PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
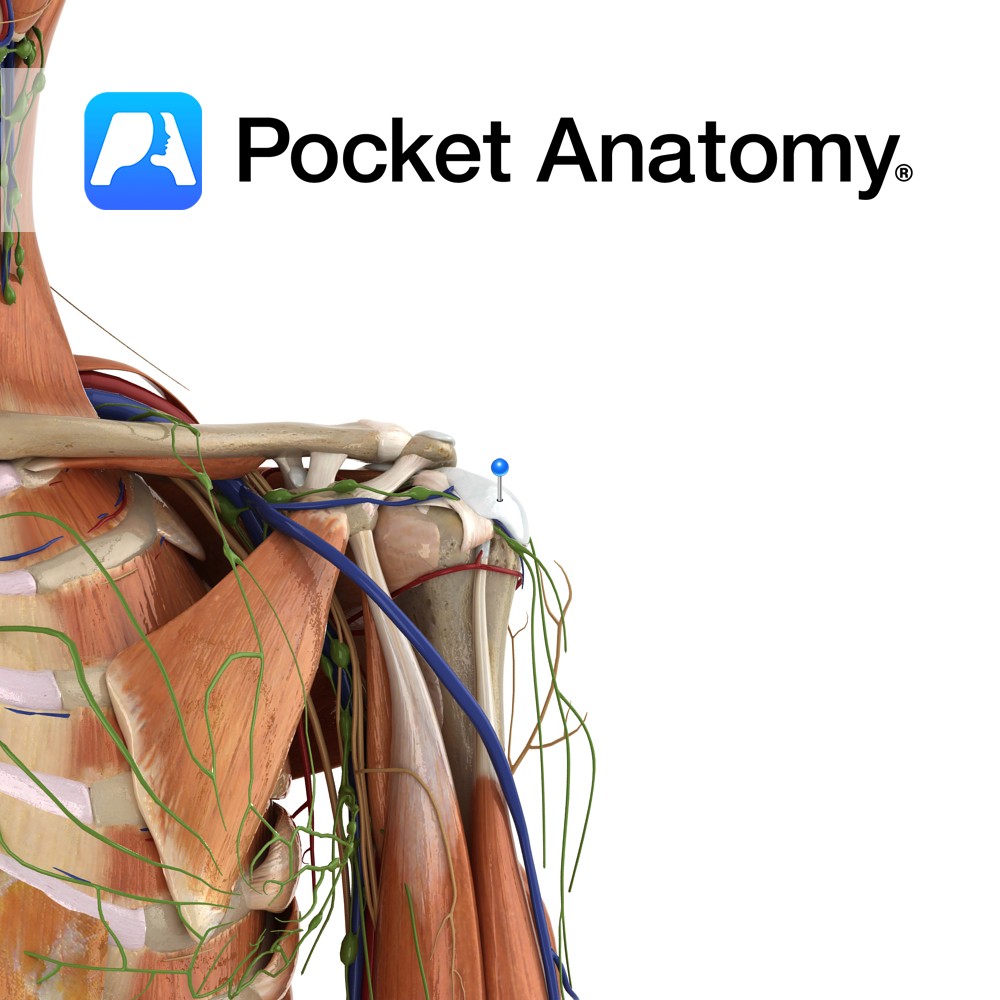
Anatomy Located between the acromion and supraspinatus muscle (or joint capsule). Functions Reduces friction between the acromion and supraspinatus muscle and tendon. Clinical Subdeltoid bursitis is inflammation of the bursa. It is very rare and generally caused by infection or autoimmune inflammation. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
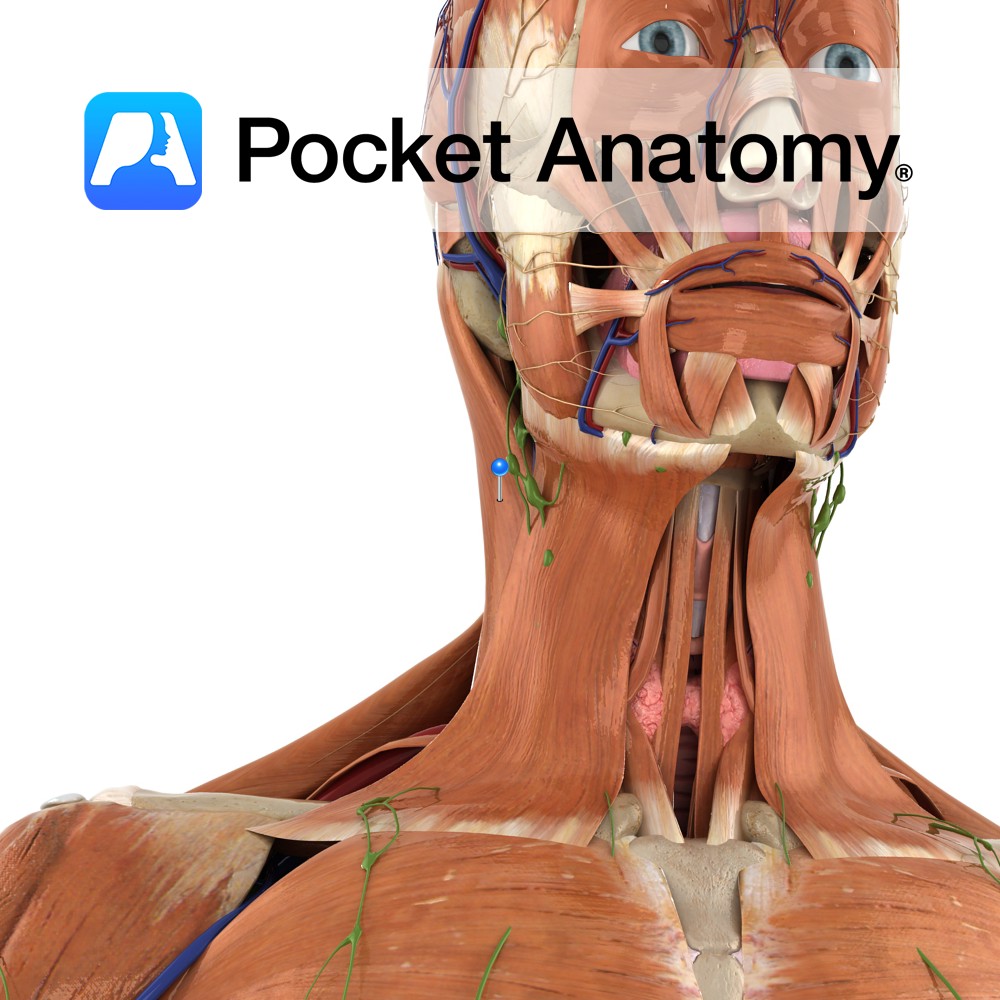
Anatomy Origin: Sternal head: Upper part of anterior surface of manubrium of sternum. Clavicular head: Superior surface of medial one third of the clavicle. Insertion: Sternal head: Lateral half of superior nuchal line. Clavicular head: Lateral surface of mastoid process. Key Relations: -Posterior edge forms anterior border of posterior triangle of the neck. -Anterior edge
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
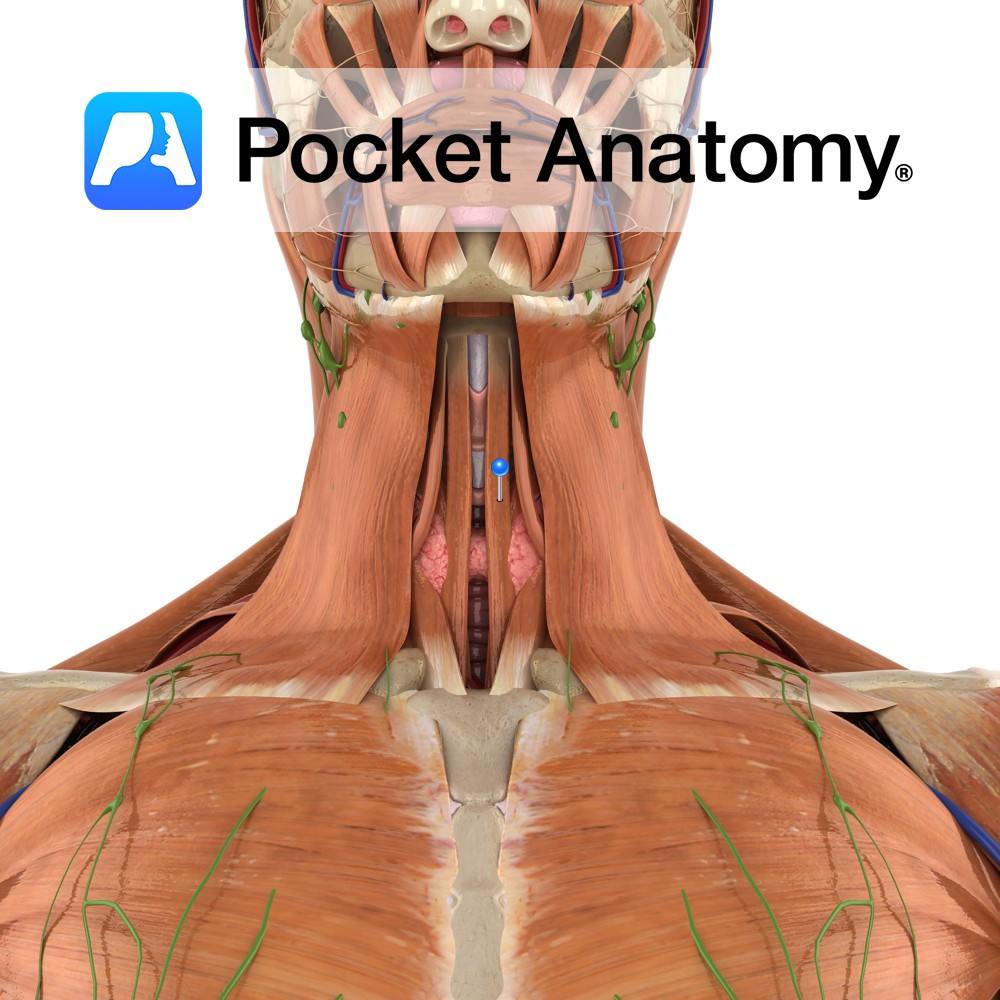
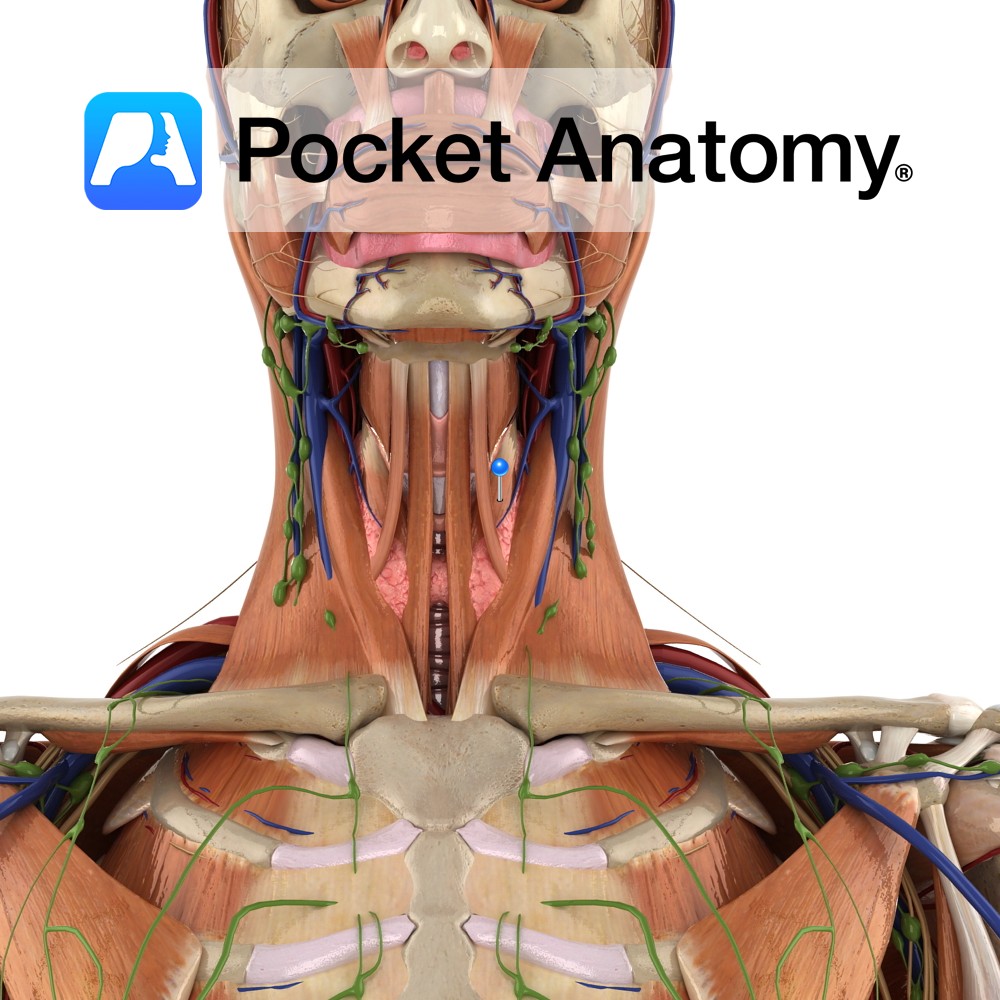
Anatomy Origin: Posterior aspect of sternocalvicular joint and adjacent manubrium of sternum. Insertion: Body of hyoid bone. Key Relations: -Is one of the infrahyoid muscles (sometimes referred to as ‘strap muscles’) lying in the muscular triangle of the neck. -Medial to omohyoid. Functions -Depresses hyoid bone after swallowing (deglutition). -Plays a role in speech and
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Posterior surface of manubrium of sternum. Insertion: Oblique line on lamina of thyroid cartilage. Key Relations: -Is one of the infrahyoid muscles (sometimes referred to as ‘strap muscles’) lying in the muscular triangle of the neck. -Is in continuity with thyrohyoid. Functions Draws the larynx (thyroid cartilage) downwards after it has been elevated
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
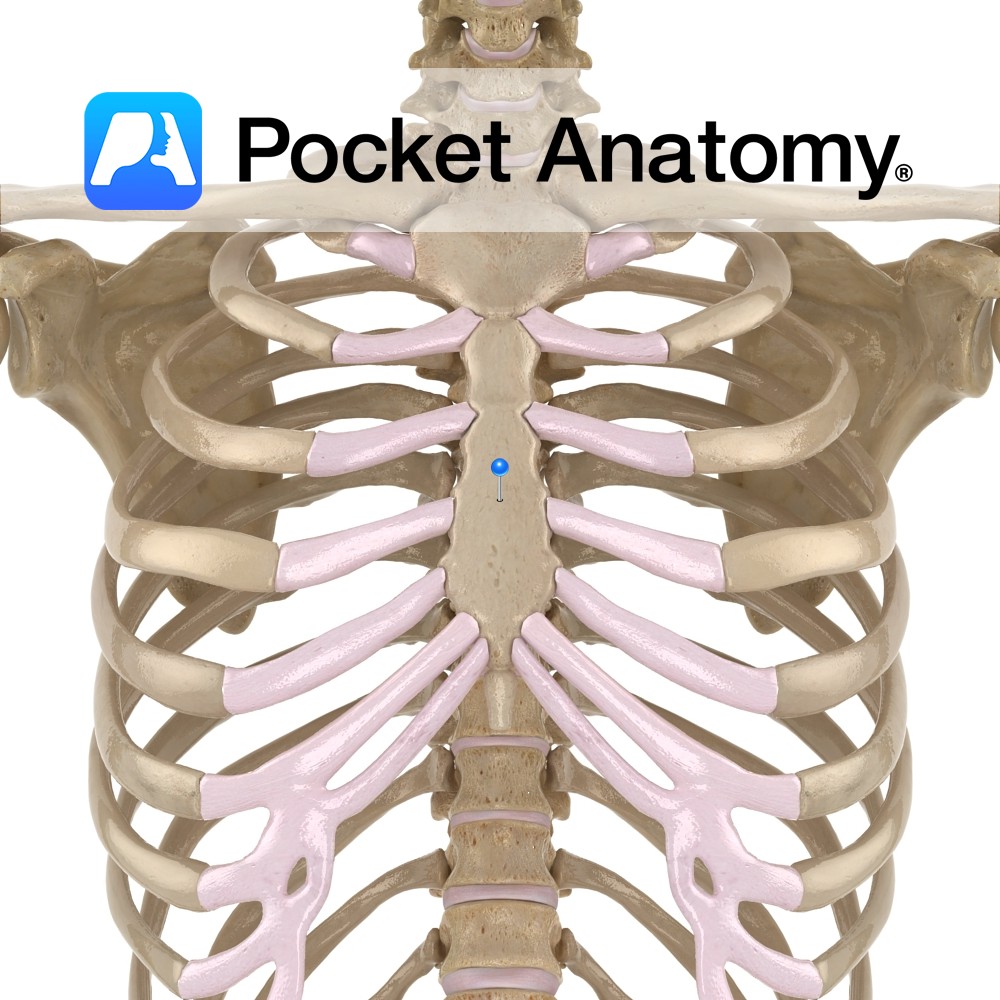
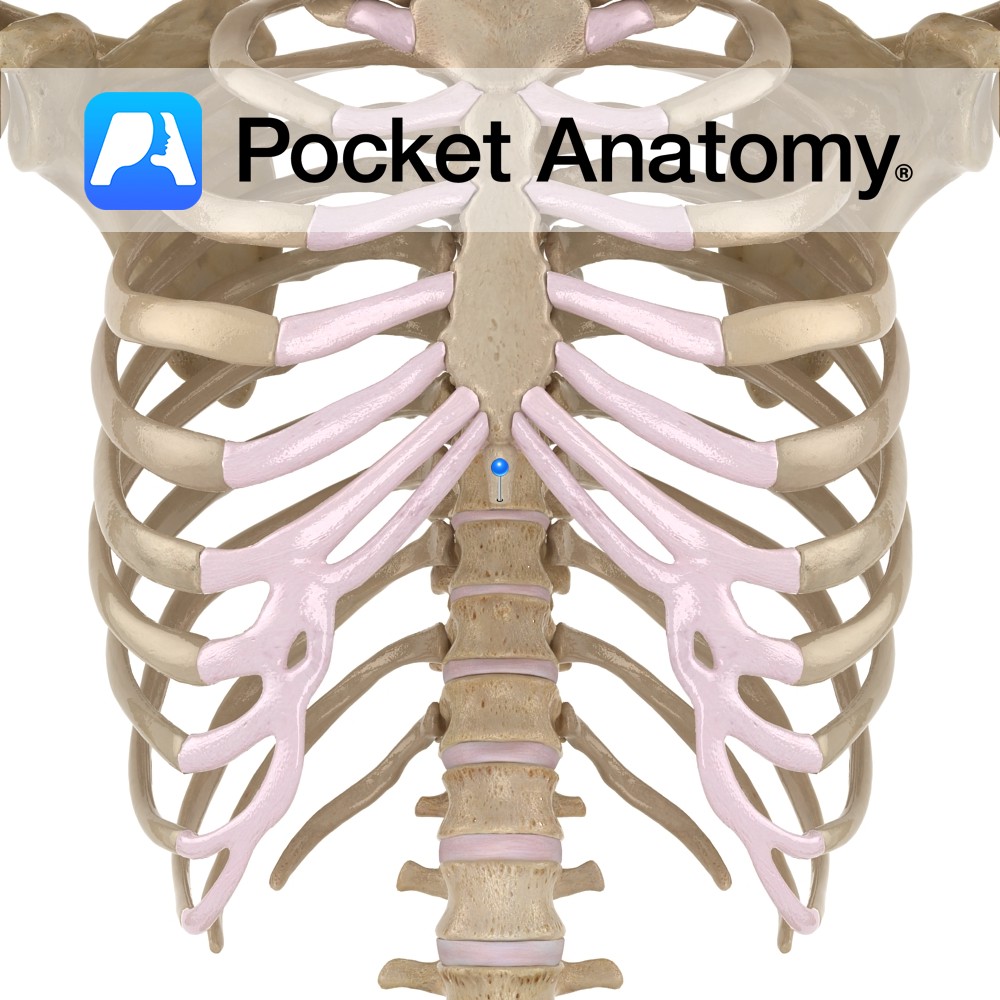
Anatomy Articulates up with manubrium, down with xiphoid process, out with costal cartilages (CC); 2nd and 7th through demifacets, 3rd through 6th with full facets, 8th through 10th indirectly through their articulation with CC above (8th with 7th etc), not at all with 11th and 12th ribs which taper to a point and end in
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
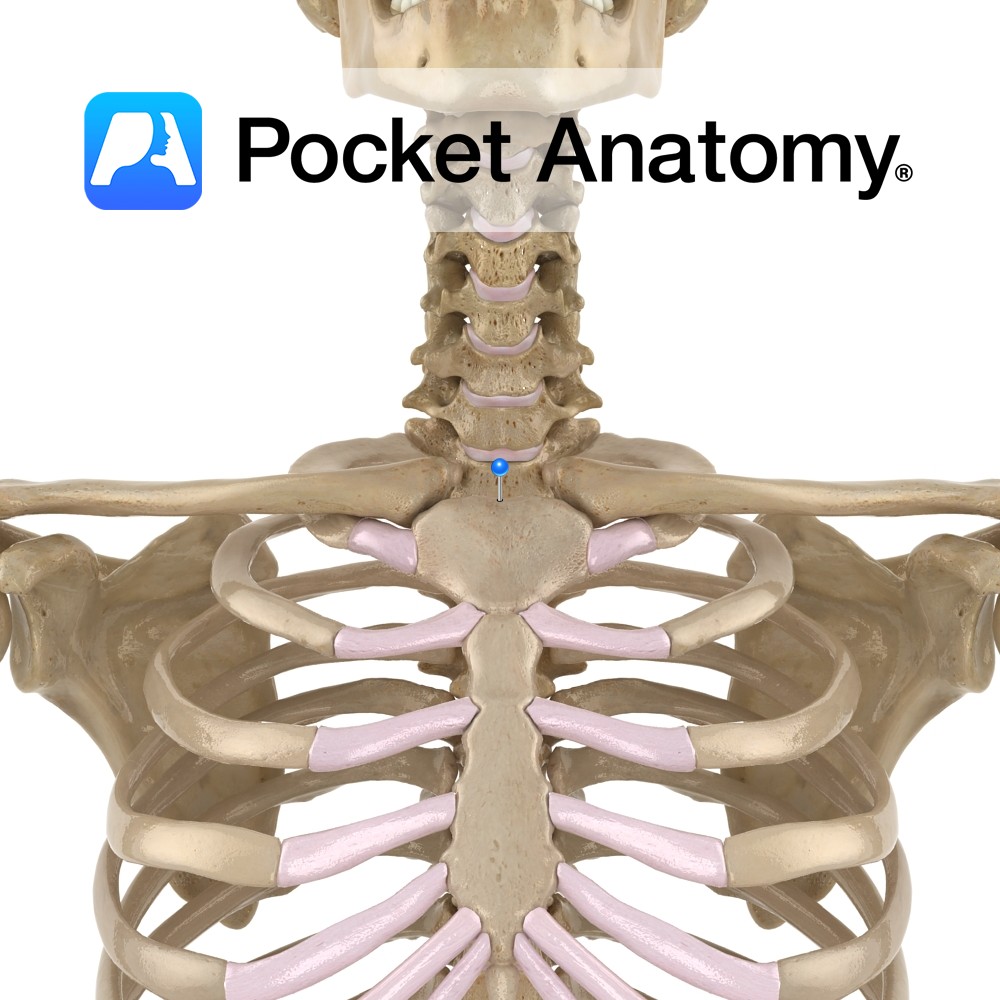
Anatomy Also known as presternal notch, a notch on the top of the manubrium, either side of which is sternocalvicualr joint. Clinical Easily visible and felt at bottom of v-shaped (sternocleidomastoid muscles make up each side of v) depression at front of neck, below chin. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
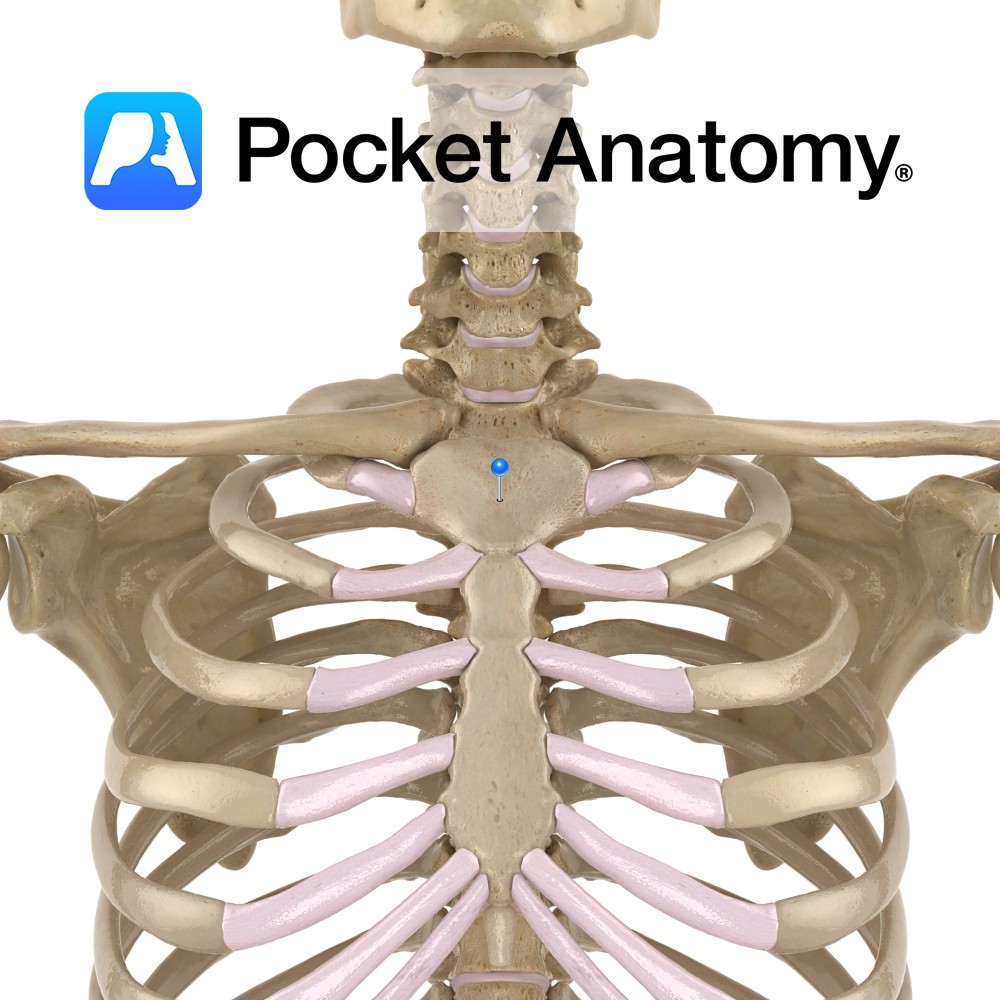
Anatomy Broadly cruciform upper part of sternum (manubrium, body xiphoid process). Articulates up with clavicles, out with 1st ribs, 2nd ribs (demifacets), down with body of sternum. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
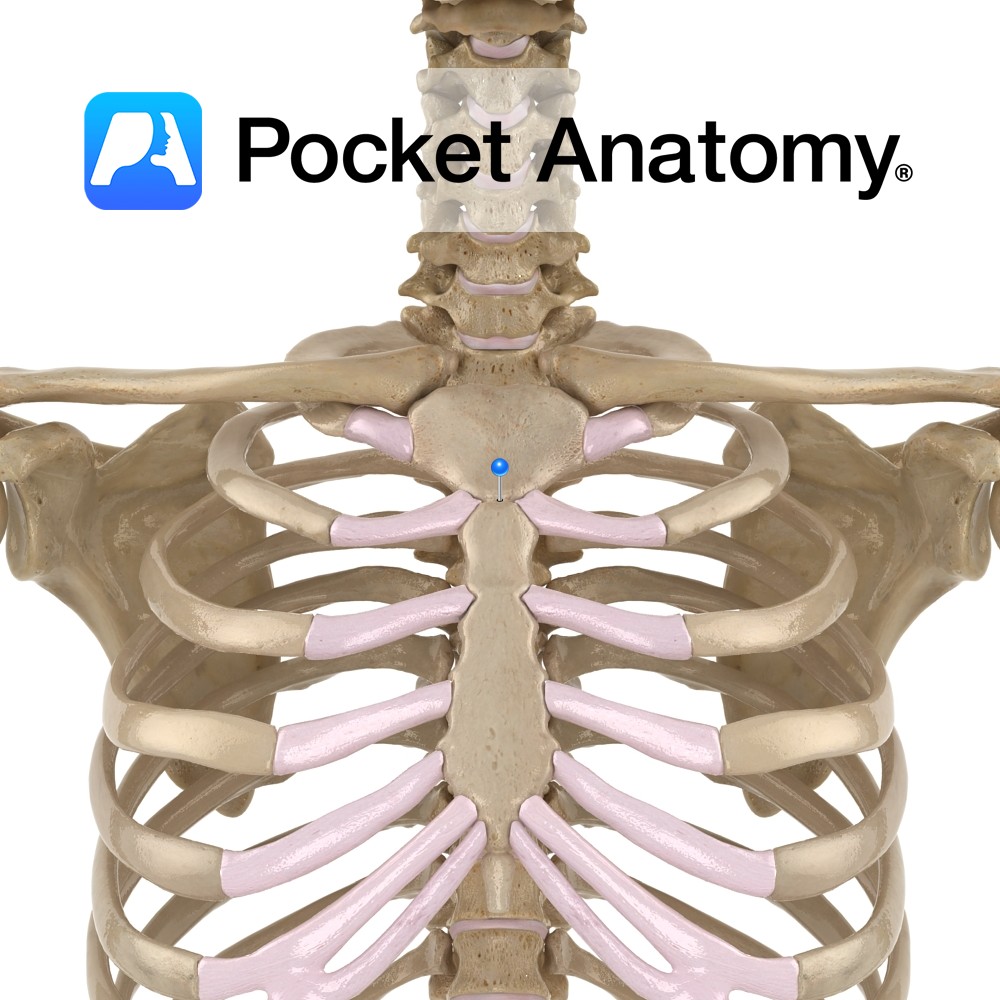
Anatomy Angle formed by junction of manubrium above and body below, with articular demifacets at their adjacent lateral edges (left and right) for articulation with sternal end of 2nd costal cartilage. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Initially cartilaginous lowest section of sternum, ossifies by age 15-30. Articulates up with sternal body, out (demi-facet) with 7th costal cartilages (CC) and gives attachment down to linea alba. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
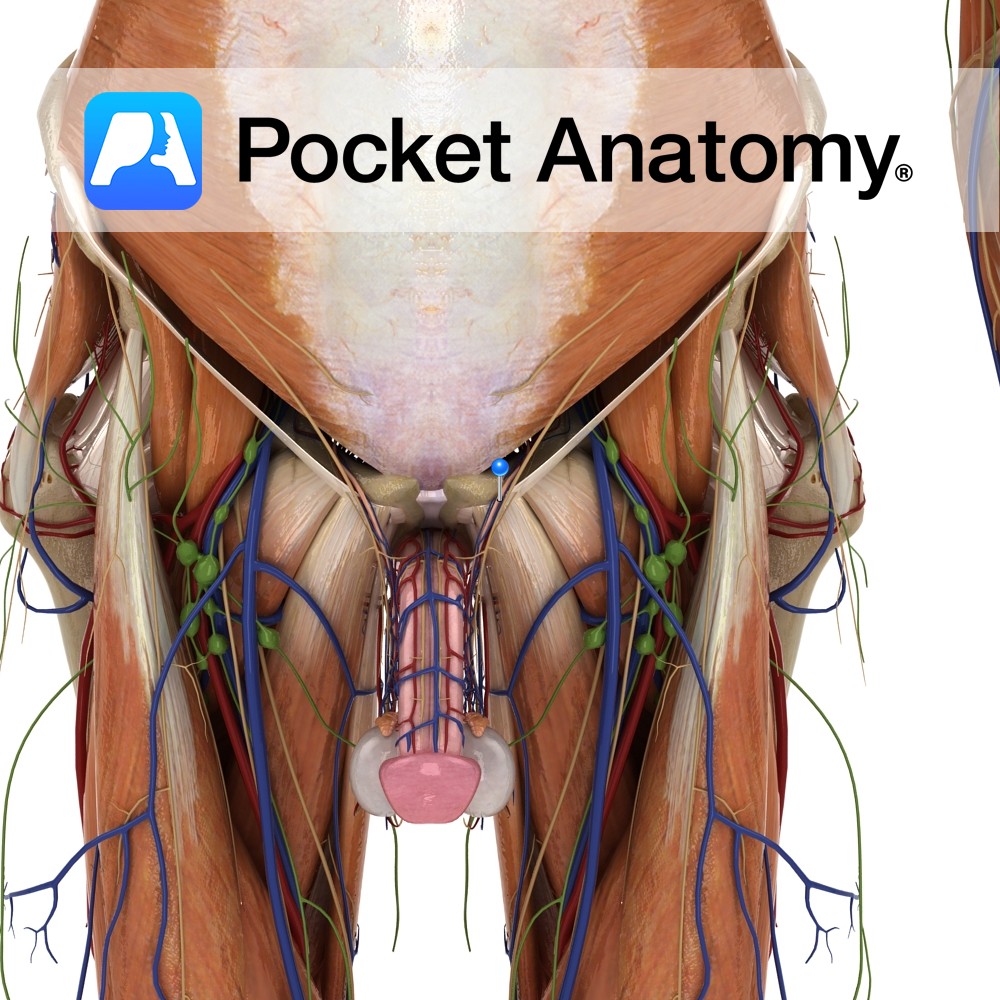
Anatomy In development, the testes bulge/bubble down and out of the abdomen (to escape to a lower temperature), through a passage in the abdominal wall (the inguinal canal) bringing with them layers and structures (abnormal bulging is called herniation). The Spermatic Cord reflects this abdominal origin and connects the testis to the abdomen; its fascias
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins