PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
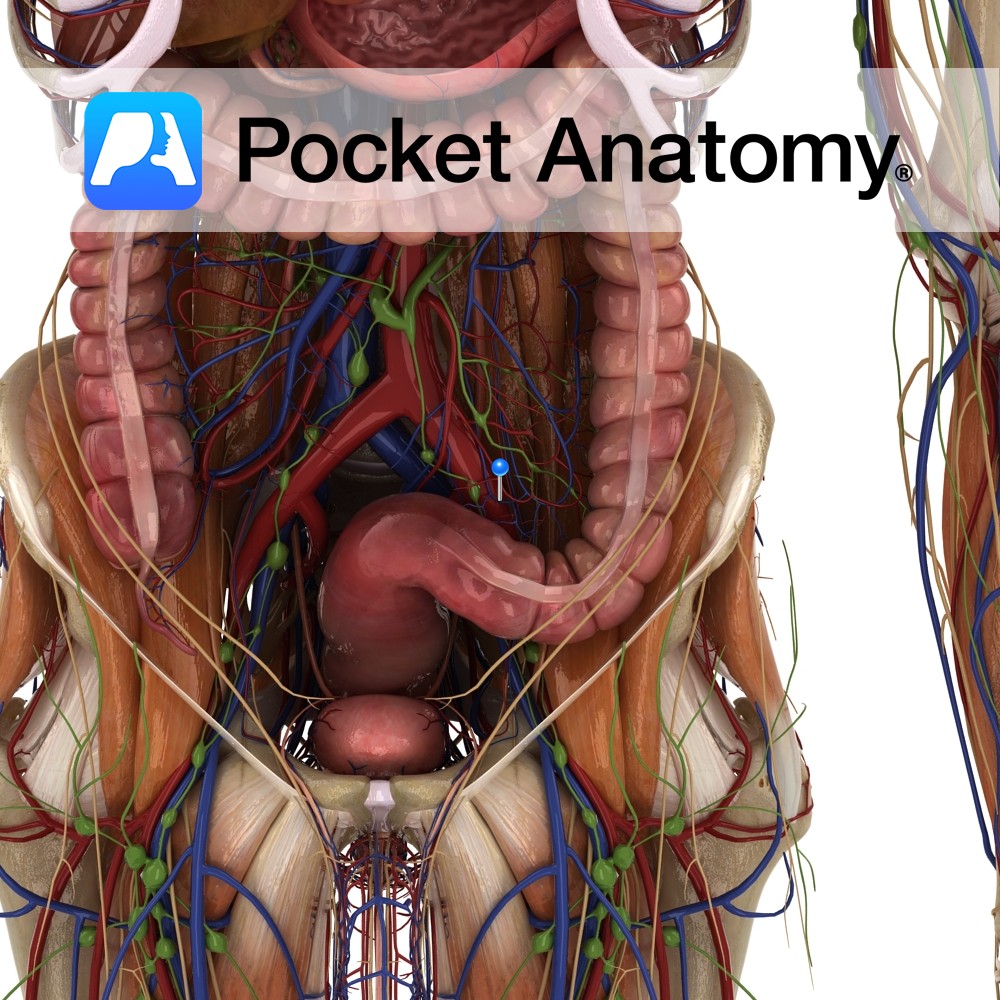
Anatomy Course Begins from a series of veins that drain the sigmoid colon. It drains into the superior rectal vein. Drain Drains the sigmoid colon. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
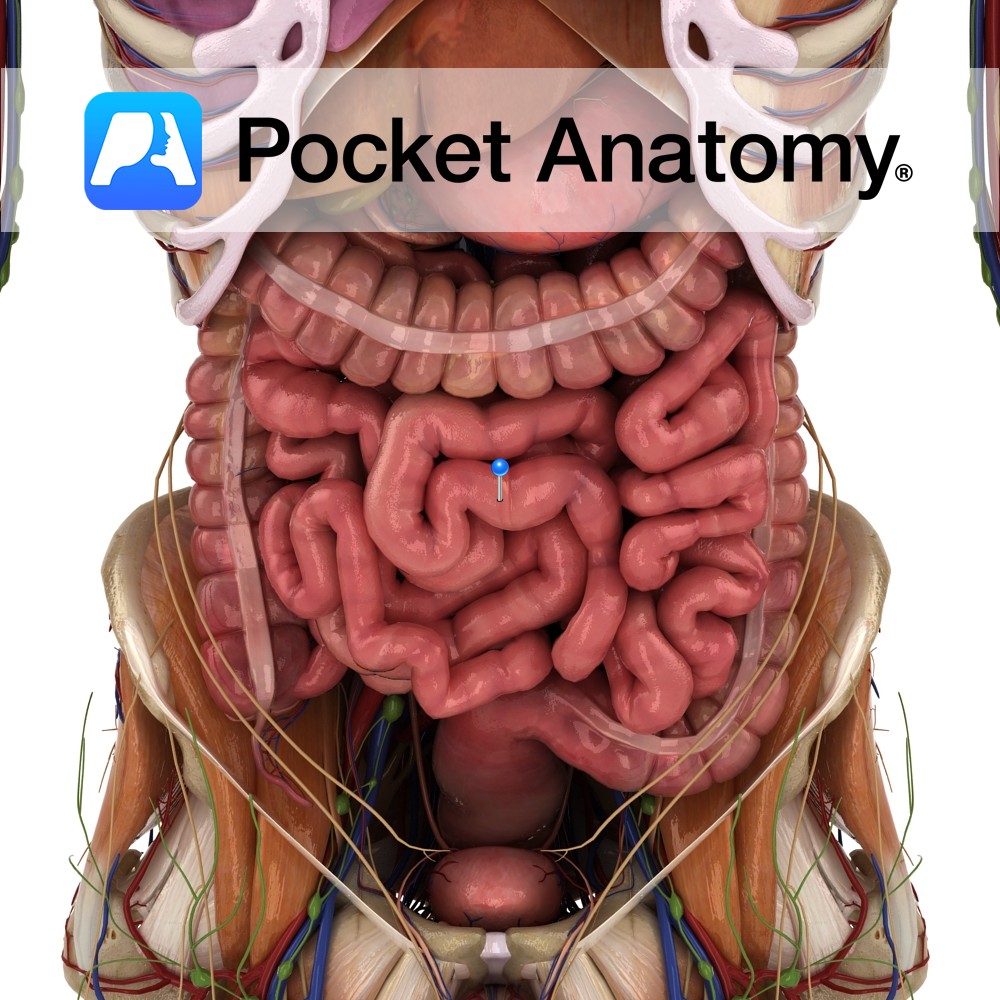
Anatomy Between stomach and colon (pyloric sphincter to ileocecal valve), comprising duodenum, jejunum and ileum, convoluted coils occupying much of abdomen/pelvis, framed at sides and above by colon, c. 23′ long in adult), attached to posterior abdominal wall by fan-shaped mesentery (invaginated peritoneum, containing lymph nodes and vessels) other than duodenum (mostly retroperitoneal). Supplied by
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
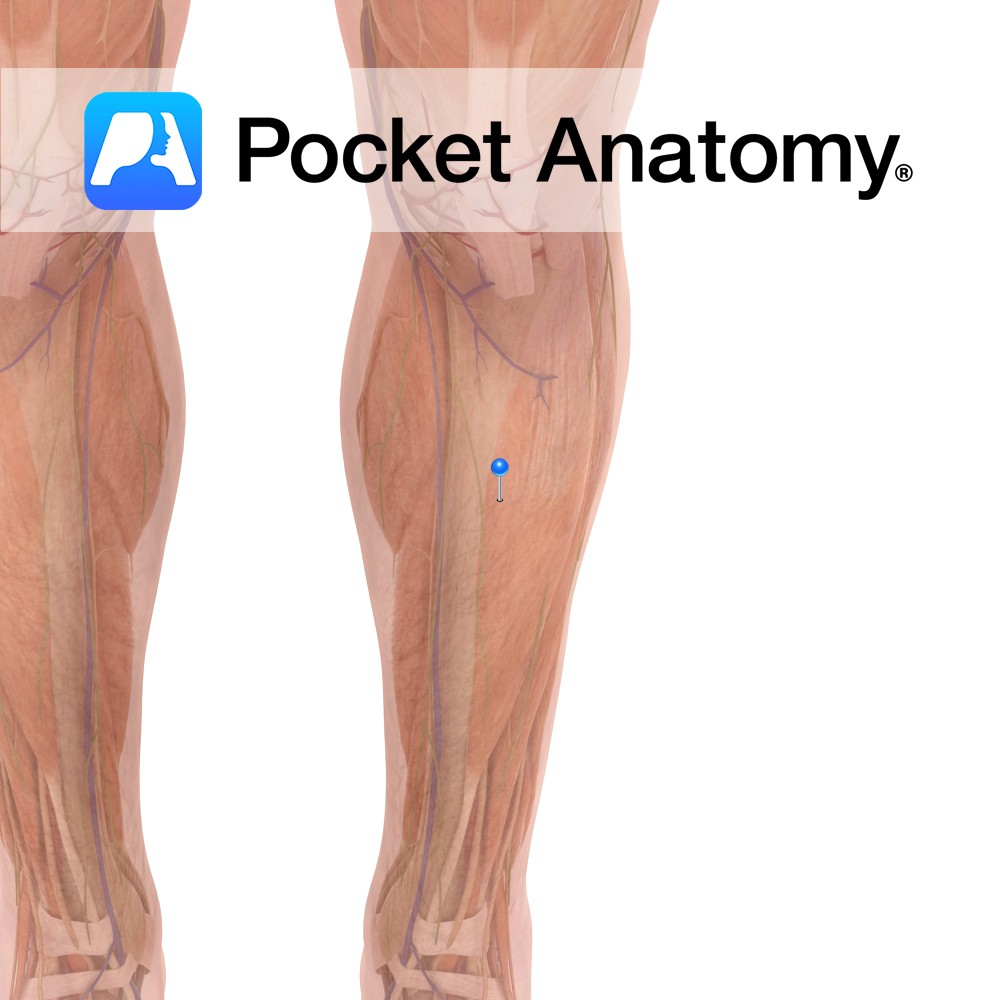
Anatomy Origin: Posterior surfaces of the head and upper third of the fibula, the soleal line of the tibia and the middle third of the medial border of the tibia. Insertion: Middle part of the posterior surface of the calcaneus by the tendo calcaneus (Achilles tendon). Key Relations: -One of the three muscles of the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Clinical Common skin conditions among adolescents include acne, atopic dermatitis, and herpes. Acne affects mainly the face, upper chest, and back (the areas of the skin with the densest concentration of sebaceous glands). Acne affects approximately 80%-90% of teenagers, usually the result of increases in testosterone during puberty (in both genders). Atopic dermatitis (eczema) is
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
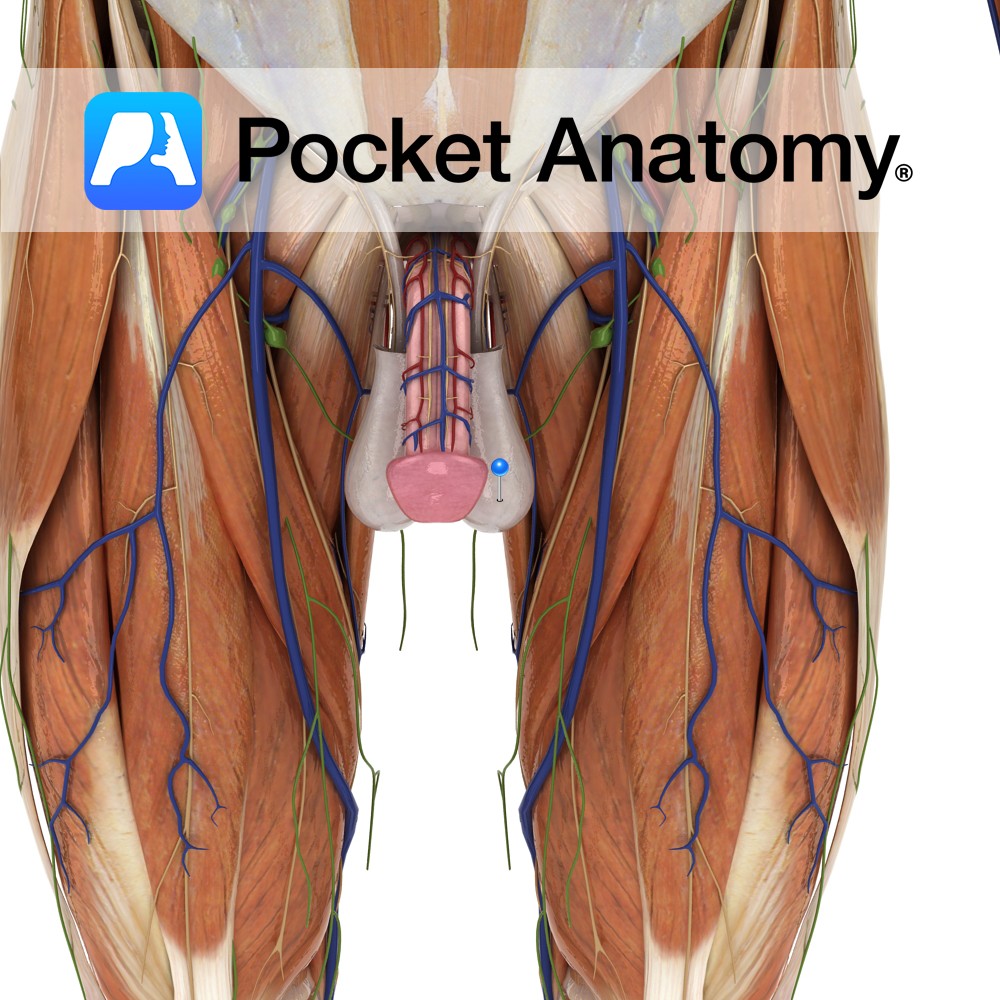
Anatomy Skin and (smooth/involuntary) muscle (tunica dartos) sac, just below and behind the penis, in front of anus, in pubic region, covered (sparsely) with hair by puberty, divided into two pouches, each containing a testis and associated vessels, ducts and muscles. Physiology Cremaster muscle and scrotum contract/relax to shorten/lengthen separation of testes (right and left
