PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
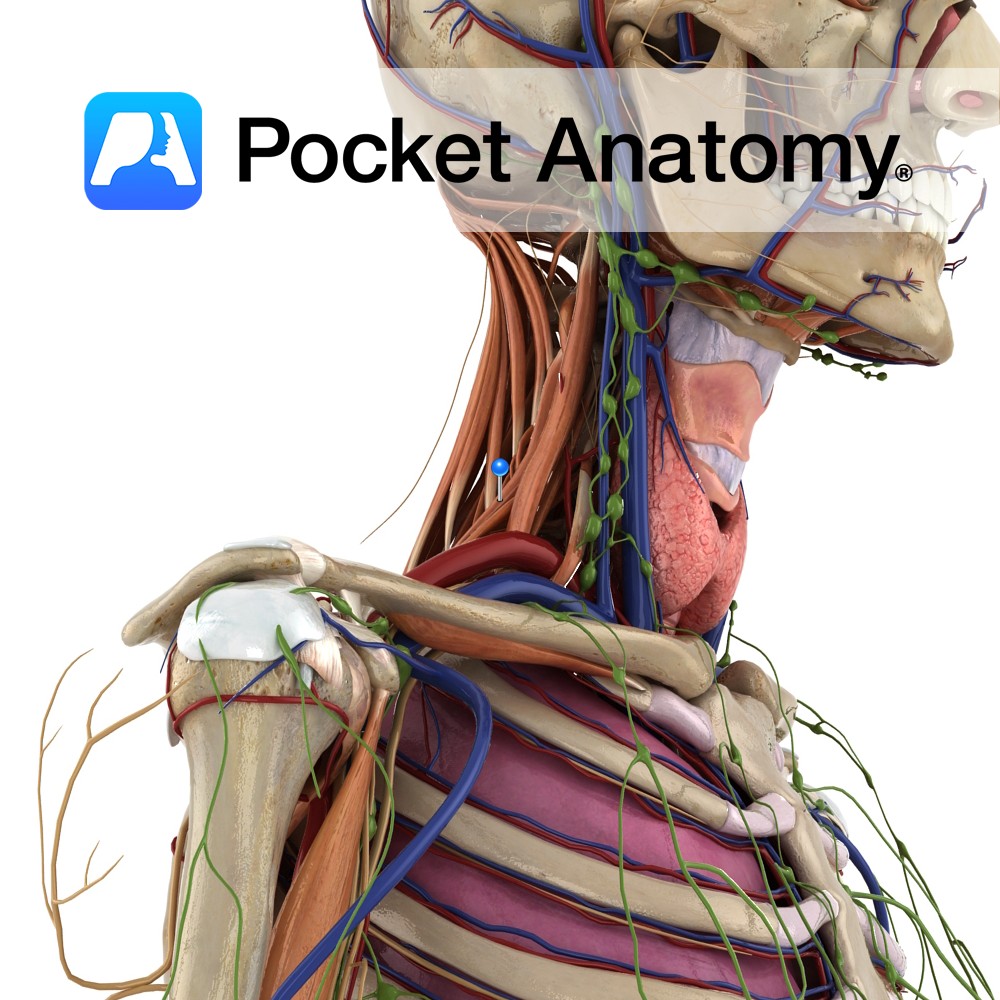
Anatomy Origin: Posterior tubercles of the transverse processes of C4 to C7. Insertion: Upper surface of the 2nd rib, posterior to the attachment of serratus anterior. Key Relations: Smallest and deepest of the scalenes. Functions -Elevates the 2nd rib. -Lateral flexes the neck to the same side. -An accessory muscle of inspiration. Supply Nerve Supply:
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
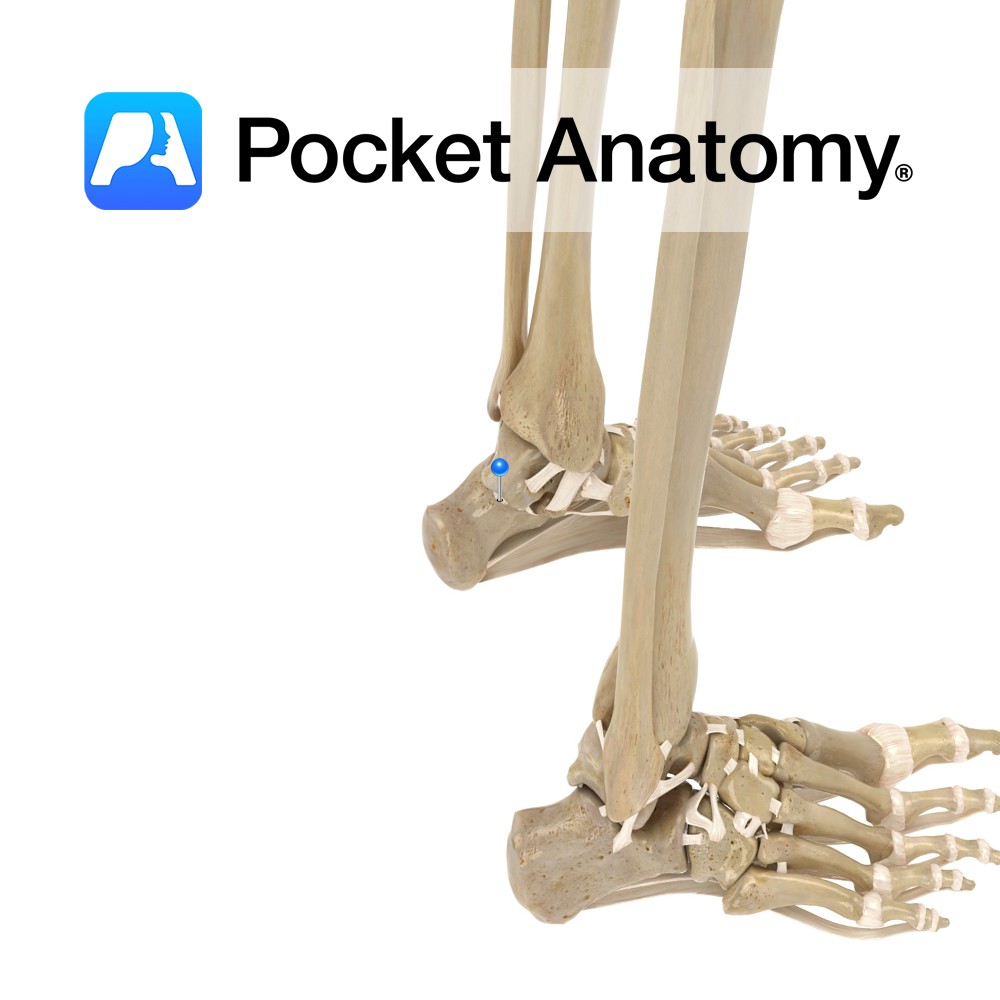
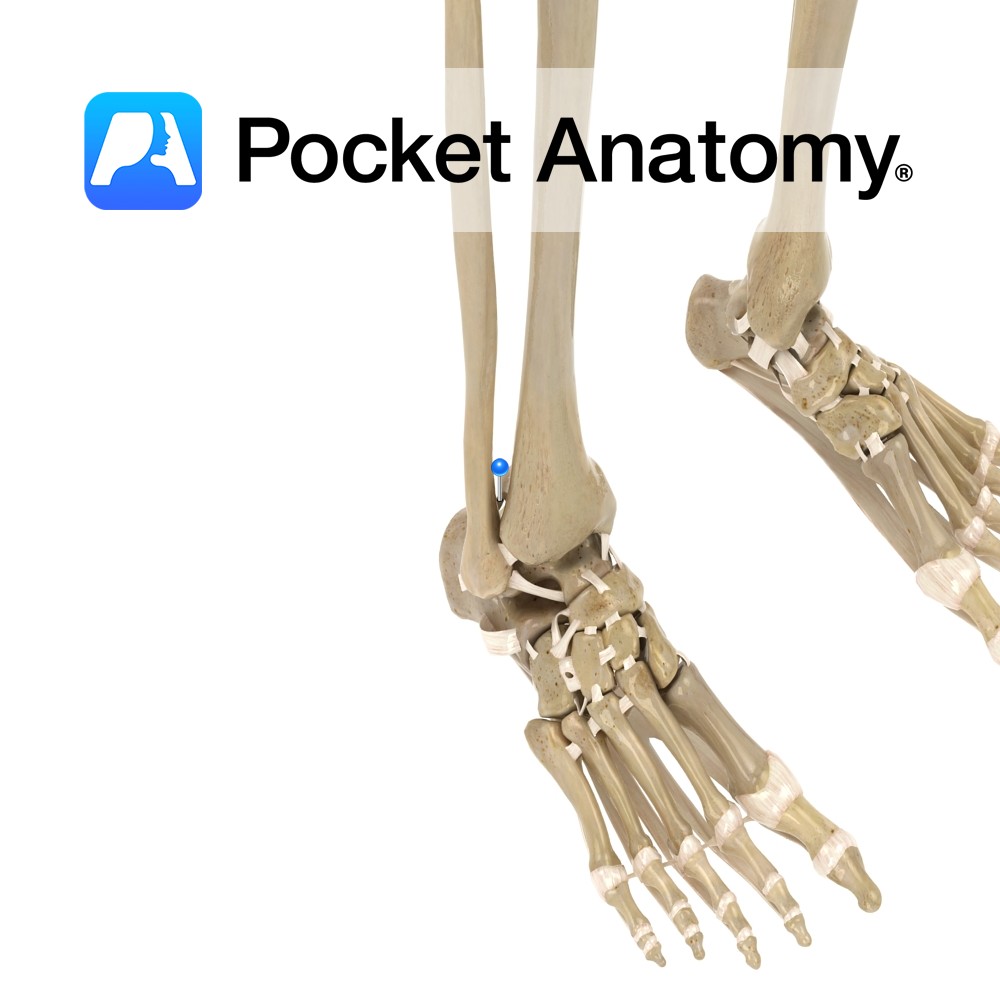
Anatomy Attaches from the lateral tubercle of the talus to the upper and medial aspect of the calcaneus. Functions Provides static stability to the talocalcaneonavicular. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
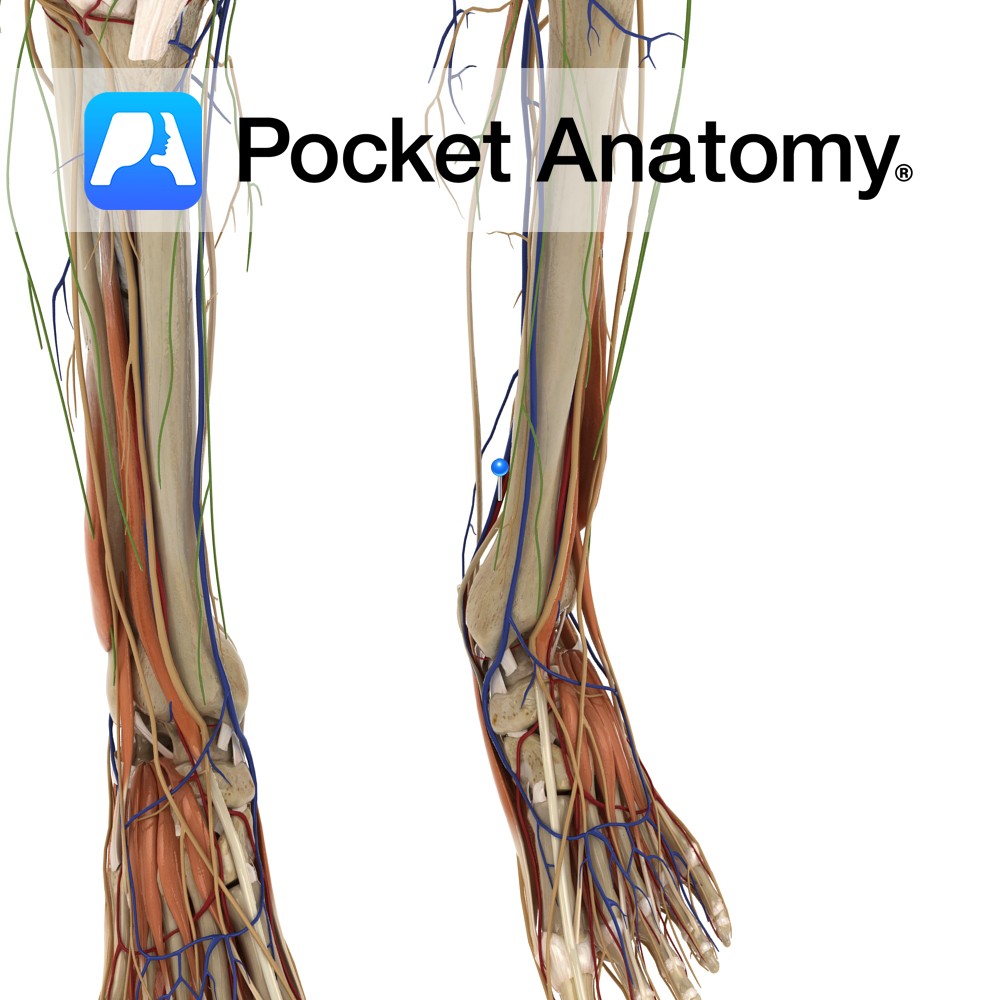
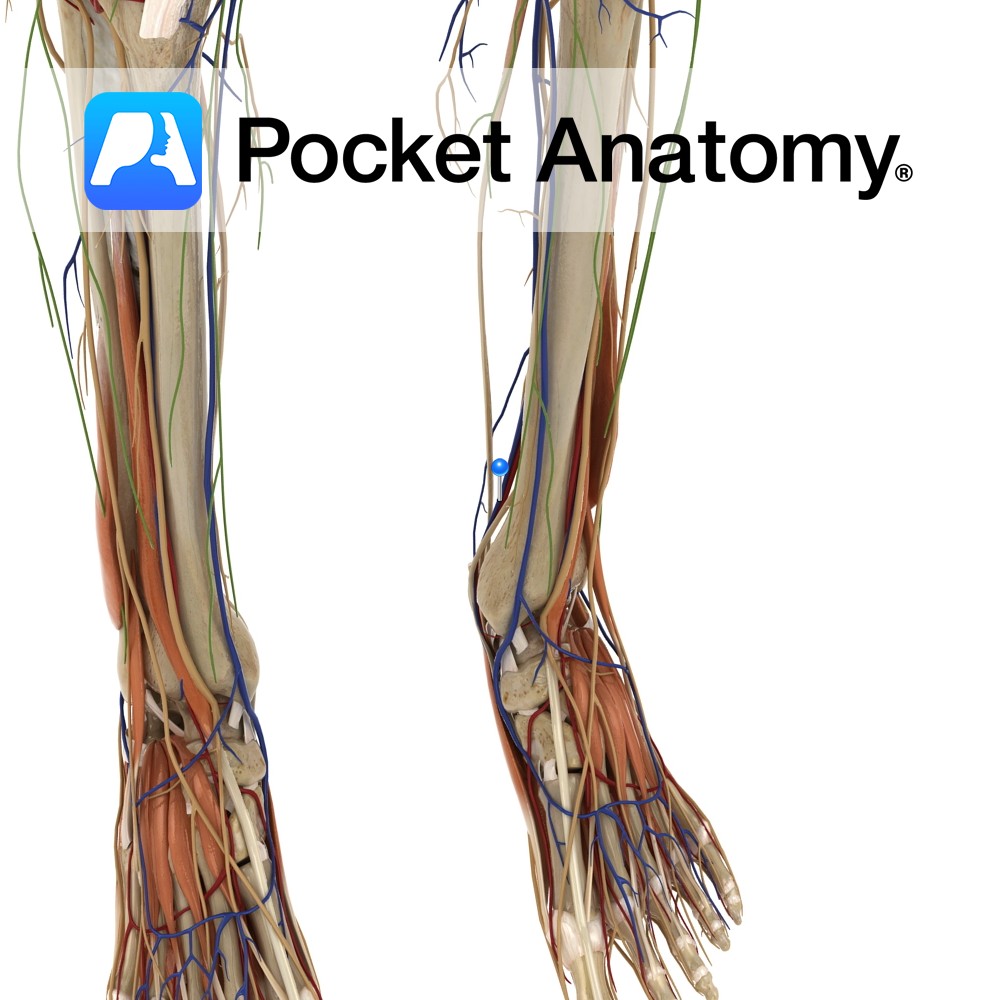
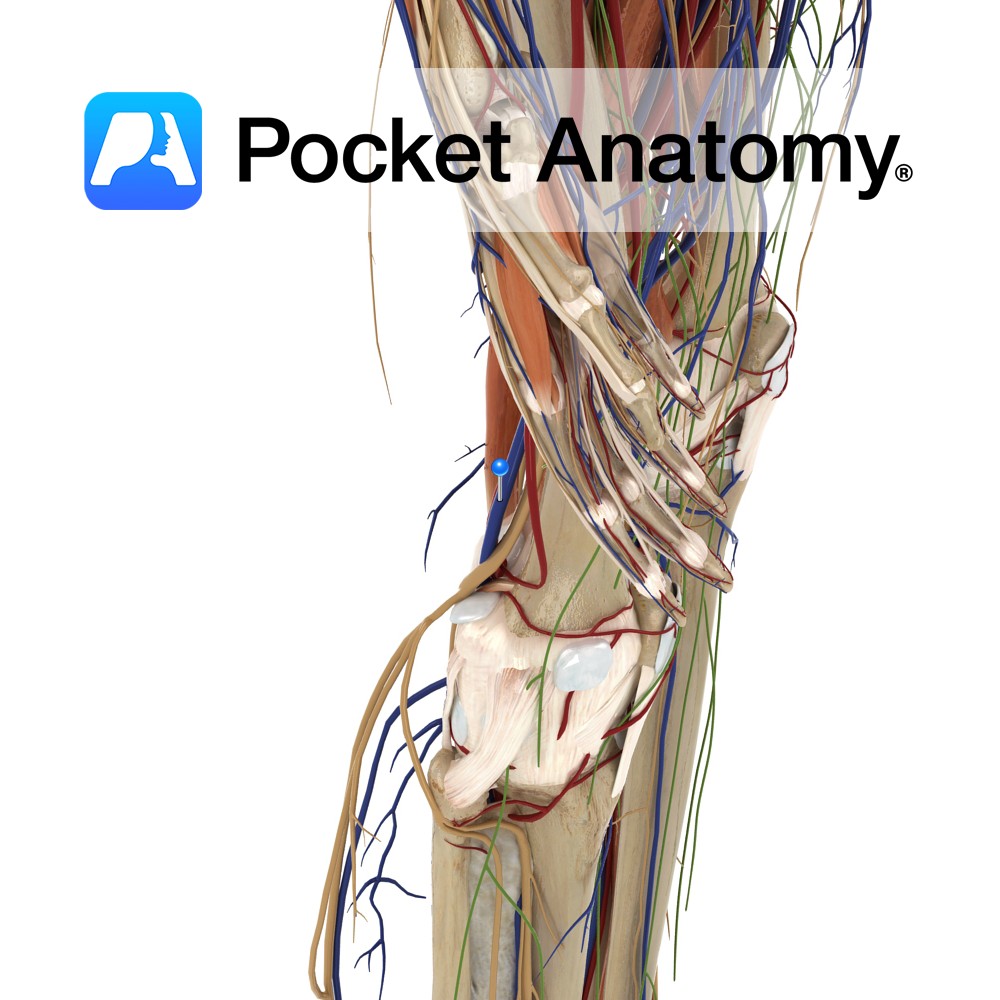
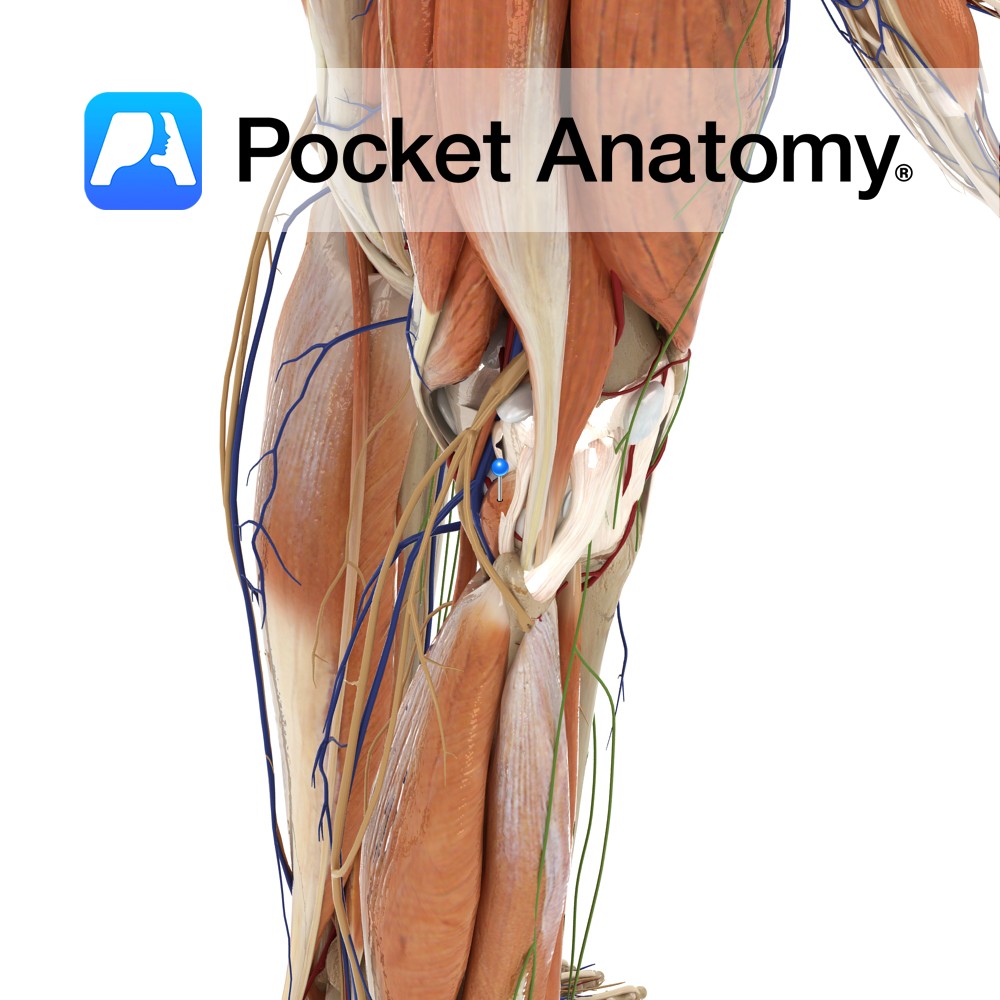
Anatomy Course A branch of the popliteal artery. It originates after the popliteal artery exits the popliteal fossa. It passes under the tendinous arch formed by the soleus muscle and descends in the plane between the solus and the tibialis posterior muscle. It enters the foot by passing behind the medial malleolus, through the tarsal
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Begins at the junction of the lateral and medial plantar veins. It ascends to the leg, passing behind the medial malleolus and travels deep in the posterior aspect of the leg. It passes under the tendinous arch formed by the soleus muscle and becomes the popliteal vein in the popliteal fossa. Drain Drains
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Attaches from the posteriolateral surface of the distal tibia to the posterior medial surface of the lateral malleolus. Functions Firmly links the distal ends of the tibia and fibula. This is essential to produce the framework for the articulation of the ankle with the leg. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Two layered membrane in thorax, folded on itself like a deflated but tied balloon, ie there is a potential cavity (if it were re-inflated). Between the pleural layers is a small amount of lubricant fluid that allows touching sides to slide over each other. One side (parietal – sensitive to pain) is externally attached
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
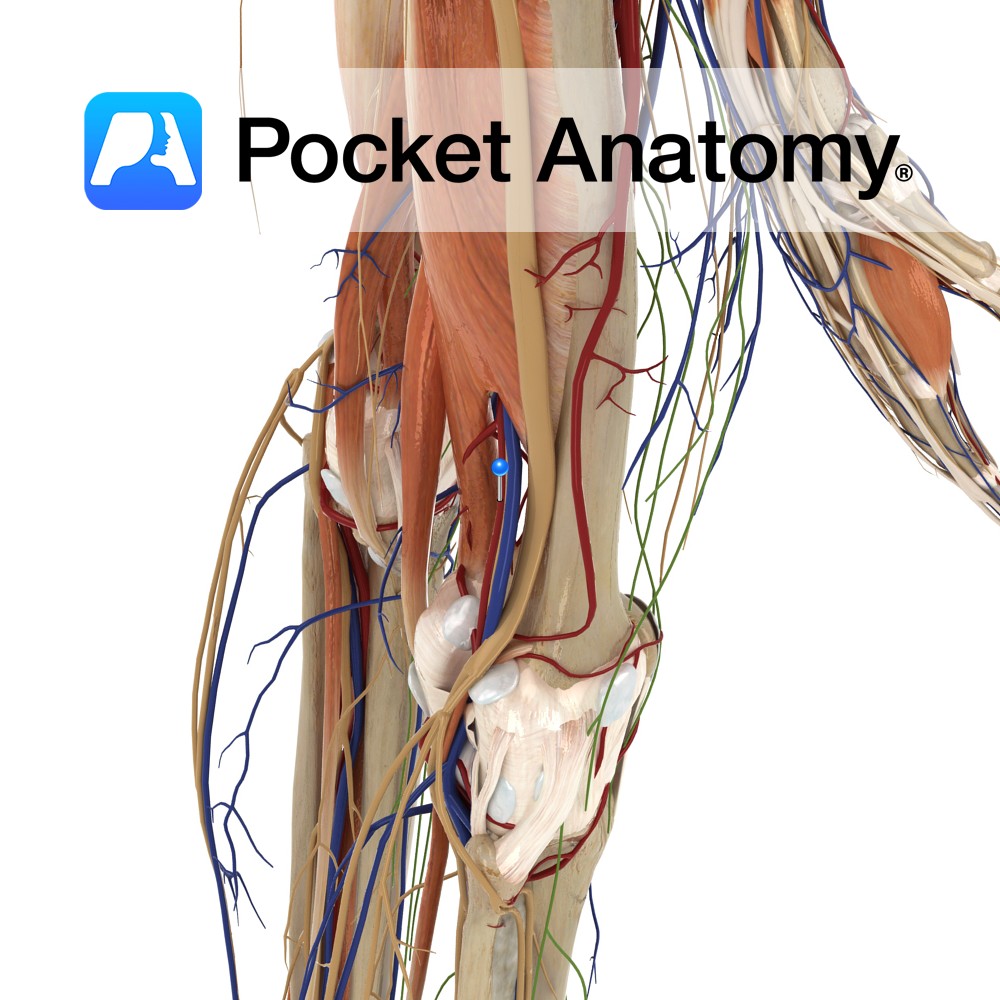
Anatomy Course An extension of the superficial femoral artery once it passes through the adductor canal and enters the popliteal fossa behind the knee. The popliteal artery is the deepest of the structures in the popliteal fossa and descends from the upper medial side. On leaving the popliteal fossa it bifurcates into the anterior and
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Formed on the posterior aspect of the leg, as the two tibial veins merge. It ascends through the popliteal fossa and becomes the femoral vein. Drain Drains the lower leg and knee joint. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Lateral surface of the lateral condyle of the femur and the lateral meniscus. Insertion: Medial half of the triangular area above the soleal line on the posterior surface of the tibia. Key Relations: -One of the four muscles of the deep posterior compartment of the leg. -The popliteus forms part of the floor
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
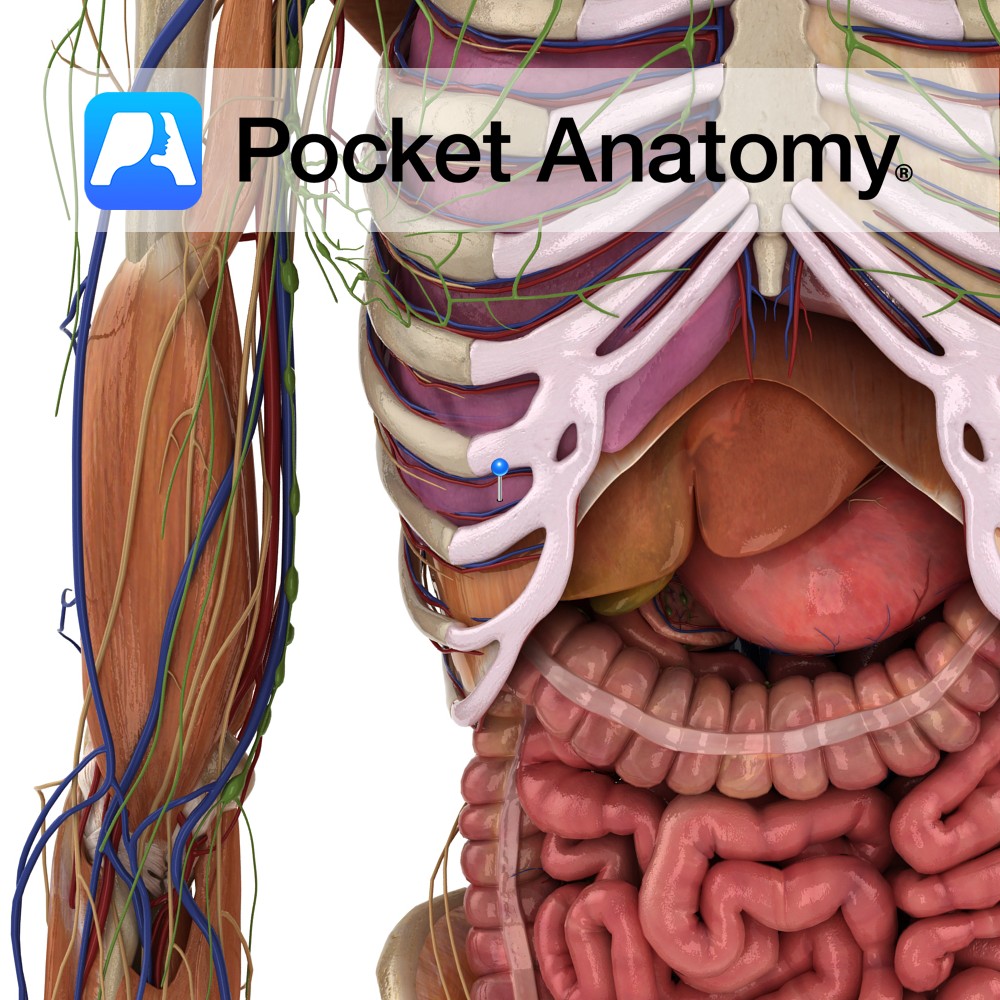
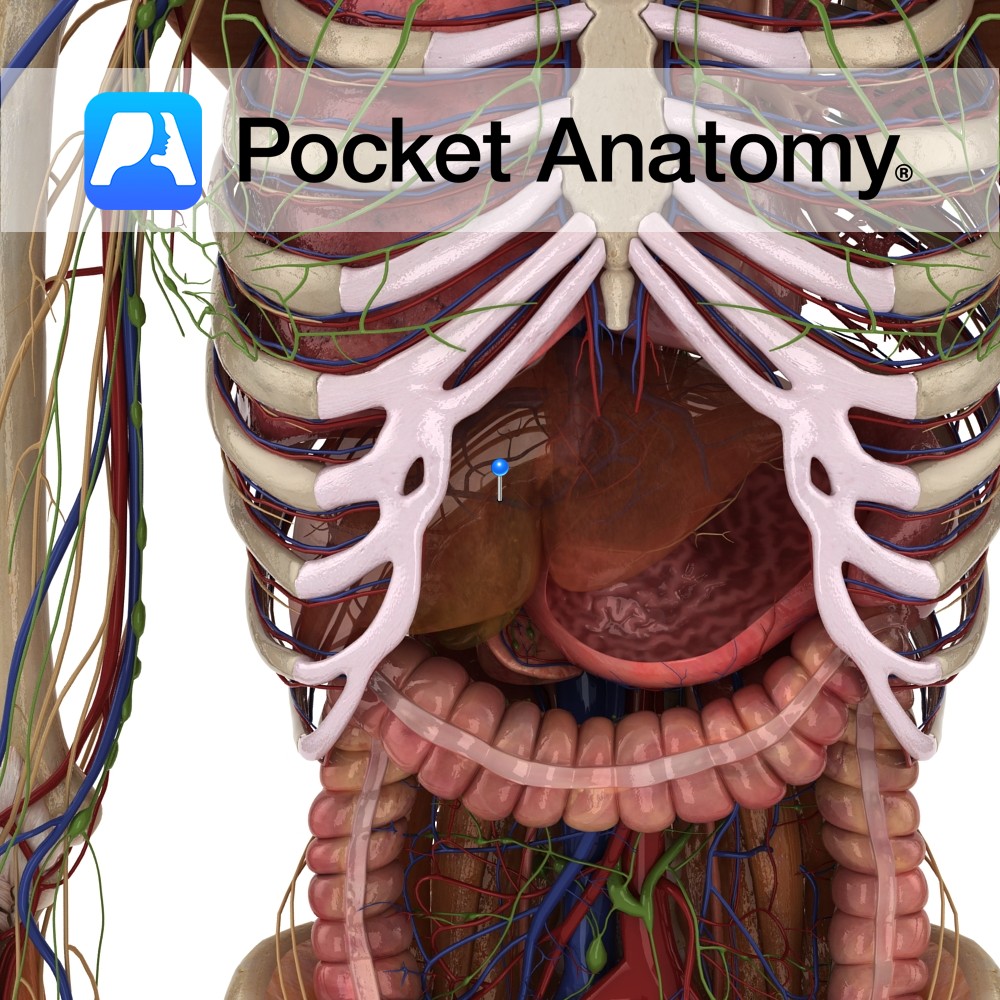
Anatomy Course Formed when the splenic and superior mesenteric veins merge behind the pancreas. It ascends to the liver, passing posterior to the superior duodenum. It divides into right and left branches as it enters the liver. Drain Brings blood for detoxification from the gastrointestinal system to the liver, where it rejoins the systemic circulation.
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins