PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
Anatomy Pyramid shaped cartilages sitting on top of the cricoid cartilage. The base is concave and articulates with the slopping articular facet on the superior lateral surface of the lamina of the cricoid cartilage. The anterior angle of the base is extended out into a vocal process. The apex articulates with a corniculate cartilage. Both
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
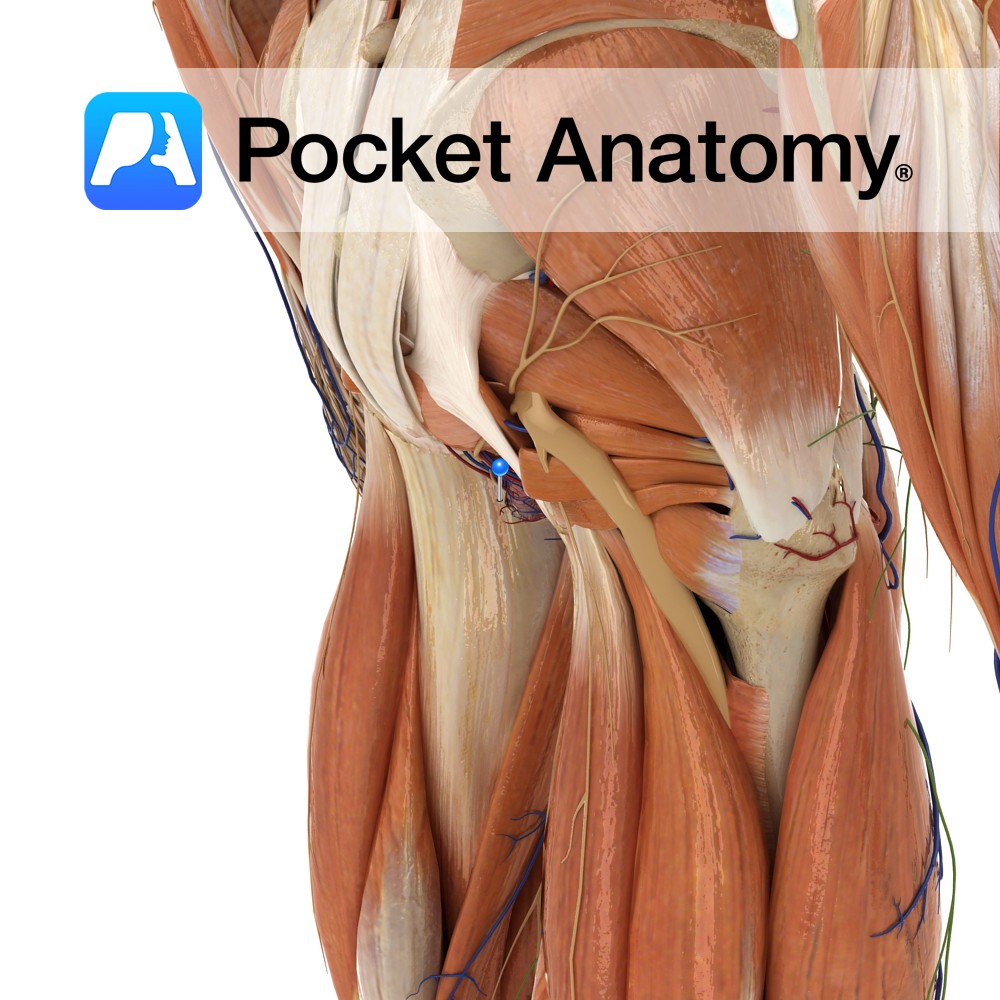
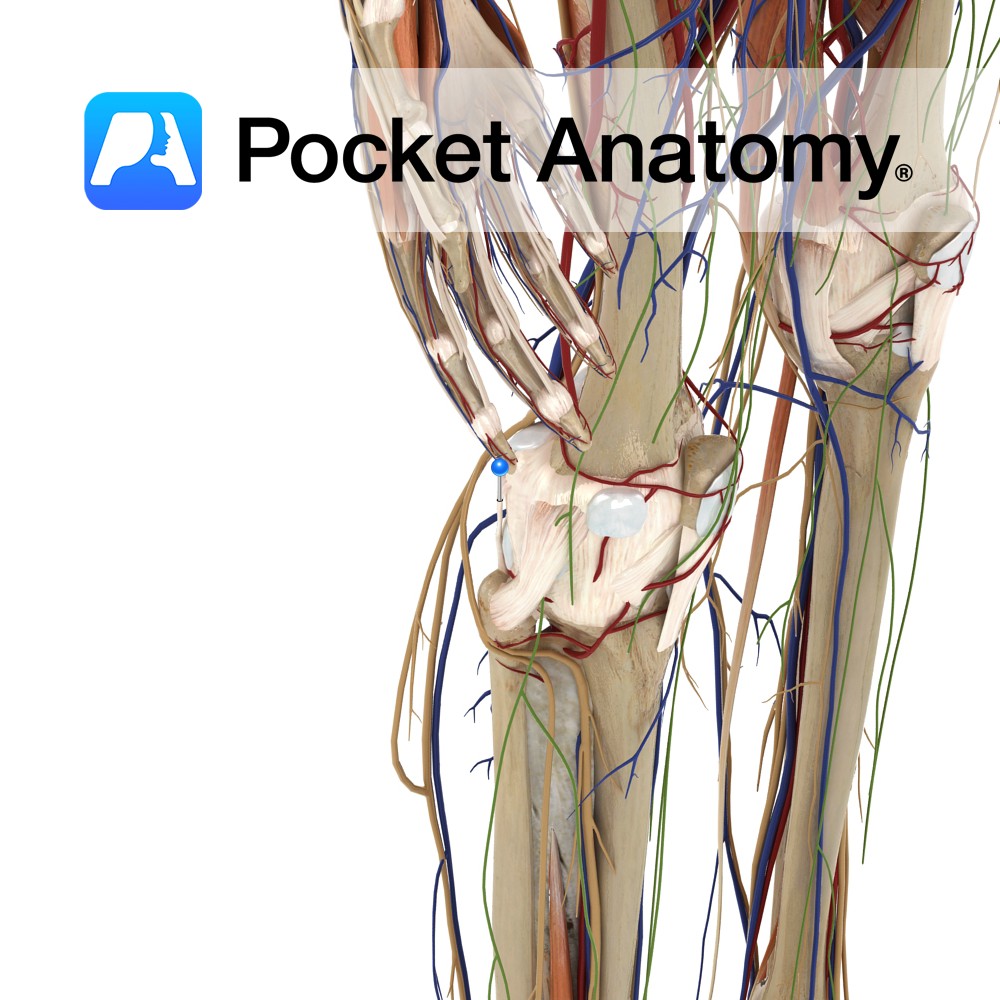
Anatomy An extrinsic ligament of the knee joint. The ligament is Y-shaped and extends from the fibular head. One slip going to the intercondylar area of the tibia. The second slip to the lateral epicondyle of the femur, where it blends with the lateral head of the gastrocnemius. Functions One of the ligaments that help
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
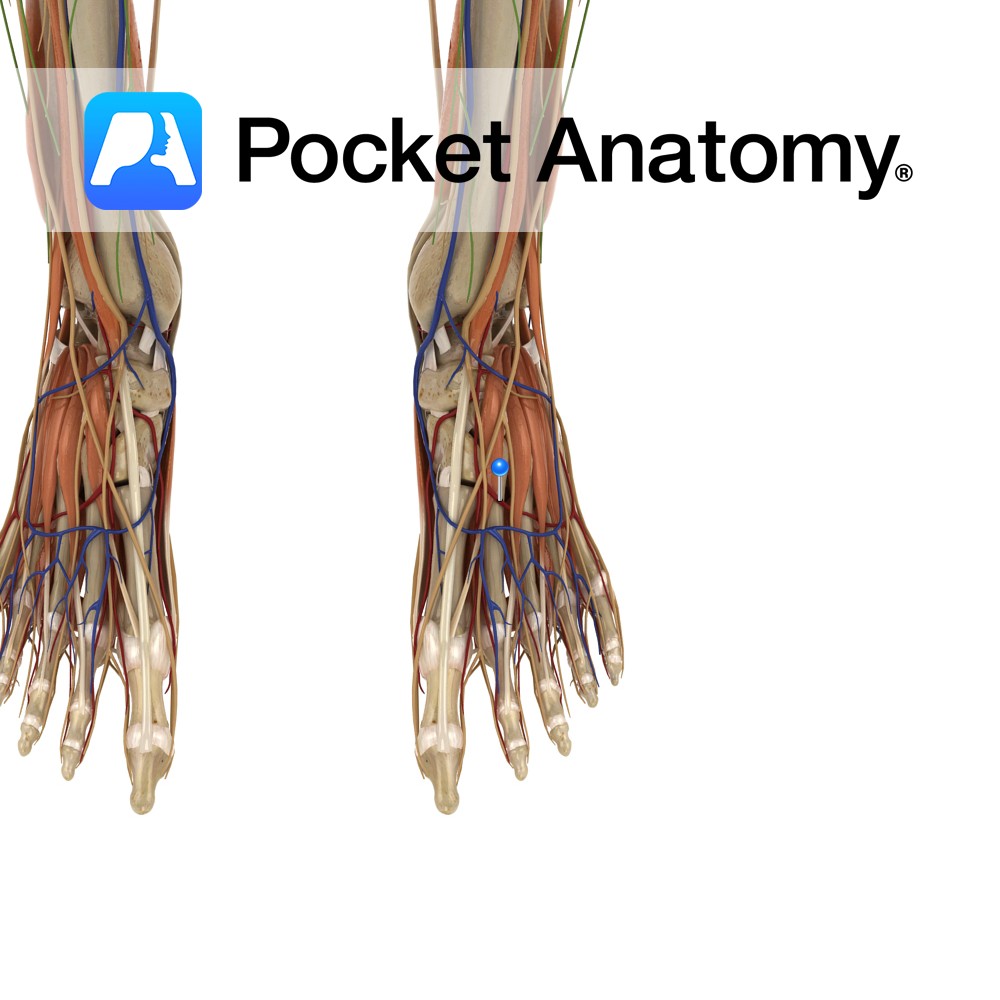
Anatomy Course Branches off the dorsalis pedis artery, where it then proceeds laterally over the dorsal aspect of the metatarsal bones to give off three dorsal metatarsal arteries. Supply Supplies digits two to five. Clinical Not found in all individuals. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Vermiform (worm-like) blind vestigial sac, 1-8″, arising from 2 cm below ileocecal valve in cecum, right lower quadrant, roughly surface equivalent McBurney’s point (2/3 way from umbilicus to anterior superior iliac spine); base constant but body can lie behind cecum, or in pelvis, or points in between, and can be retroperitoneal. Common site of
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Lowest part of intestine, from lower end sigmoid, down and back about 2.5-4 cms to anus, no peritoneal covering, double sphincter (internal along length and external at anus), supported sling-like by levator ani (thin muscle group of pelvic floor which support its organs and act sphincter-like in maintaining continence and opposing increases in pelvic
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
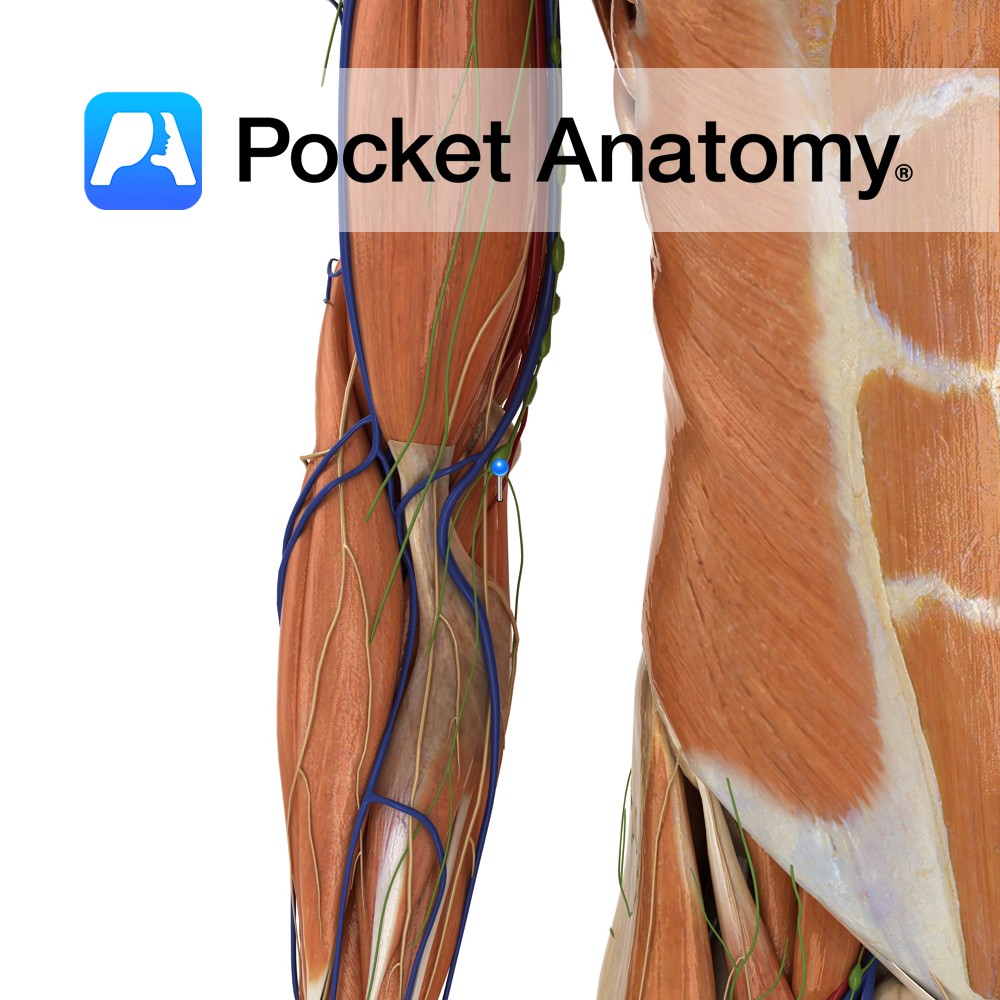
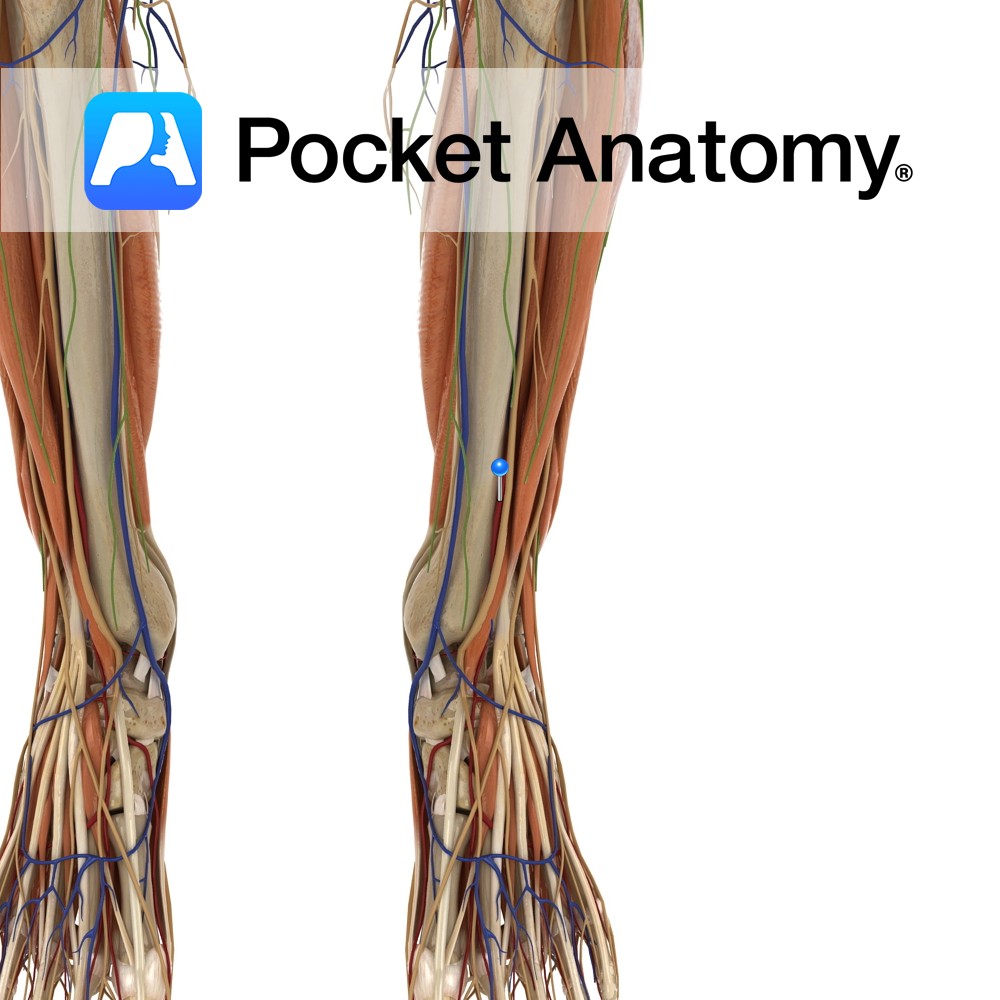
Anatomy Course One of the branches of the ulnar recurrent artery, which assists in the formation of an anastomotic network around the elbow joint. It arises below the elbow joint and rises between the brachialis and pronator teres muscles until it anastomoses with the ulnar collateral arteries. Supply Supplies brachialis and pronator teres muscles as
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
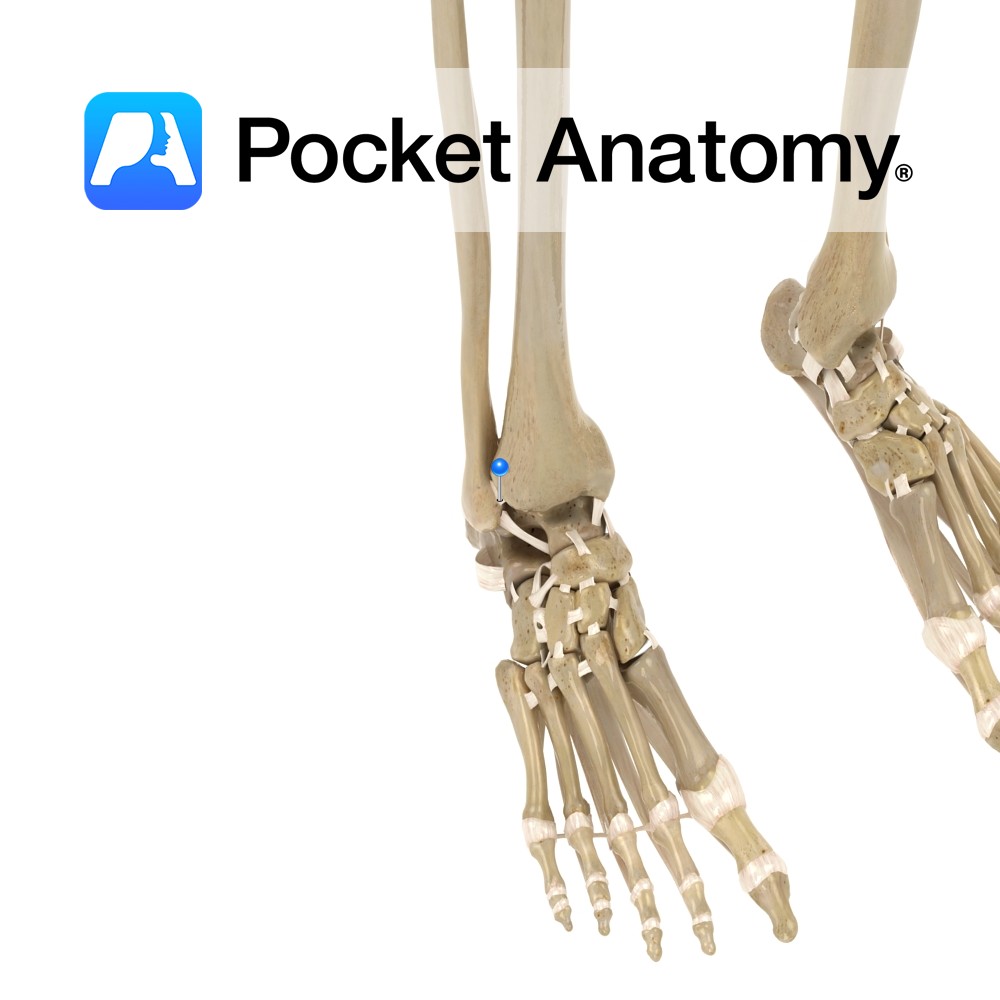
Anatomy Part of the distal tibiofibular joint. It attaches from the lateral surface of the anterior distal tibia, and travels obliquely downwards to attach to the lateral malleolus. Functions Holds the distal end of the tibiofibular joint together tightly. It is key for the skeletal framework and articulation of the foot at the ankle. Interested
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
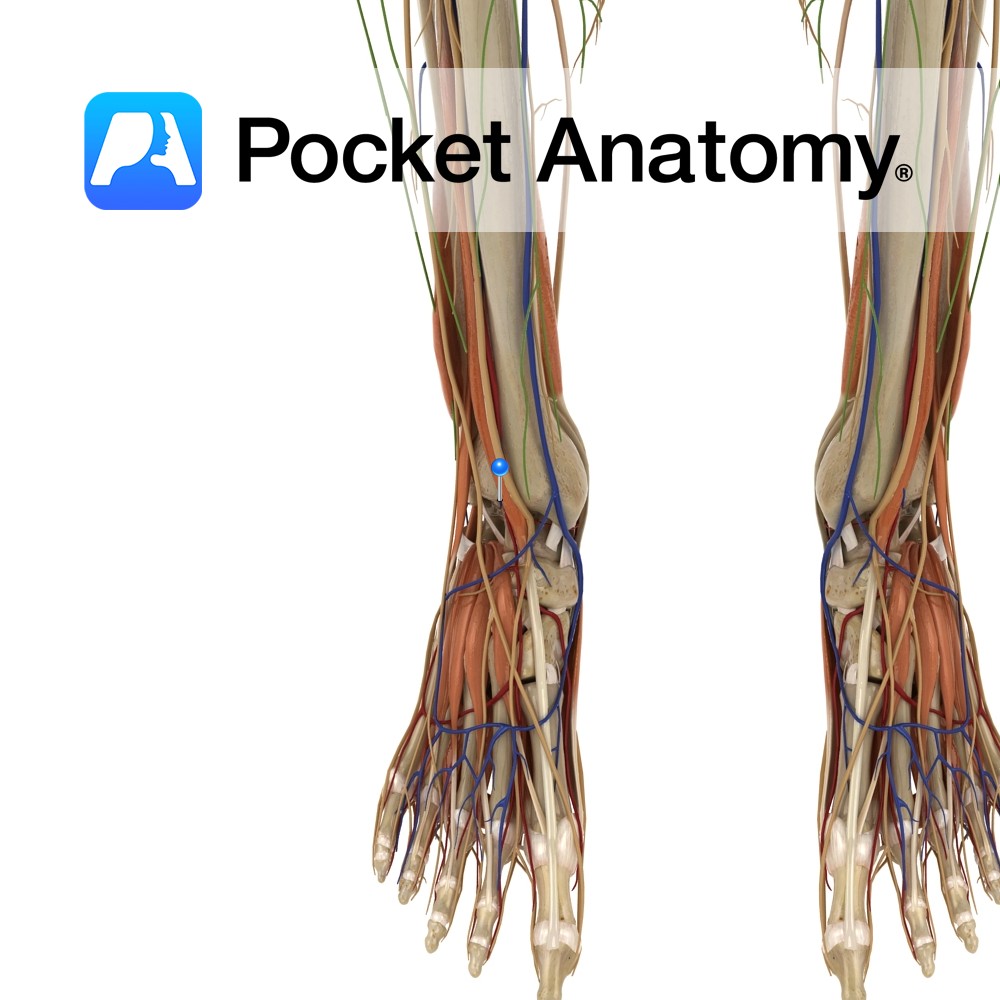
Anatomy Course Follows its counterpart artery until it drains into the popliteal vein. Drain Drains the anterior compartment of the lower limb. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Continuation of the popliteal artery when it passes through the interosseous membrane to cross into the anterior leg. It then descends on the anterior side of the interosseous membrane until it reaches the distal end of the tibia and ankle. It then continues into the foot as the dorsalis pedis artery. Supply Supplies
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
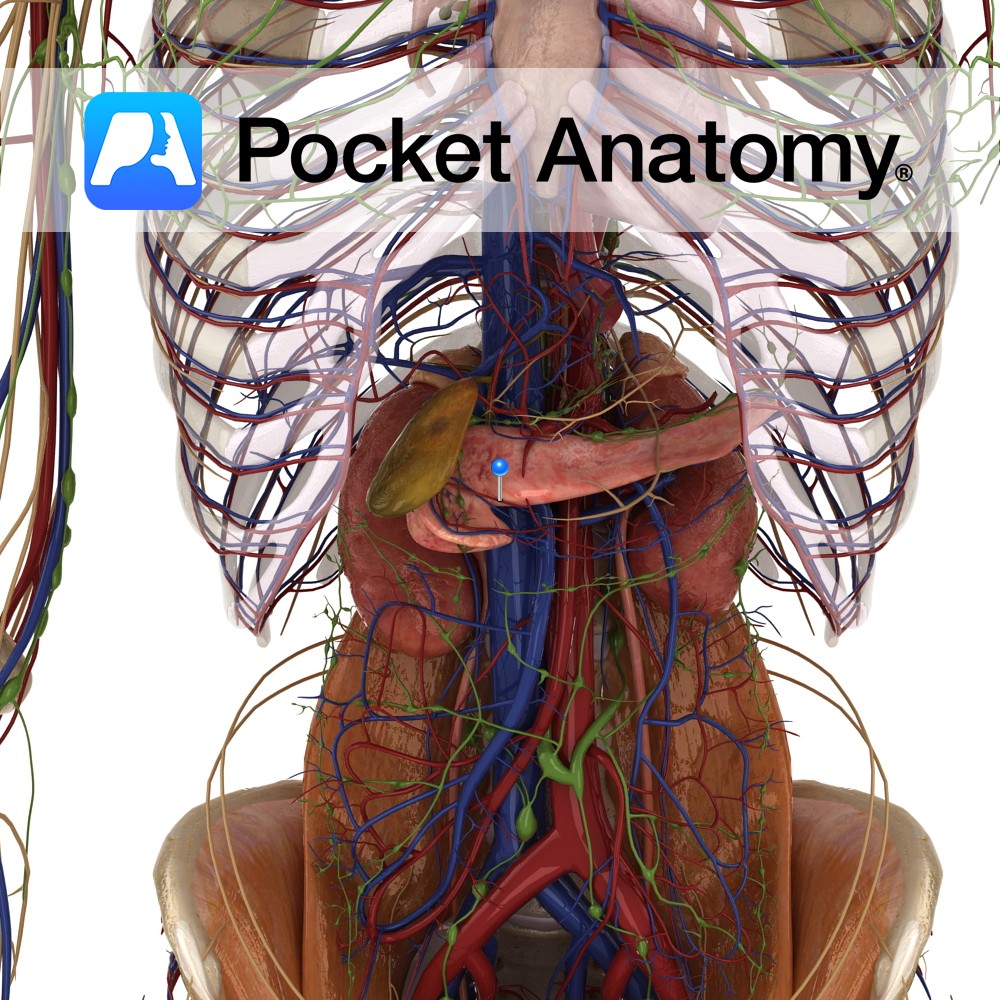
Anatomy Course Branch of the pancreaticoduodenal artery which itself originates from the gastroduodenal artery. Anastamoses with branches of the splenic artery. Supply Responsible for supplying the head of the pancreas as well as the anterior aspect of the duodenum. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins

.jpg)