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
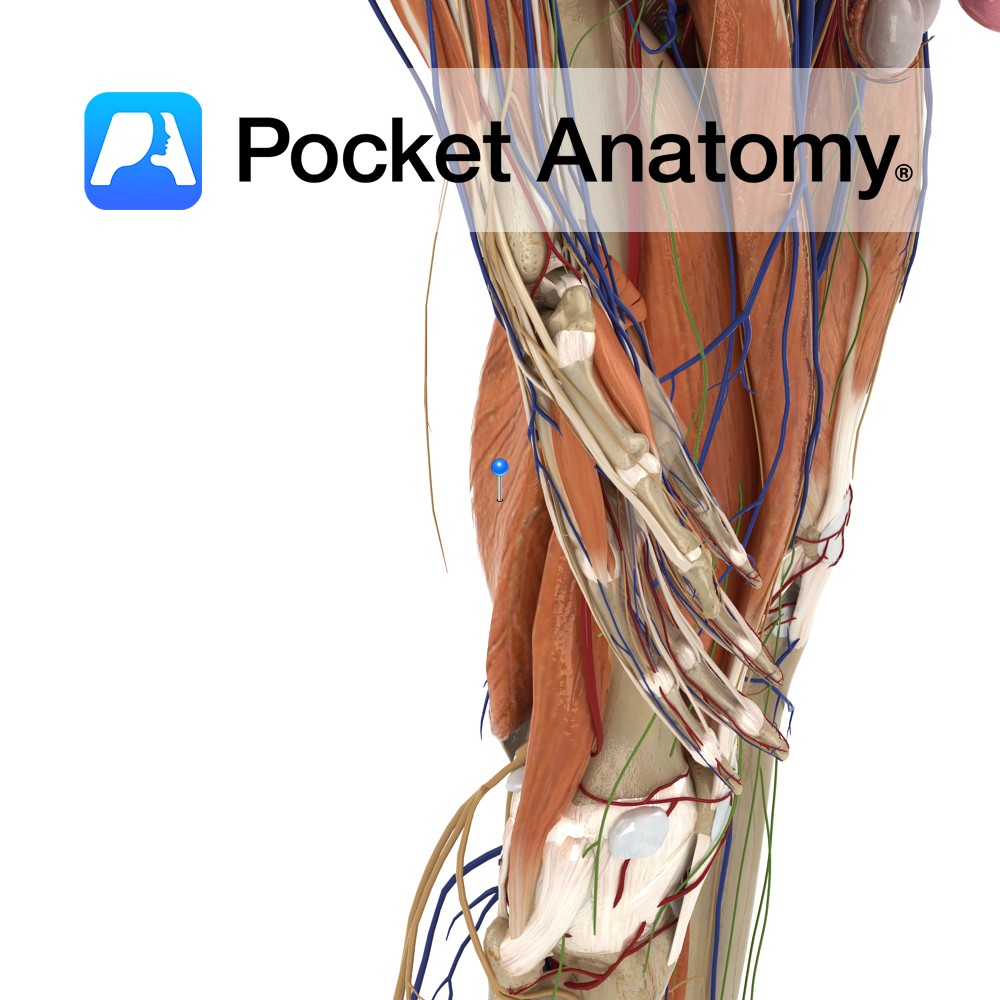
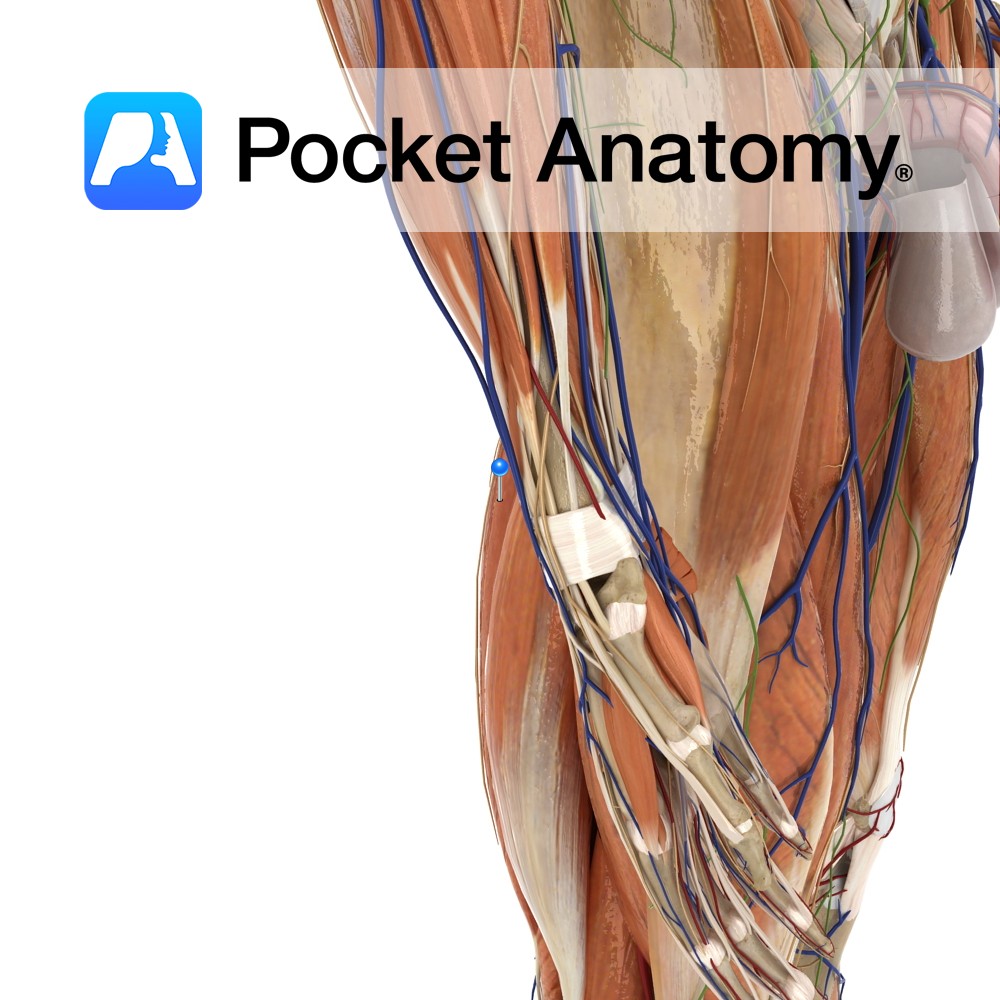
Anatomy Origin: Superolateral impression on ischial tuberosity. Insertion: Posteromedial surface of medial condyle of the tibia. Key Relations: -One of the three muscles of the posterior compartment of the thigh. -Lies posteromedial to semitendinosus and the long head of biceps femoris. -Along with semitendinosus forms the superomedial boundary of the popliteal fossa. Functions -Flexes the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
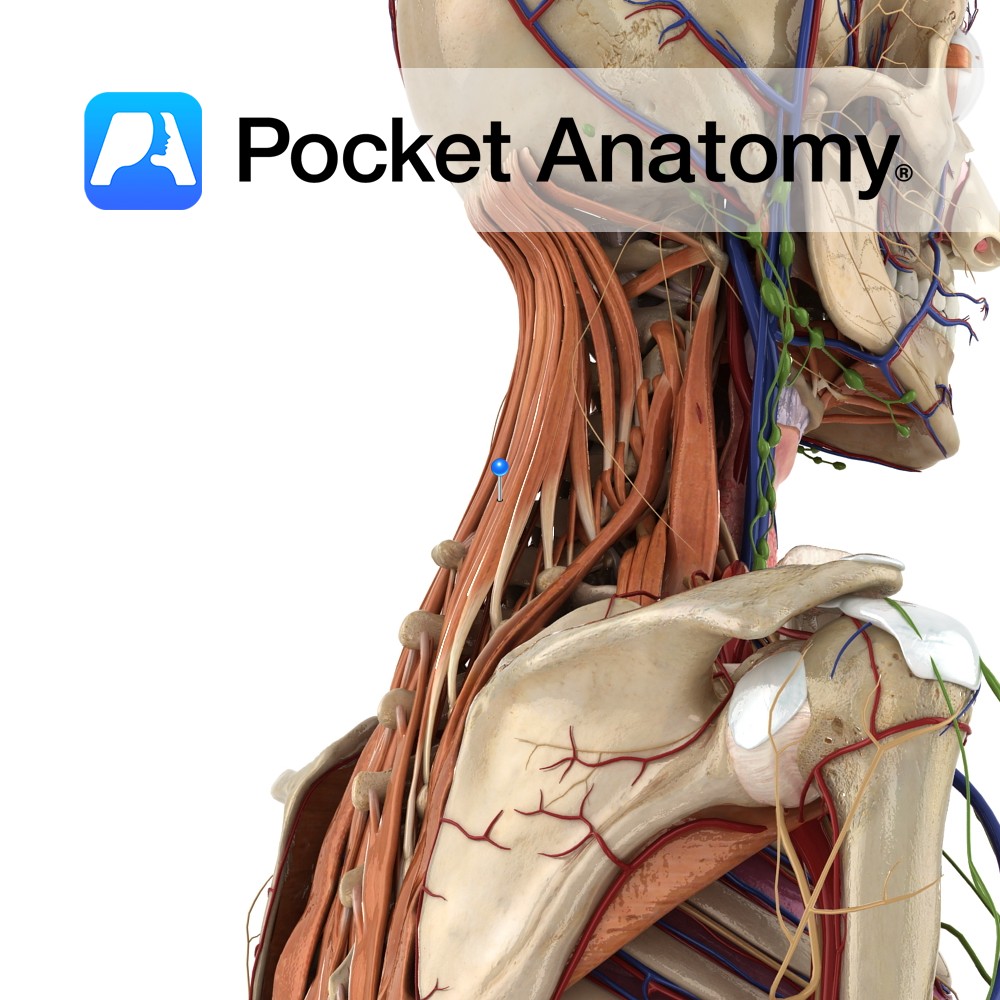
Anatomy One of the intrinsic muscles of the back. Consists of semispinalis capitis, cervicus and thoracis. Semispinalis capitis: Origin: Articular processes of C4 to C6 and transverse processes of C7 to T7. Insertion: Occipital bone on the area lying between the superior and inferior nuchal lines. Semispinalis cervicis: Origin: Transverse processes of T1 to T5/6.
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
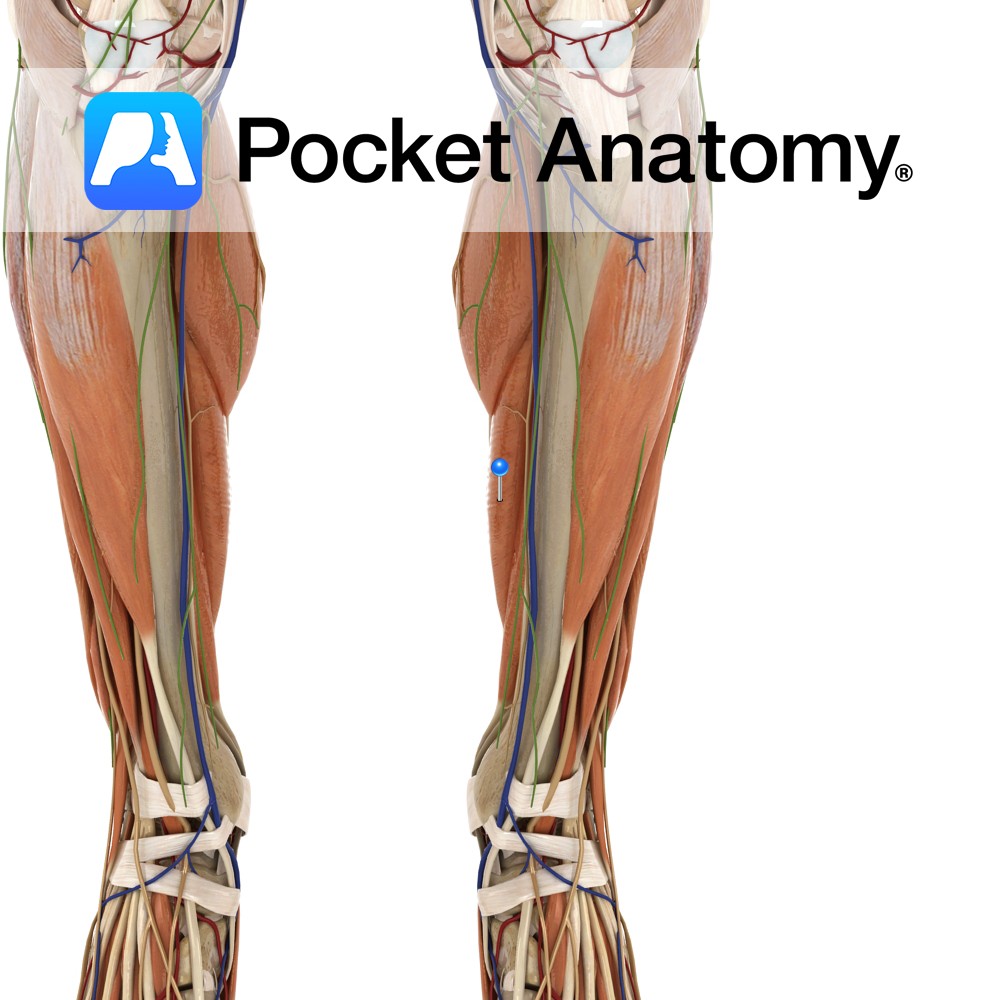
Anatomy Origin: Superomedial area of ischial tuberosity (with biceps femoris). Insertion: Superior part of medial tibia. Key Relations: -One of the three muscles of the posterior compartment of the thigh. -Along with semimembranosus forms the superomedial boundary of the popliteal fossa. -At its insertion to the tibia, the tendon of semitendonosus is located just posterior
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: External surface of lateral surface of upper eight ribs. Insertion: Medial border of scapula. Key Relations: The long thoracic nerve travels inferiorly on the surface of the muscle. Functions -Protracts the scapula laterally rotates the scapula e.g. as in the forward motion of throwing a punch. -Stabilises and holds the medial border of
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Spinous processes of T11 to L3 and supraspinous ligaments. Insertion: Lower border of the 9th to the 12th ribs just lateral to their angles. Key Relations: -Serratus posterior inferior shares it’s aponeurosis of origin with latissimus dorsi. -Sometimes referred to as part of the respiratory group. Functions -Depresses 9th to the 12th ribs,
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins