PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
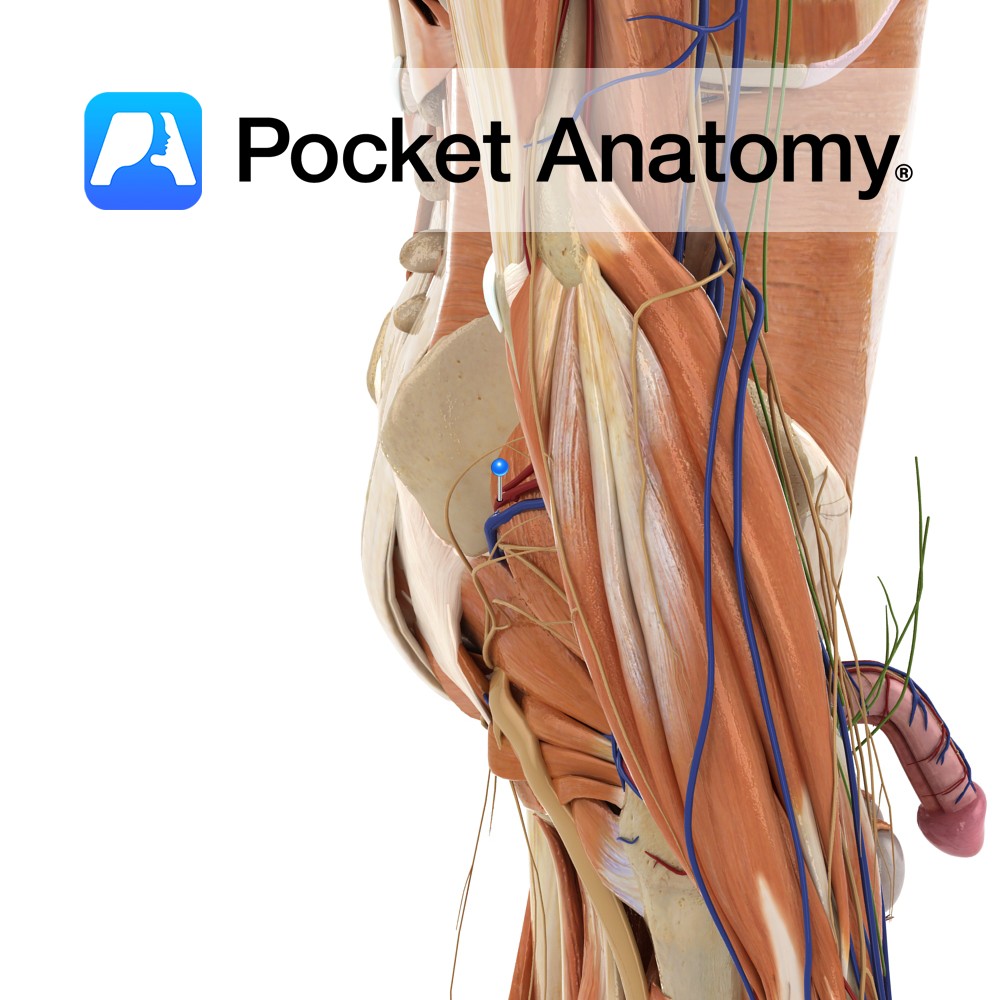
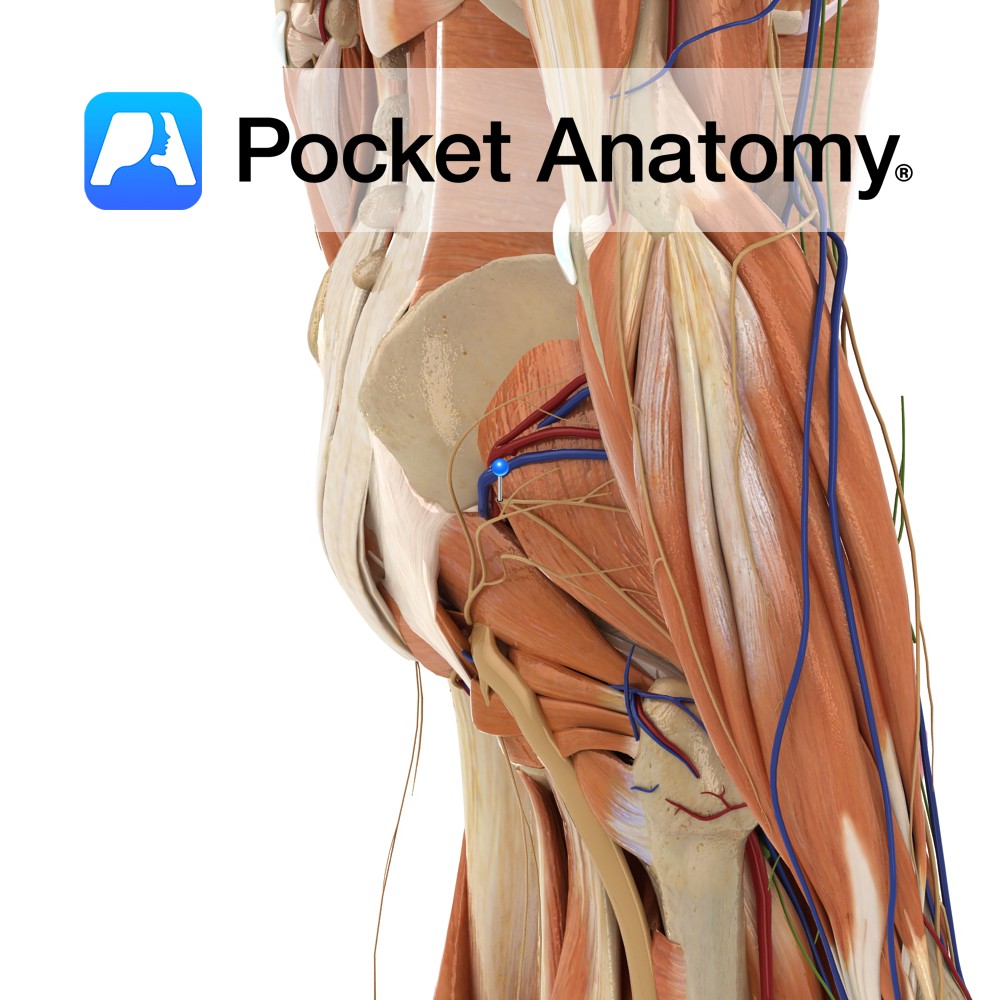
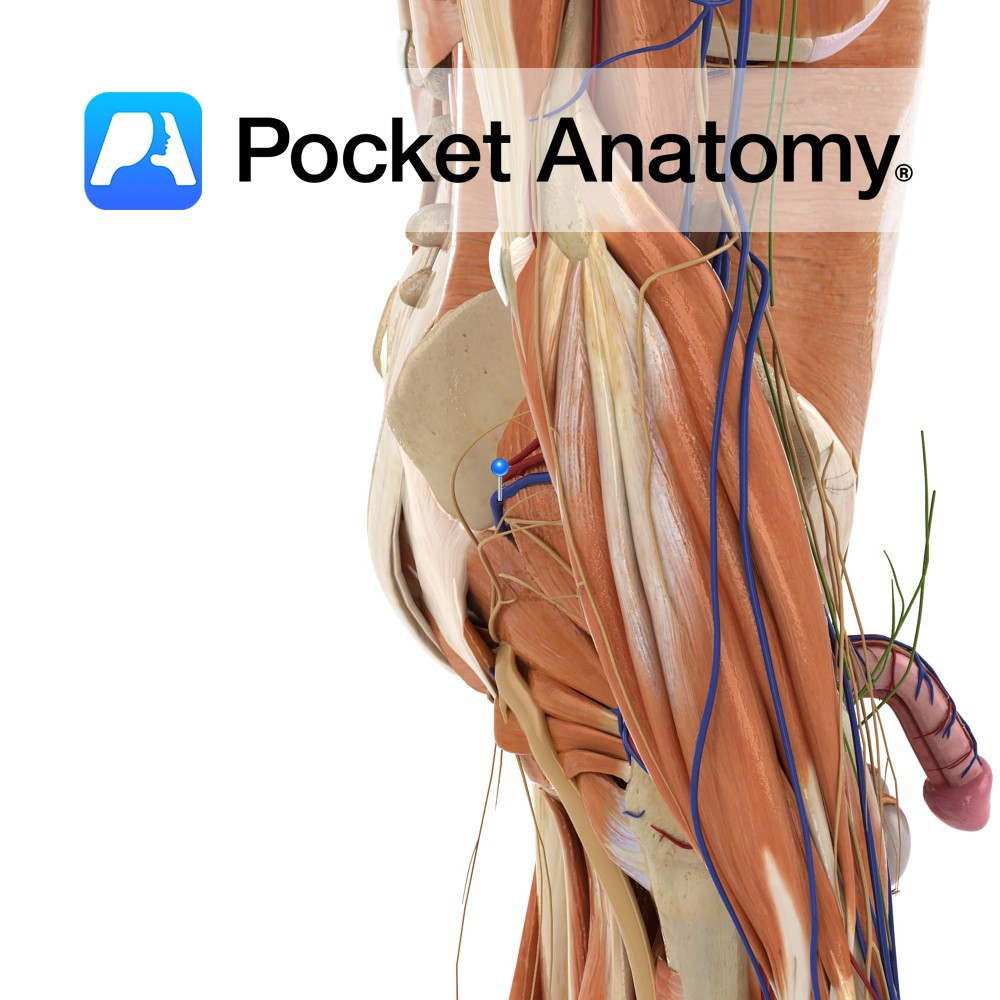
Anatomy Origin: Dorsal surface of the ischial spine. Insertion: Blends with the more superior fibres of the tendon of the obturator internus and attaches with the tendon to the medial border of the greater trochanter of the femur. Key Relations: Lies superior to the obturator internus muscle. Functions Working with gemellus inferior and obturator internus,
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course A terminal branch of the posterior trunk of the internal iliac artery. It travels posteriorly, passing through the space between the lumbosacral trunk and the anterior ramus of spinal nerve S1. It exits the pelvic cavity by passing through the greater sciatic foramen. On leaving the greater sciatic foramen it divides into a
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course A terminal nerve of the lumbosacral plexus. It is formed by fibres from spinal segments L4 – S1. It exits the pelvic cavity by passing through the greater sciatic foramen, above the piriformis muscle. It travels anterolaterally between gluteus medius and minimus, and terminates in the tensor fasciae latae muscle. Supply The superior
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
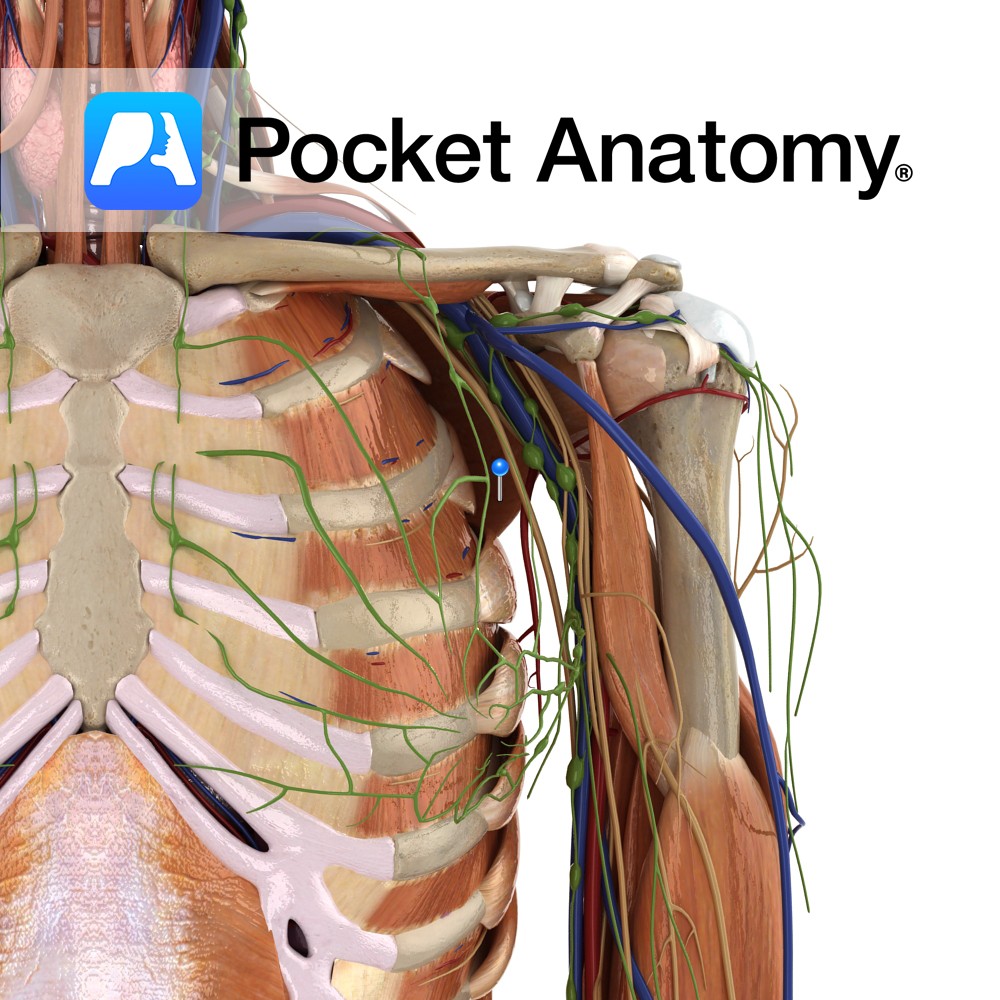
Anatomy Course Begins in the gluteal region, where a number of smaller veins come together. It travels towards the greater sciatic foramen, where it enters the pelvic cavity. It travels along the posterior pelvic wall to drain into the internal iliac vein. Drain Drains the gluteal region. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
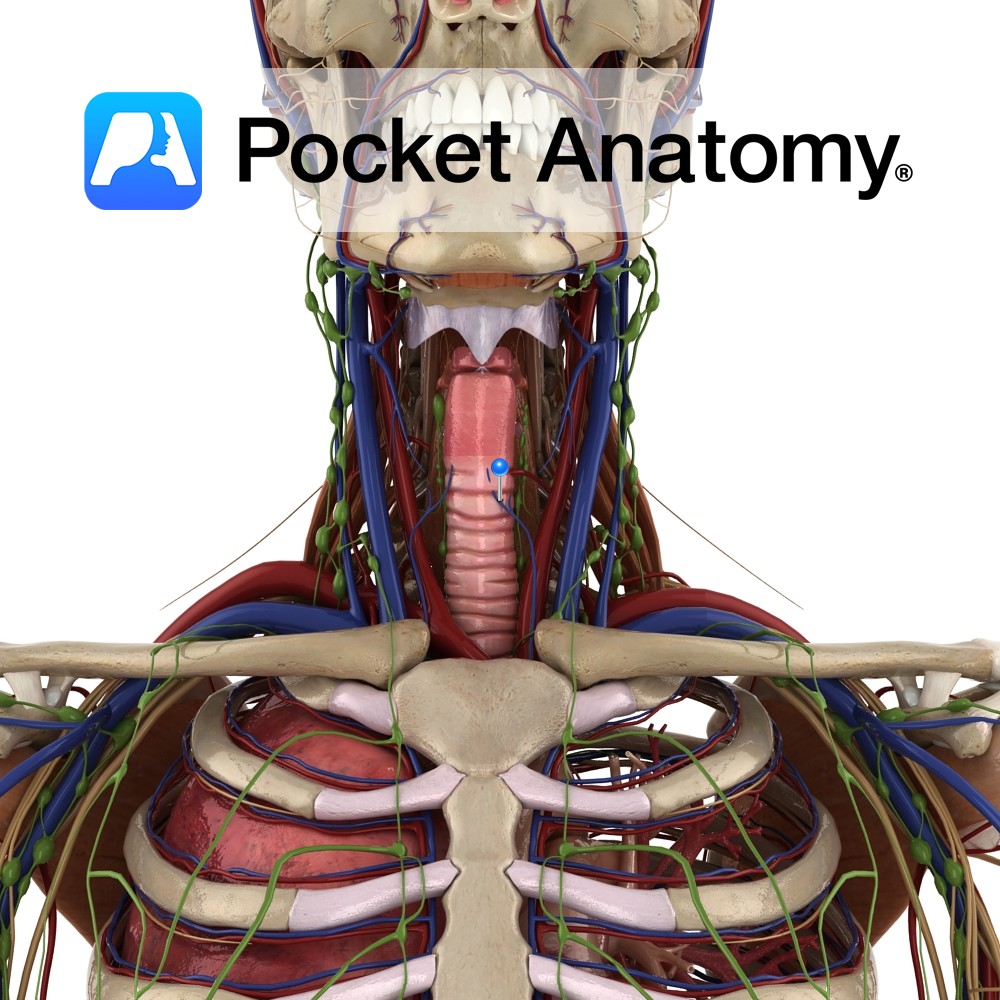
Anatomy Course Begins from a network of veins within the larynx. It exits the larynx by piercing the hyothyroid membrane and drains into the superior thyroid vein. Drain Drains the larynx and its mucous membranes. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
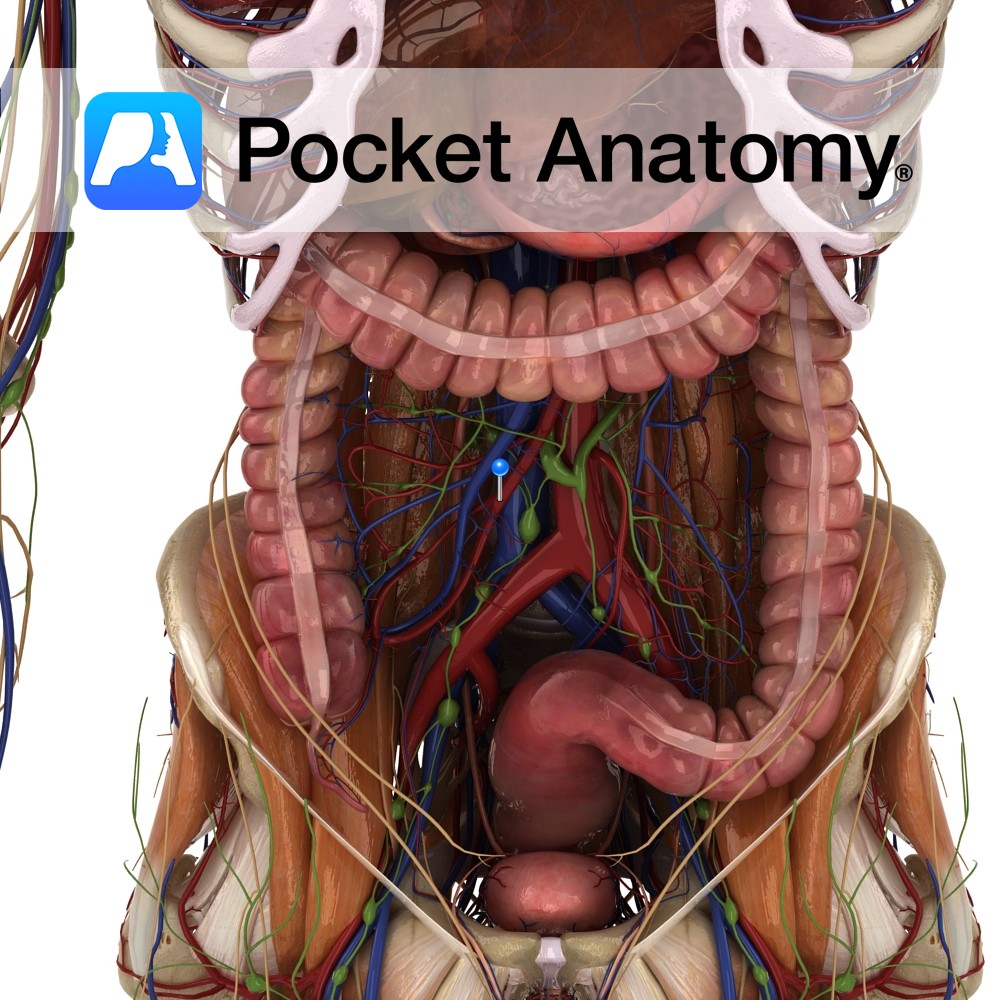
Anatomy Course An anterior branch of the abdominal aorta that arises at approximately the vertebral level of L1. It descends into the abdomen, passing in front of the left renal vein and the inferior duodenum and passing behind the neck of the pancreas and the splenic vein. It also crosses in front of the uncinate
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
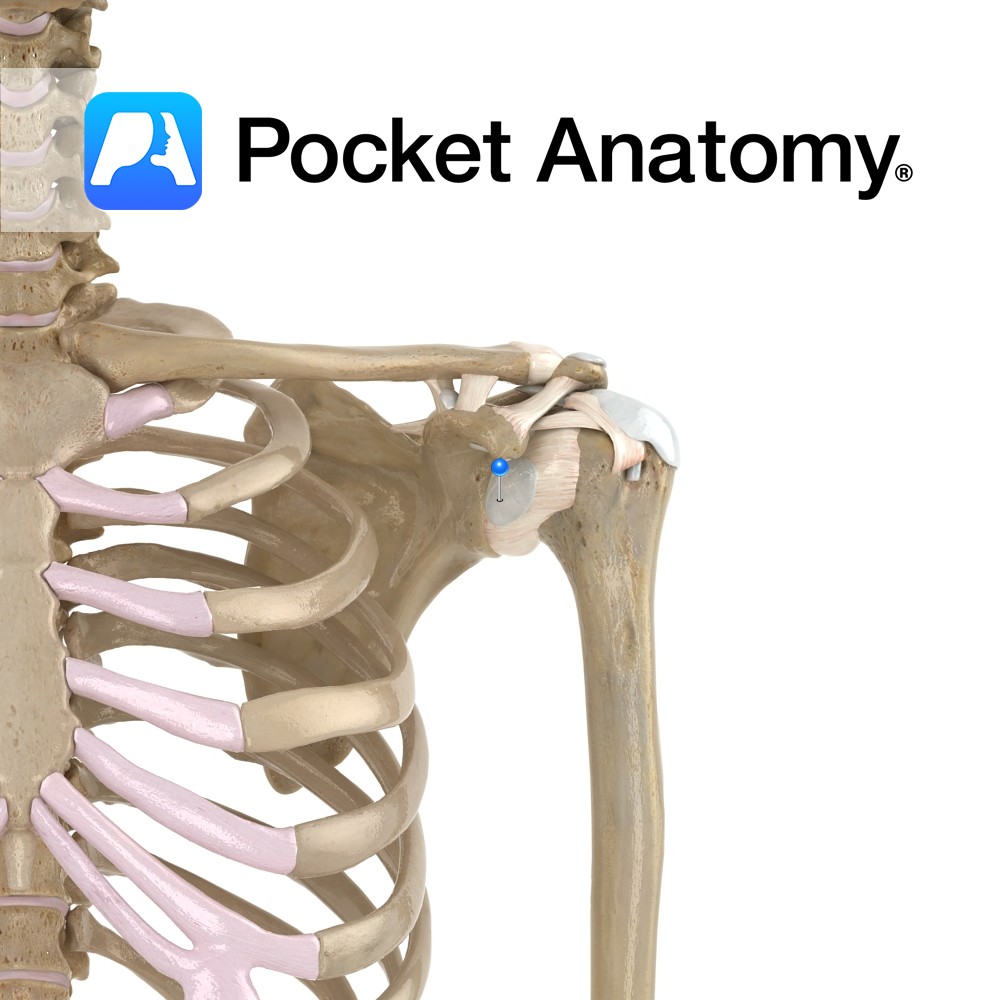
Anatomy The subdeltoid bursa lies between the tendon of subscapularis and the fibrous membrane of the glenohumeral joint capsule. Functions The subdeltoid bursa reduces friction between the glenohumeral joint and the tendon of the subscapularis muscle. Clinical Bursitis is swelling of the bursa from infection or overuse. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Medial two thirds of the costal surface of the scapula. Insertion: Lesser tubercle of humerus and anterior of capsule of shoulder joint. Key Relations: -Forms much of the posterior axillary wall. -One of the four muscles of the rotator cuff muscle group. Functions -Medially rotates the arm at the glenohumeral joint. -Adducts the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Branches off from the radial nerve just beyond the lateral epicondyle of the humerus, beneath the brachioradialis muscle. From there it continues to course distally beneath the brachioradialis. Just proximal to the wrist, it emerges from underneath the tendon of the brachioradialis muscle, between it and the tendon of the extensor carpi radialis
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
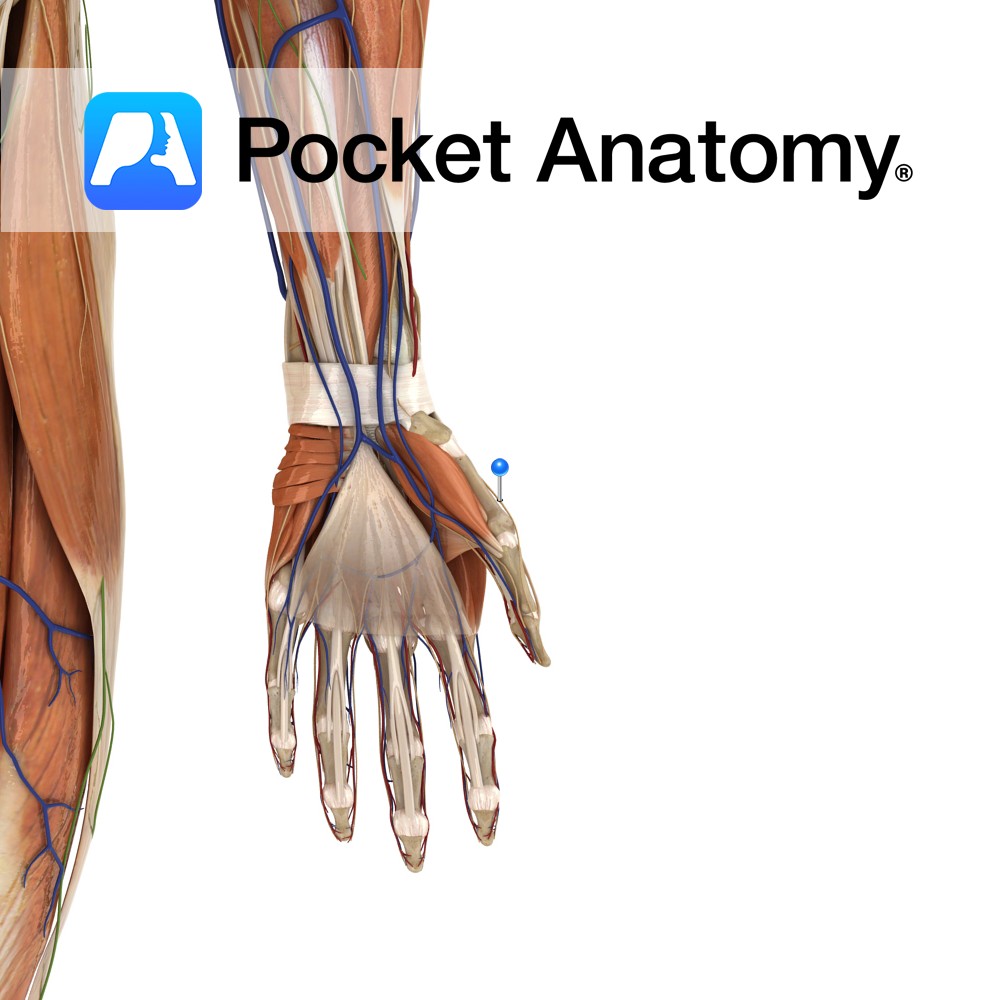
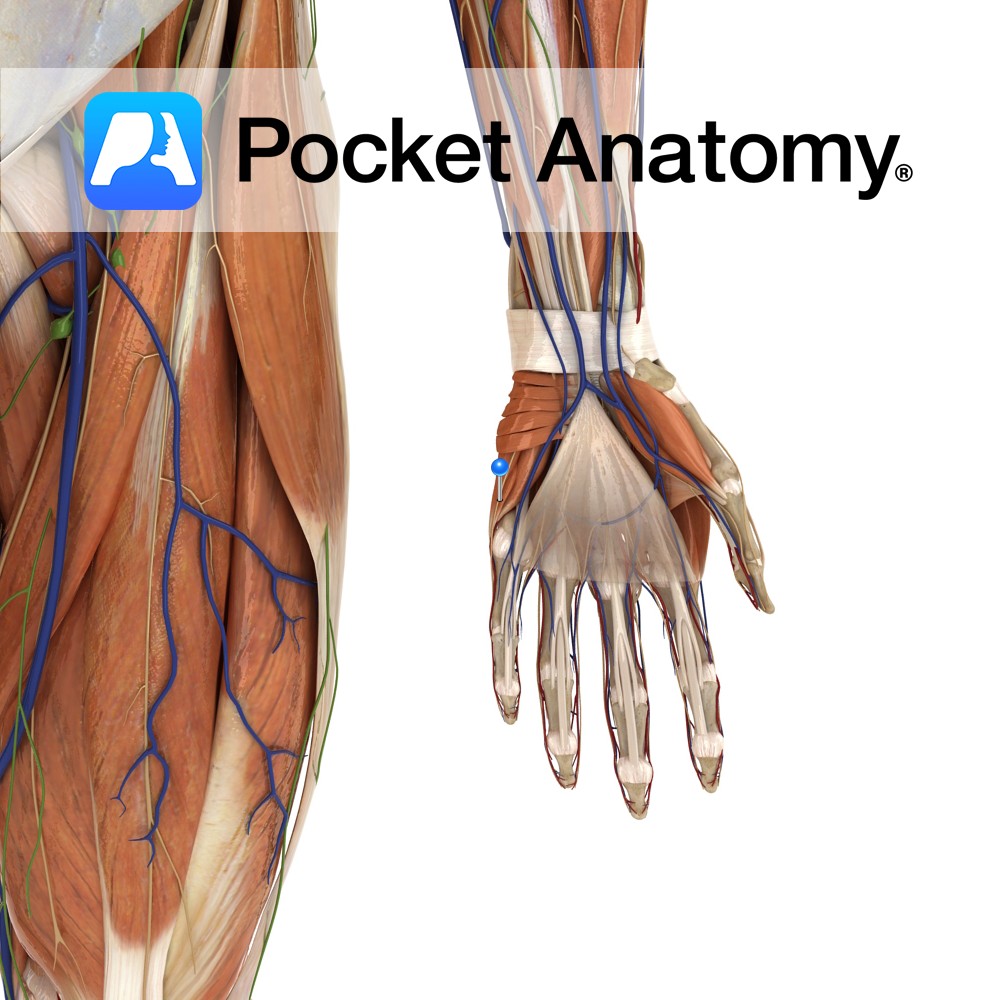
Anatomy Course A terminal branch of the ulnar nerve. Supply Supplies the skin on the medial aspect of the palm with sensory innervation. Clinical Damage may result in pain, a tingling sensation or numbness in its region of distribution. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins