PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
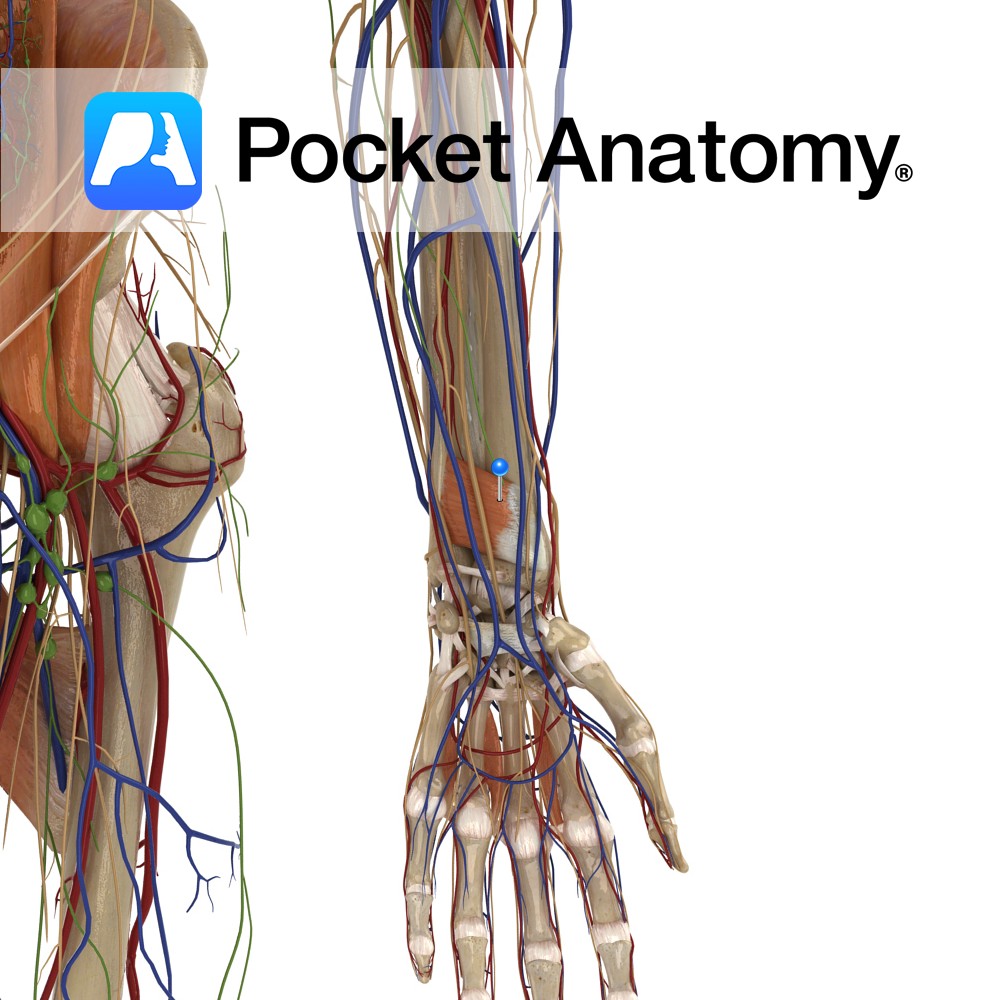
Anatomy Origin: Medial surface of distal ulna. Insertion: Lateral Surface of distal radius. Key Relations: One of the three muscles in the deep anterior compartment of the forearm. Functions -Pronates the forearm and hand at the radioulnar joint. -Deep fibres bind the radius and ulna together. e.g.: as in loosening a screw (right hand). Supply
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
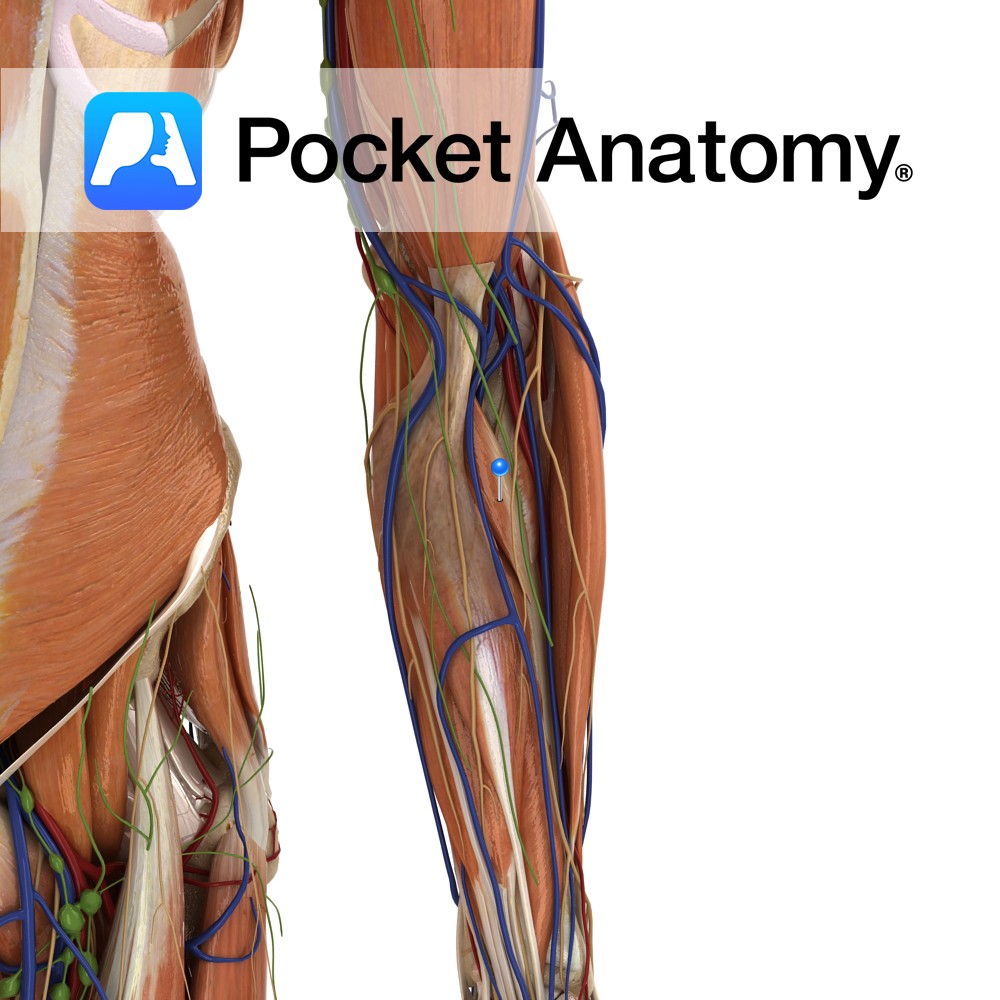
Anatomy Origin: Humeral head: Medial epicondyle of humerus via the common flexor tendon, and adjacent supraepicondylar ridge. Ulnar head: Medial aspect of the coronoid process of ulna. Insertion: Roughening on lateral surface of radial shaft near its midpoint. Key Relations: -The median nerve courses between the two heads of pronator teres in 80% of people.
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Begin at the metacarpals and drain blood into the venous palmar arch of the hand. Drain Drain into the palmar venous plexus. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Articulates up with 1st metatarsal, down with 1st distal phalanx (big toe has only 2 phalanges). Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Articulates proximally with 3rd metatarsal, distally with 3rd middle phalanx. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
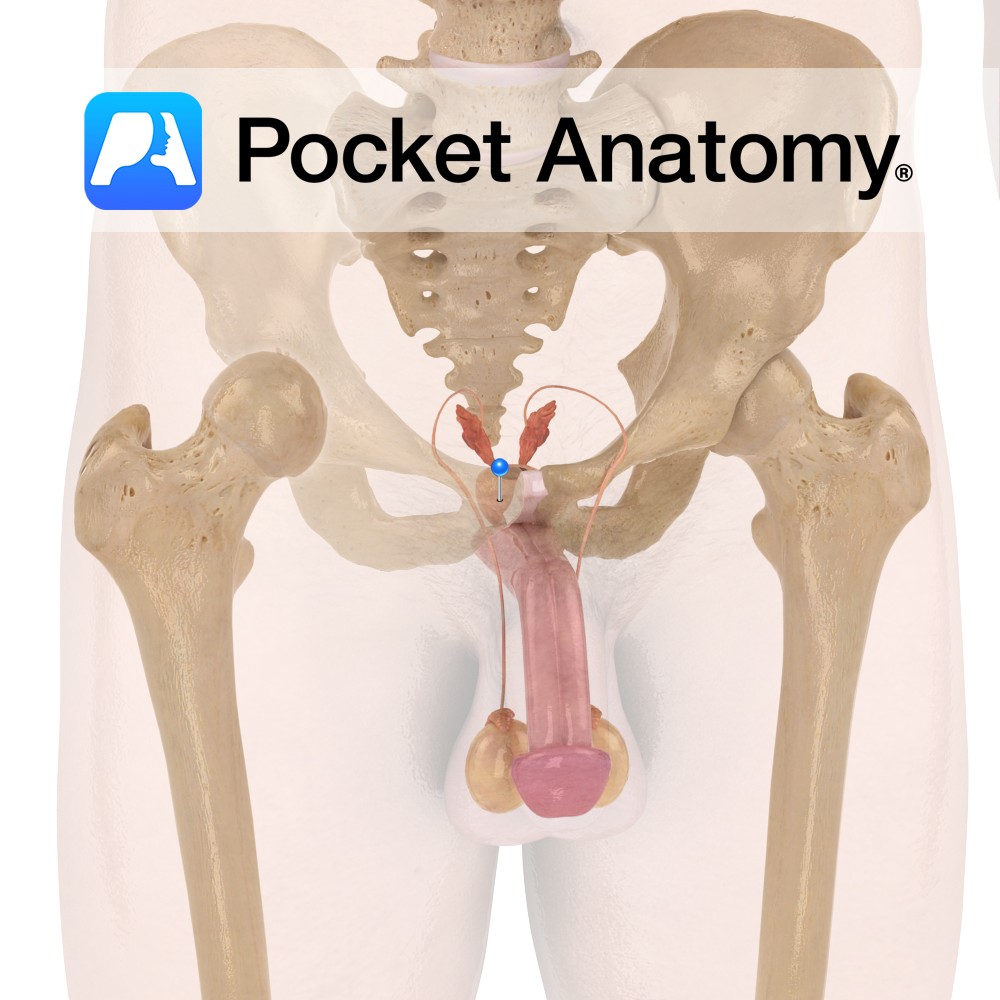
Functions Secretes alkaline fluid which constitutes ~30% of semen (with spermatozoa and seminal vesicle fluid) and protects sperm against acidic vaginal environment. This fluid is produced constantly, with the excess being expelled in urine. Contains smooth muscles which help project sperm during ejaculation. These muscles also help in involuntary control of urine. Anatomy Complex exocrine
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
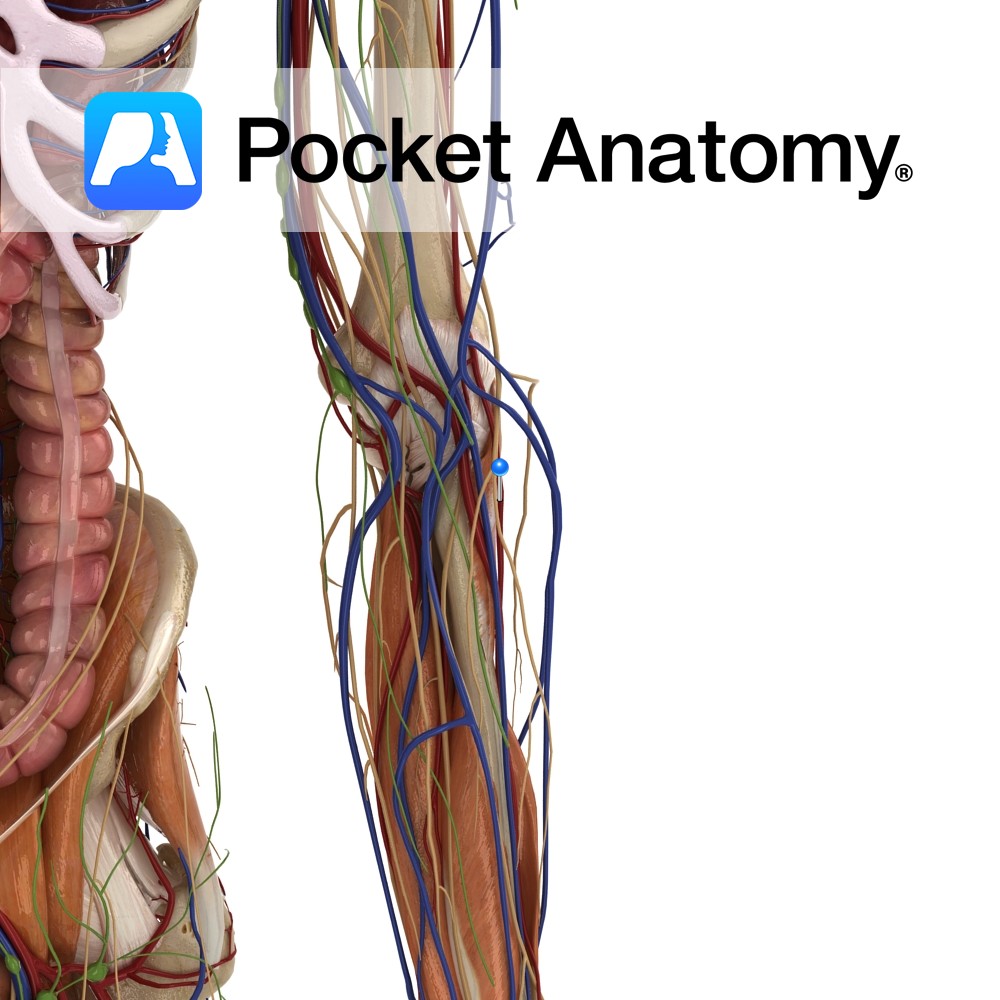
Anatomy Course A branch of the ileocolic artery that branches off near the junction of the ileum and the cecum. It can branch off together with the anterior cecal artery as a trunk, or individually. Supply The posterior cecal artery supplies the cecum and the appendix. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
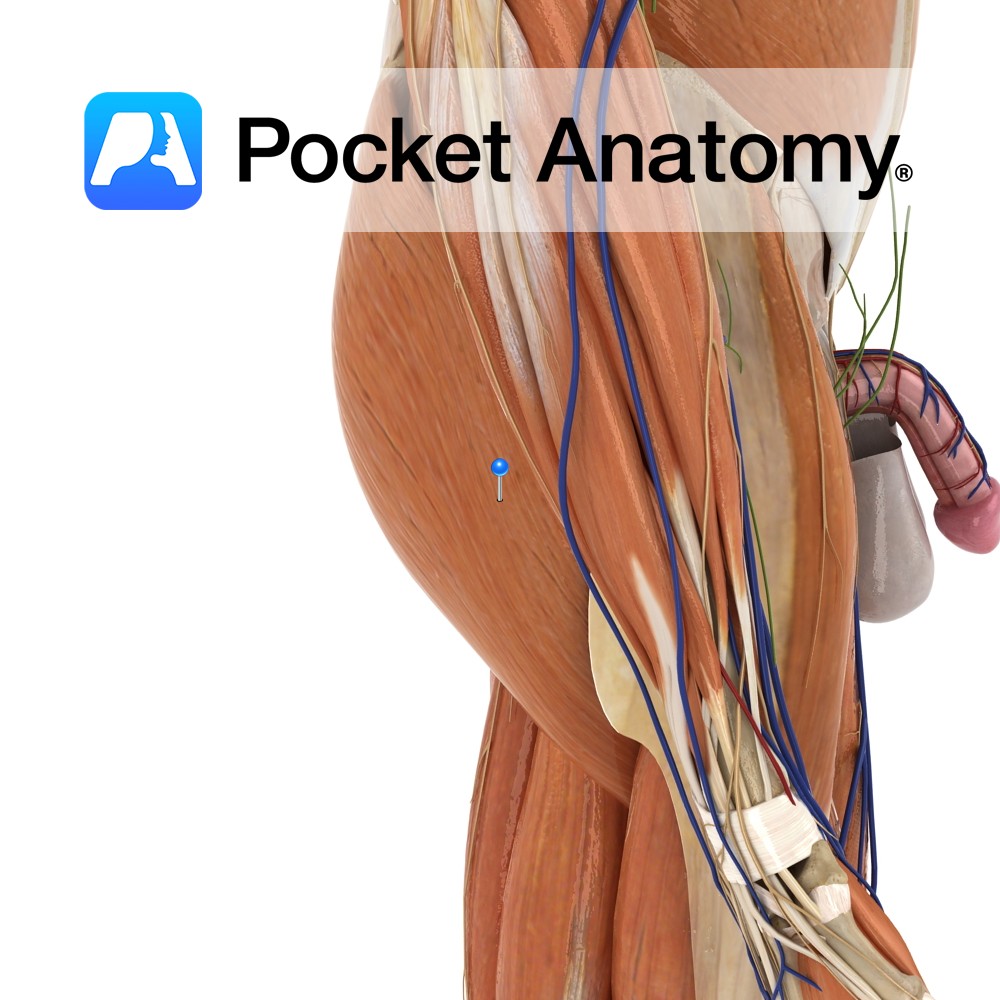
Anatomy Course Arises from the sacral plexus in the pelvis. It exits the pelvic cavity through the greater sciatic foramen inferior to the piriformis muscle. It passes to the back of the leg and travels distally beneath the gluteus maximus, and then passes over the long head of the biceps femoris muscle, remaining deep to
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Originates from the common interosseous artery, which is a branch of the ulnar artery. It branches from the common interosseous artery just above the margin of the interosseous membrane, running dorsally. It then runs distally on the posterior aspect of the forearm, until it reaches the wrist joint where it joins with the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
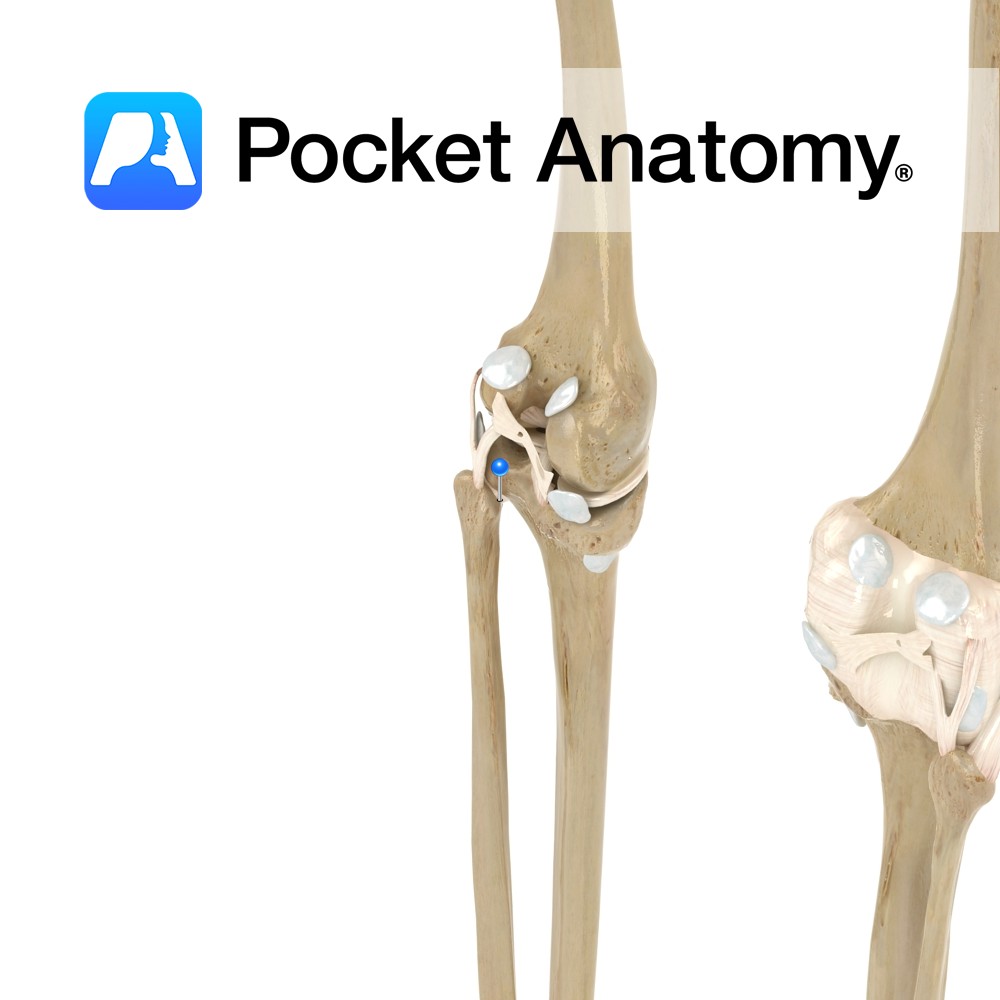
Anatomy Attaches from the head of the fibula, and passes obliquely upwards to attach to the lateral condyle of the tibia. Functions Provides static stability to the proximal tibiofibular joint. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins


.jpg)
.jpg)