PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
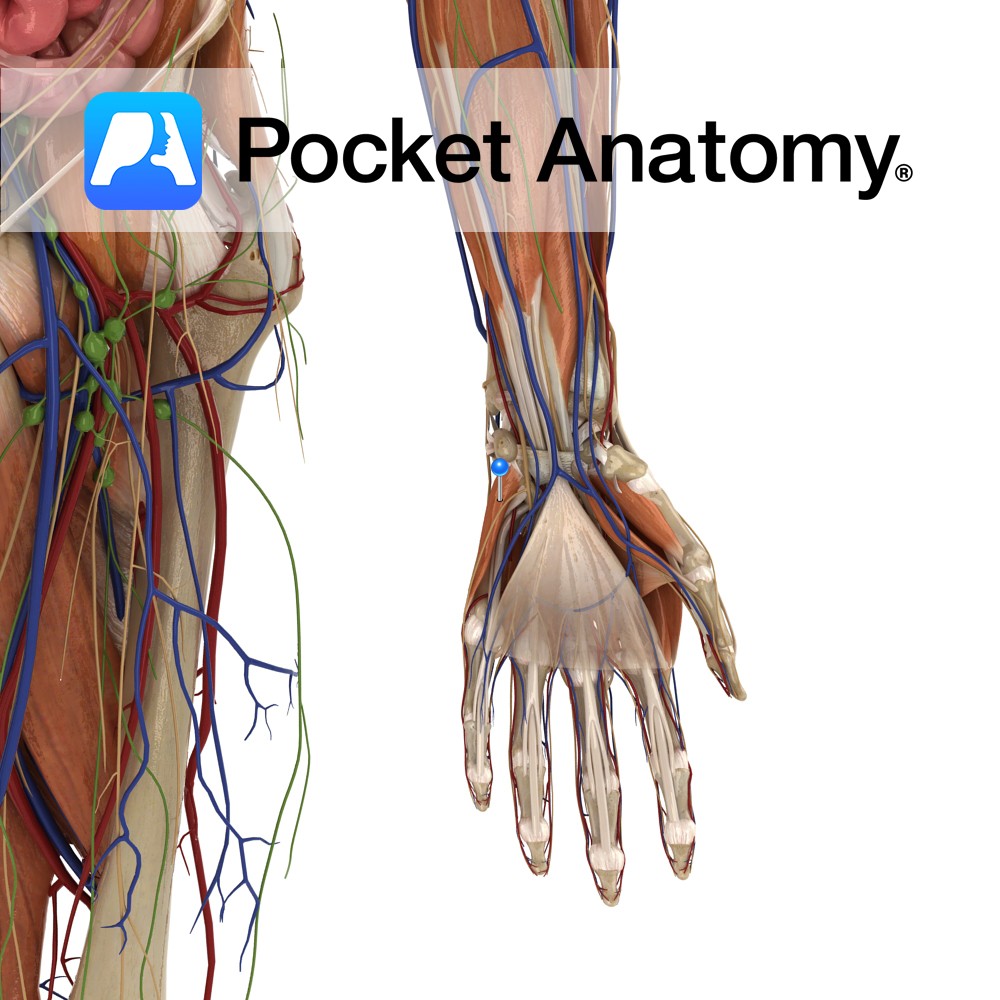
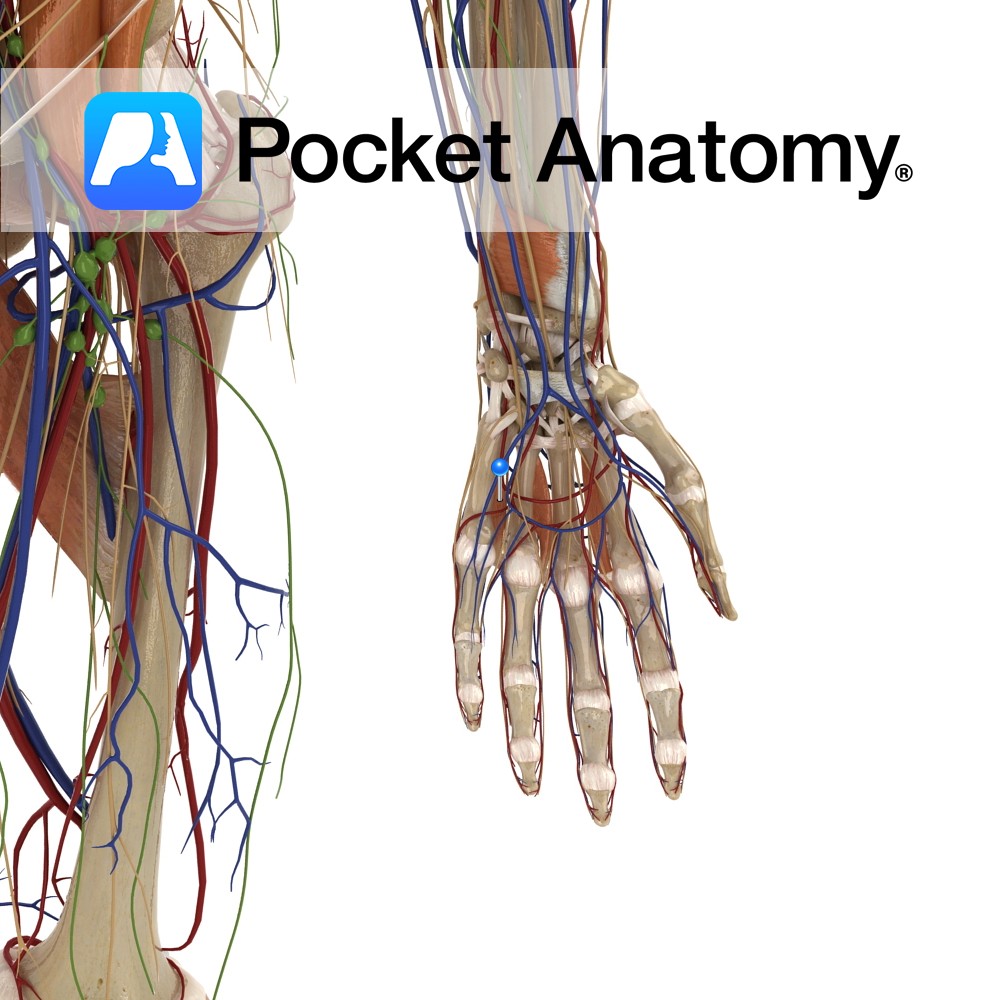
Anatomy Course Branches from the superficial palmar arch, just after the deep palmar artery branches from it. It travels medially towards the little finger and runs along the medial side to the tip. The blood it carries is mainly from the ulnar artery. Supply Supplies the medial aspect of the little finger with blood. Interested
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
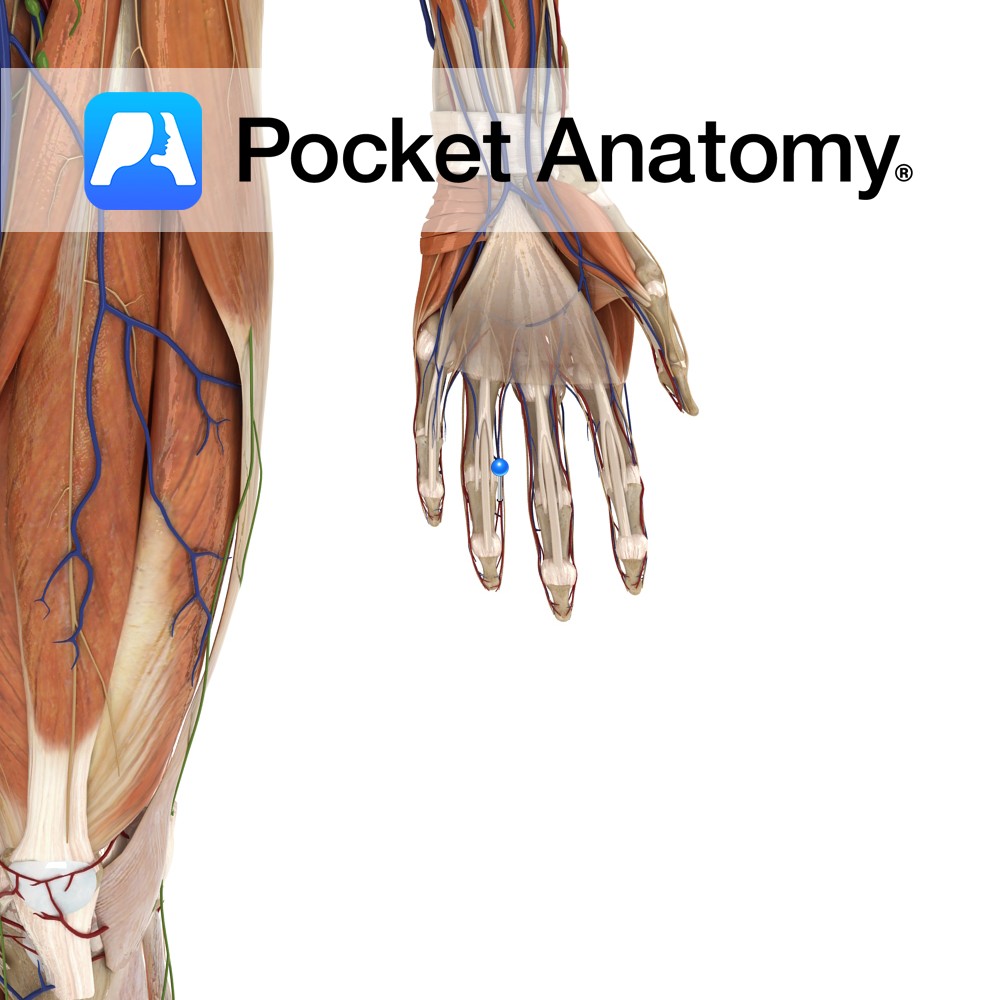
Anatomy Origin: Entire length of side of metacarpal (1st = ulnar aspect, 2nd, 3rd = radial aspect) Insertion: Extensor hood and base of proximal phalanges of the index, middle and ring fingers. Functions Flexion of the index, middle and ring digits at the metacarpophalangeal joint. Adducts the index, middle and ring digits at the metacarpophalangeal
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
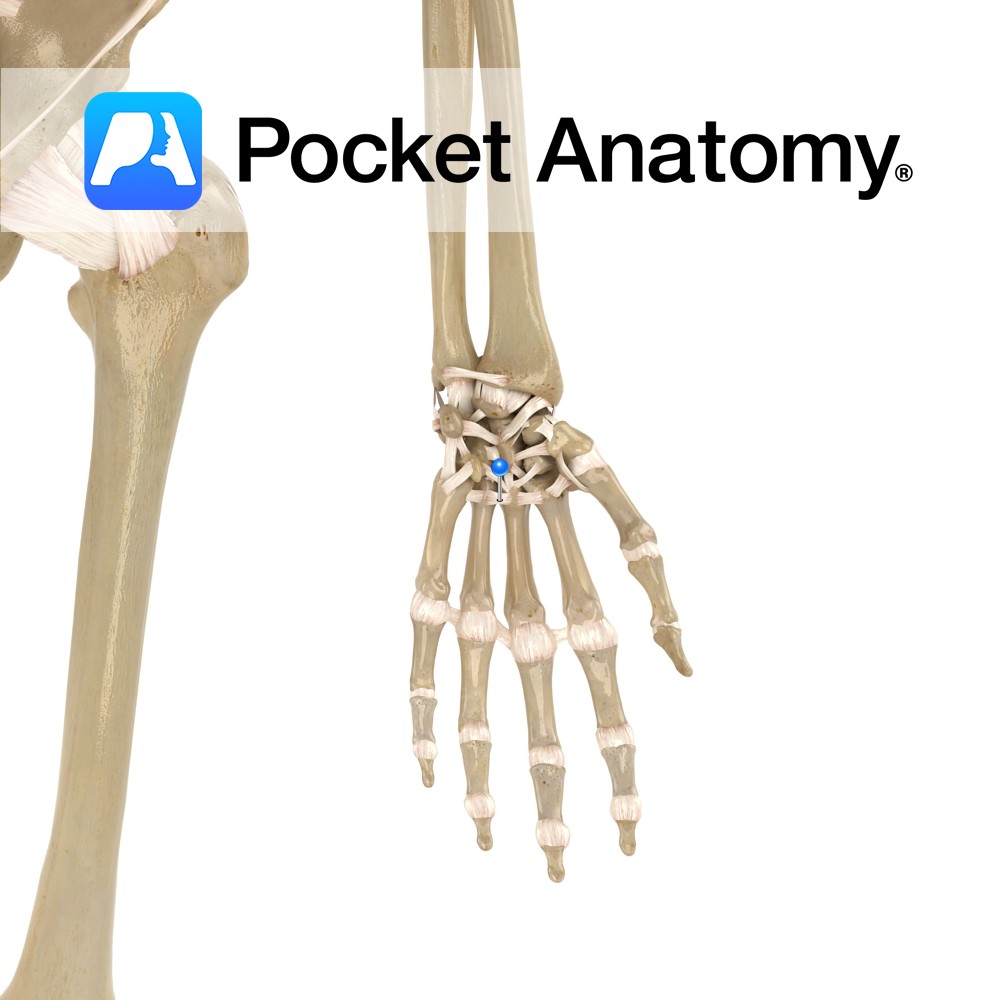
Anatomy A series of transverse ligaments passing from the palmar surface of the base of metacarpals one to five. Functions Provide static stability to the metacarpal joints. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
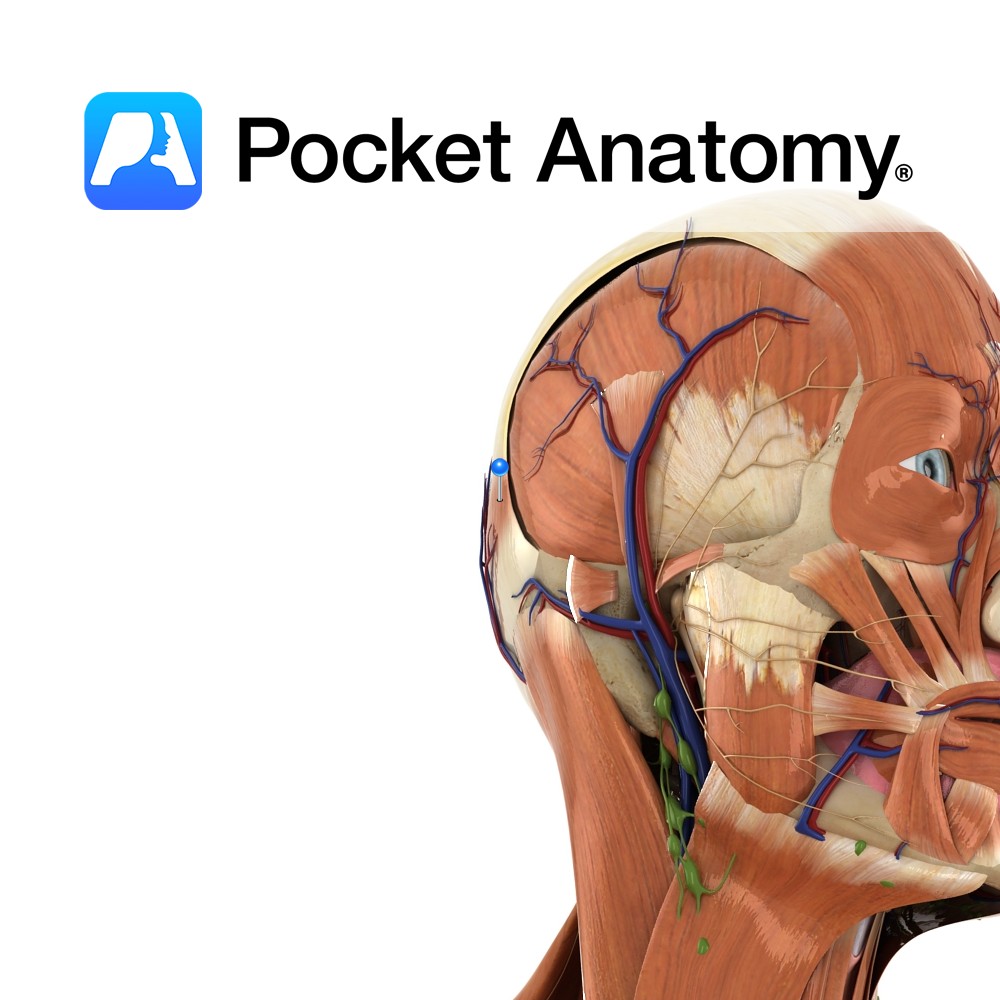
Anatomy Origin: Occipitalis has no bony origin. Its fibres are continuous with those of the muscles procerus and corrgator supercilii. Insertion: Fibres join the galea aponeurotica (epicranial aponeurosis) below the coronal suture. Key Relations: Many consider frontalis and occipitalis as one muscle (called occipitofrontalis) with an aponeurotic tendon between two bellies- a frontal belly and
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Arises from olfactory receptors in the epithelium of the nasal cavity. Course: The olfactory receptor axons enter the cranial cavity through the foramina of the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone. They synapse in the olfactory bulb located on the inferior surface of the frontal lobe. Information is carried from the olfactory bulb
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course: The superior and inferior ophthalmic veins begin on their respective sides of the eye. They drain backwards towards the cranial cavity, merging to form a single vessel that empties into the cavernous sinus. Supply Drains the orbit of the eye and its structures. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course: The superior and inferior ophthalmic veins begin on their respective sides of the eye. They drain backwards towards the cranial cavity, merging to form a single vessel that empties into the cavernous sinus. Supply Drains the orbit of the eye and its structures. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
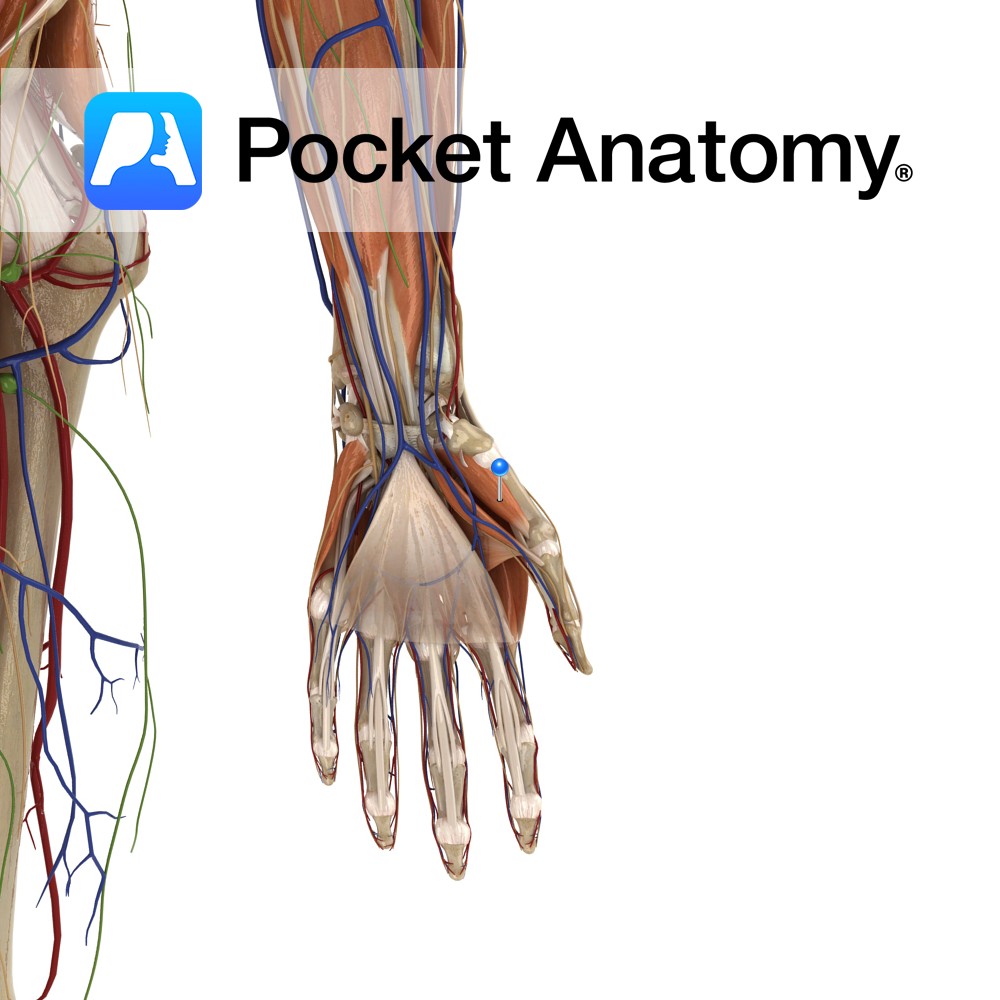
Anatomy Origin: Hook of the hamate and the flexor retinaculum. Insertion: Ulnar aspect of the fifth metacarpal. Key Relations: Is one of the muscles of the hypothenar eminence of the hand. Functions Flexion and lateral rotation (i.e.opposition) of the fifth metacarpal at the carpometacarpal and metacarpophalangeal joint. Supply Nerve Supply: Deep branch of the ulnar
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Tubercle of trapezium and flexor retinaculum. Insertion: Radial border and adjacent palmar surface of the first metacarpal (thumb). Key Relations: Is one of the muscles of the thenar eminence of the hand. Functions Flexion, abduction, and medial rotation (i.e. the action of opposition) of the metacarpal of the thumb at the carpopmetacarpal and
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
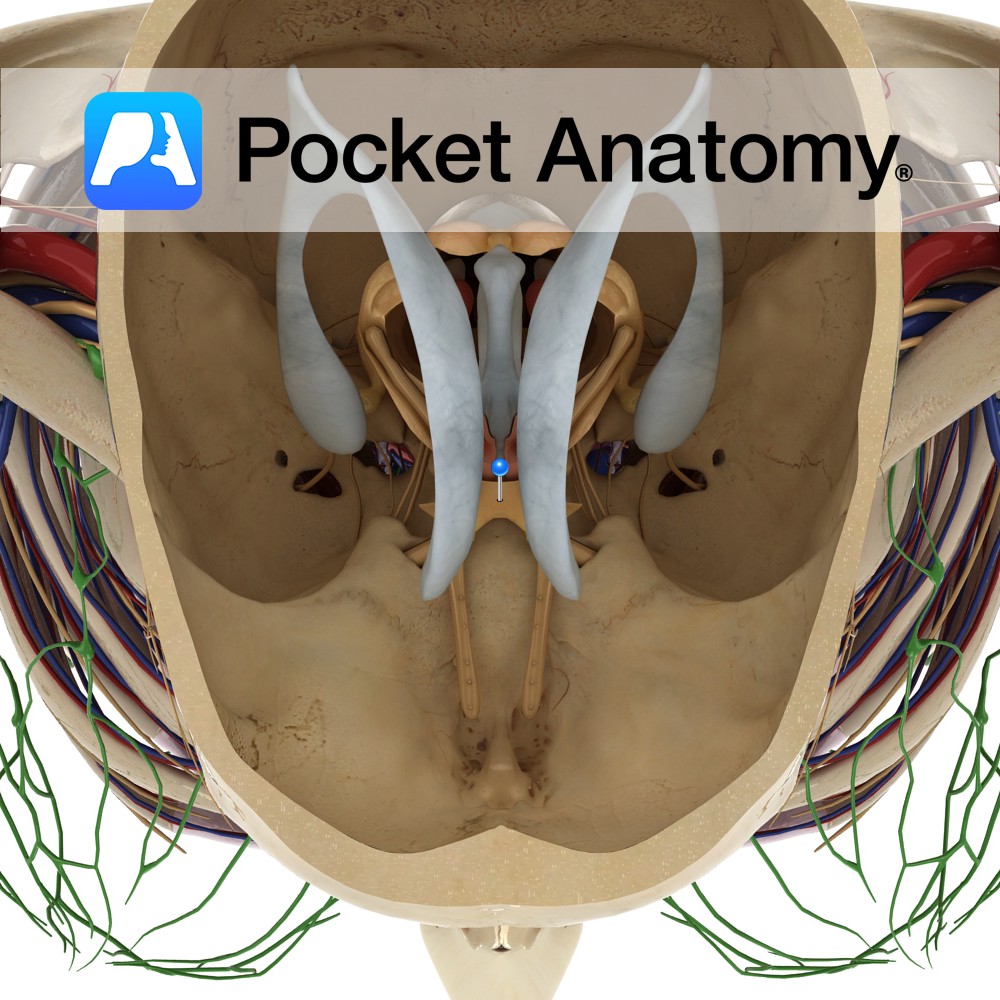
Anatomy The two optic nerves unite at the optic chiasm which is located at the base of the brain in the interpeduncular cistern. It is situated between the two internal carotid arteries, and the tuber cinereum of the hypothalamus lies posterior to the chiasm. Blood Supply: Supplied by the branches of many vessels, particularly the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)