PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
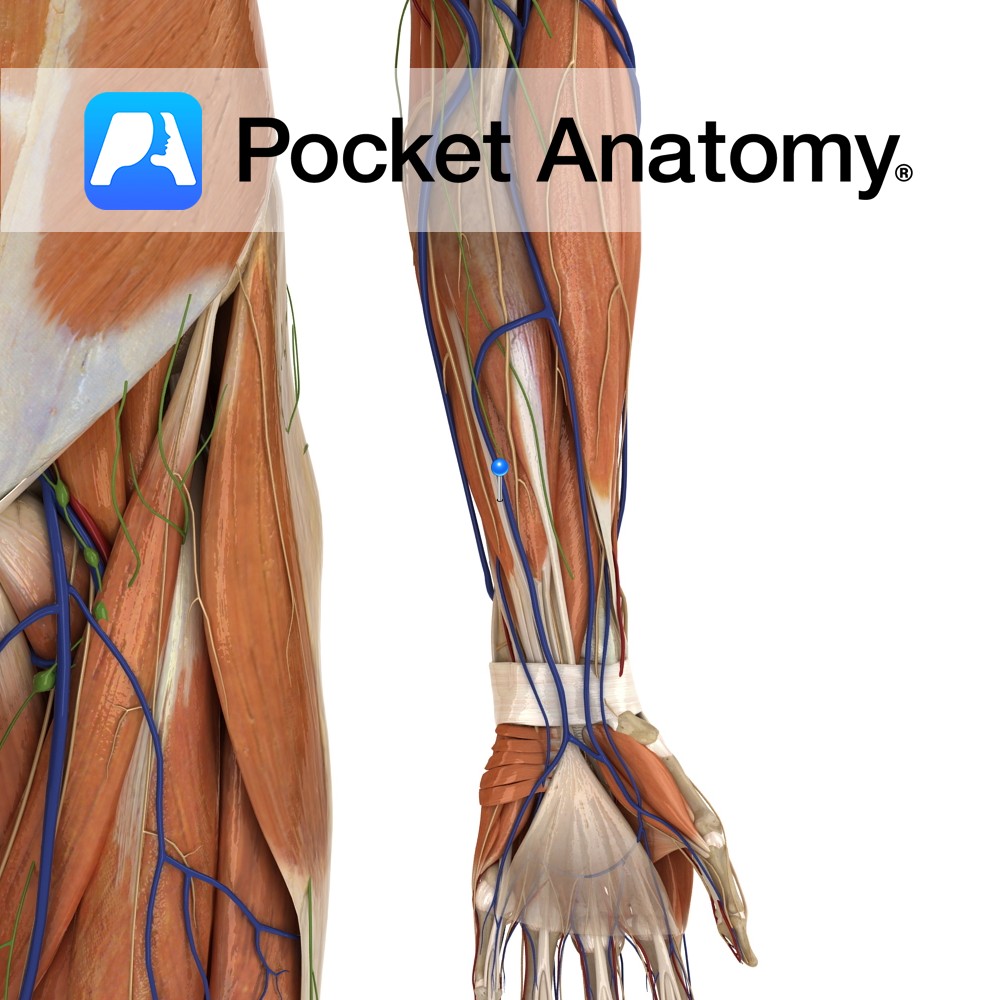
Anatomy Origin: Medial epicondyle of humerus via the common flexor tendon. Insertion: Palmar aponeurosis of hand. Key Relations: One of the four muscles in the superficial anterior compartment of the forearm. Functions -Tenses the palmar aponeurosis, thereby anchoring the skin of the hand and resisting the shear forces in gripping. Its absence however has been
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
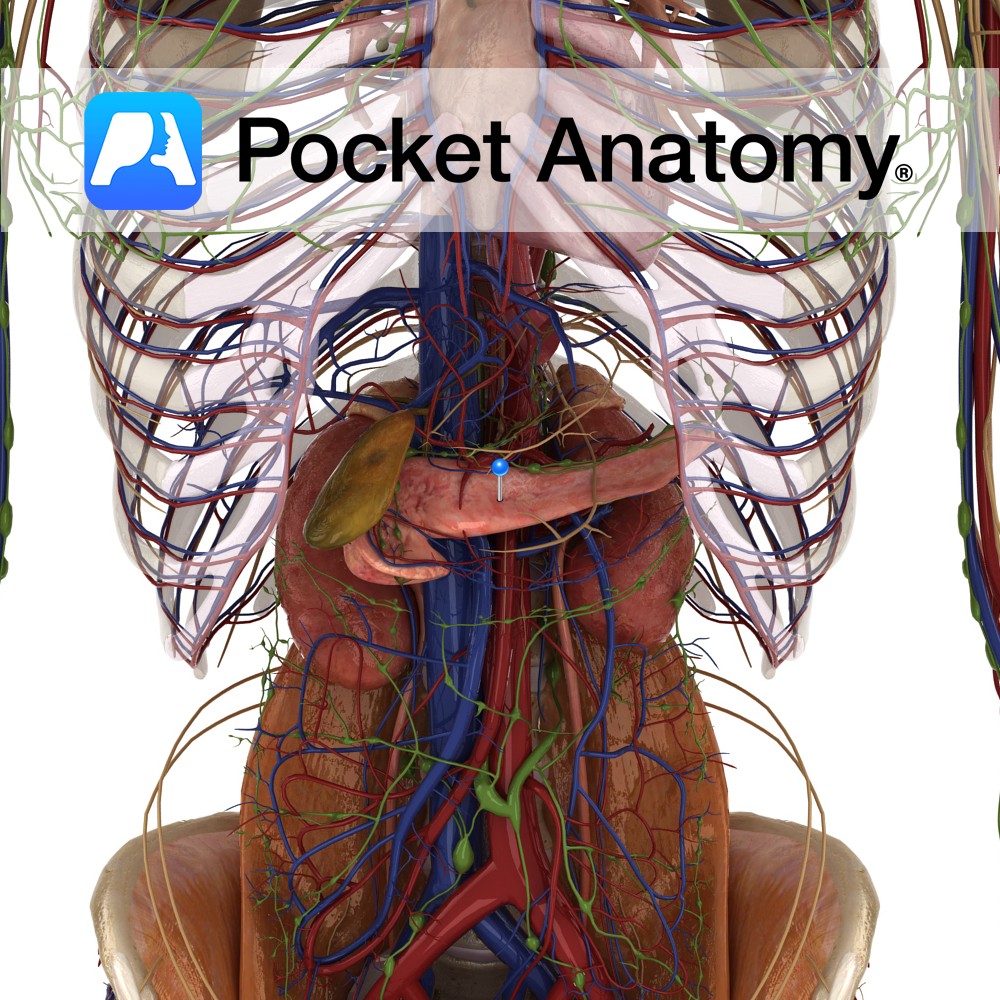
Anatomy 6″ long pennant-shaped gland/organ, transverse on back wall left hypochondriac and epigastric regions of abdomen, retroperitoneal except for tail. Head nestles in curve of duodenum, tail sits front of spleen, neck (slight narrowing) and body behind stomach. Two types of parenchymal (characteristic) tissue; clusters (about a million) of Islets of Langerhans associated with rich
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
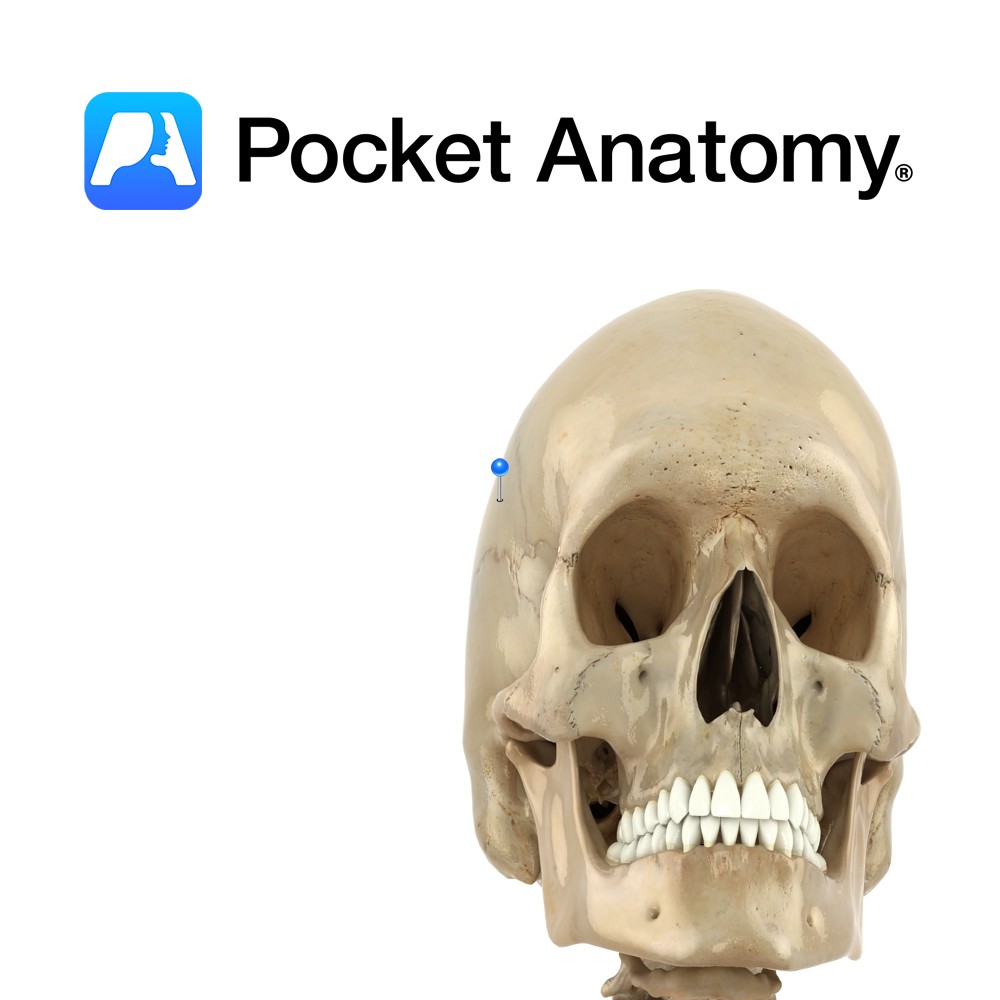
Anatomy Paired bones forming the side-walls and roof of the cranium, meeting each other at the sagittal suture, also articulating with frontal bone, sphenoid anteroinferiorly (below and in front) each side, temporal bones laterally below and occipital below and behind. Vignette Pariet (Latin); wall. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
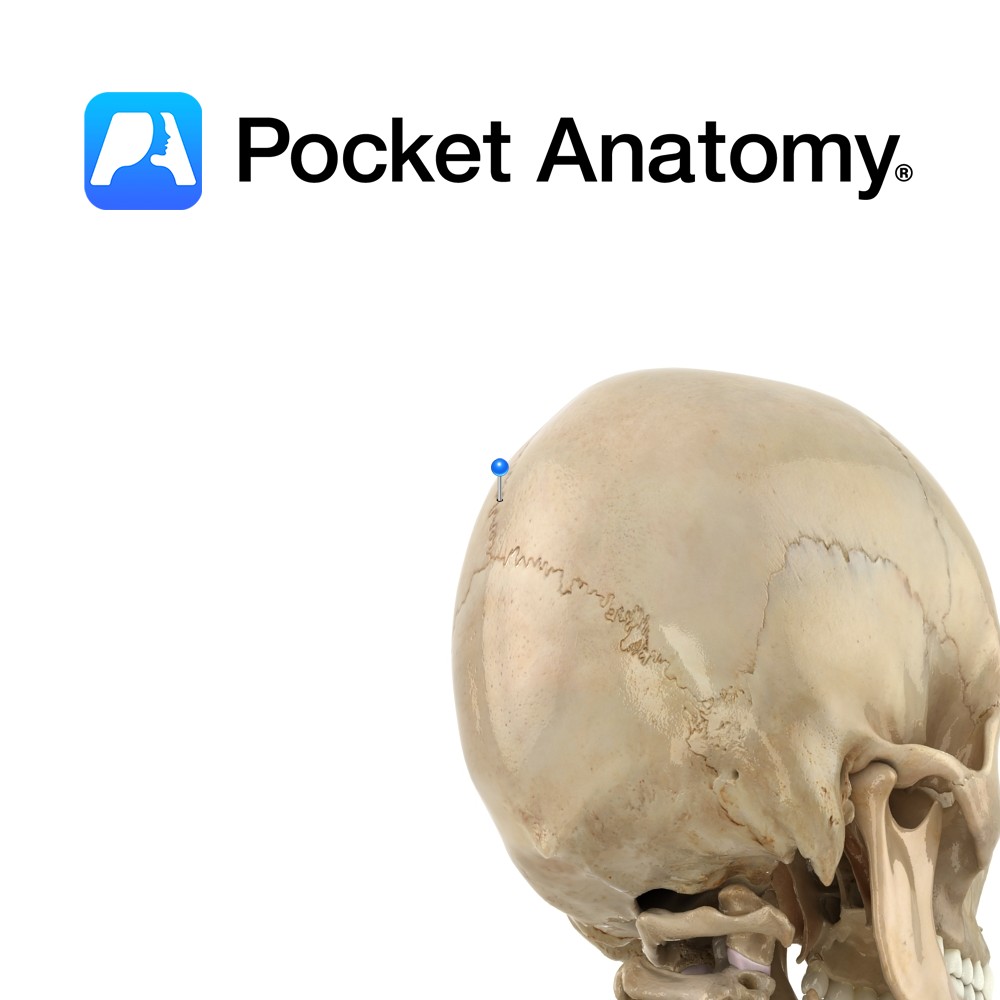
Anatomy Rigid midline joint or seam between paired parietal bones, deeply serrated towards front. Vignette Sagitta (Latin); arrow – With Sagittal suture the shaft and lambdoid suture as the tuft of the arrow. Anterior fontanelle is gap at the junction of sagittal, coronal and frontal sutures which persists until closure in 2nd year; it allows
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
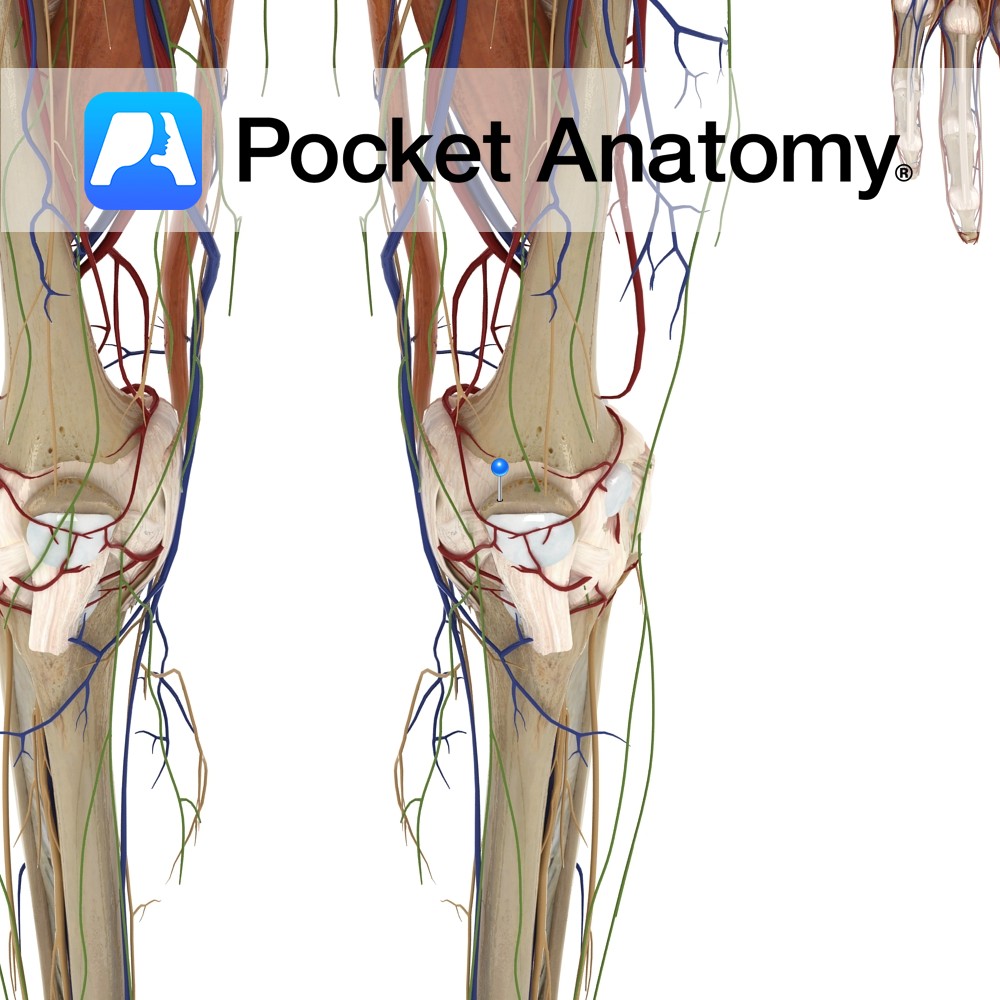
Anatomy Kneecap, largest sesamoid (embedded in tendon) bone, triangular (base up, tip down) articulates with femur. Clinical Increases angle and leverage of quads in their extension of knee. Visible, palpable, moveable a little side to side when leg straight and quads relaxed. Patellar dislocation is usually lateral, accompanied by pain and swelling, can often be
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
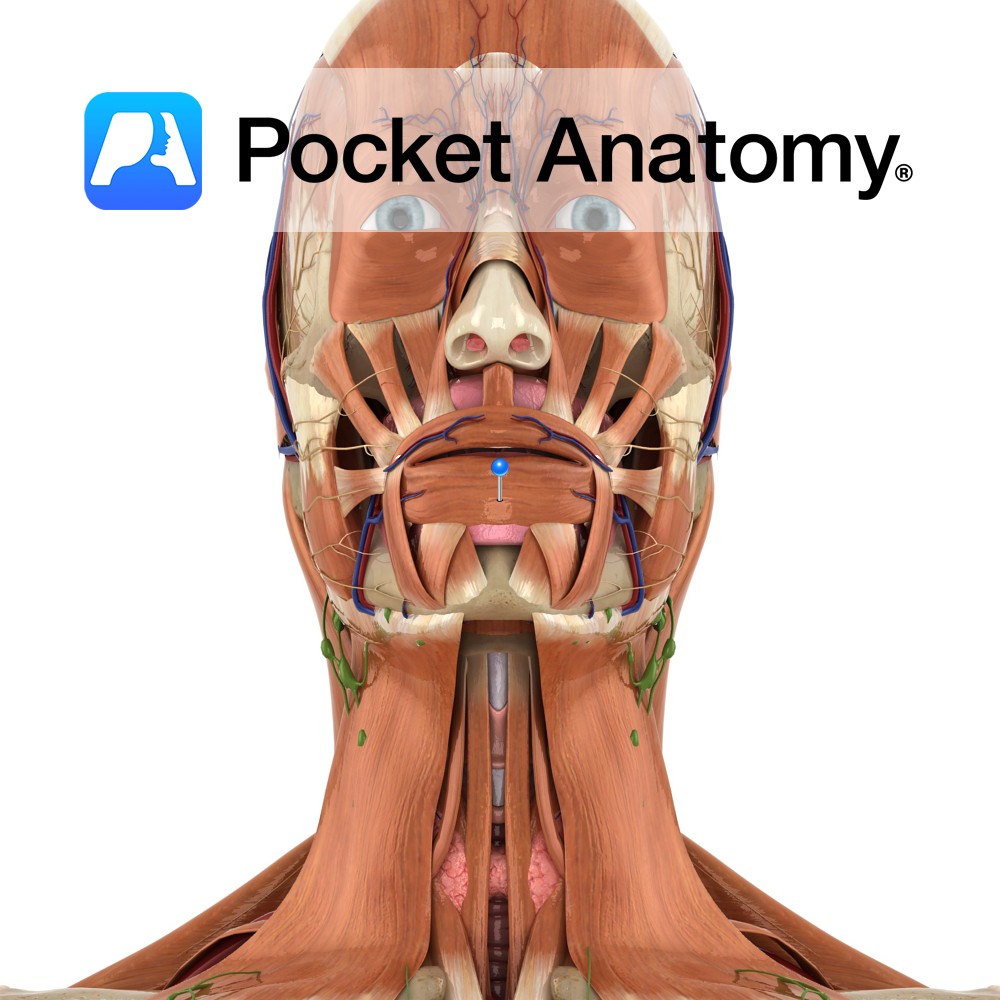
Anatomy Origin: Mandible below and maxilla above, some fibres originate from other muscles of the face (buccinator, depressor anguli oris, zygomaticus major and minor, quadratus labii inferioris and superioris) Insertion: The skin of the lips and the mucous membrane beneath the lips. Key Relations: Fibres completely encircle the mouth. Functions -Acts in the manner of
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
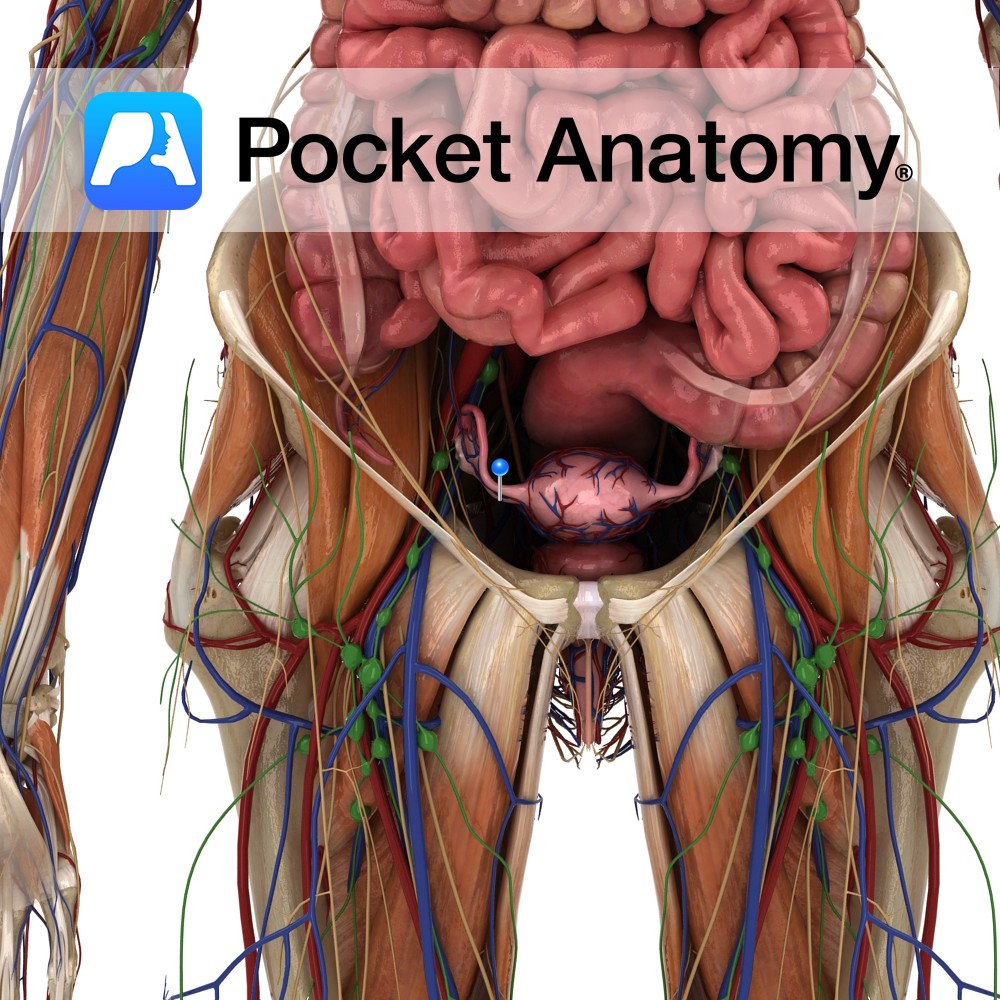
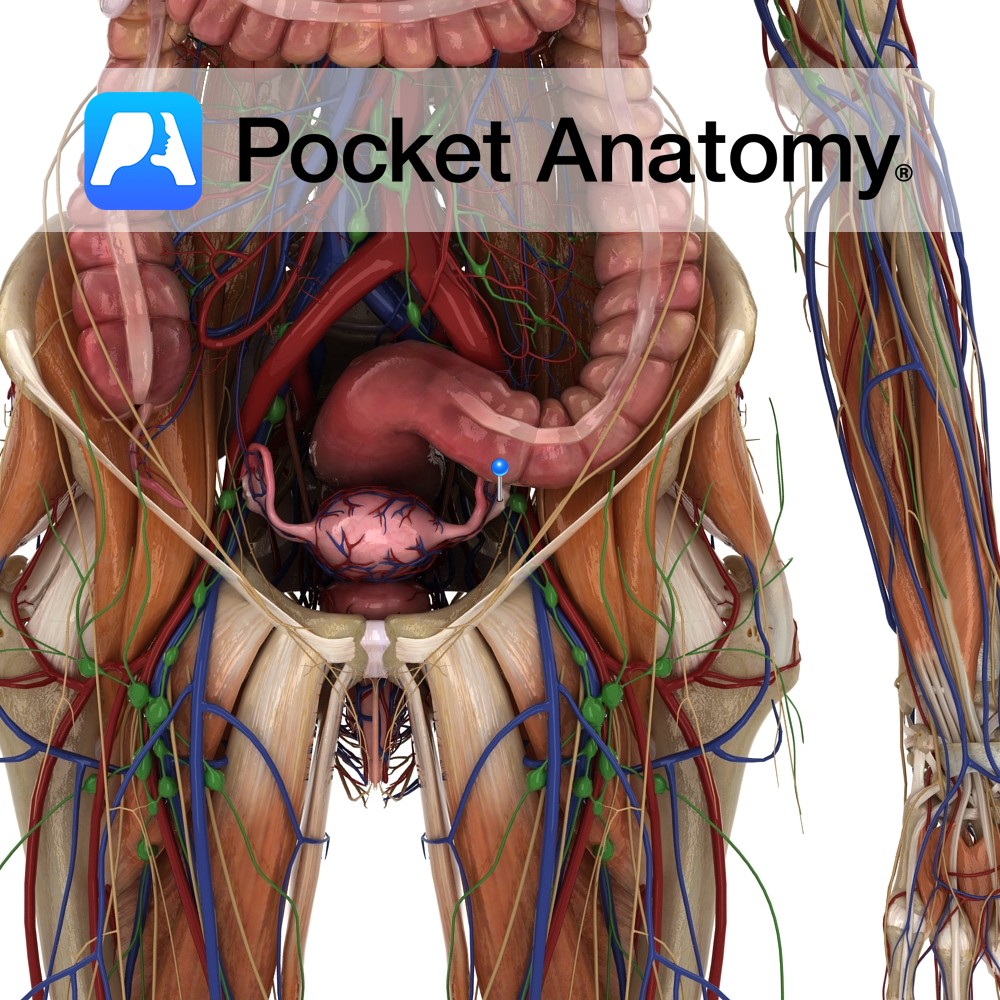
Anatomy Fibromuscular ligament connecting the lower/uterine extremity of the ovary to the side of the uterus, near the fundus and the uterotubal junction. Clinical Not to be confused with the suspensory ligament of ovary, a part of the upper edge of the broad ligament which connects the other, upper, tubal extremity of the ovary to
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Female gonad (organ which secretes gametes – male/female secretes sperm/eggs). Paired, 4X2X1cm, 2-3.5gm (smaller with age from puberty), almond-shaped (long axis vertical), grey-pink, surface smooth (or puckered after repeated ovulation), sits at side of uterus, just below uterine/fallopian tube, in pelvic cavity, at or below level of umbilicus, in shallow ovarian fossa in lateral
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
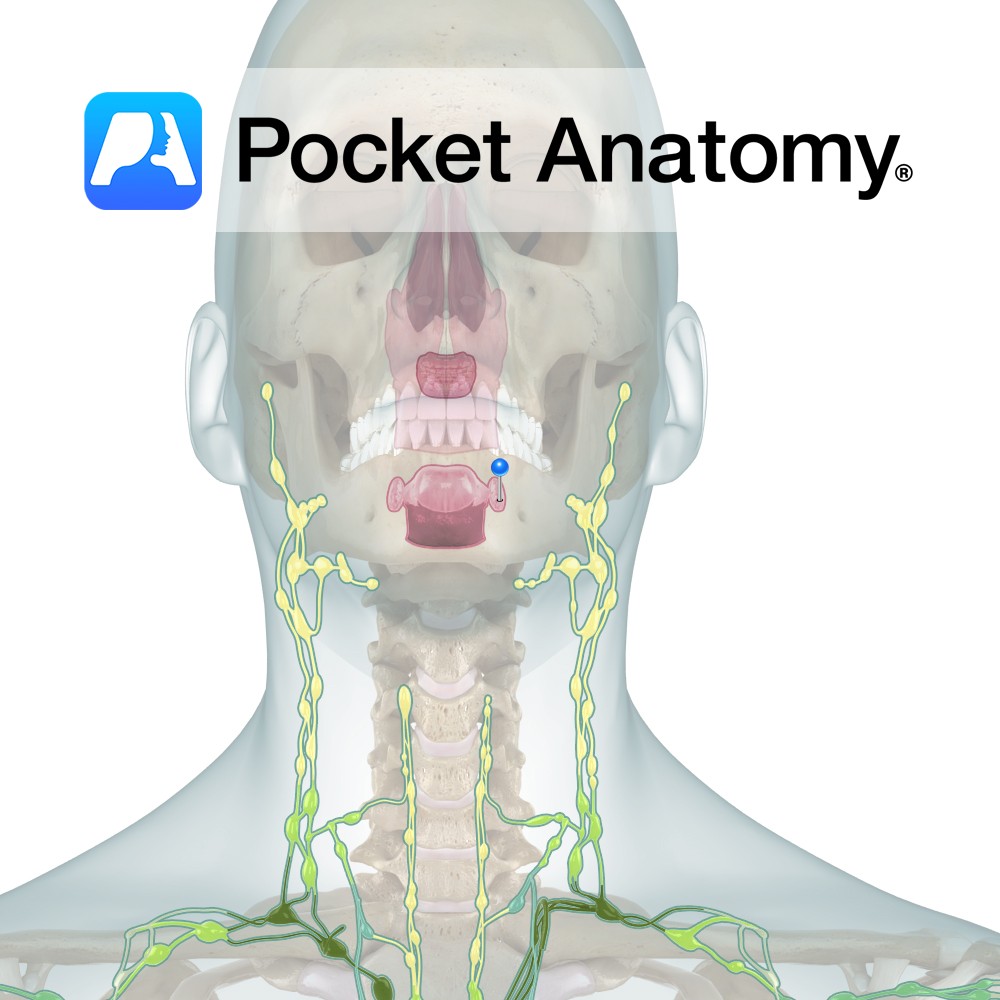
Anatomy The tonsils most commonly referred to, visible either side of the Oropharynx at the back of the tongue. Surface folded on itself, forming 15 or so crypts. Clinical Normal Palatine Tonsils vary considerably in size. Can swell significantly when inflamed/infected, though rarely to the point of blocking the Oropharynx. Tonsillectomy was once very common
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
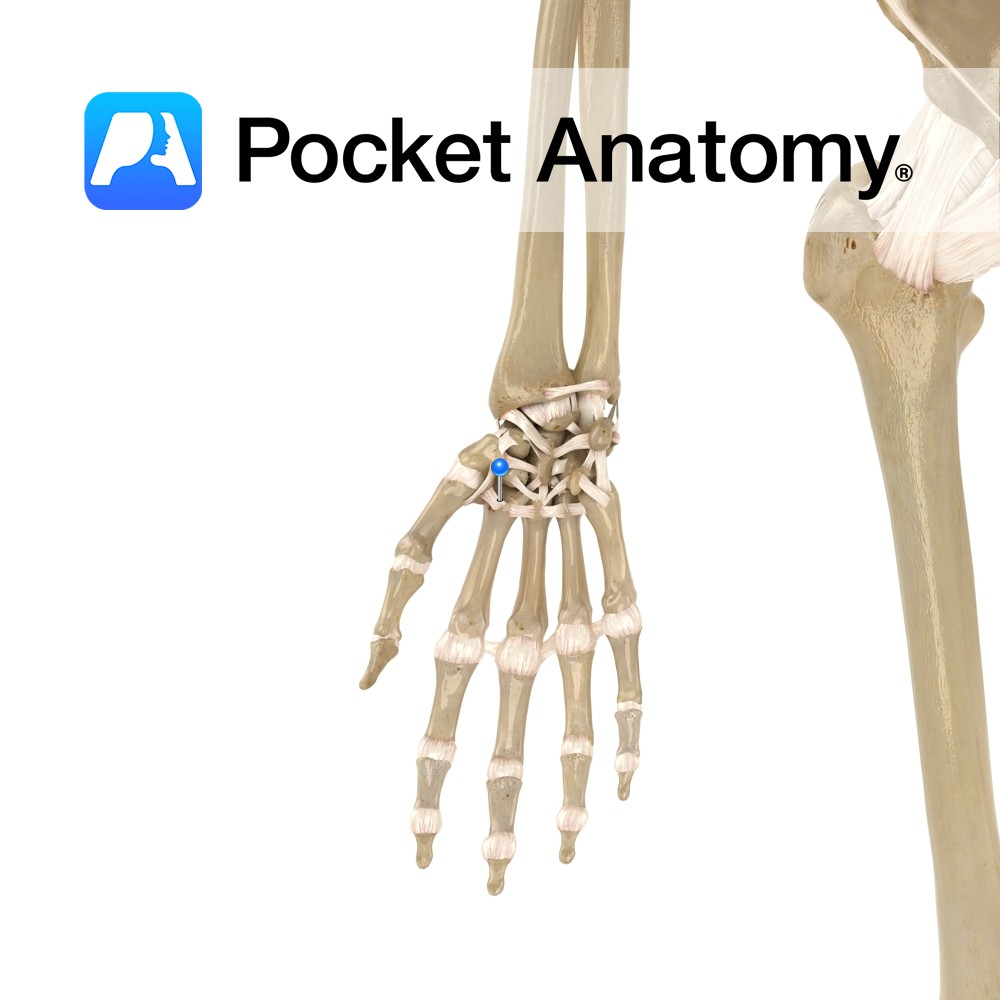
Anatomy Small fibrous bands connecting from the distal row of carpal bones to the proximal end of the metacarpal bones. Functions Provide static stability to the carpometacarpal joint. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins