PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
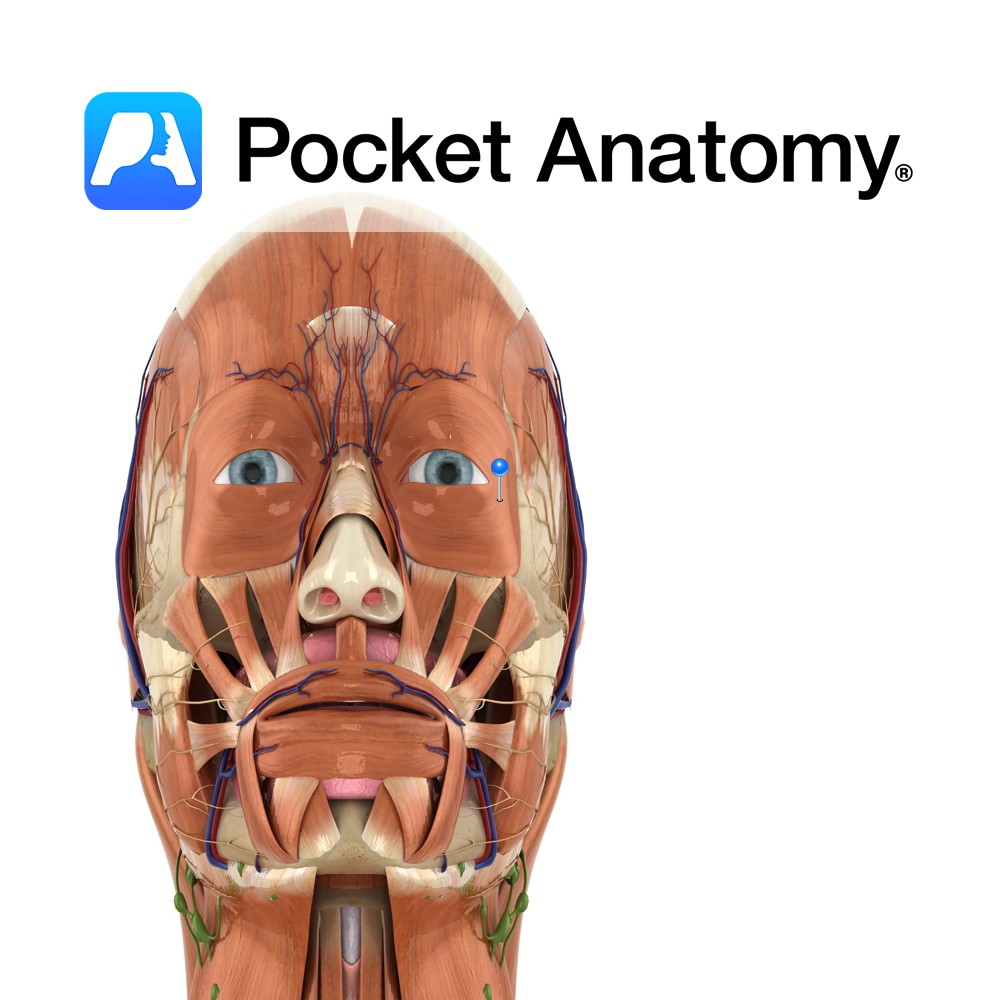
Anatomy Origin: Optic nerve fibers are the axons of the cells in the ganglionic layer of the retina. Structure: The three sheaths surrounding the nerve are continuous with the meninges. The outermost sheath originates from the dura mater and merges with the sclera of the eyeball, the middle sheath is continuous with the arachnoid mater
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Palebral part: Medial palpebral ligament. Orbital part: Nasal portion of frontal bone, frontal process of maxilla, medial palebral ligament. Insertion: Palebral part: Lateral palebral raphe at outer corner of eye. Orbital part: Fibres converge and form uninterrupted elipse around orbit of the eye. Key Relations: A third part of the muscle exists known
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
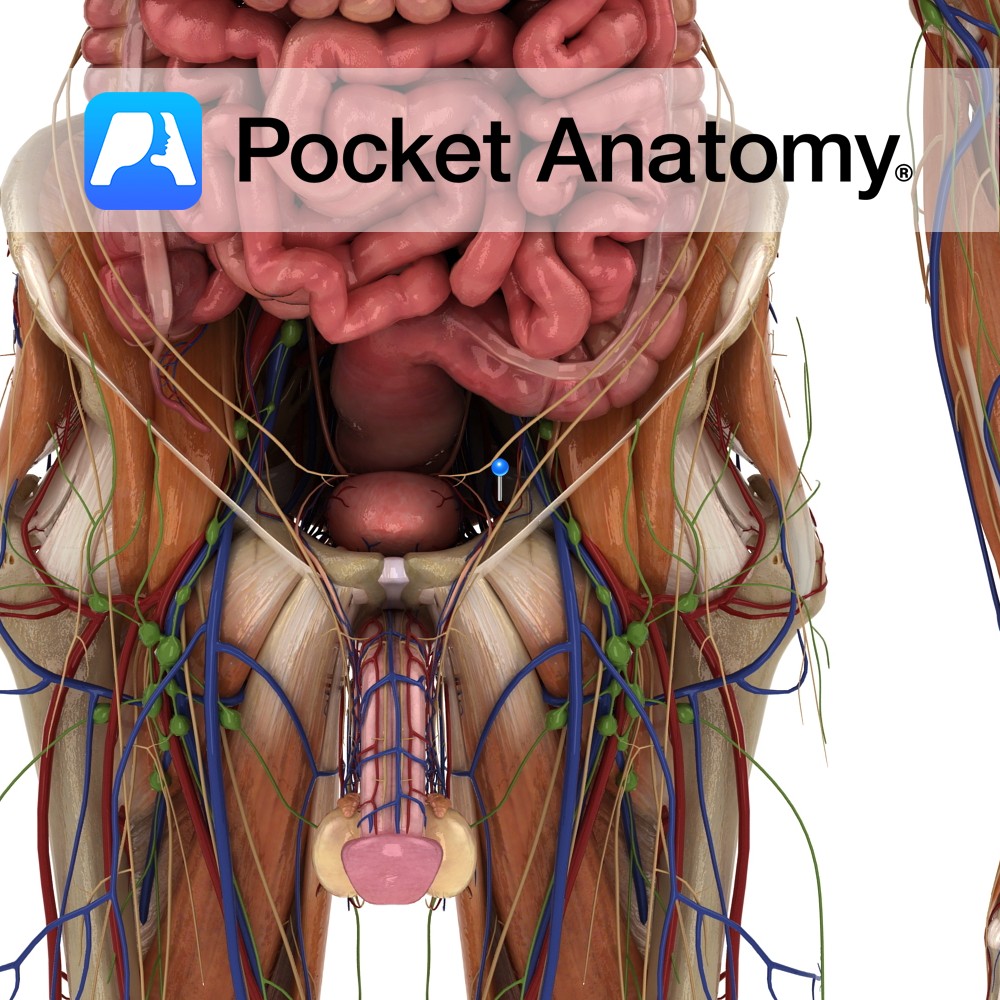
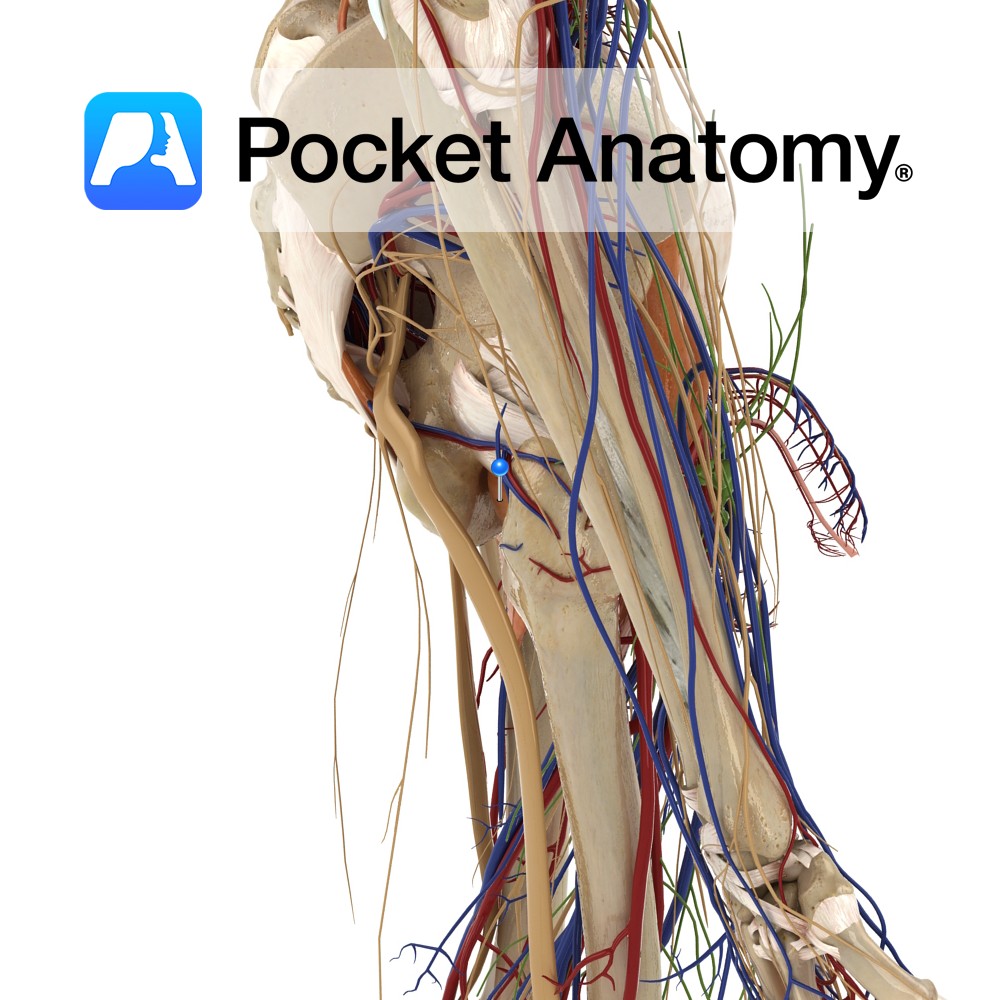
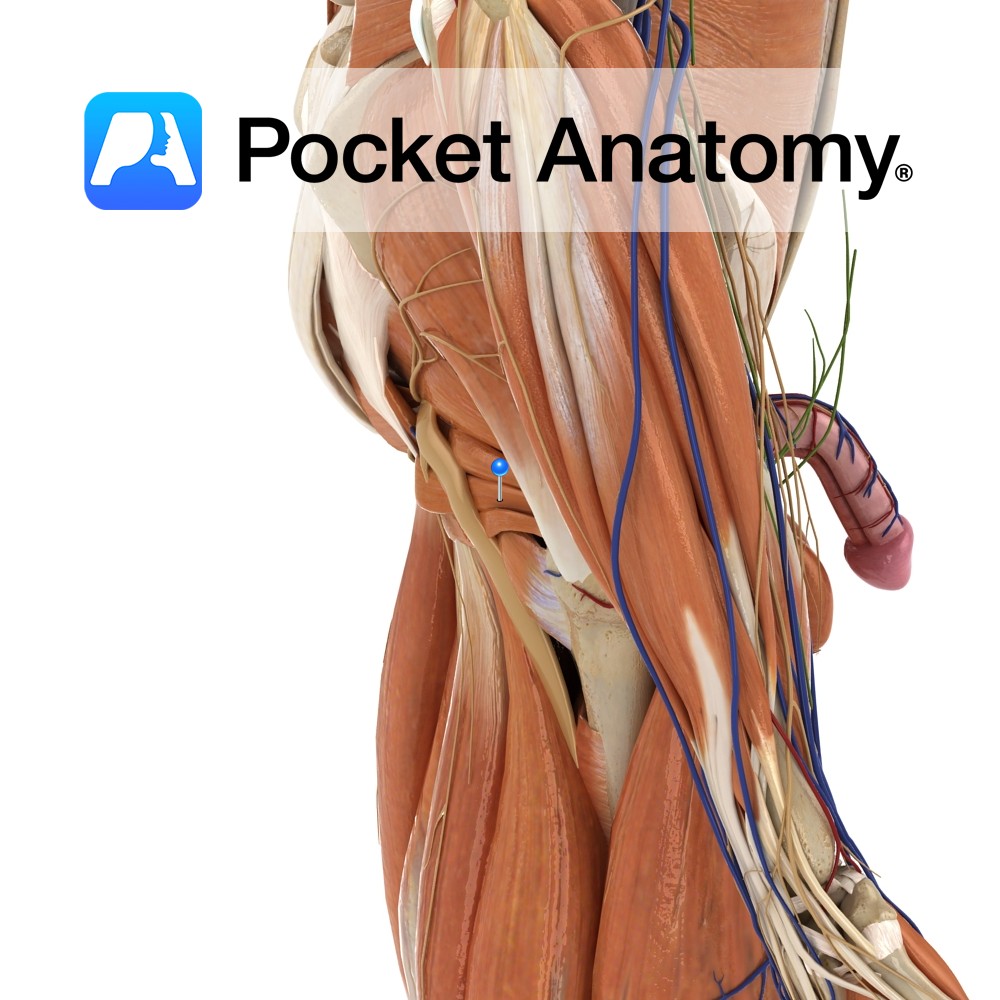
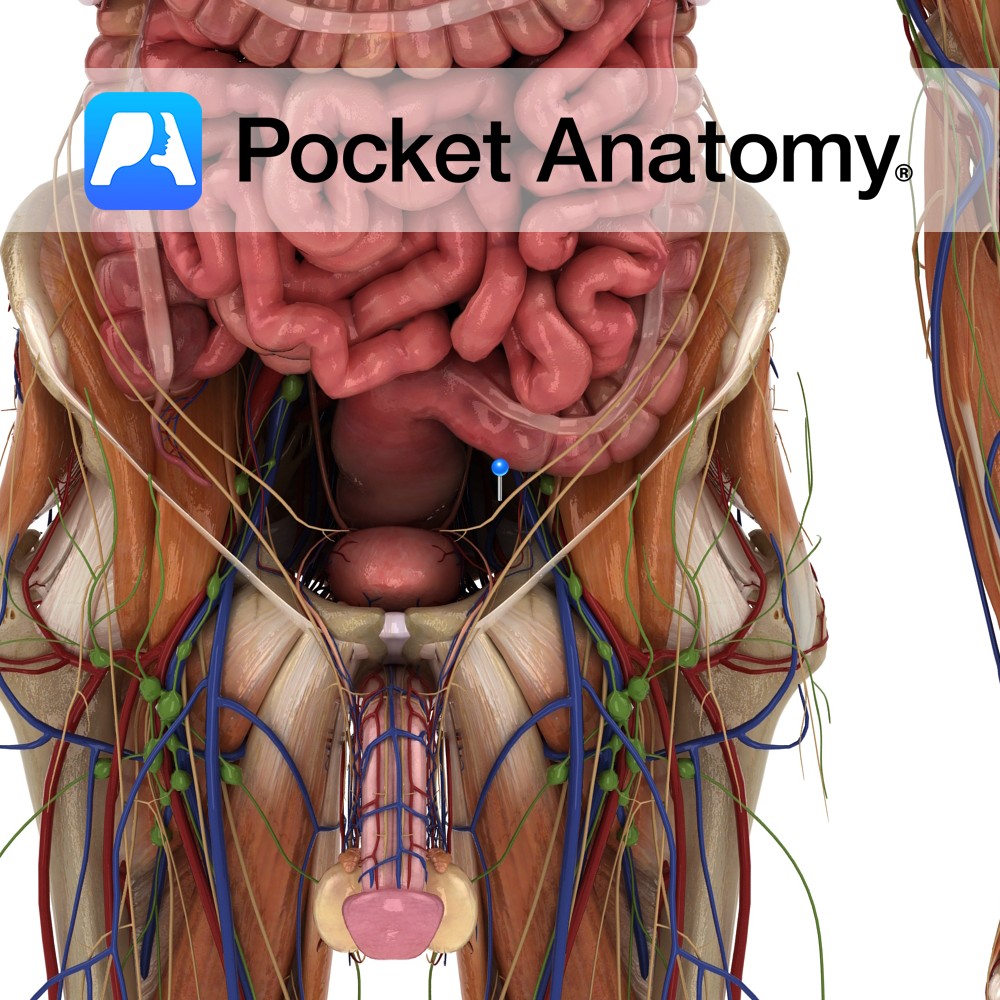
Anatomy Course A branch of the anterior trunk of the internal iliac artery. It branches from the anterior trunk just below the pelvic inlet, and runs anteriorly along the margin of the pelvic inlet. It leaves the pelvic cavity via the obturator canal. As it passes through the obturator canal it splits into two terminal
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
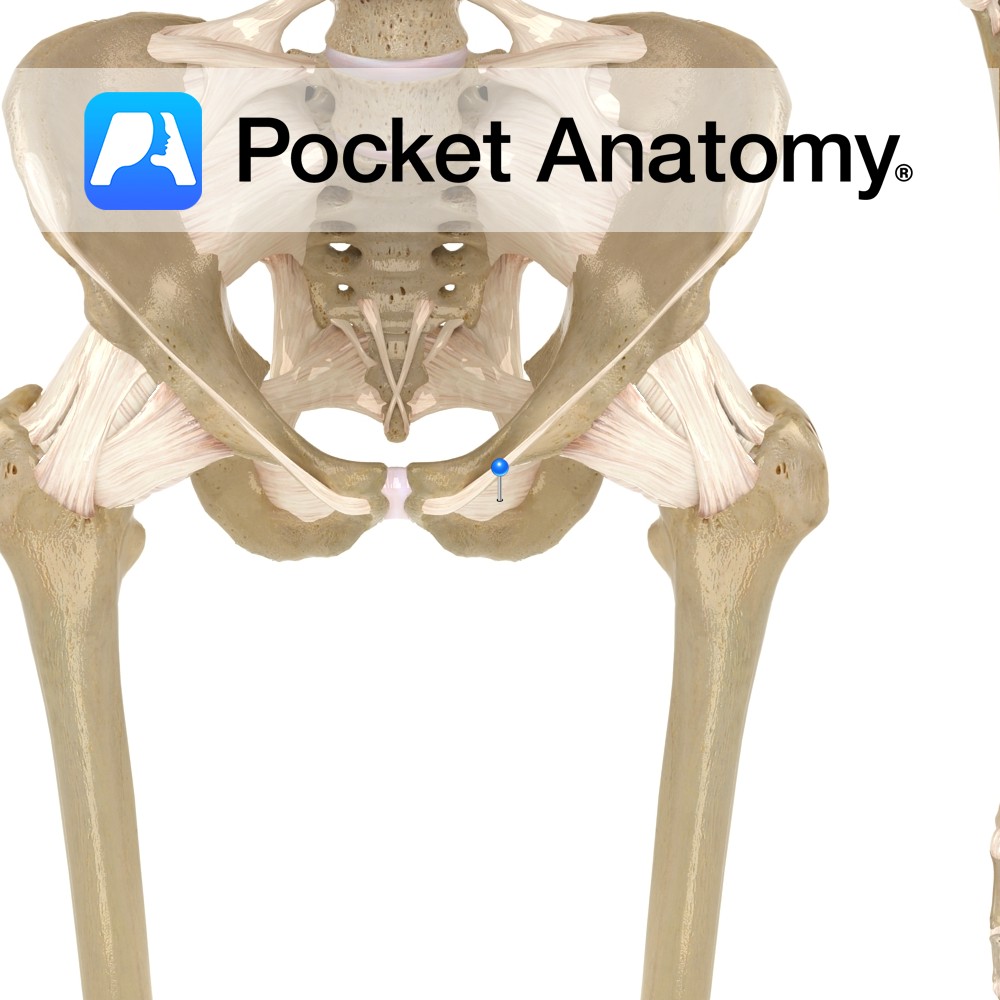
Anatomy Origin: Outer margins of the obturator foramen, the medial two thirds of the obturator membrane and the pubic and ischial rami. Insertion: Trochanteric fossa on the medial aspect of the greater trochanter of the femur. Key Relations: -One of the six muscles of the medial compartment of the thigh. -The obturator vessels lie between
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Anterolateral wall of the pelvis, pelvic surface of the obturator membrane and margins of obturator foramen(i.e. inferior rami of pubis and ischium). Insertion: Medial surface of the greater trochanter of the femur. Key Relations: -Within the pelvis, forms lateral wall of ischiorectal fossa. -Outside the pelvis, it’s tendon lies between the superior and
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy A thin fibrous sheet, which largely occludes the obturator foramen. Its fibers are mainly transverse. Both obturators externus and internus connect with the membrane. Functions May help the obturator muscles laterally rotate the extended thigh at the hip joint. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Begins in the adductor region of the hip joint. It enters the pelvic cavity via the obturator canal. It travels posteriorly in the pelvic cavity to drain into the internal iliac vein. Drain Drains the adductor region of the hip. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
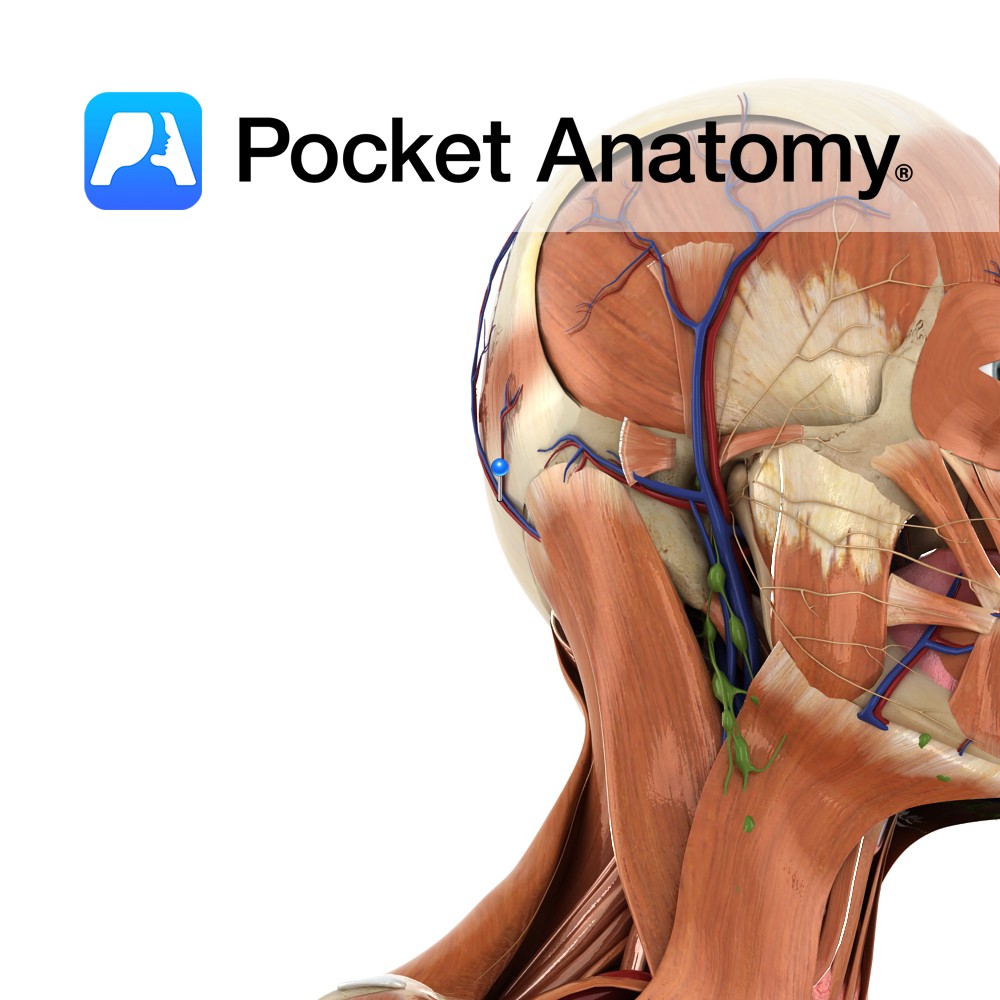
Anatomy Course A branch of the external carotid artery. It branches from the external carotid just before it passes behind the posterior belly of the digastric muscle and is crossed by the hypoglossal nerve. It ascends travelling posteriorly, and passes through the space between the transverse process of the atlas vertebra and the mastoid process
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
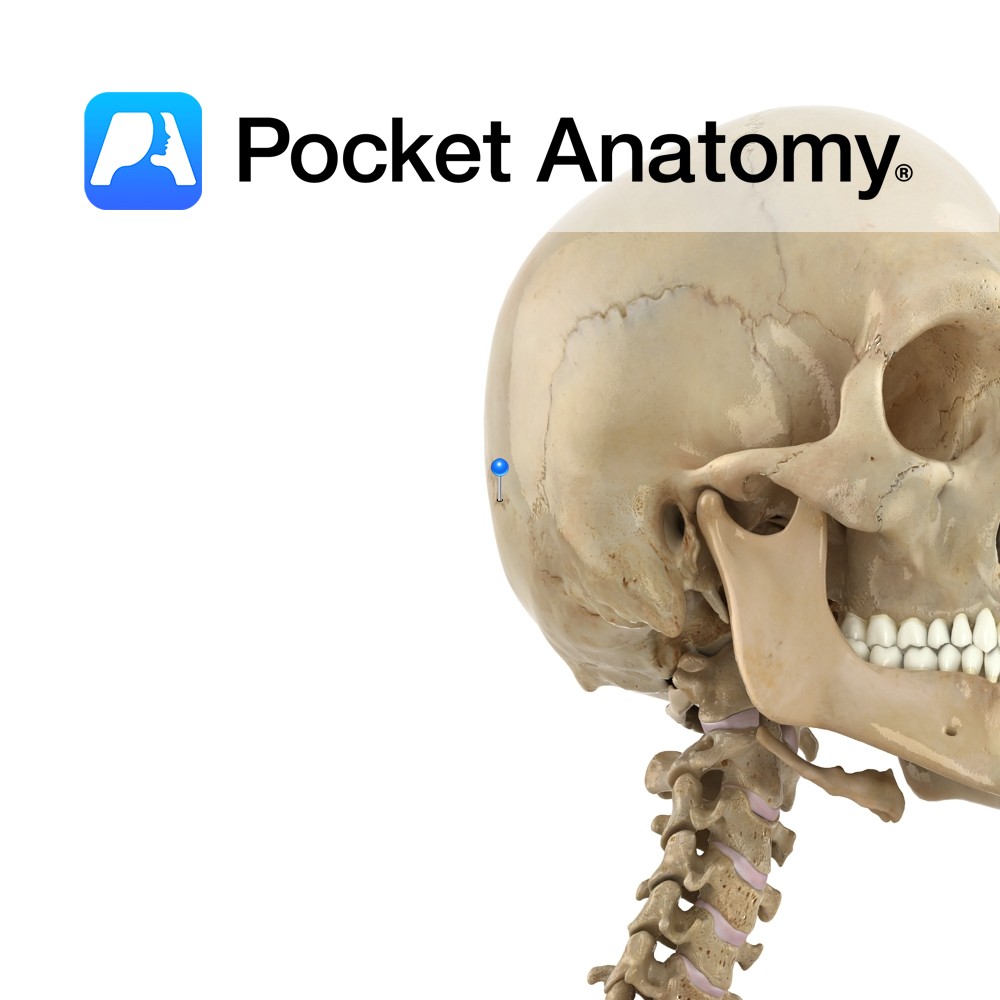
Anatomy A midline bump on back of head, on the external surface of satellite-dish-like vertical part (squama) of occipital bone, halfway between the foramen and its highest point. The highest nuchal lines run laterally from the protuberance, with the superior nuchal lines located slightly below. The median nuchal line runs inferiorly to the foramen, with
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Rigid, fibrous joint between the occipital, and left and right parietal bones. Vignette Suture shaped like Greek letter Lambda (λ). Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins

.jpg)