PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
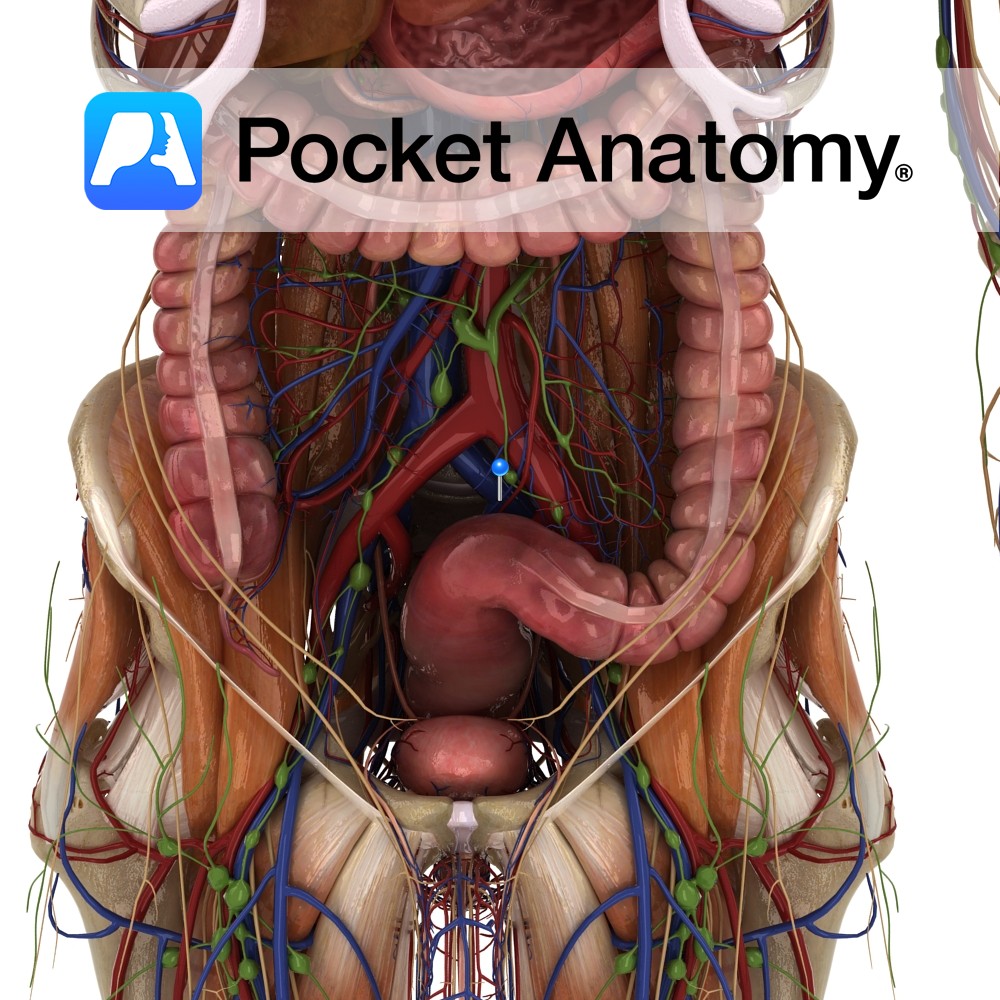
Anatomy Course Begins as tributaries from the venous plexus around the rectum and the sigmoid colon. It ascends in the pelvis and crosses the internal iliac vein to become the inferior mesenteric vein. Drain Drains the rectum and sigmoid colon. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
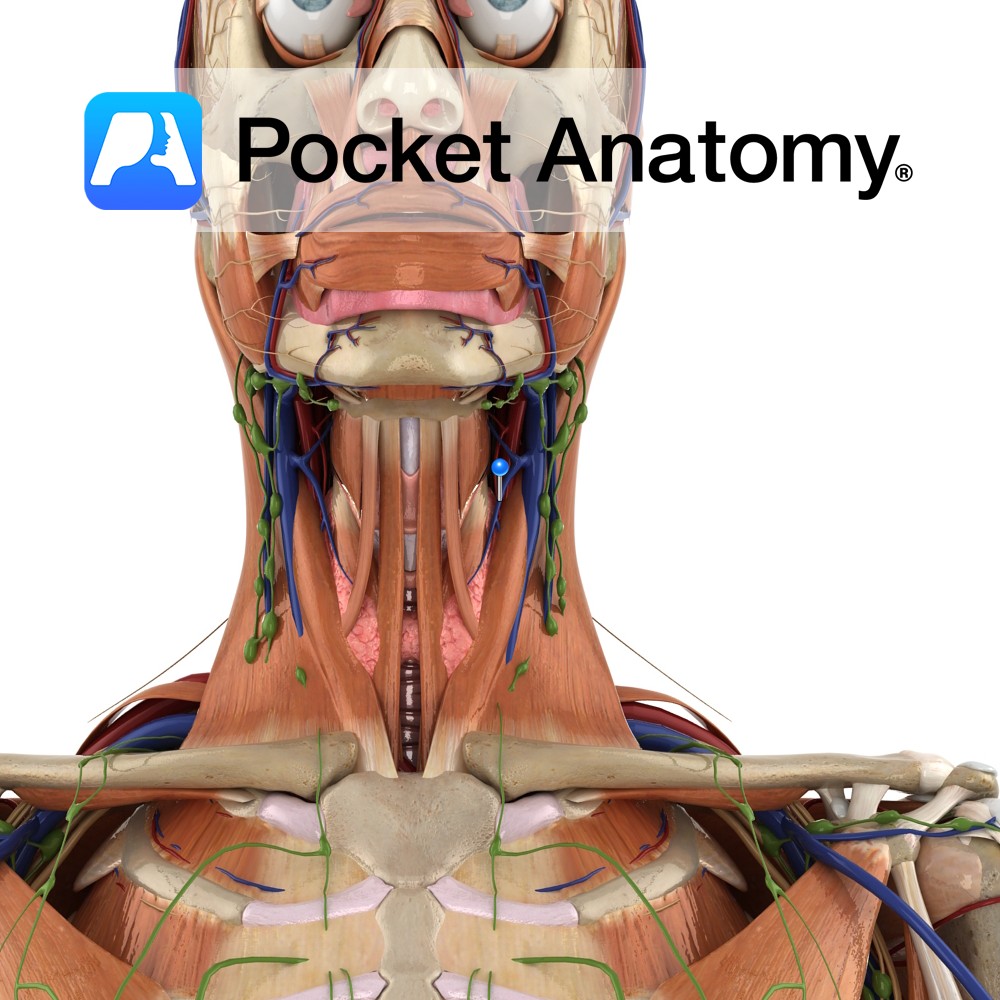
Anatomy Course Begins in the superior region of the thyroid. It emerges from the thyroid to run laterally, crossing the common carotid artery and draining into the internal jugular vein. Drain Drains the superior region of the thyroid gland. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
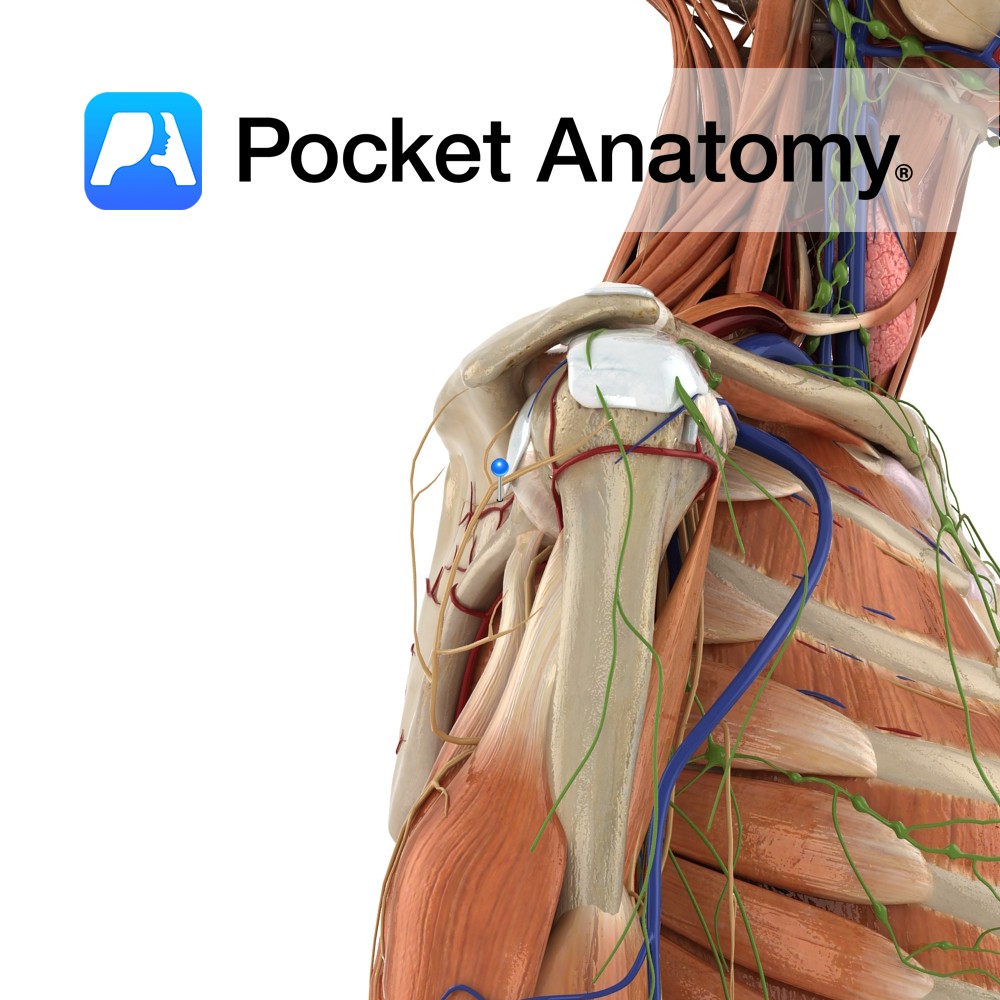
Anatomy Course Branches from the brachial artery about a third of the way along the humerus. It travels along the medial head of the triceps towards the elbow joint, where it anastomoses with the posterior ulnar recurrent artery. Supply Contributes to the blood supply of the medial aspect of the arm and to the elbow
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
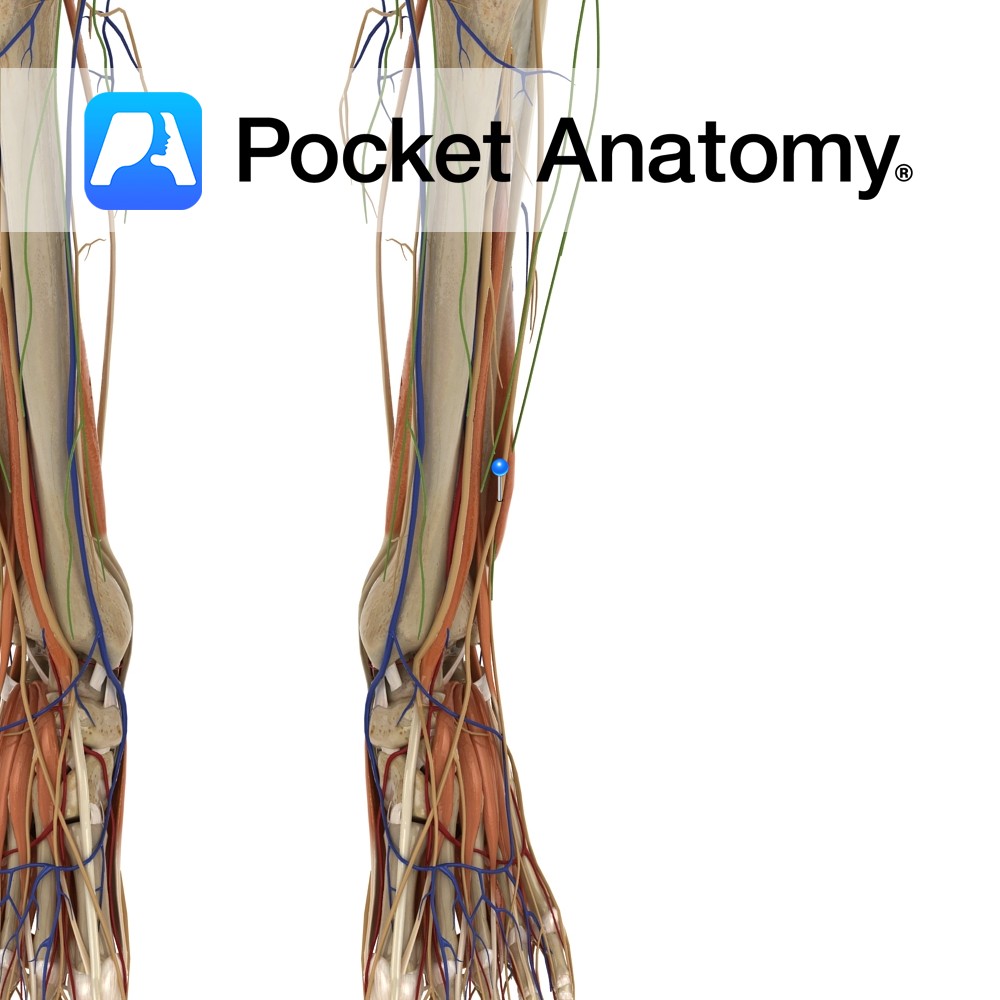
Anatomy Origin: Superficial head (tendinosus): Lateral epicondyle of humerus, Radial collateral and annular ligaments Deep head (muscular): Supinator crest and fossa of ulna. Insertion: Lateral aspect of the proximal third of the radius. Key Relations: -The posterior interosseus nerve travels between the two heads of supinator as it enters the posterior forearm. -One of the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
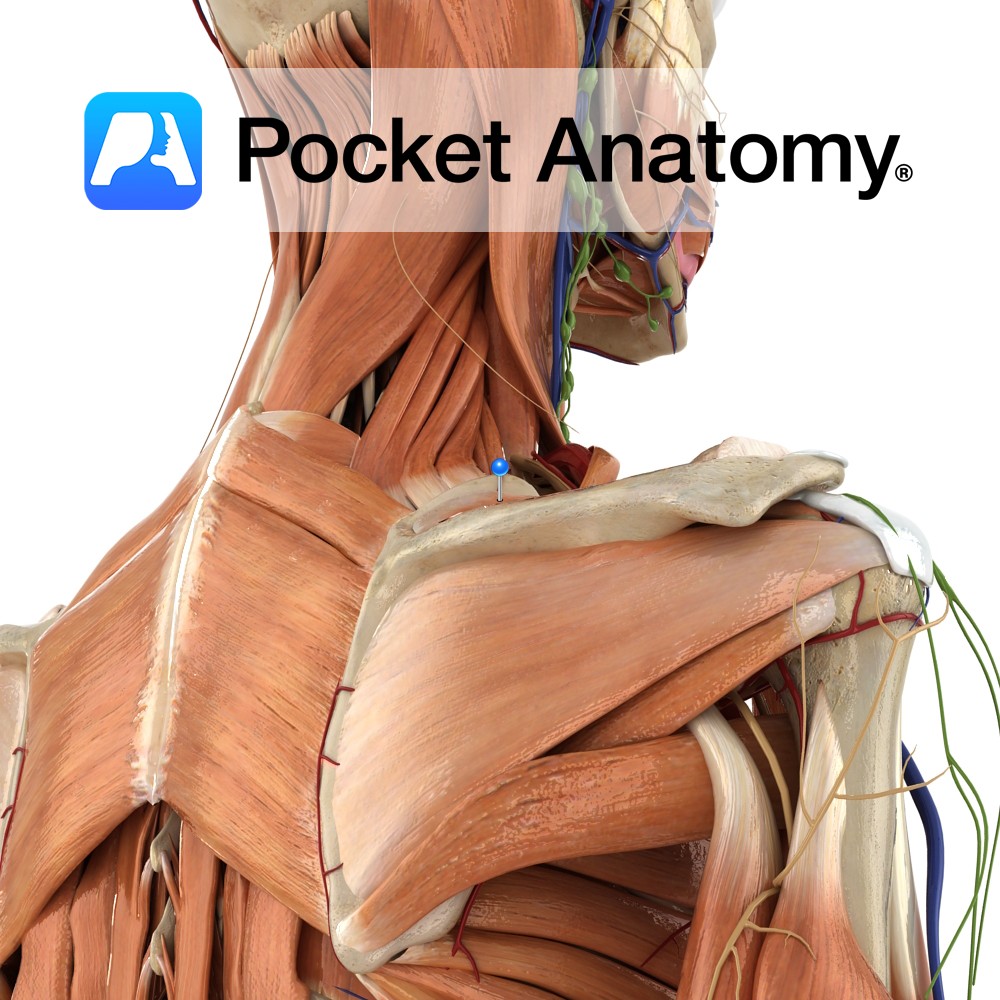
Anatomy Course Arises in the upper trunk of brachial plexus (formed by the union of C5 and C6). Passes downward, laterally (deep to the omohyoid and trapezius, then posteriorly beneath trapezius) before reaching the suprascapular notch. Travels beneath the suprascapular notch before dividing into two branches; one supplies supraspinatus, the other supplies infraspinatus. Supply Sends
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Medial two-thirds of the supraspinous fossa of scapula. Insertion: Superior facet of greater tubercle of humerus. Key Relations: -The muscle forms a tendon that passes under the acromion and above the shoulder joint. -One of the four muscles of the rotator cuff muscle group. Functions -Initiates abduction of the arm to 15° at
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Branches from the common peroneal nerve just below the knee joint on the anterolateral side of the leg. It descends towards the foot passing between the peroneus longus and extensor digitorum longus muscles. It then becomes more superficial, piercing through the deep fascia approximately half-way down the leg. It ends in branches which
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
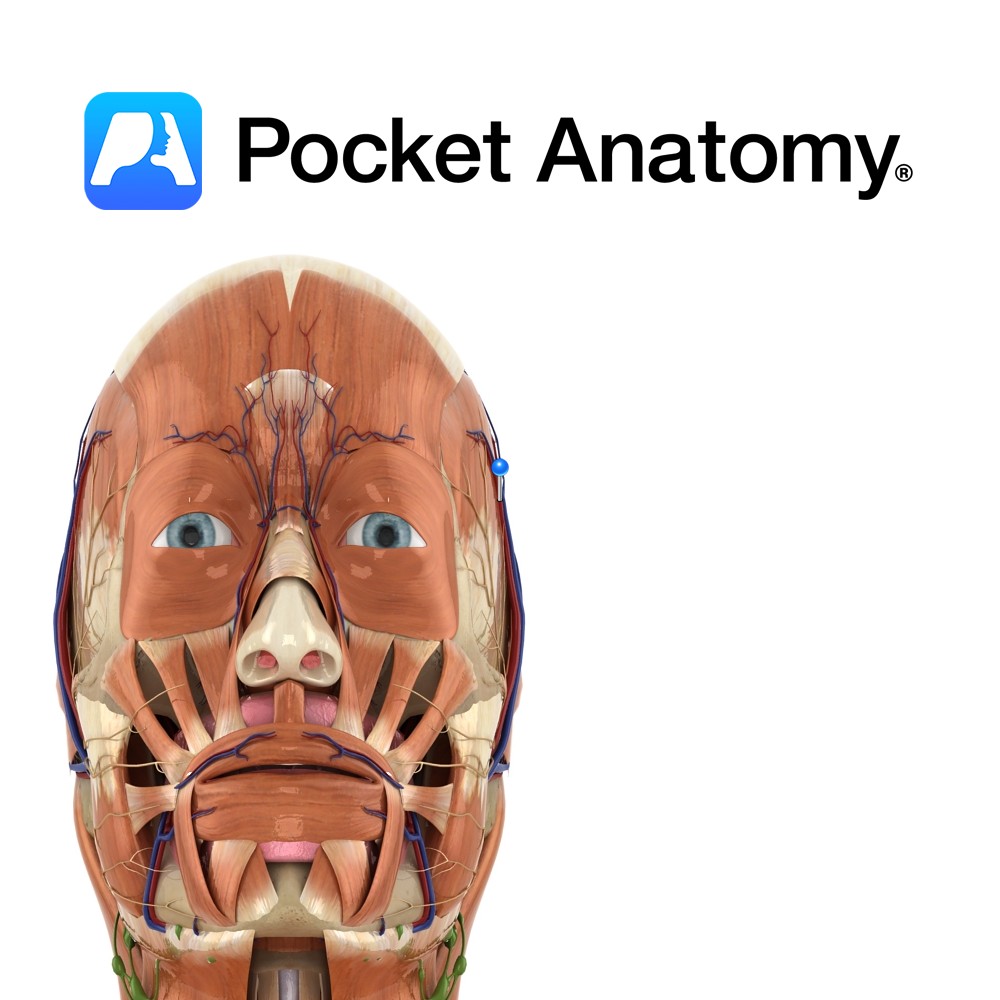
Anatomy Course A branch of the external carotid artery. It is a terminal branch of the external carotid and is said to begin in the parotid gland. It ascends anterior to the ear and divides into branches that travel in the connective tissue layer of the scalp. Supply Supplies most of the scalp. Interested in
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Begins in a venous plexus on the side of the scalp. It travels through the connective tissue layer of the scalp, to just above the parotid gland, where it unites with the maxillary vein to form the retromandibular vein. Drain Drains the superficial temporal aspect of the scalp. Interested in taking our award-winning
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Paired structure that forms a superficial elevation on the dorsal side of the rostral midbrain. It is located within the tectum of the midbrain. The superior and inferior colliculi are collectively known as the corpora quadrigemina. Blood Supply: Supplied by branches of the posterior cerebral arteries. Functions Tectospinal fibers arise from the superior colliculus.
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins