PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
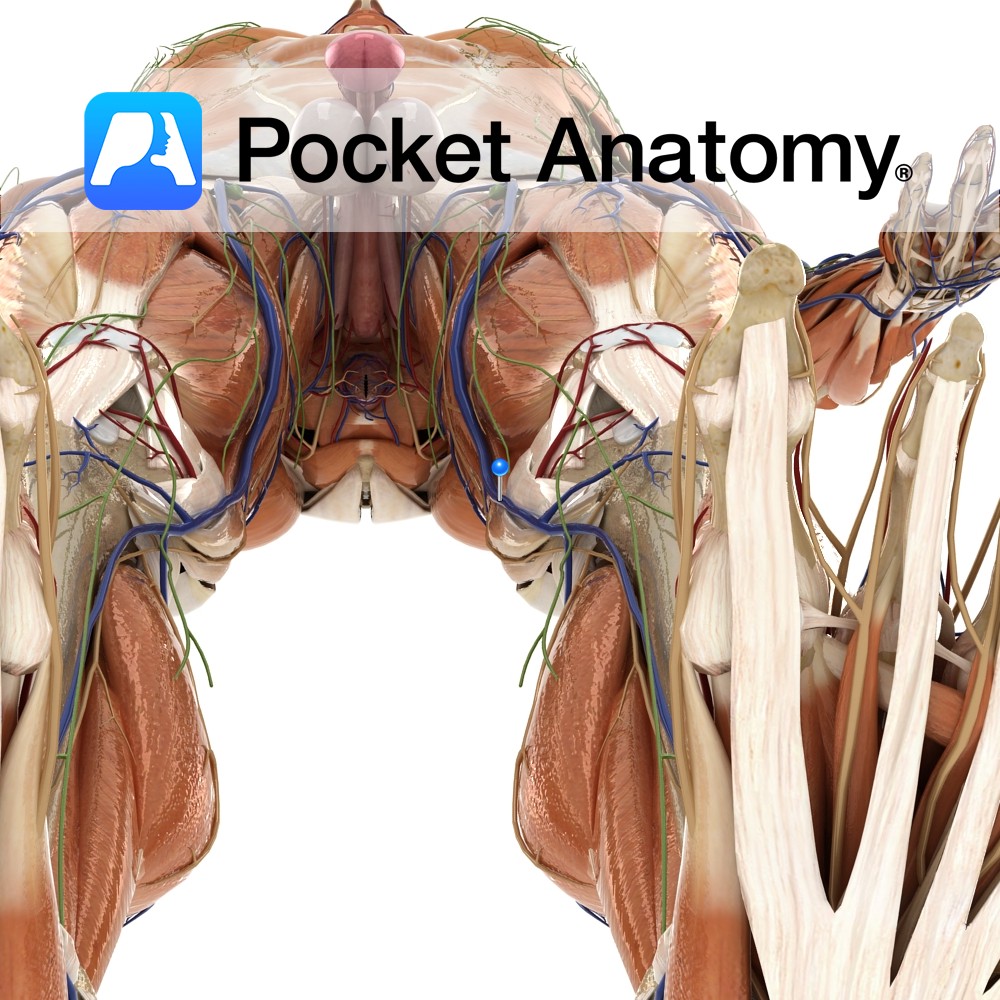
Anatomy Course The popliteal vein becomes known as the femoral vein after the adductor canal. It runs superiorly until it ends at the inferiorly to the inguinal ligament, where it then drains into the external iliac vein. Properly known as the femoral vein, though used by some specialists (e.g. radiologists) to differentiate the femoral vein
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
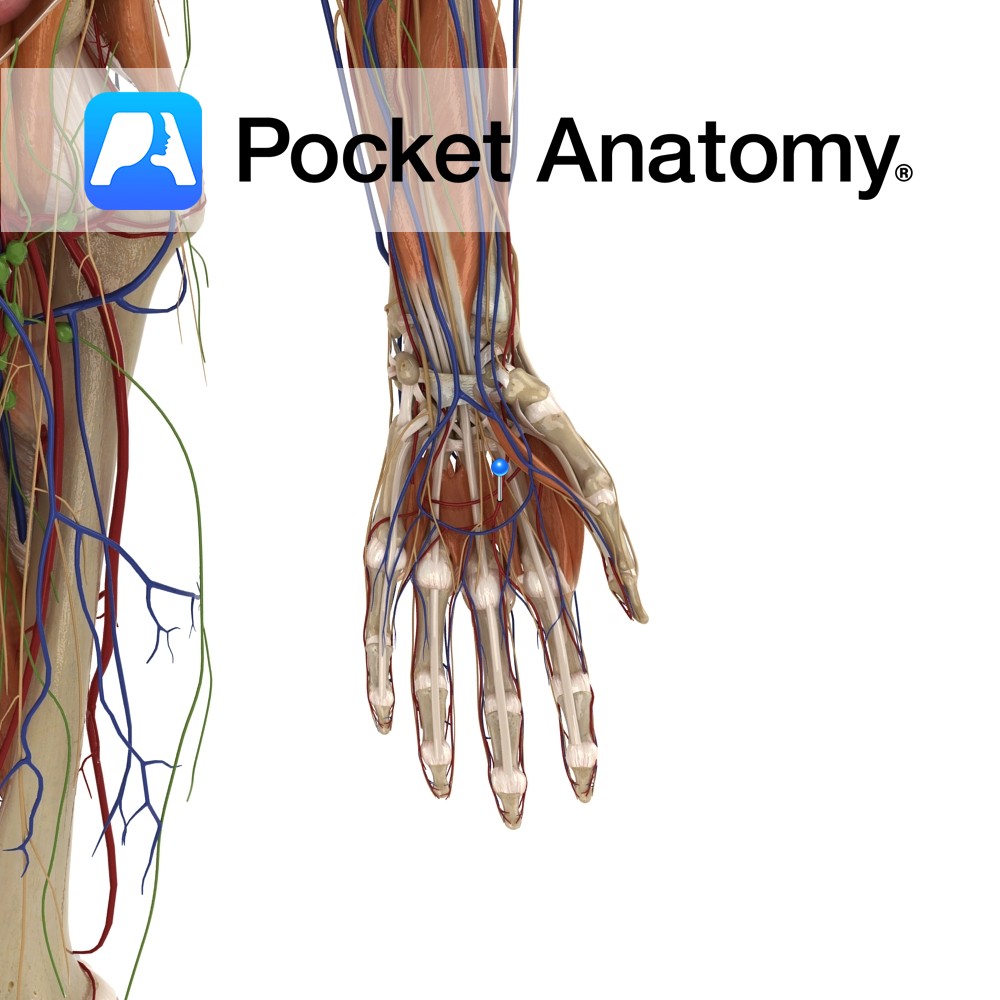
Anatomy Course Mainly contributed to by the ulnar artery, though it connects both ulnar and radial arteries, as it anastomoses with the superficial palmar branch of the radial artery. It runs across the palm in the plane, just deep to the palmar aponeurosis and lies on the flexor tendons of the digits. Supply Supplies blood
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
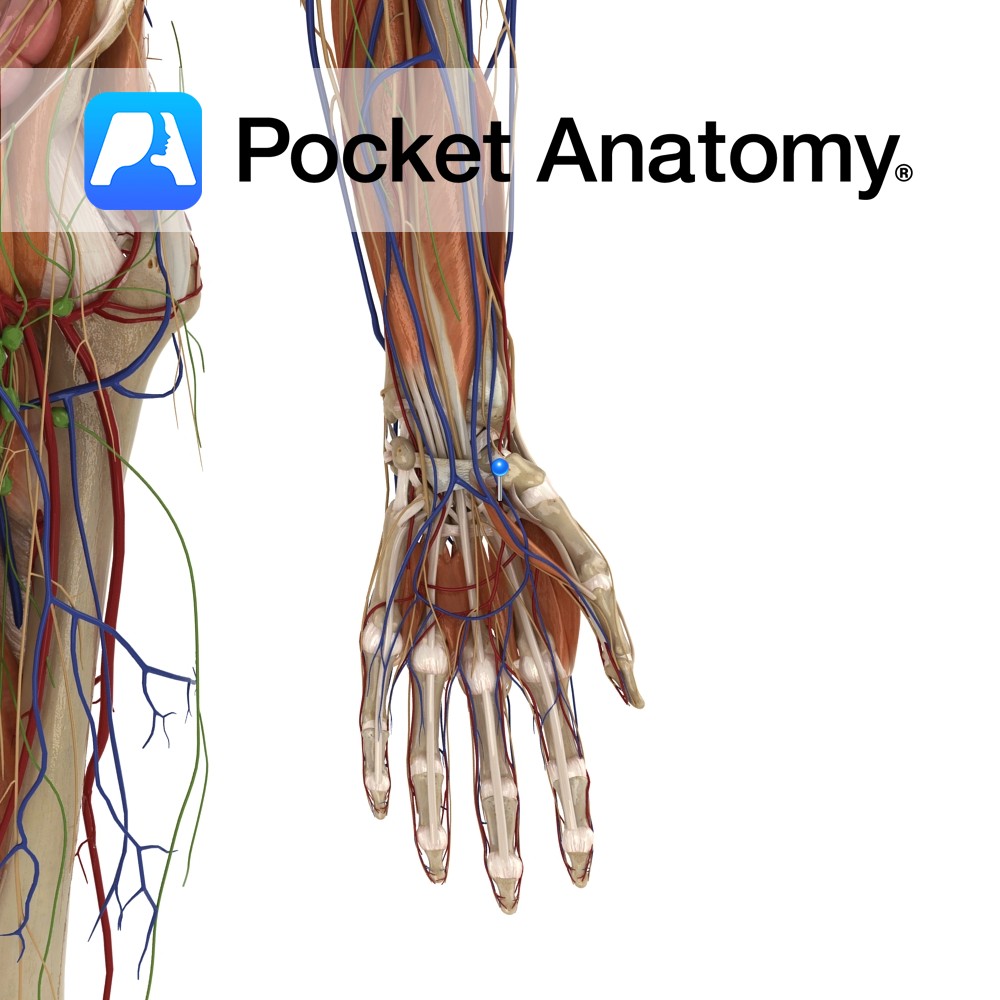
Anatomy Course Contributes to the superficial palmar arterial arch, even though the ulnar artery is the main supply. It branches from the radial artery just before the radial artery curves under the lateral side of the wrist. The artery passes between the thenar muscles close to their origin, travelling beneath adductor pollicis brevis and above
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
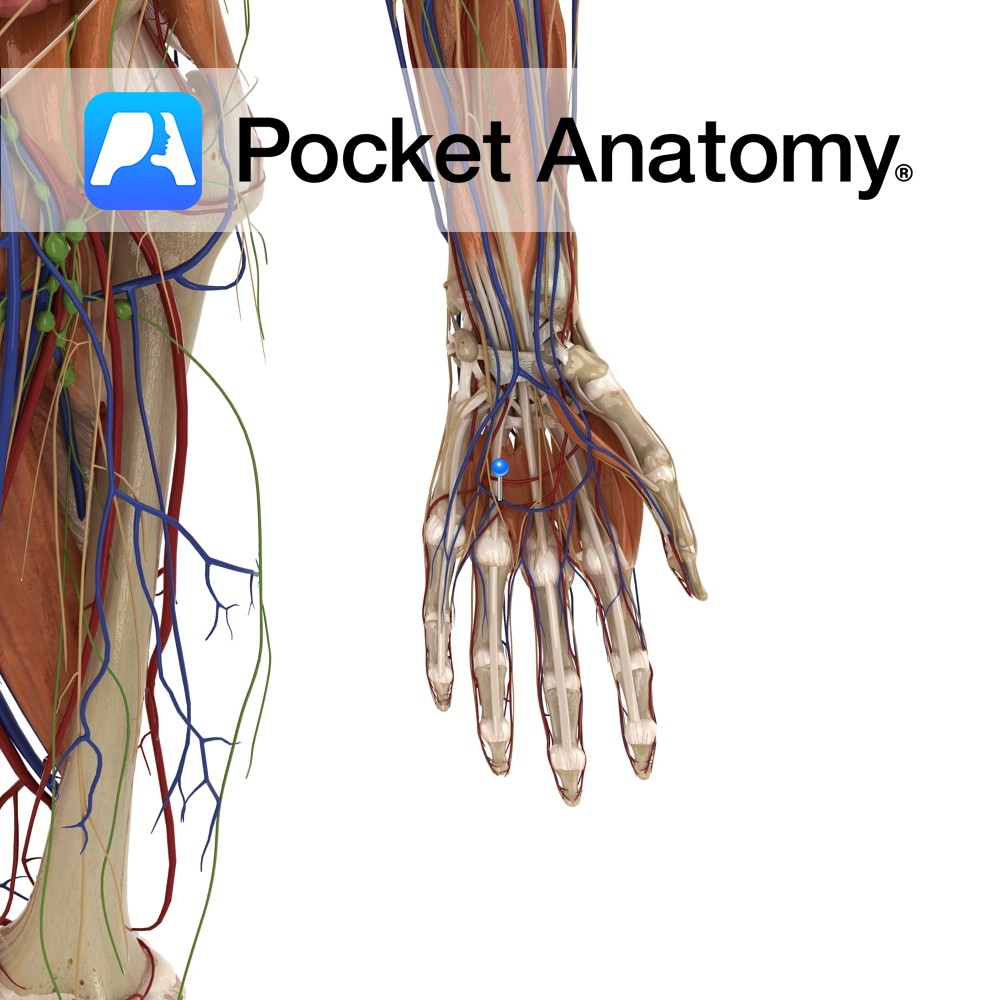
Anatomy Course Receives blood from the palmar digital veins. It forms an arch around the palm and drains into the radial and ulnar veins of the forearm. Drain Drains the superficial aspect of the palm. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
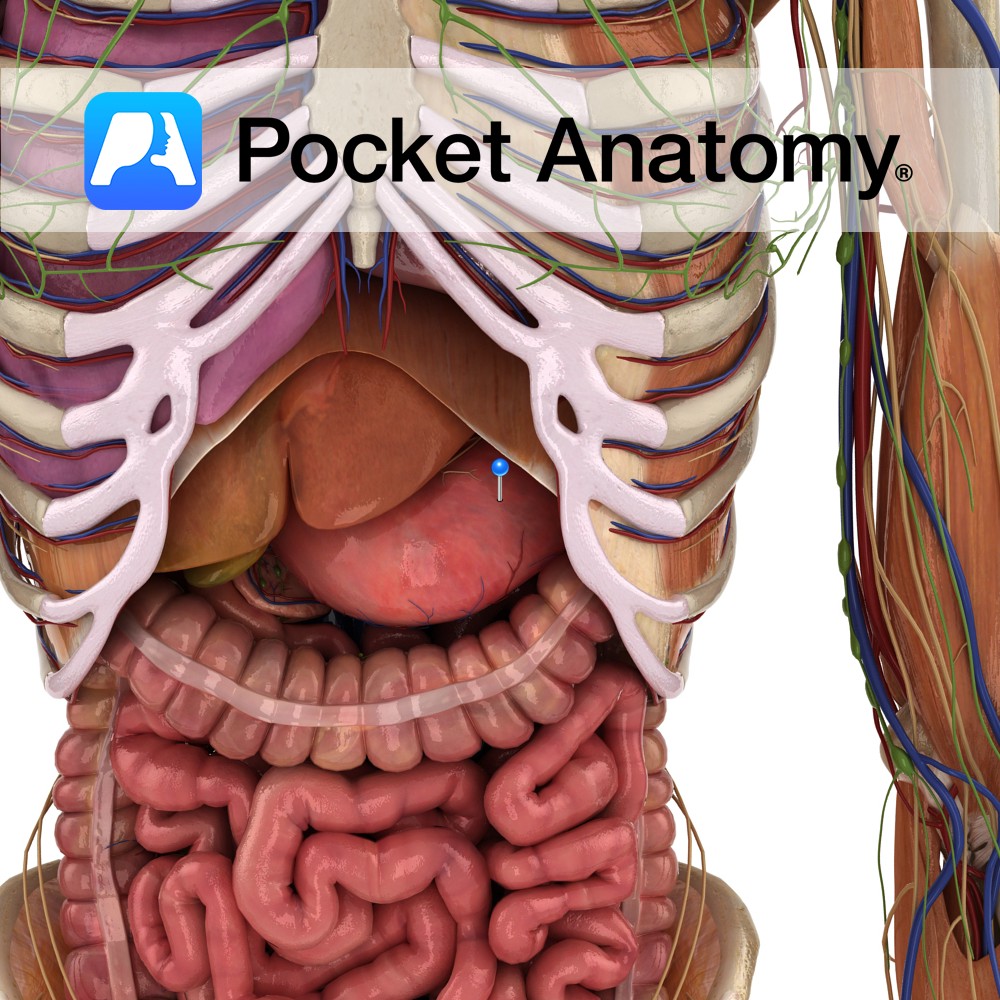
Anatomy Dilated part/organ of alimentary tract, left upper quadrant abdomen, shape of reversed C (concave part – lesser curvature, convex – greater), capacity 1- 3L, connecting esophagus and small intestine, under diaphragm (first part of tract in abdomen), receives bolus (masticated food) through esophageal sphincter, secretes enzymes (proteases such as pepsin) and acid (HCl) and
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
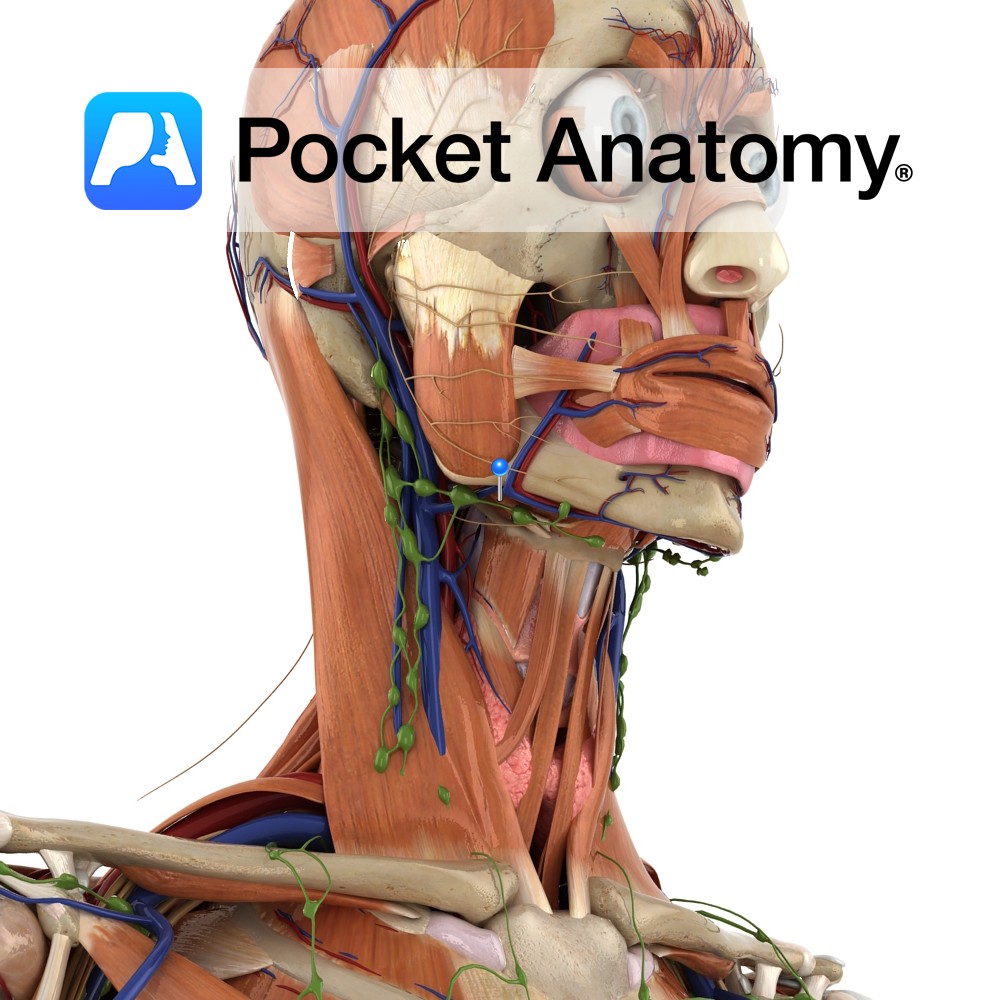
Anatomy Origin: Base of styloid process of the temporal bone. Insertion: Base of greater cornu of hyoid bone. Key Relations: -Is one of the suprahyoid muscles lying in the anterior triangle of the neck. -Perforated near it’s insertion by the intermediate tendon of the digastric muscle. -Anteromedial to stylohyoid is another suprahyoid muscle geniohyoid. Functions
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
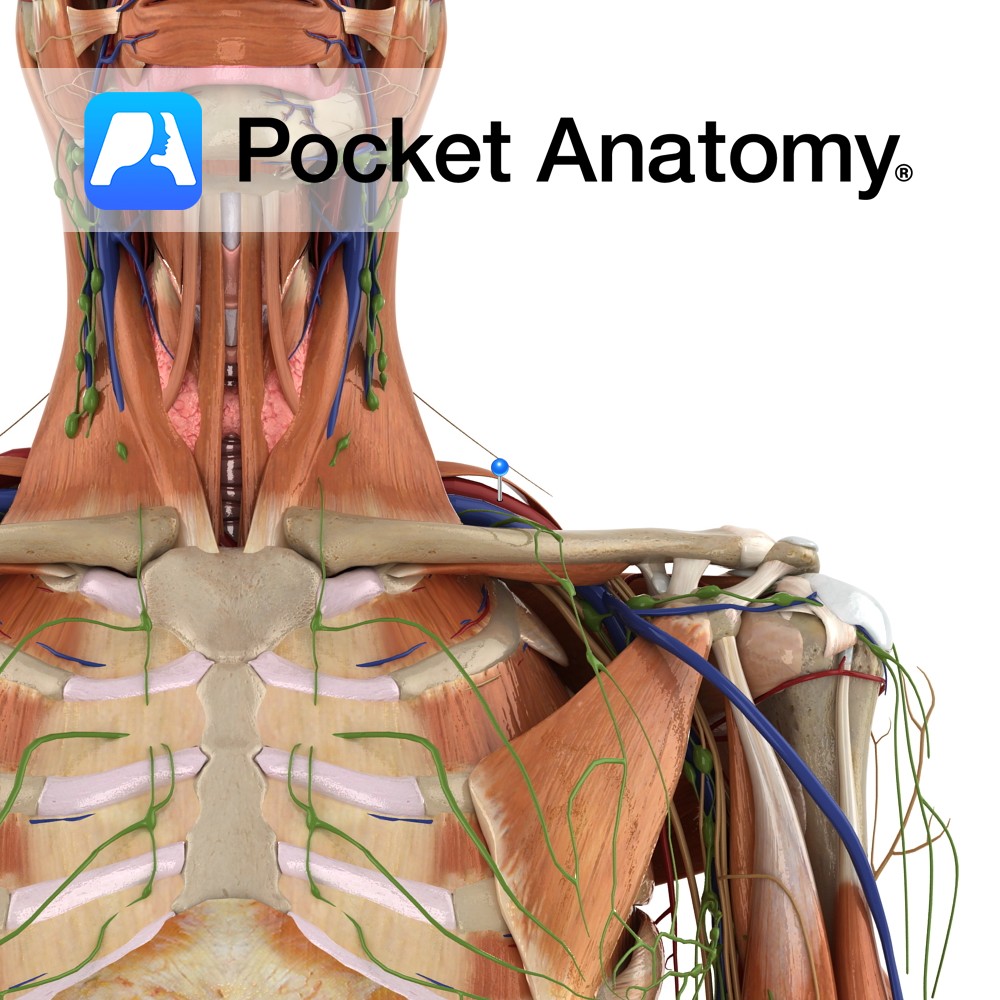
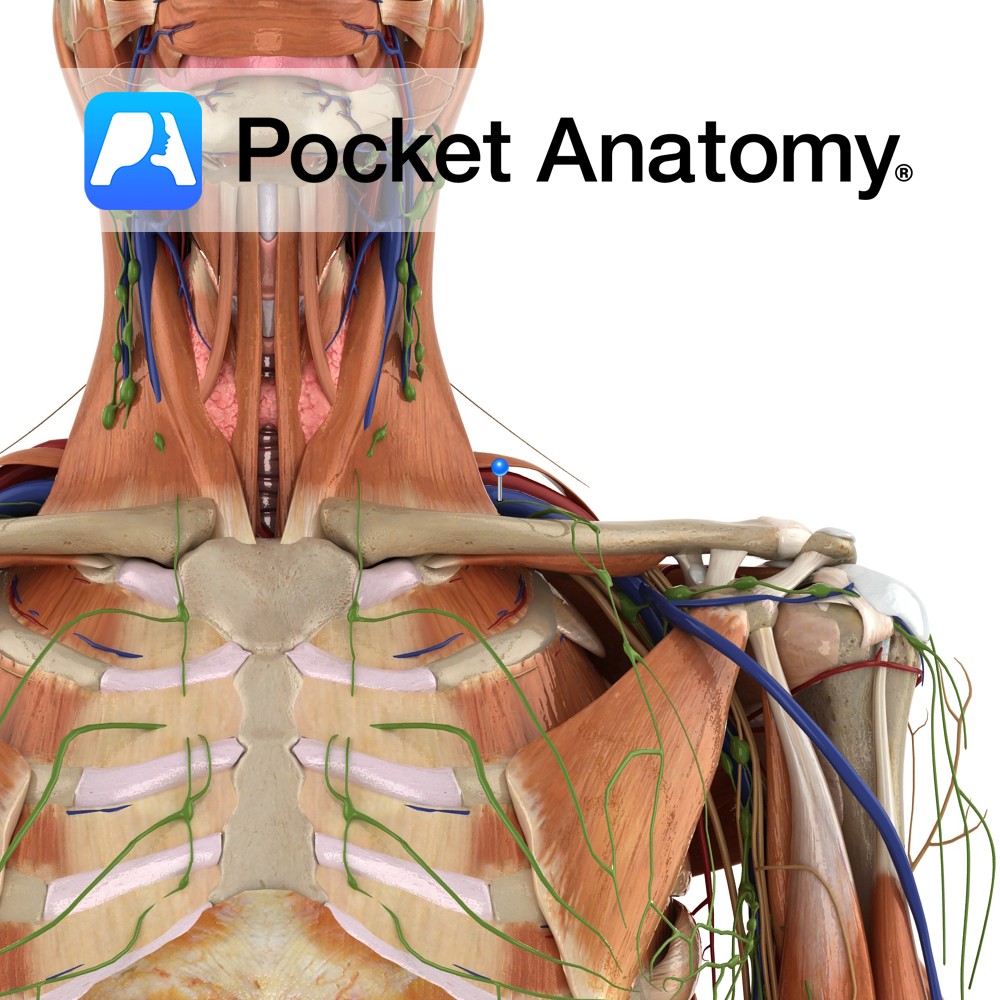
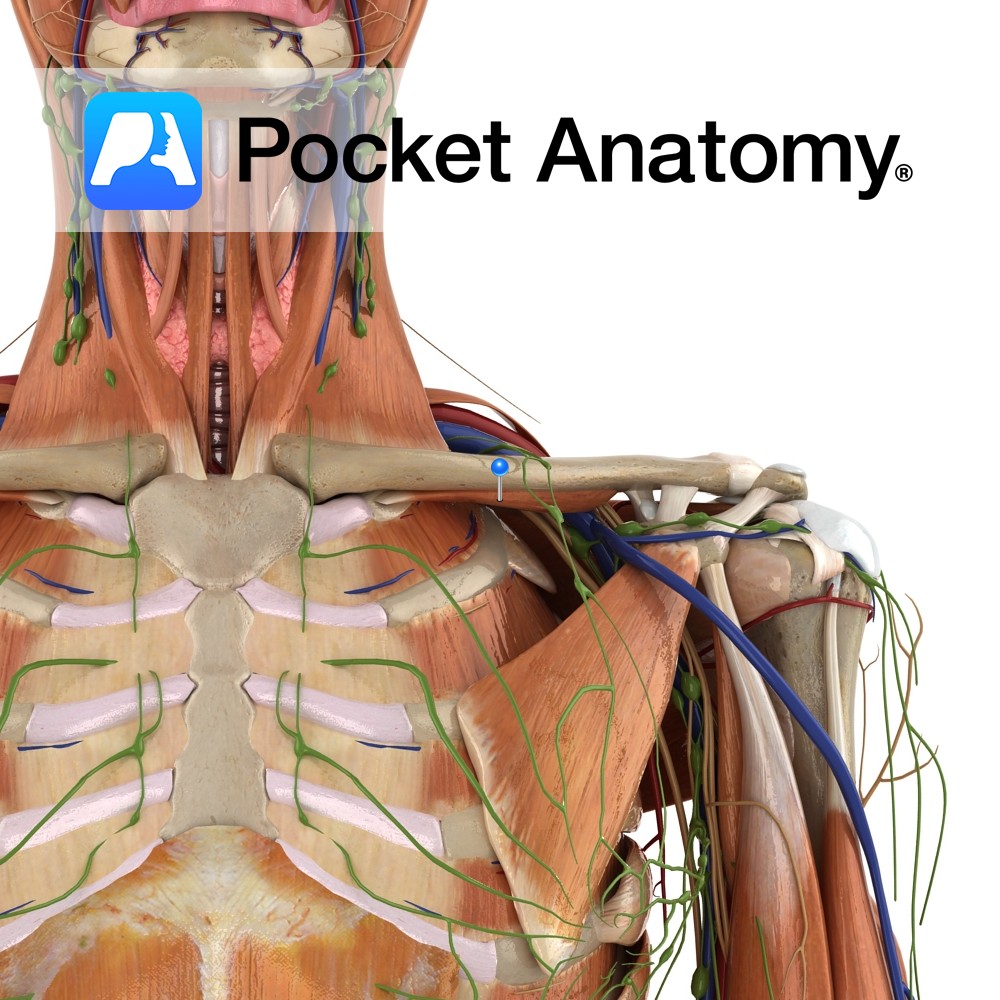
Anatomy One of the 4 paired lymphatic trunks (Jugular, Subclavian, Bronchomediastinal, Lumbar). Subclavian Trunk drains Upper limb, is a triubutary of the Thoracic (or Right Lymphatic) Duct just before it empties into the Subclavain Vein (on L, can be into the L Brachiocephalic Vein). Clinical Lymph and blood capillaries intwerweave basket-like. Lymph Capillaries have no
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course The subclavian arteries are two major vessels in the thorax that pass beneath the clavicles. The left and right subclavian arteries have slightly different courses. The left subclavian artery branches directly from the arch of the aorta, just before it begins its descent. It begins lower in the thorax than the right subclavian
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
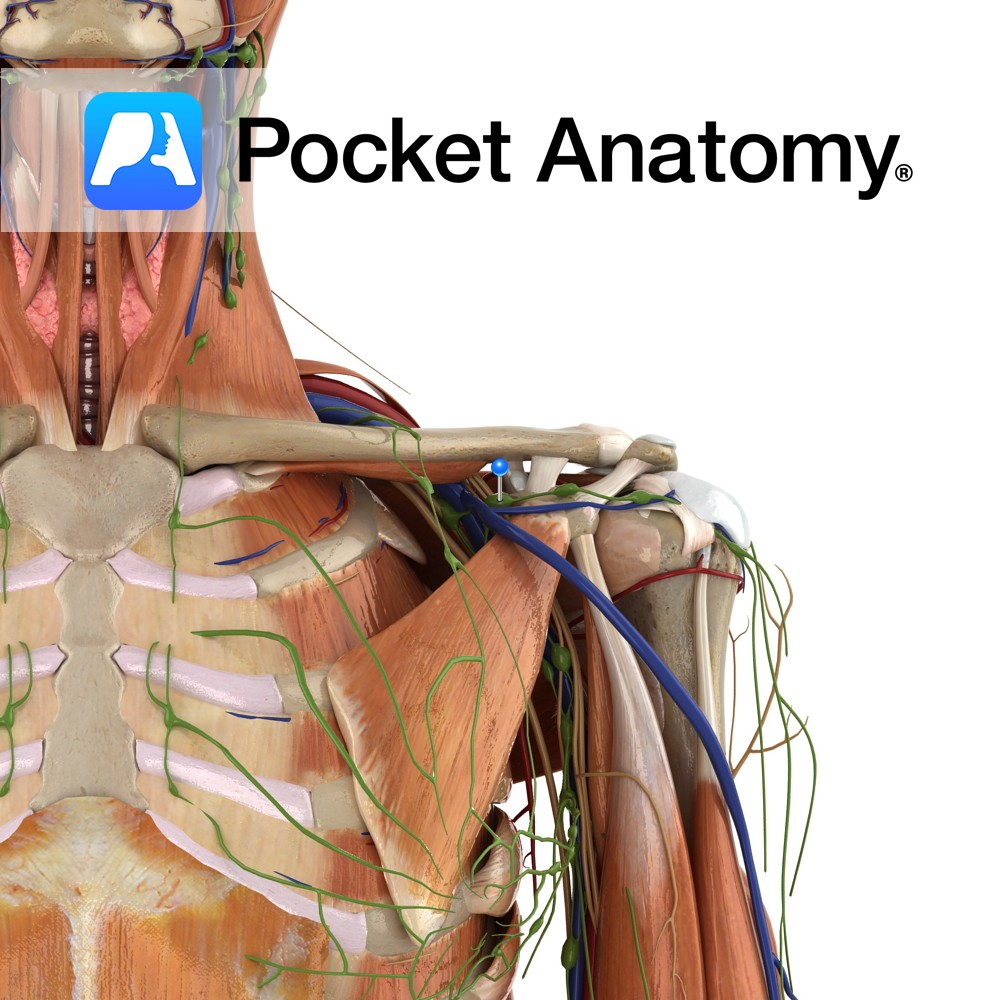
Anatomy Course A continuation of the axillary vein. It runs along the the margin of the first rib, posterior to the clavicle. It joins with the internal jugular vein at the medial margin of the anterior scalene to form the brachiocephalic vein. Drain Responsible for the venous drainage of the arm and axilla. Interested in
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Junction of first rib and costal cartilage. Insertion: Inferior surface of middle third of clavicle in subclavian groove. Key Relations: -Separated posteriorly from the first rib by the subclavian vessels and brachial plexus. -Its insertion is located between the costoclavicular and conoid ligaments. Functions Stabilises the clavicle in the sternoclavicular joint during shoulder
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins