PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
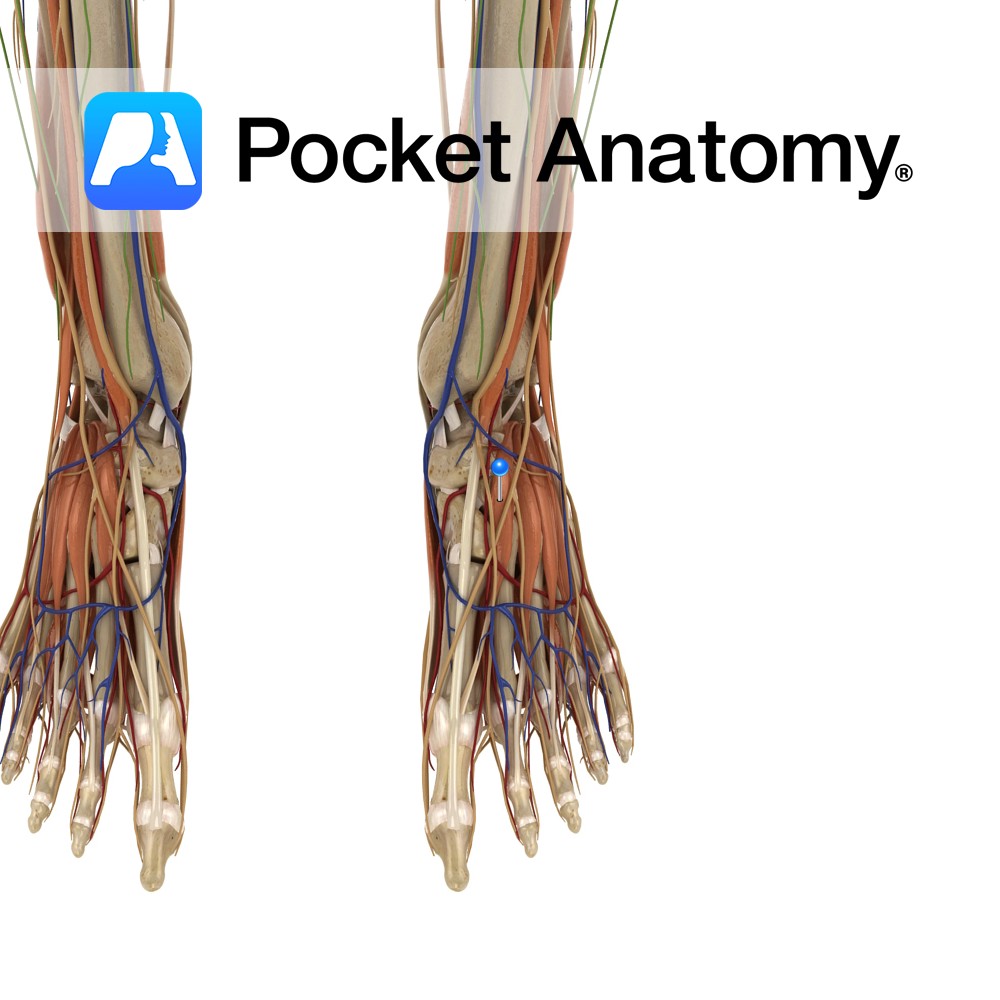
Anatomy Origin: Middle half of the anteromedial surface of the fibula and the interosseous membrane. Insertion: Dorsal surface of the base of the distal phalanx of the hallux (big toe). Key Relations: -One of the four muscles of the anterior compartment of the leg. -The extensor hallucis longus tendon crosses anterior to the ankle joint
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Anterolateral part of the superior surface of calcaneus and inferior extensor retinaculum. Insertion: Dorsal surface of the base of the proximal phalanx of the hallux (big toe). Key Relations: Merely the medial part of extensor digitorum brevis. Functions Extends the hallux at the interphalangeal joint (assists extensor hallucis longus). Supply Nerve supply: Deep
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
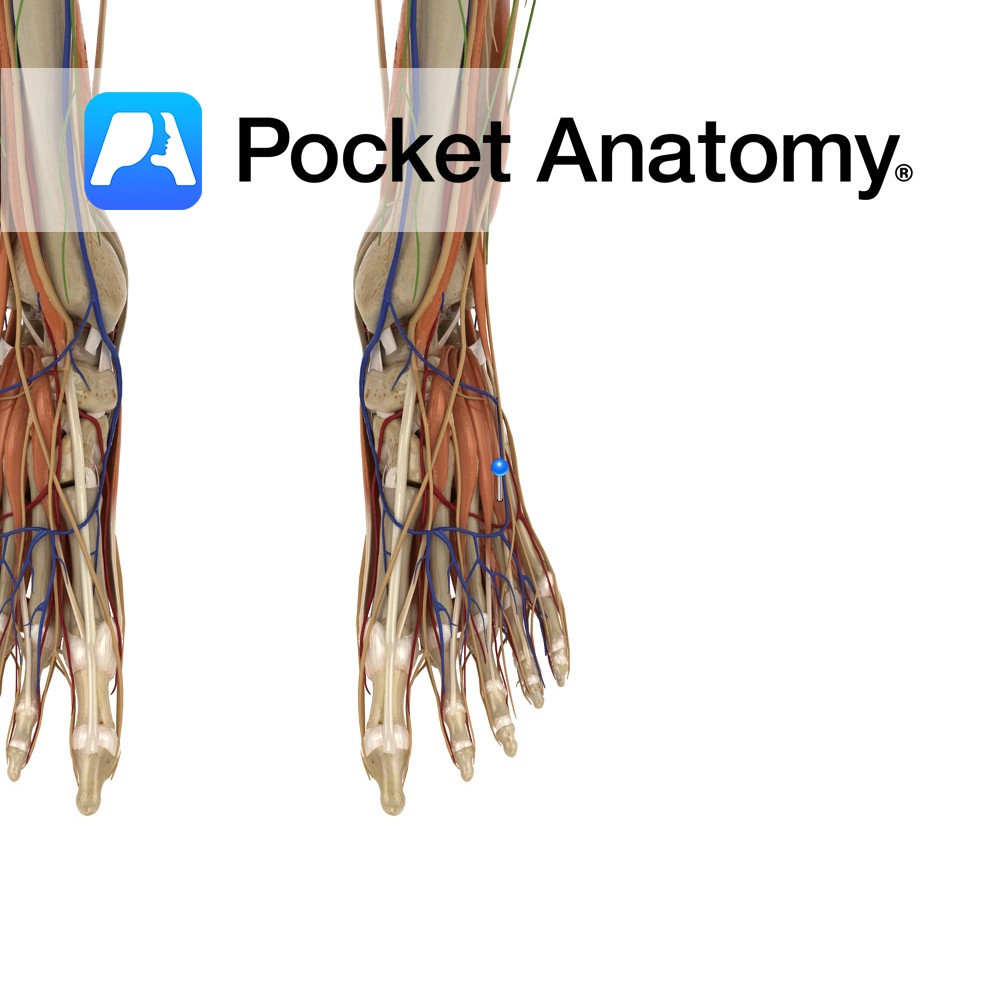
Anatomy Origin: Inferior aspect of lateral condyle of tibia, upper three-fourths of the anterior surface of the interosseous membrane and the anterior intermuscular septum. Insertion: The extensor digitorum longus tendon divides into four slips deep to the inferior extensor retinaculum. The four slips insert onto the dorsal aspects of the middle and distal phalanges of
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Anterolateral part of the superior surface of calcaneus and inferior extensor retinaculum. Insertion: Lateral aspect of the extensor digitorum longus tendons of 2nd, 3rd and 4th toes. Key relations: Runs anteromedially across the foot and can be palpated inferomedially to the lateral malleolus on the dorsum of the foot. Functions Extends the 2nd,
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
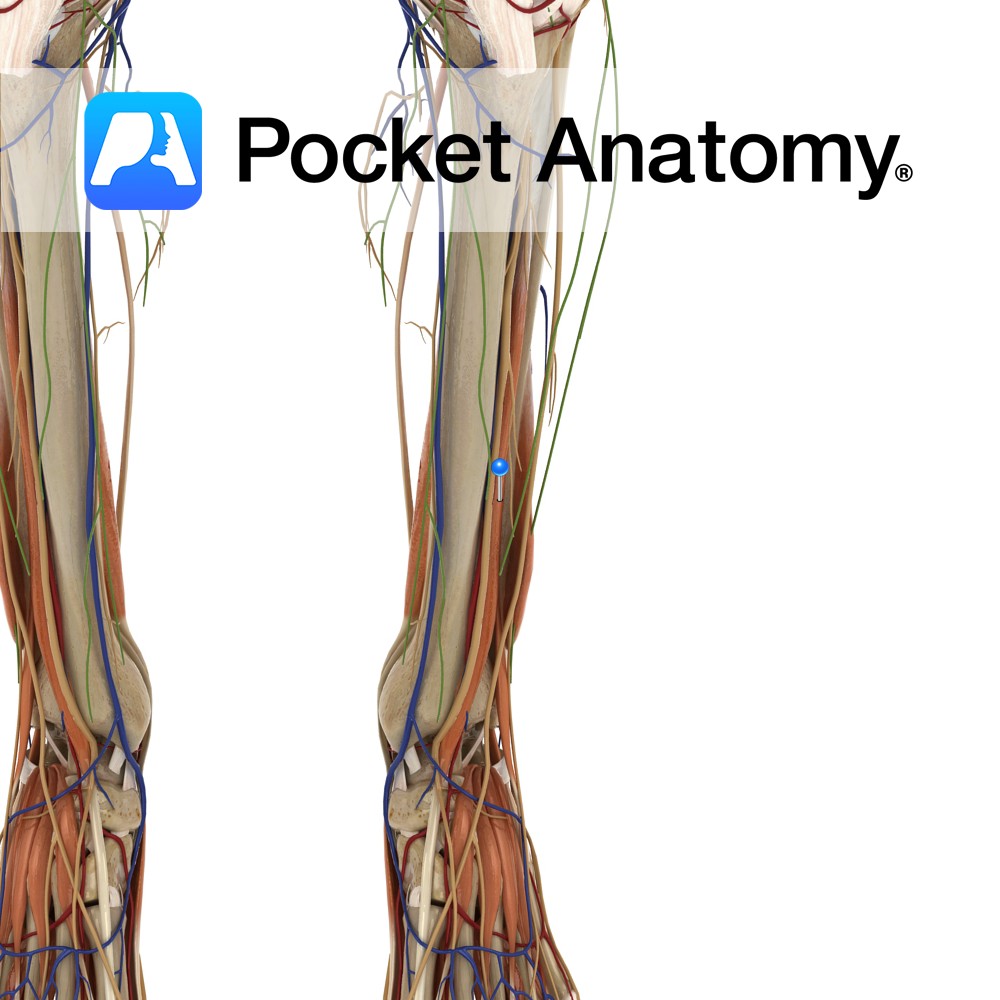
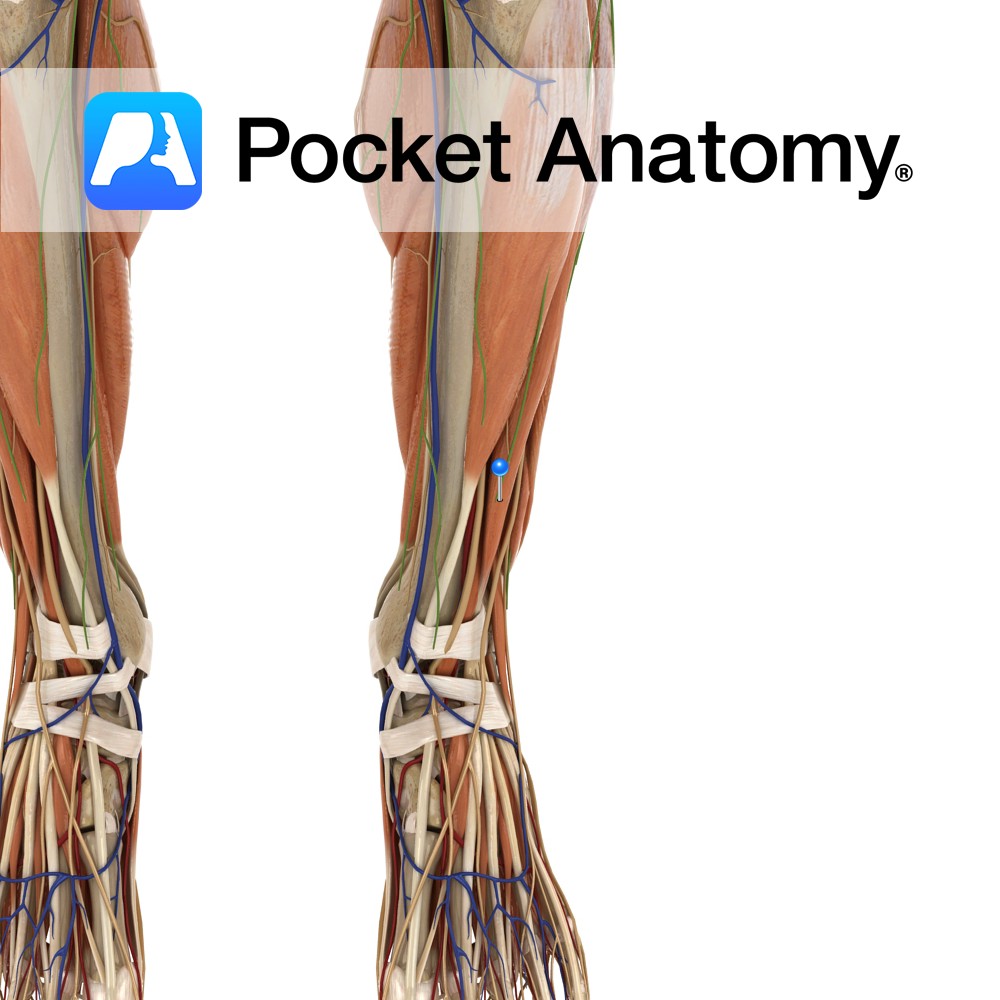
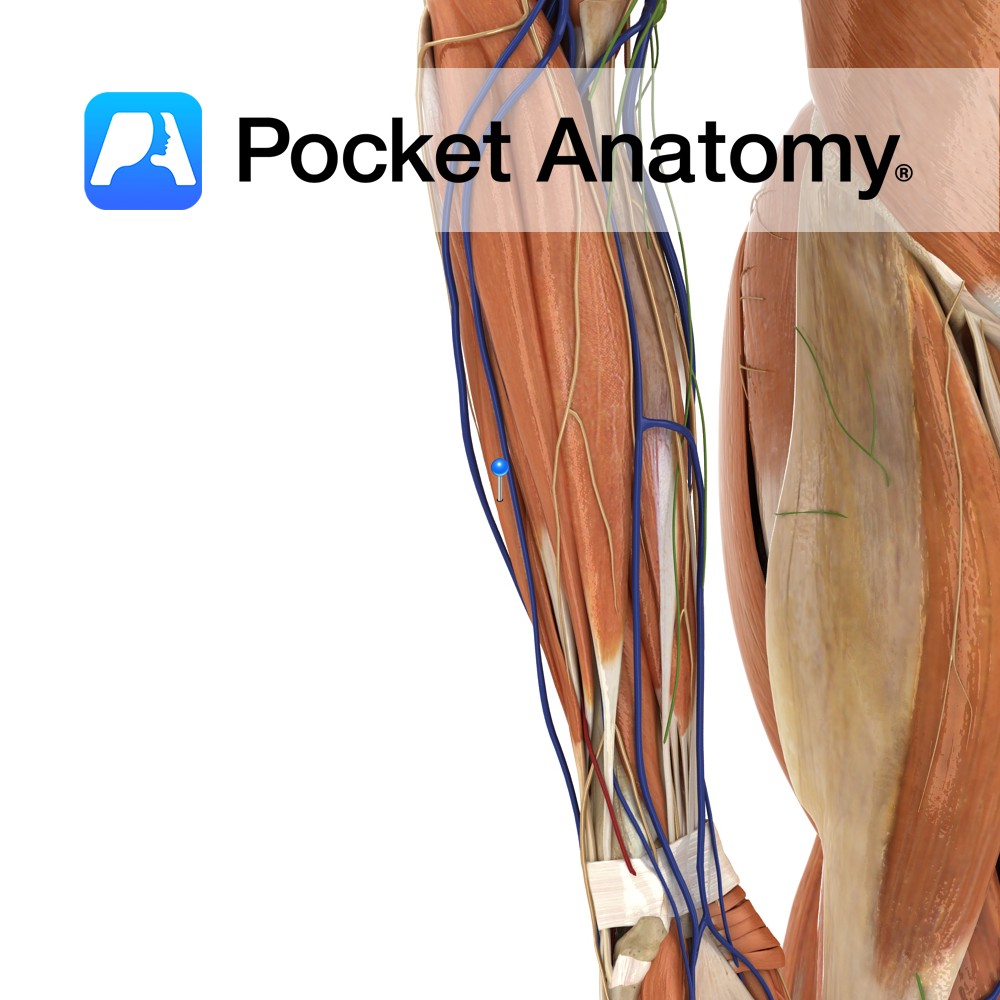
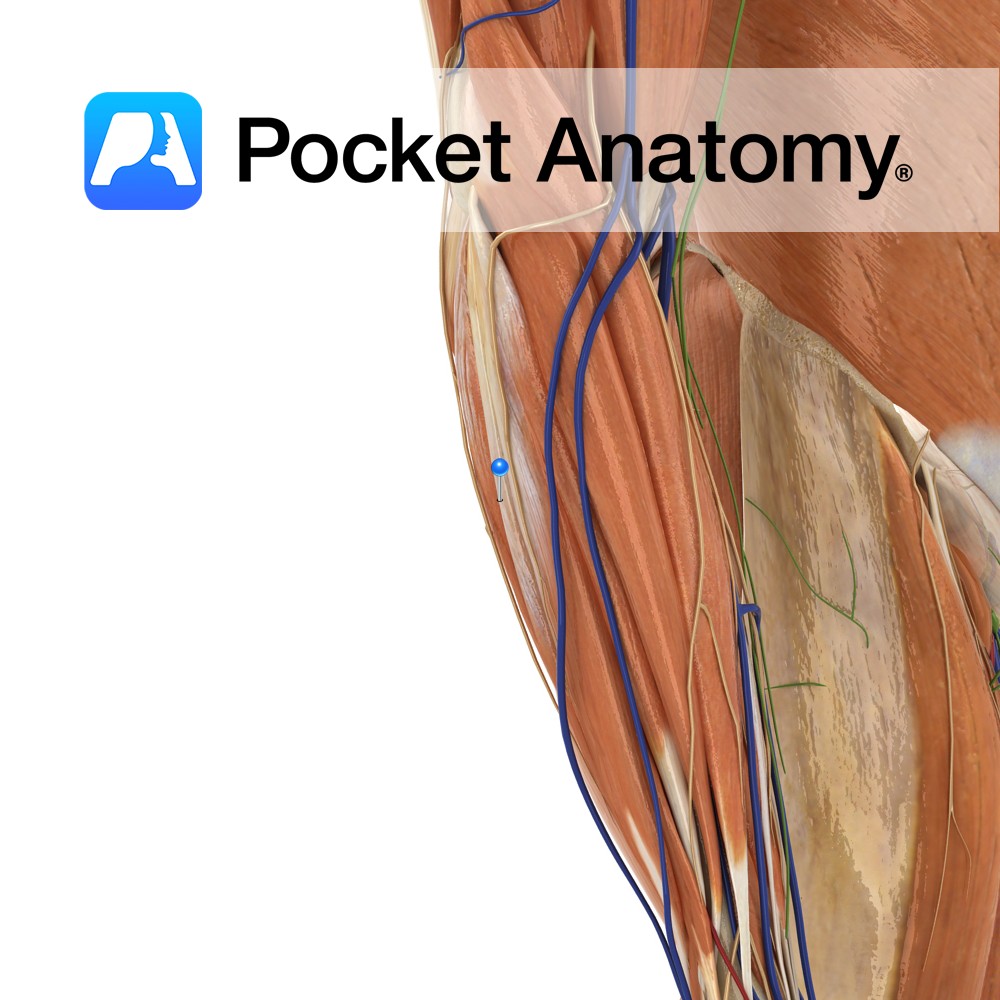
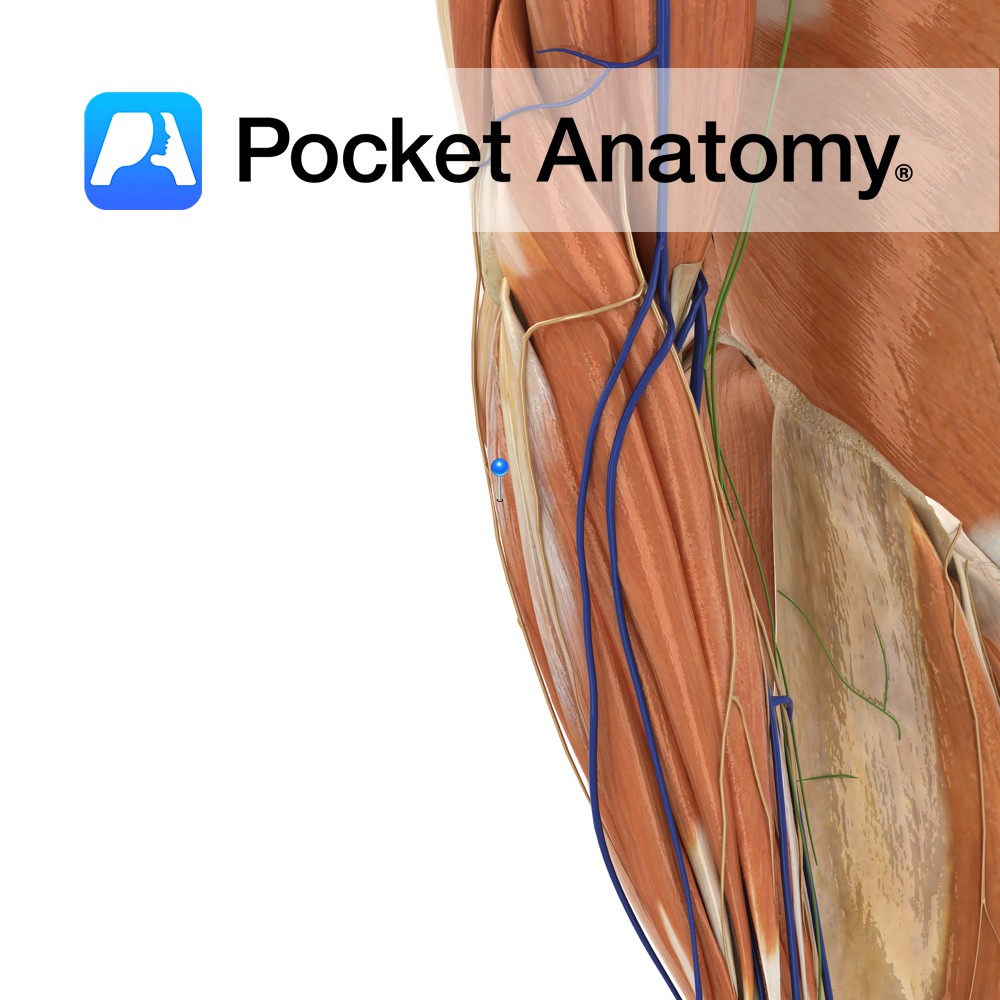
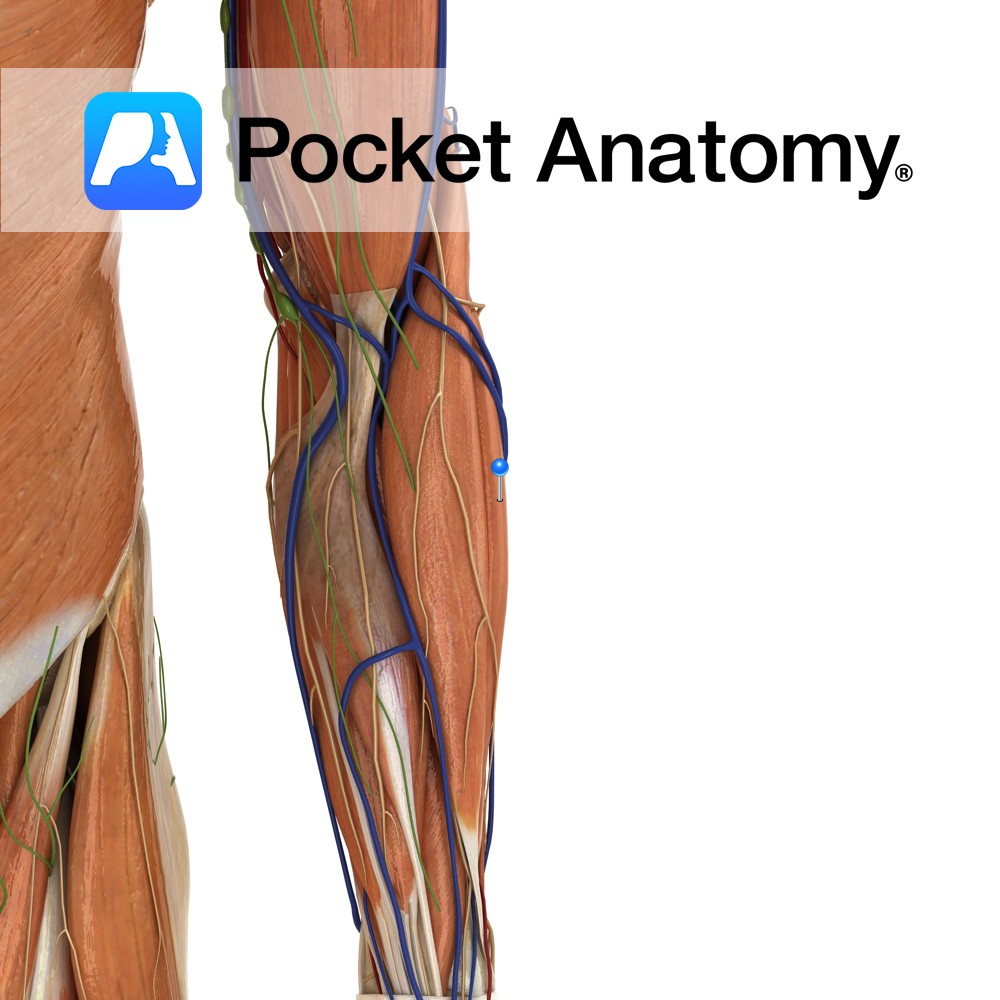
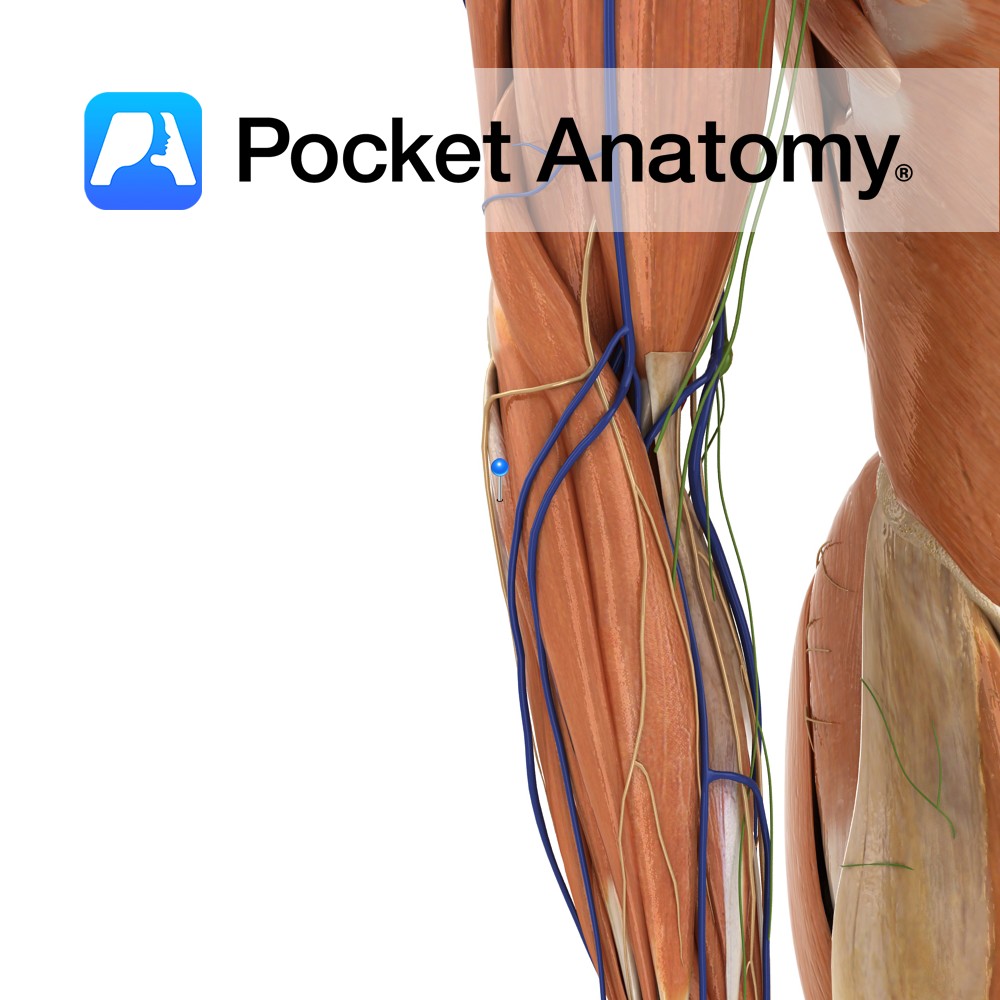
Anatomy Origin: Lateral epicondyle of humerus via the common extensor tendon and adjacent intermuscular septum. Insertion: Through separate tendons inserting into extensor hoods on dorsal surface of middle and distal phalanges of the four fingers. Key Relations: One of the two muscles in the intermediate posterior compartment of the forearm. Functions -Extension of four fingers
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Lateral epicondyle of humerus via the common extensor tendon, adjacent intermuscular septum. Insertion: Dorsal hood of the little finger. Key Relations: One of the two muscles in the intermediate posterior compartment of the forearm. Functions -Extends the little finger at the metacarpophalangeal joint. -Extends the interphalangeal joints of the little finger. -Helps extend
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: First head: Lateral epicondyle of humerus via the common extensor tendon. Second head: Posterior border of ulna. Insertion: Medial aspect of base of fifth metacarpal Key Relations: One of the four muscles in the superficial posterior compartment of the forearm. Functions -Extends the hand at the wrist joint. -Adducts the hand at the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Distal third of lateral supracondylar ridge of humerus and lateral intermuscular septum. Insertion: Posterior aspect of base of second metacarpal. Key Relations: One of the four muscles in the superficial posterior compartment of the forearm. Functions -Extends the hand at the wrist joint. -Abducts the hand at the wrist (radial deviation) particularly when
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Lateral epicondyle of humerus via common extensor tendon, adjacent intermuscular septa. Insertion: The dorsal aspect of base of second and third metacarpal. Key Relations: -One of the four muscles in the superficial posterior compartment of the forearm. Functions -Extends the hand at the wrist joint -Abducts the hand at the wrist (radial deviation)
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Projects down from body of ethmoid (unpaired bone inside skull, between orbits, forming part cranial floor and part roof nasal cavity), forms part of nasal septum. Thin, flat, polygonal, usually deviated a little left or right. Septal cartilage attached below. Articulates with frontal, sphenoid, nasals. Clinical Ethmoid made up of perpendicular plate, cribriform plate
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins