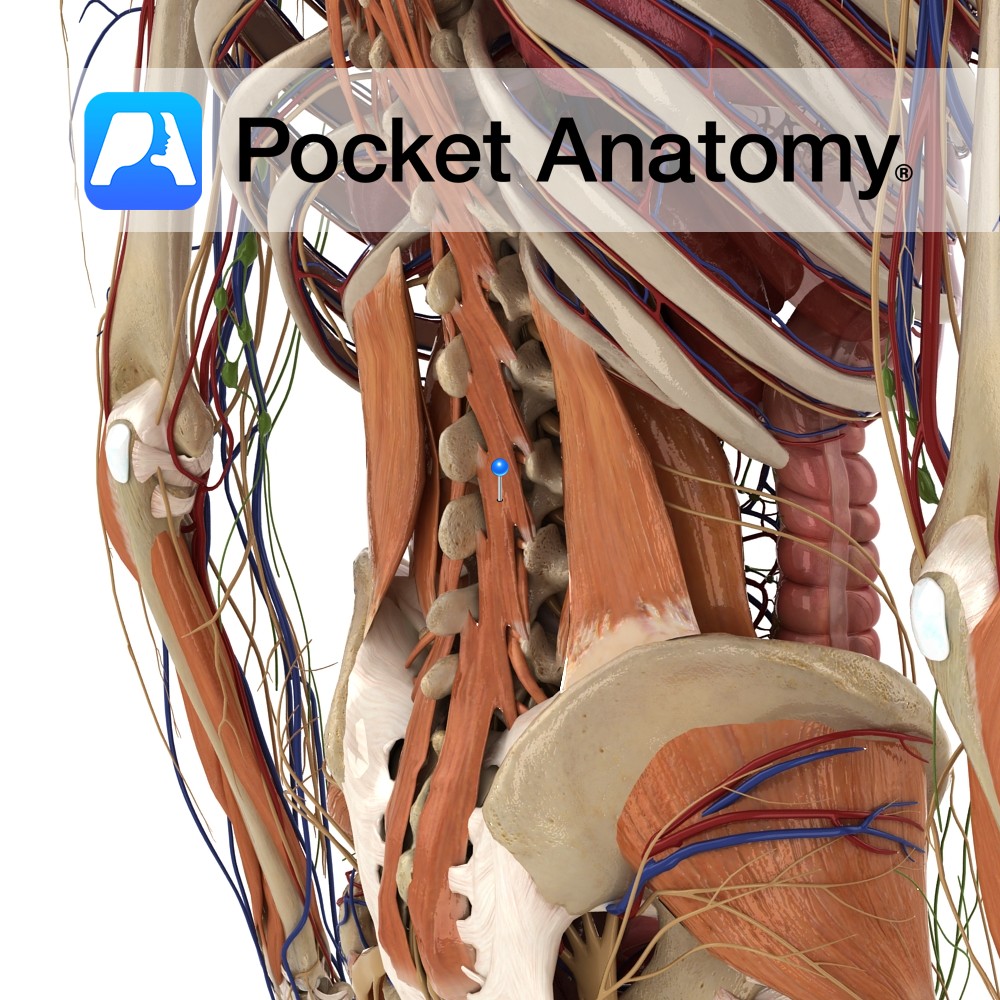
Anatomy One of the intrinsic muscles of the back. Origin: Fasiculi of sacrum, origin of erector spine, posterior superior iliac spine, mamillary processes of lumbar vertebrae, transverse processes of thoracic vertebrae and articular processes of lower four cervical vertebrae. Insertion: Whole length of spinous processes of one of the vertebrae above. Key Relations: Deep to
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course A terminal branch of the lateral cord of the brachial plexus. It exits the axilla, piercing the coracobrachialis muscle, to pass between the biceps brachii and brachialis muscles in the anterior compartment of the arm. It continues distally towards the elbow, and crosses into the forearm over the lateral epicondyle of the humerus.
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
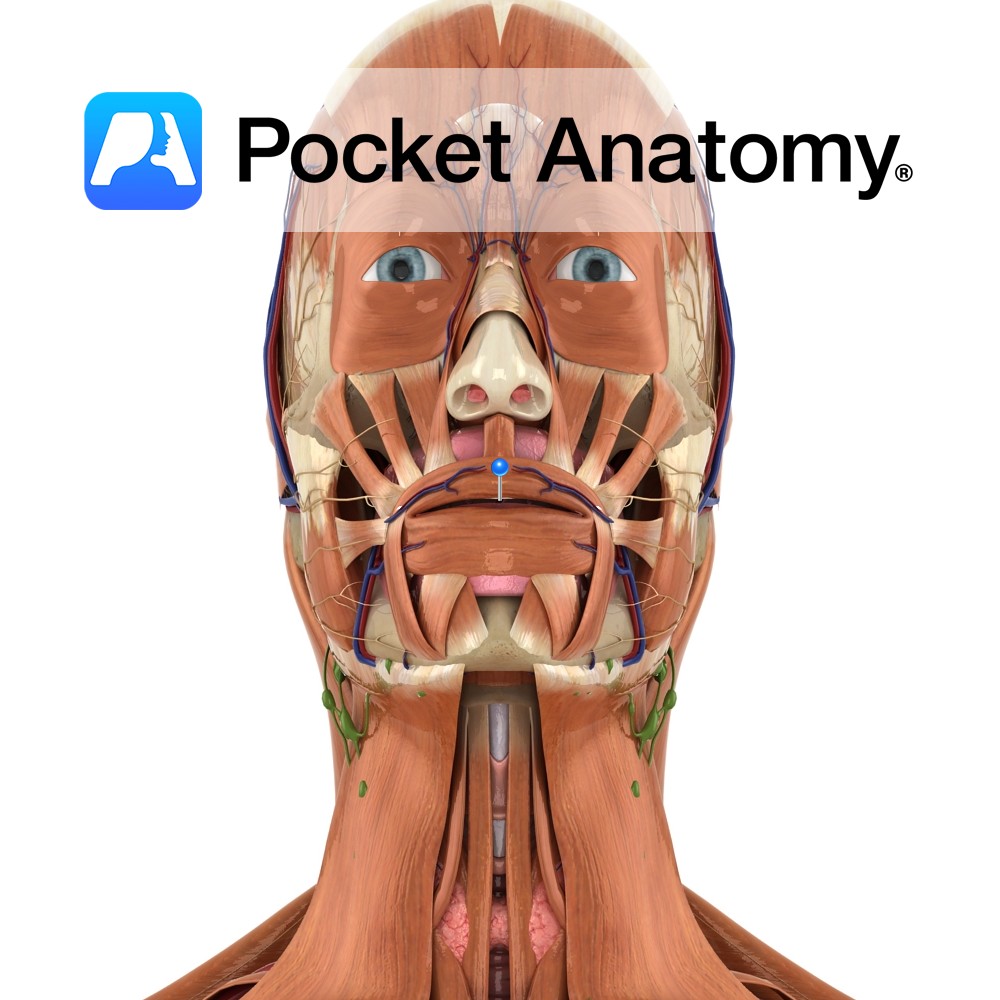
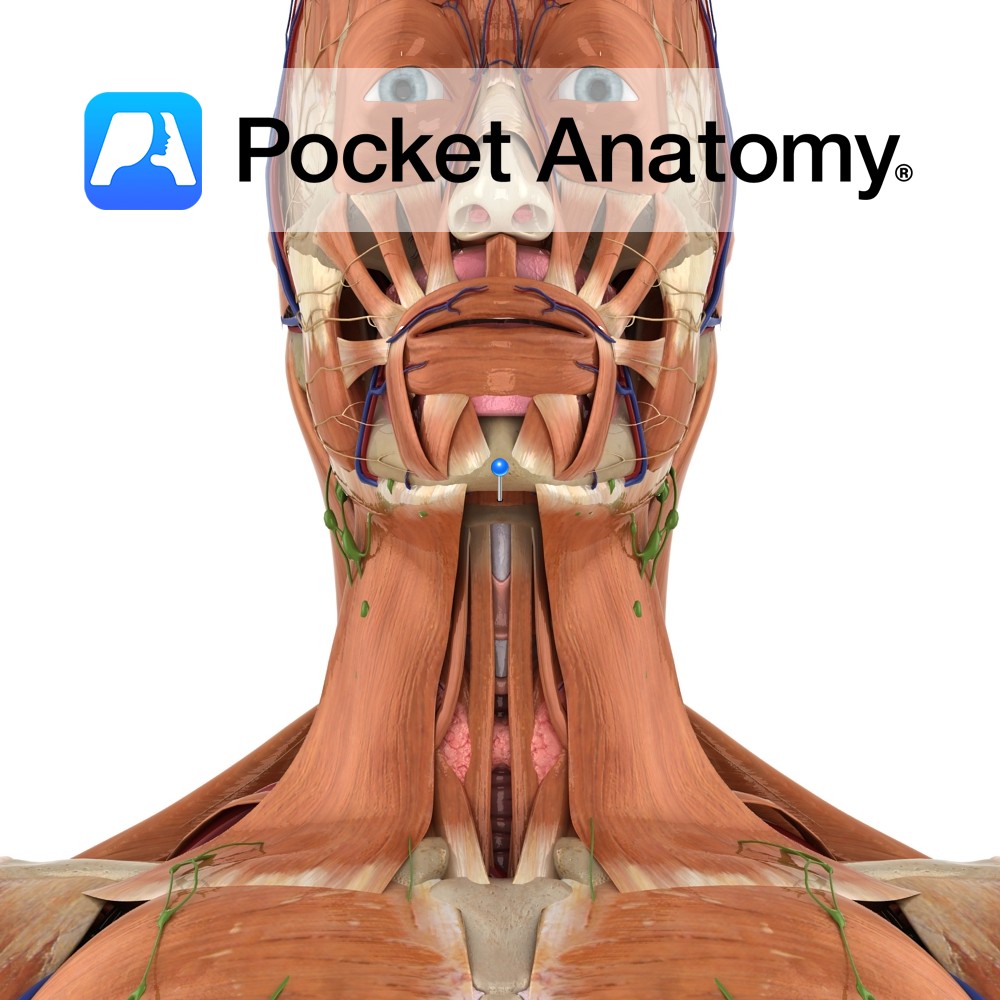
Anatomy Origin: Mylohyoid line on the mandible. Insertion: Body of the hyoid bone and fibres from the muscle on the opposite side. Key Relations: -Is one of the suprahyoid muscles lying in the anterior triangle of the neck. -Forms the floor of the oral cavity with its partner from the opposite side. -Is immediately superior
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
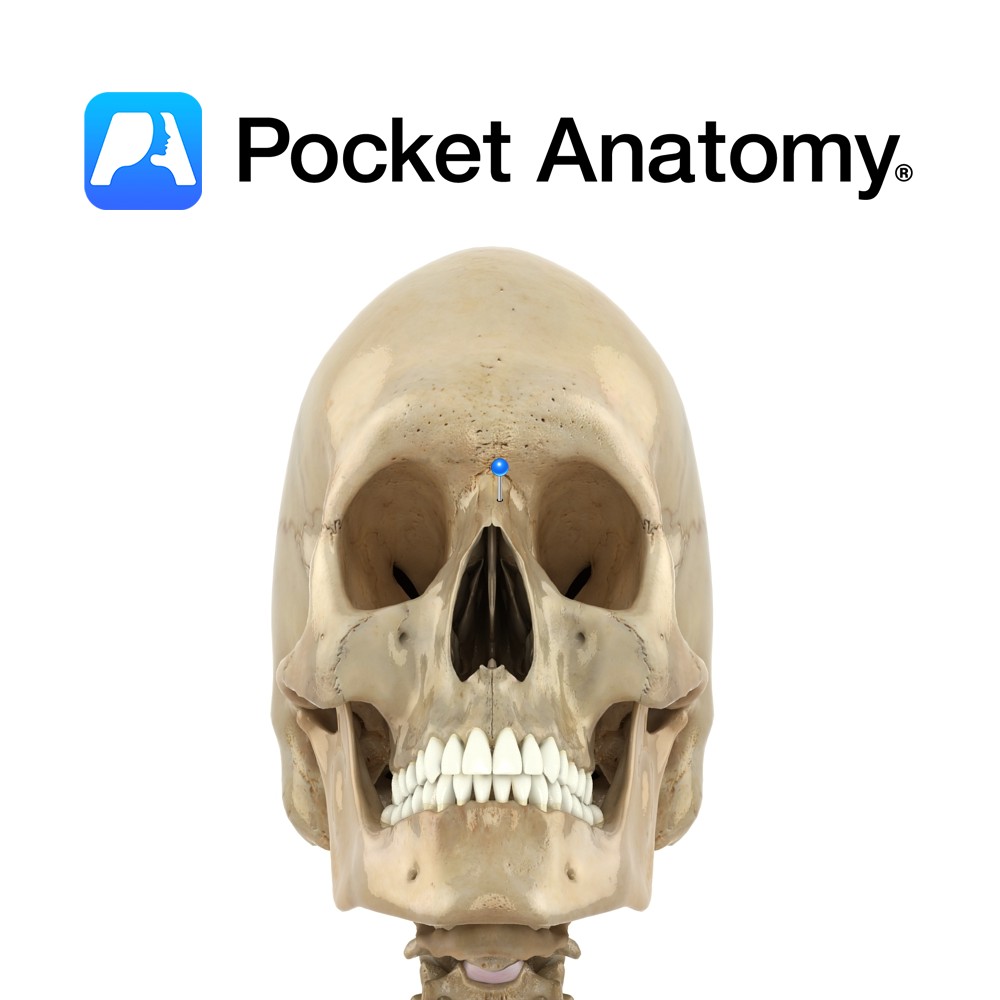
Anatomy Paired, short, oblong. Right and left articulate to form bridge of nose. A crest underneath joint forms part of nasal septum and articulates with spine of frontal, perpendicular plate of ethmoid, and septal cartilage. Each nasal bone articulates with frontal at upper edge, and frontal process of maxilla at lateral edge. Lateral cartilage of
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Quadrilateral in shape and thicker at its margins than the centre. It attaches to palatine process of the maxilla bone posterosuperiorly, the vomer bone posteroinferiorly, anterosuperiorly it is continuous with the anterior margin of the lateral cartilages and anteroinferiorly connects to the medial crura of the greater alar cartilages by fibrous tissue. Functions Forms
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
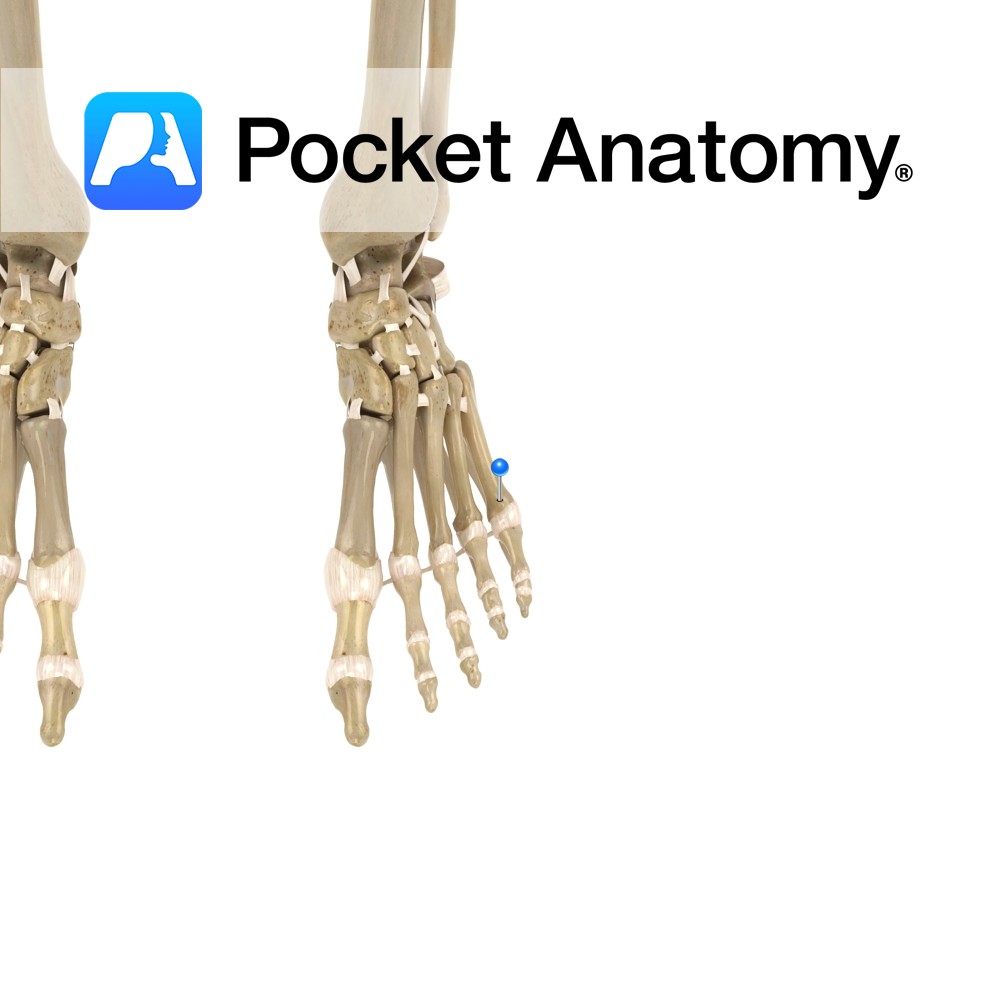
Anatomy On lateral edge foot behind little toe, articulates proximally with cuboid and in (from base) with 4th metatarsal, distally with 5th proximal phalanx. Vignette Metatarsal – tarsal articulations; 1st – medial (1st) cuneiform, 2nd – all 3 cuneiforms, 3rd – lateral (3rd) cuneiform, 4th – lateral cuneiform and cuboid, 5th – cuboid. Interested in
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Motion The metatarsophalangeal joints are ellipsoid type synovial joints formed between the sphere shaped heads of the metatarsal bones and the bases of the proximal phalanges of the toes.The joints allow flexion and extension with restricted abduction, adduction, rotation and circumduction. Stability The fibrous capsule surrounding the joint plays a role in its stability. Ligaments
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
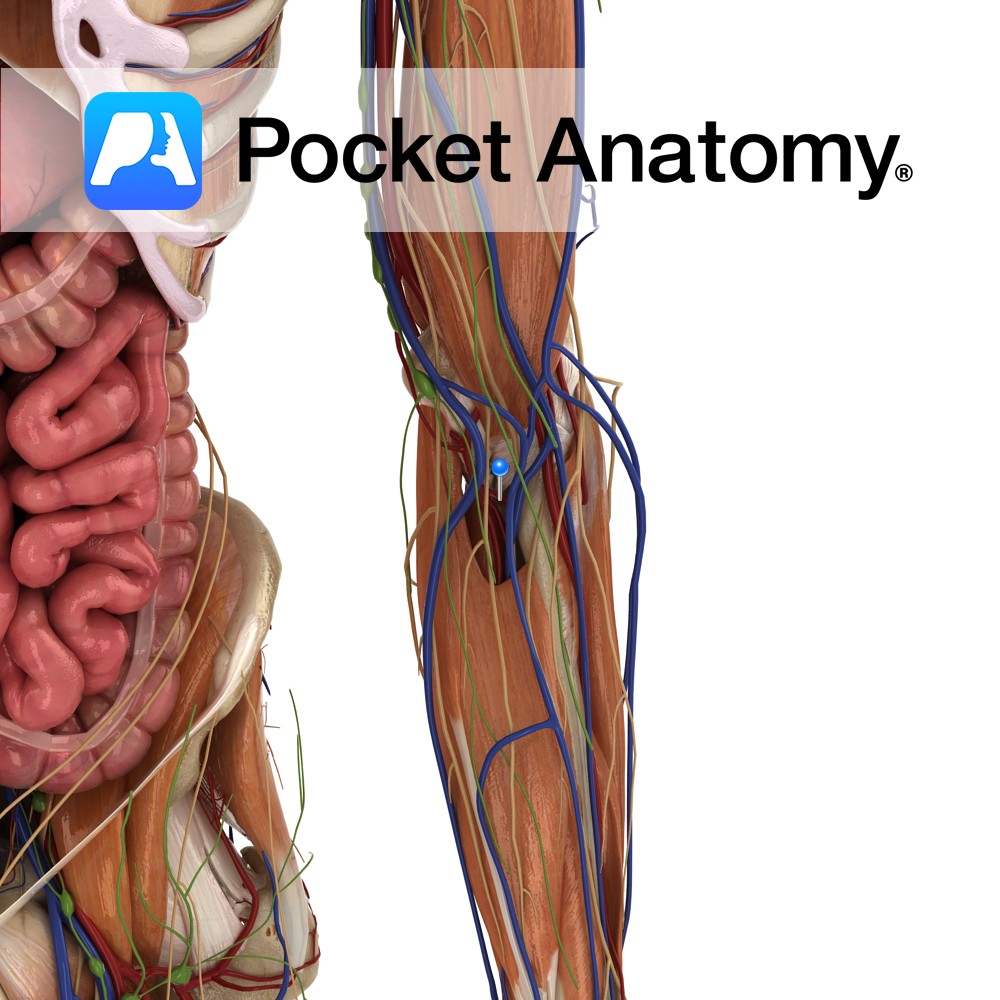
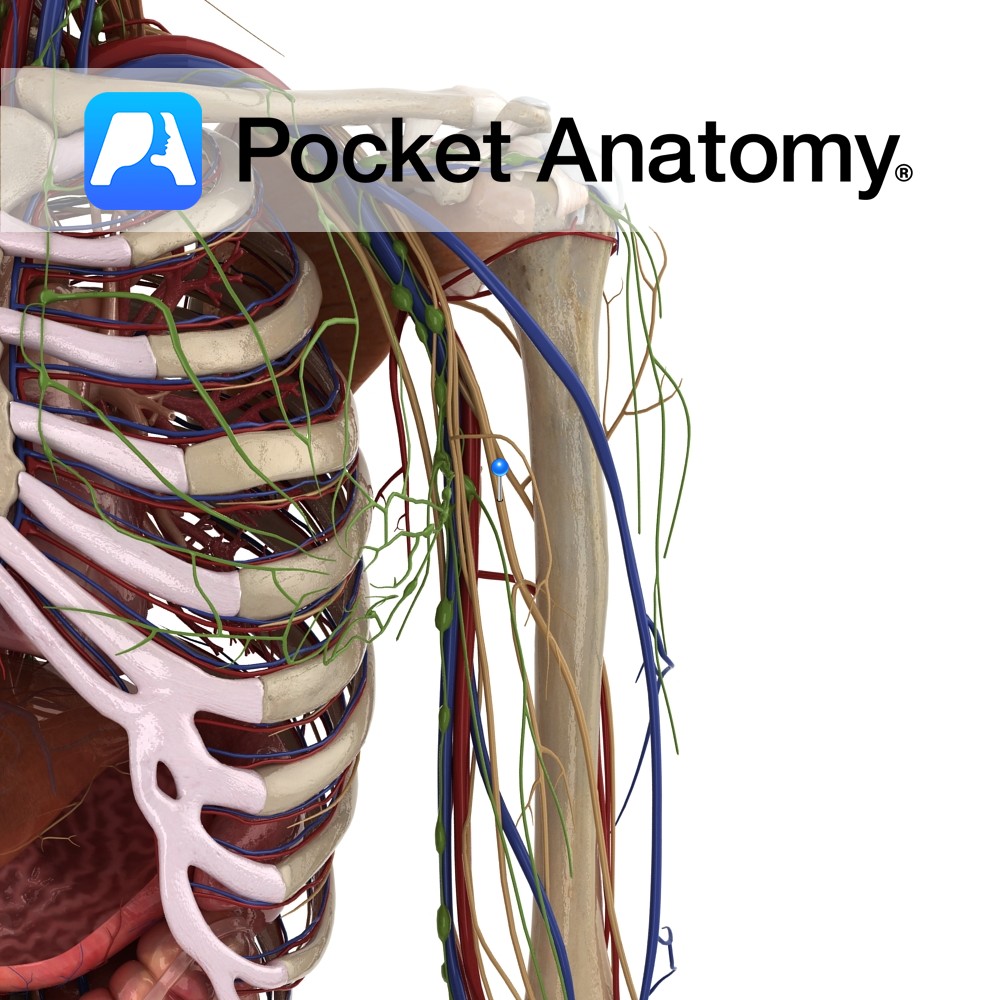
Anatomy Course Branches from the deep brachial artery in the arm, about halfway down the humerus, before the deep brachial artery leaves the radial groove. It then descends to the elbow joint on the posterior aspect of the humerus until it reaches the elbow joint, where it anastomoses with the interosseous recurrent artery. Supply Contributes
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins

.jpg)