PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
Anatomy One of the intrinsic muscles of the back. Consists of rotatores cervicus, thoracis and lumborum. Rotatores cervicis: Origin: Articular processes of cervical vertebrae. Insertion: Spinous processes of cervical vertebrae. Rotatores thoracis: Origin: Transverse processes of thoracic vertebrae. Insertion:Spinous processes of thoracic vertebrae. Rotatores lumborum: Origin: Mammillary processes of lumbar vertebrae. Insertion: Spinous processes of
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Made up of the anterior rami of S1 – S4 and the lumbosacral trunk, which is made up of L4 and L5. It is a part of the lumbosacral plexus. It is in the pelvis, located just by the posterior pelvic wall, anterior to the piriformis muscle. The anterior rami of spinal nerves
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
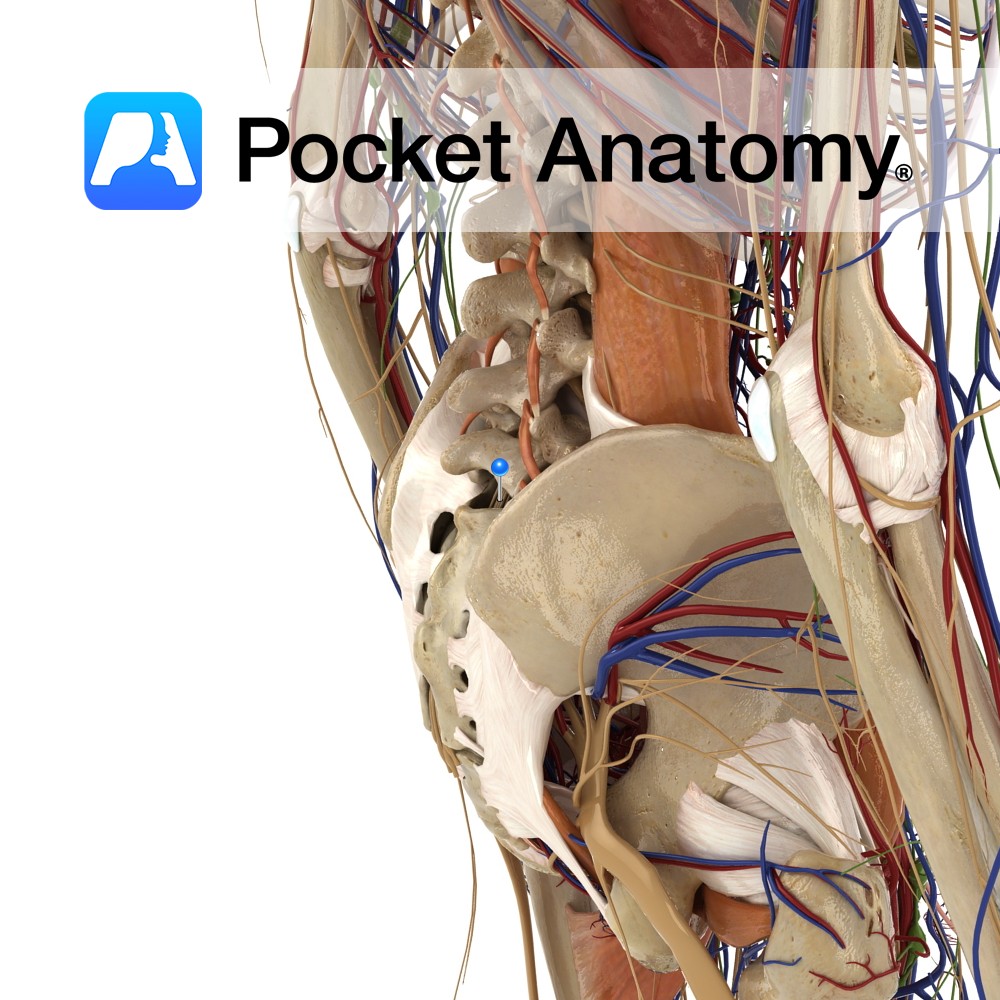
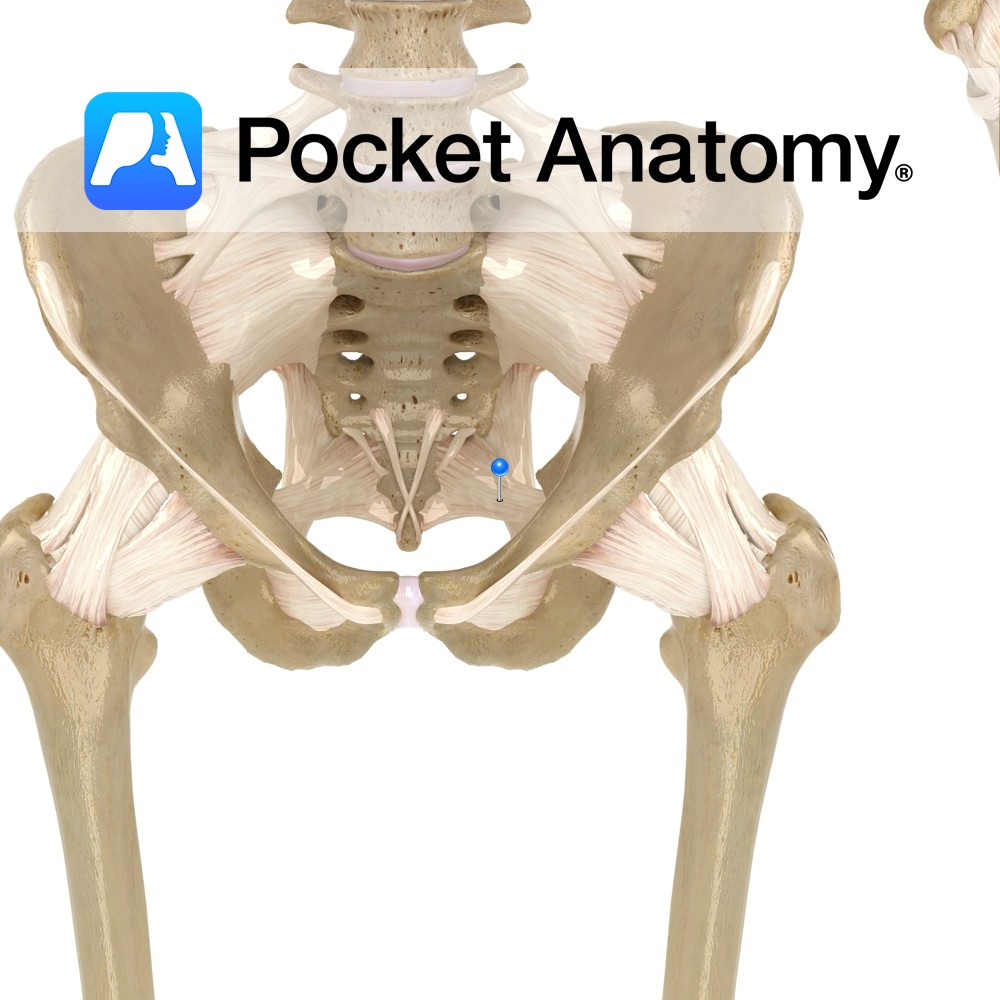
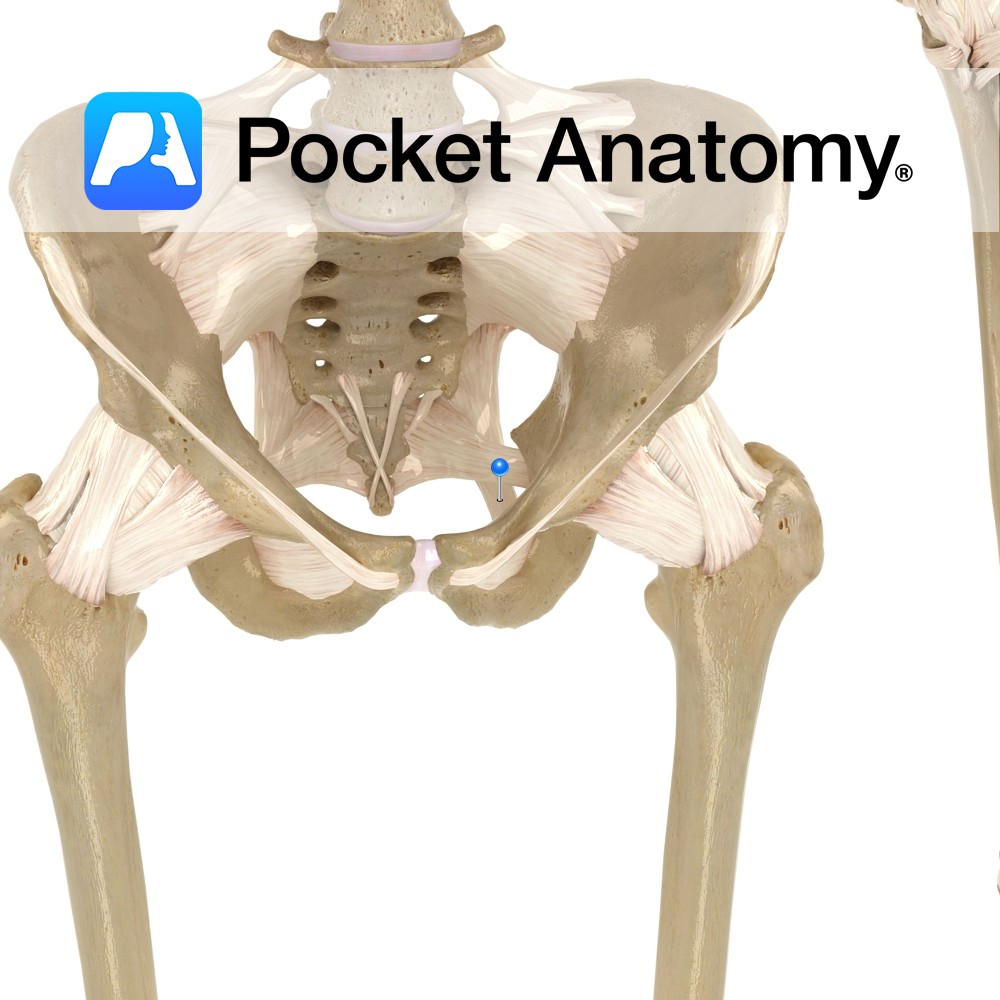
Anatomy Attaches bilaterally from the side of the inferior part of the sacrum and superior part of the coccyx, passing to the ischial spine. Functions Provides static stability to the sacroiliac joint. Also, the ligament is important in forming the pelvic wall along with the sacrotuberous ligament as they attach all the pelvic bones to
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Attaches from the posterior border of the ilium, the transverse tubercles of the sacrum, and the superior part of the coccyx, passing downwards to the ischial spine. Functions Provides static stability to the sacroiliac joint. Also, the ligament is important in forming the pelvic wall along with the sacrospinous ligament as they attach all
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
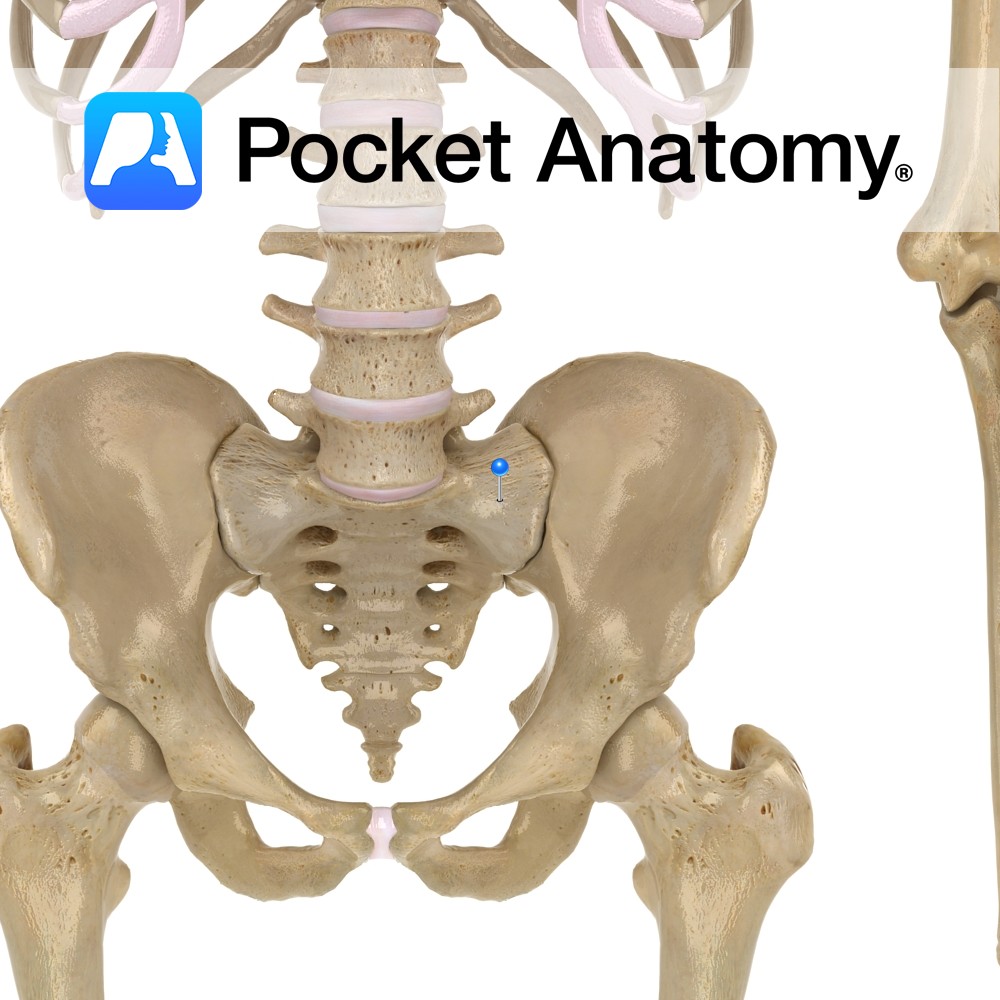
Anatomy Large triangular surface either side of sacral base, continuous with iliac fossa (akin to adapted and joined transverse and costal processes elsewhere spine). Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
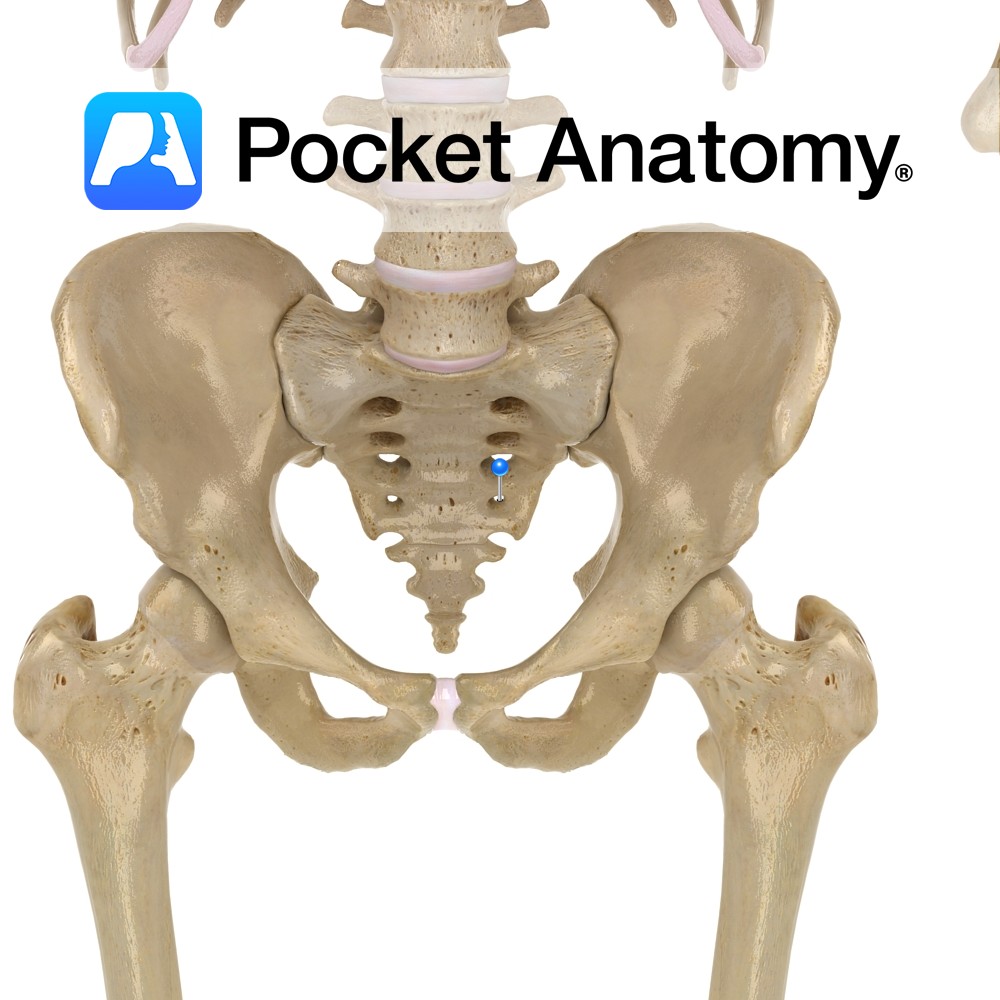
Anatomy Whereas cervical and thoracic vertebrae are distinct and afford passage of nerves through intervertebral foramina created by notches of adjacent pedicles, the fused sacrum retains foramina for this purpose, front and behind, at the lateral ends of ridges which are remnants (after fusion) of planes of separation of sacral vertebrae. Interested in taking our
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
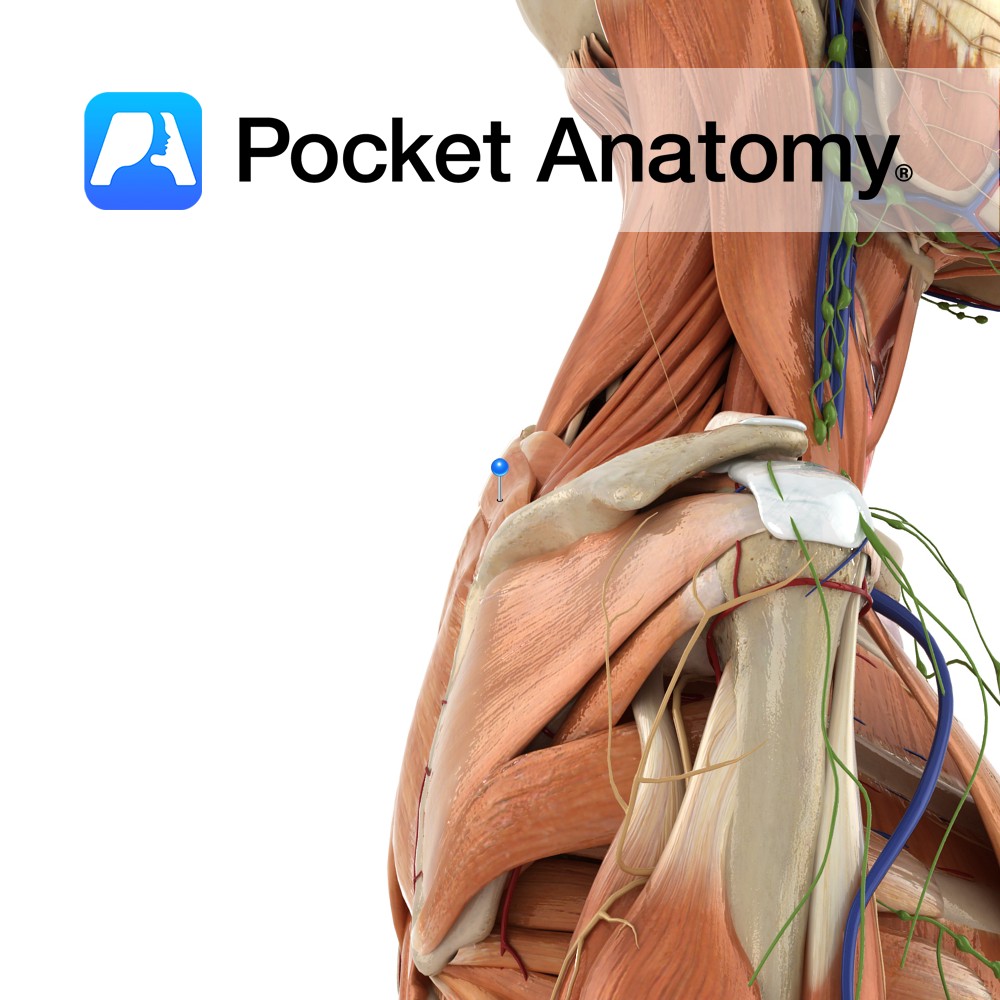
Anatomy Origin: Lower ligamentum nuchae and the spinous processes of C7 to T1. Insertion: Medial border of the scapula at the level of the spine, superior to the attachment of rhomboid major. Key Relations: -Superior to rhomboid major. -Posterior to trapezius. -Fascia of rhomboid minor and serratus anterior are tightly fused. Functions Retracts e.g. pulling
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
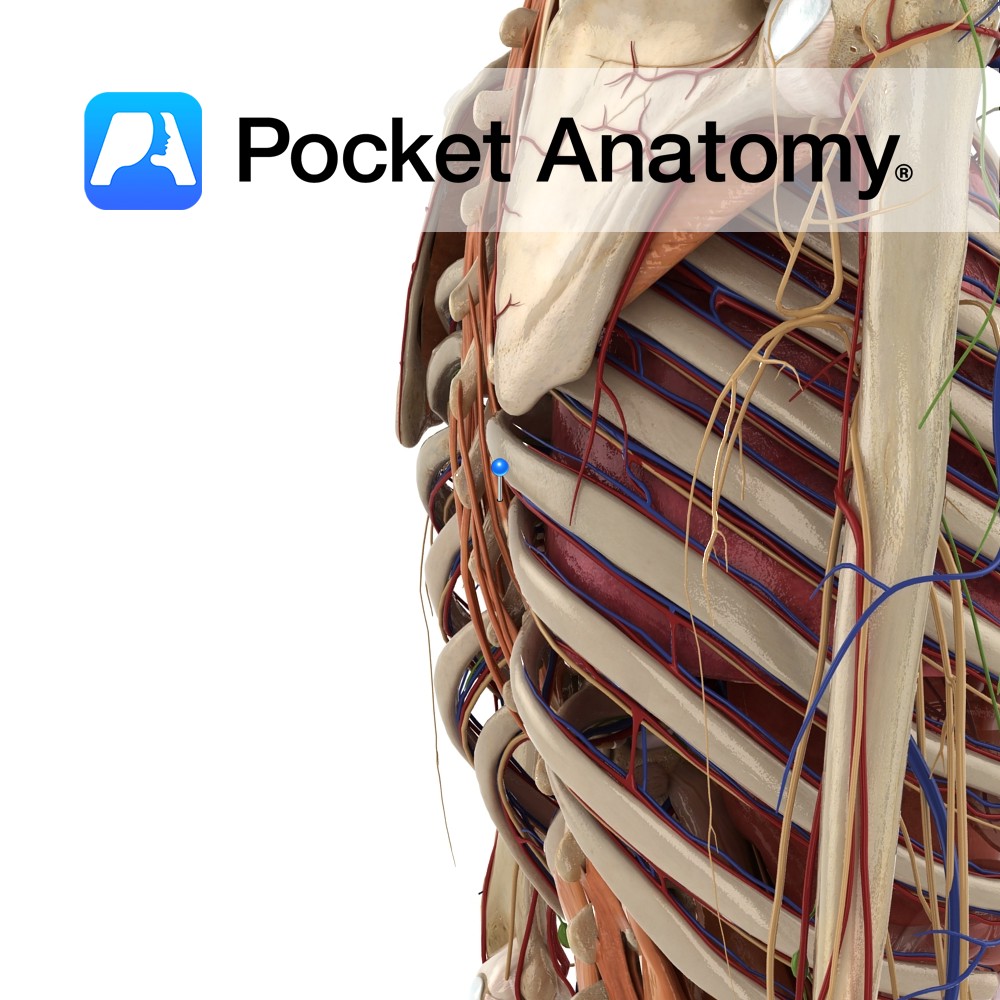
Anatomy False rib, i.e.articulates posteriorly but not anteriorly. Tapers to a pointed costal cartilage that ends in abdominal wall. Head articulates with only 1 vertebra (T11); no neck or tubercle. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy False rib, i.e. articulates posteriorly but not anteriorly. Tapers to a pointed costal cartilage that ends in abdominal wall. Head articulates with only 1 vertebra (T12); no neck or tubercle. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Most curved, usually shortest (sometimes 12th shorter). Only rib whose posterior/vertebral articulation is with only 1 vertebra (T1). Only rib whose anterior/sternal articulation is entirely with manubrium (lateral extremity of the arm of the cruciform – ross-shaped – manubrium. Clinical Ordinarily there are 12 ribs, sometimes 11, this number added to if there are
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins

-%5Bfloating-rib%5D.jpg)
-%5Bfloating-rib%5D.jpg)
-%5Btrue-rib%5D.jpg)