PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
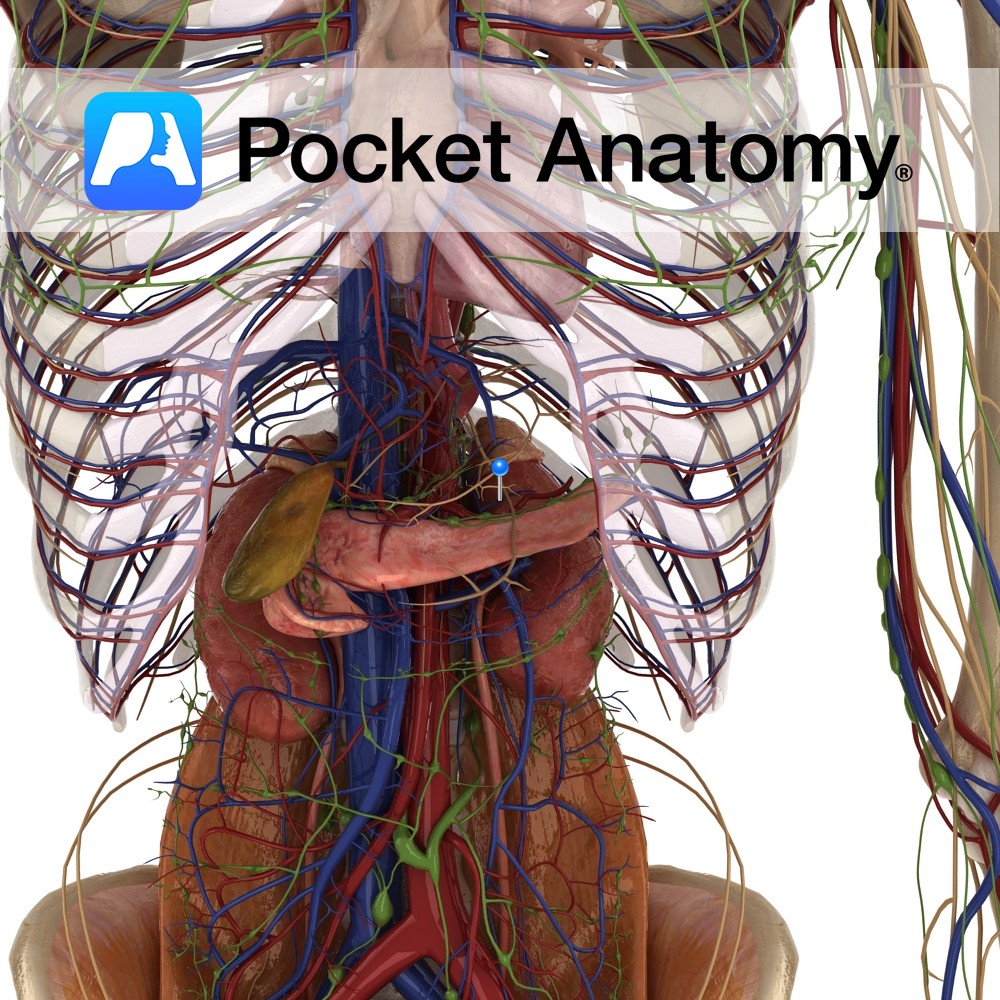
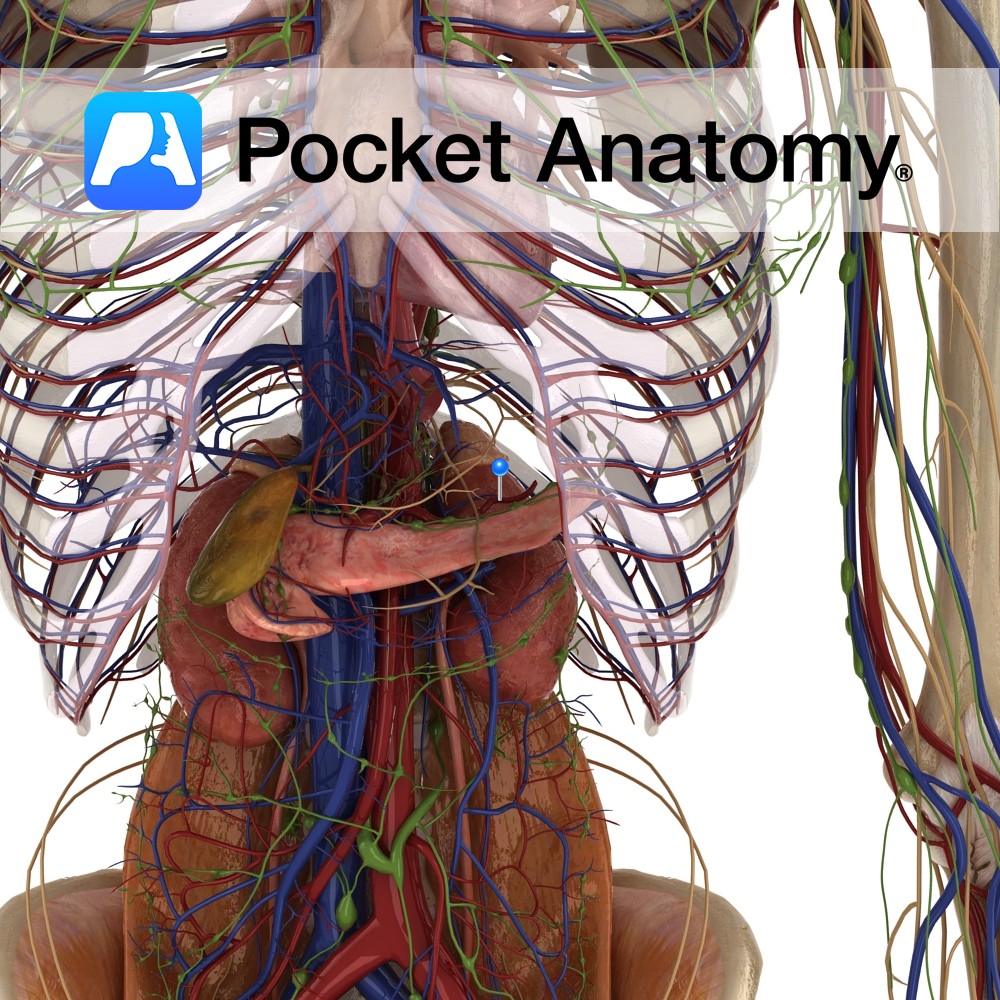
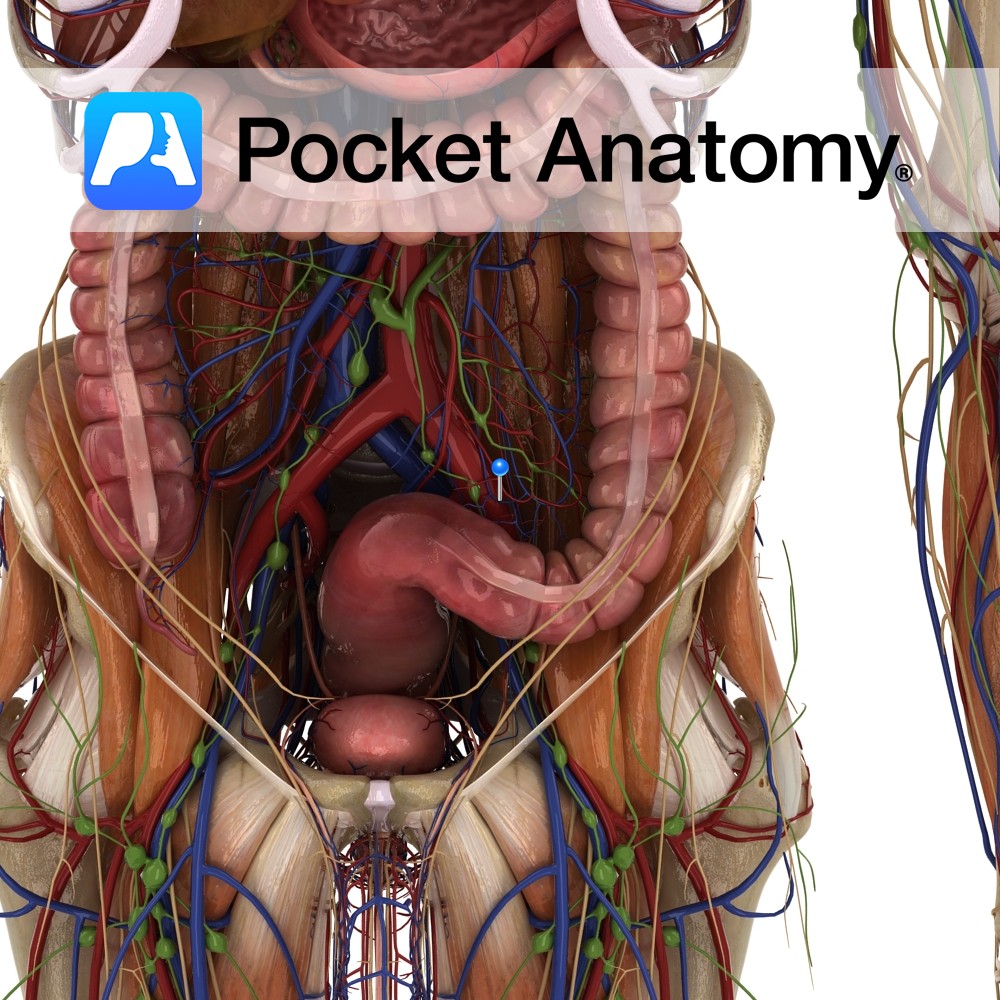
Anatomy Course Begins at the hilum of the spleen. It follows a tortuous course along the upper margin of the pancreas and travelling along the posterior abdominal wall, until it reaches the superior mesenteric vein, which it joins with to form the portal vein. Drain Drains blood from the spleen. Interested in taking our award-winning
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Largest branch of the celiac trunk of the abdominal aorta. It travels laterally from the celiac trunk within the splenorenal ligament, taking a twisted course along the superior border of the pancreas, travelling posterior to the stomach. It divides into many small branches and enters the spleen at the hilum. Supply Supplies the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
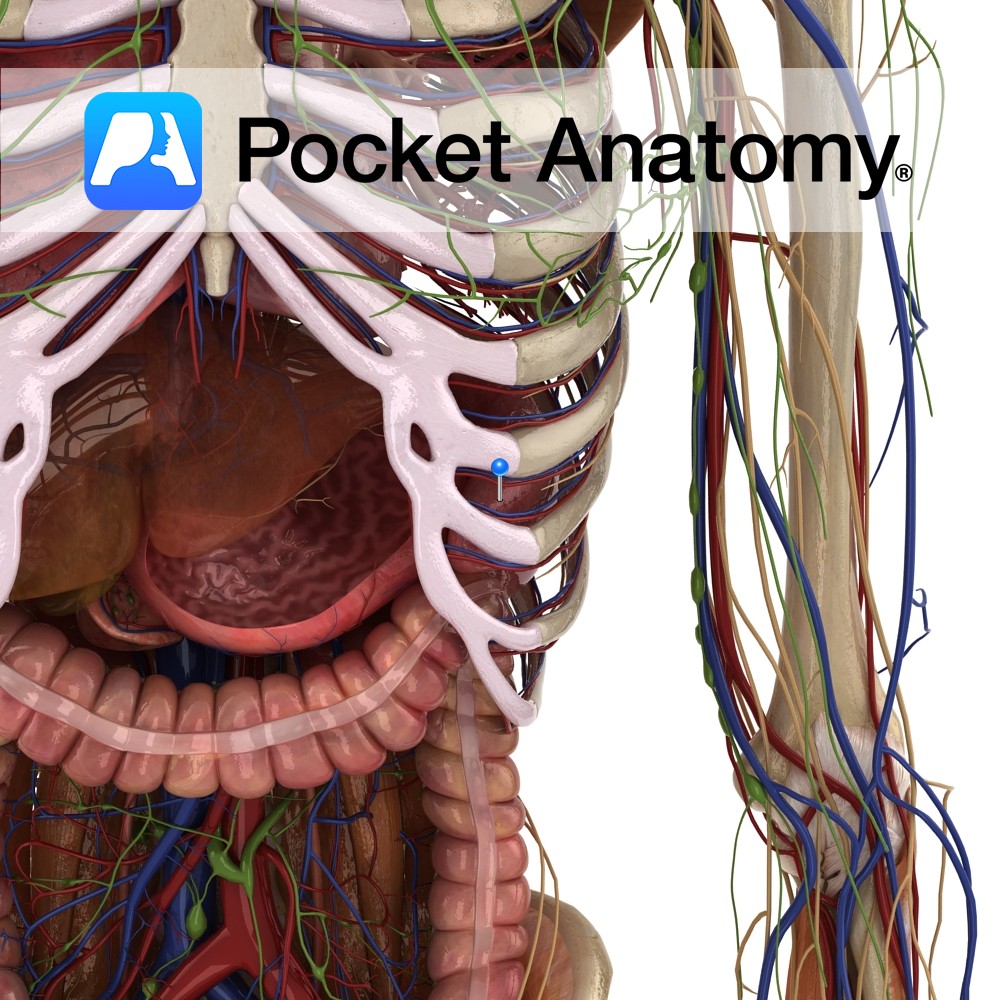
Anatomy Highly vascular, purplish, wedge-shaped (upper part thicker) organ (largest ductless), left upper quadrant abdomen; soft, as a result moulded by its contacts; diaphragmatic surface convex – diaphragm; visceral surface has anterior/ gastric, posterior/renal parts; gastric surface – back of fundus stomach, tail pancreas; renal surface – upper pole left kidney, sometimes adrenal; lower extremity
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy The dura mater of the spinal cord is the outermost layer of the meninges that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. It is the toughest of the three layers and surrounds the spinal cord like a loose fitting sock. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Unpaired bone at base of skull, in front of temporal bones, behind eye socket. Looks like bat or butterfly from front. Made up of body, greater and lesser wings, and pterygoid processes. Body has sella tursica in which pituitary gland sits. Clinical Called “Keystone bone of cranium”, as it articulates with all other cranial
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
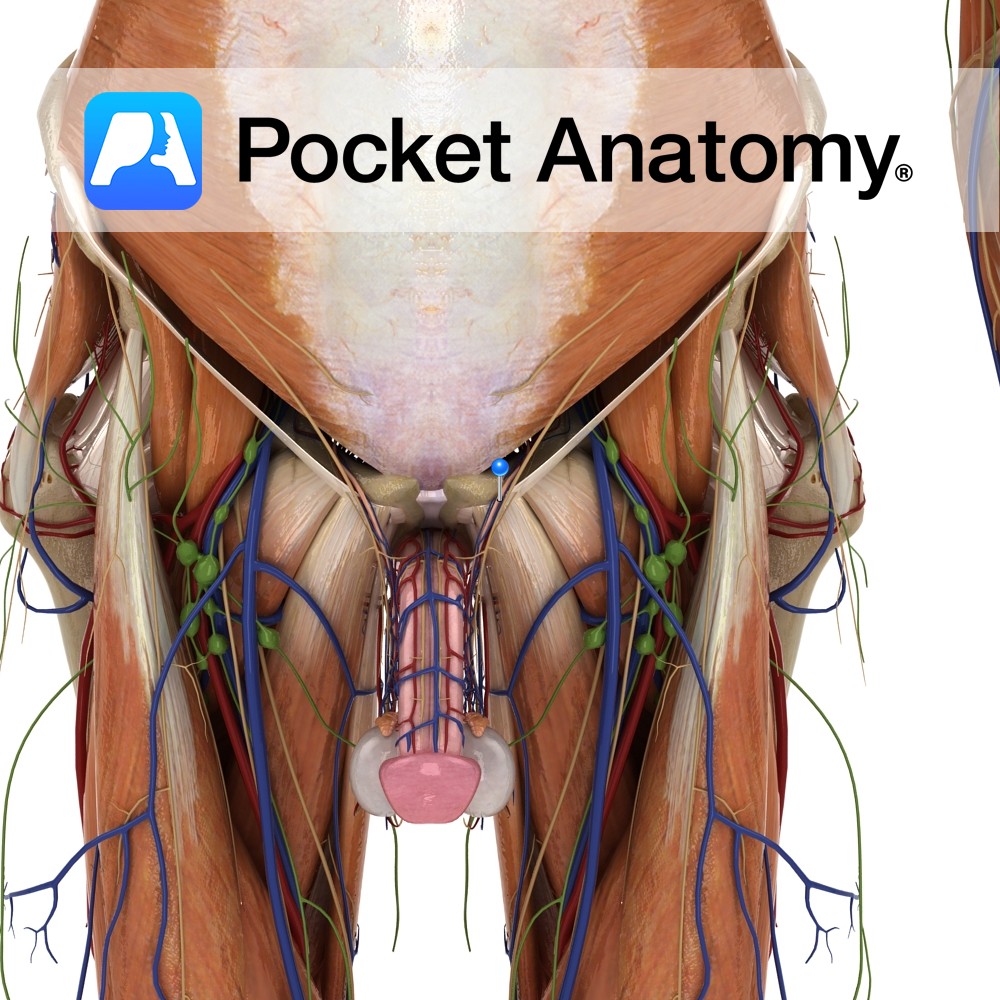
Anatomy In development, the testes bulge/bubble down and out of the abdomen (to escape to a lower temperature), through a passage in the abdominal wall (the inguinal canal) bringing with them layers and structures (abnormal bulging is called herniation). The Spermatic Cord reflects this abdominal origin and connects the testis to the abdomen; its fascias
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Clinical Common skin conditions among adolescents include acne, atopic dermatitis, and herpes. Acne affects mainly the face, upper chest, and back (the areas of the skin with the densest concentration of sebaceous glands). Acne affects approximately 80%-90% of teenagers, usually the result of increases in testosterone during puberty (in both genders). Atopic dermatitis (eczema) is
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
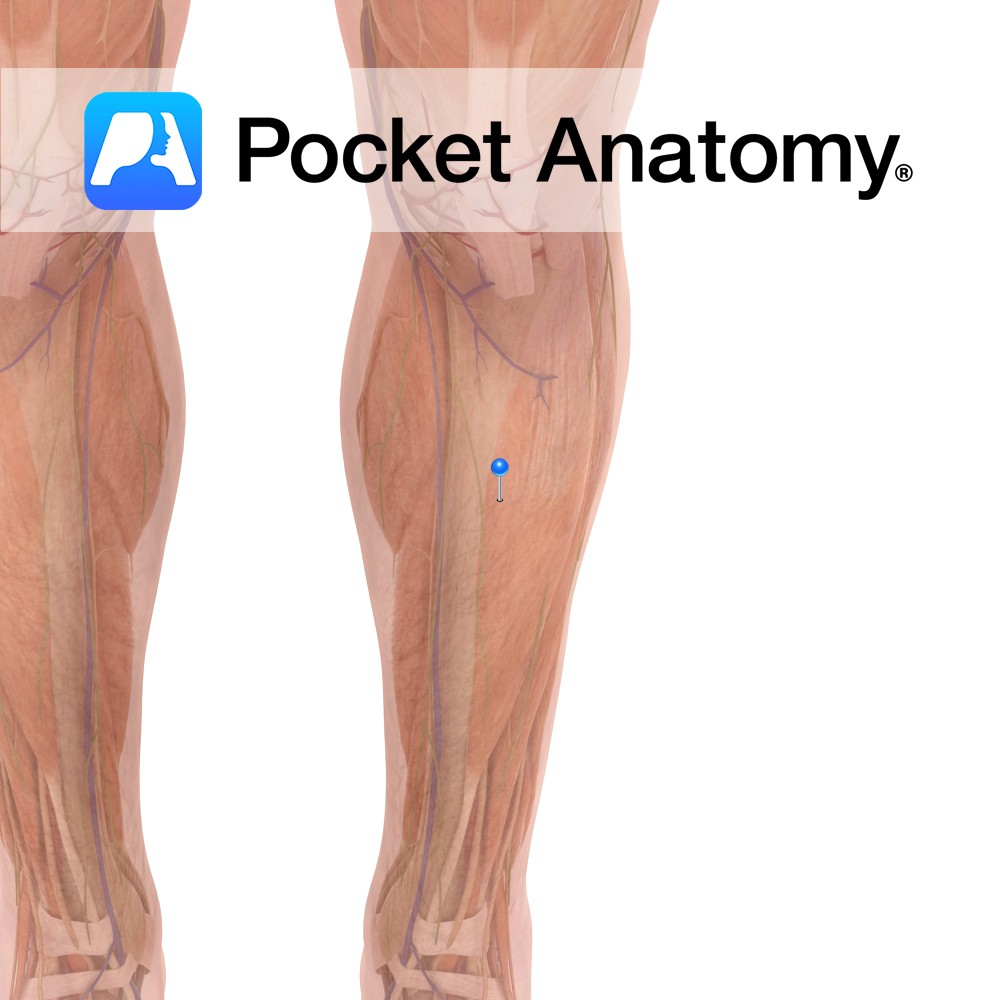
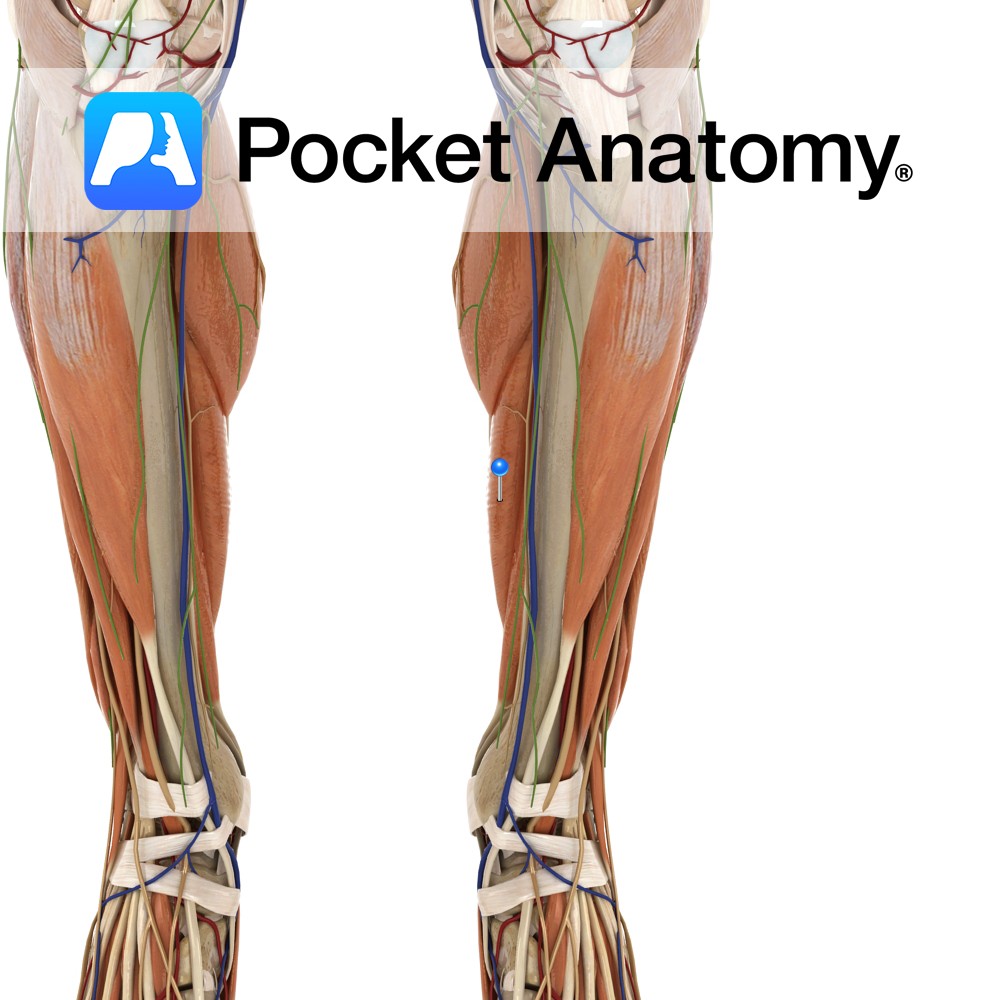
Anatomy Origin: Posterior surfaces of the head and upper third of the fibula, the soleal line of the tibia and the middle third of the medial border of the tibia. Insertion: Middle part of the posterior surface of the calcaneus by the tendo calcaneus (Achilles tendon). Key Relations: -One of the three muscles of the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
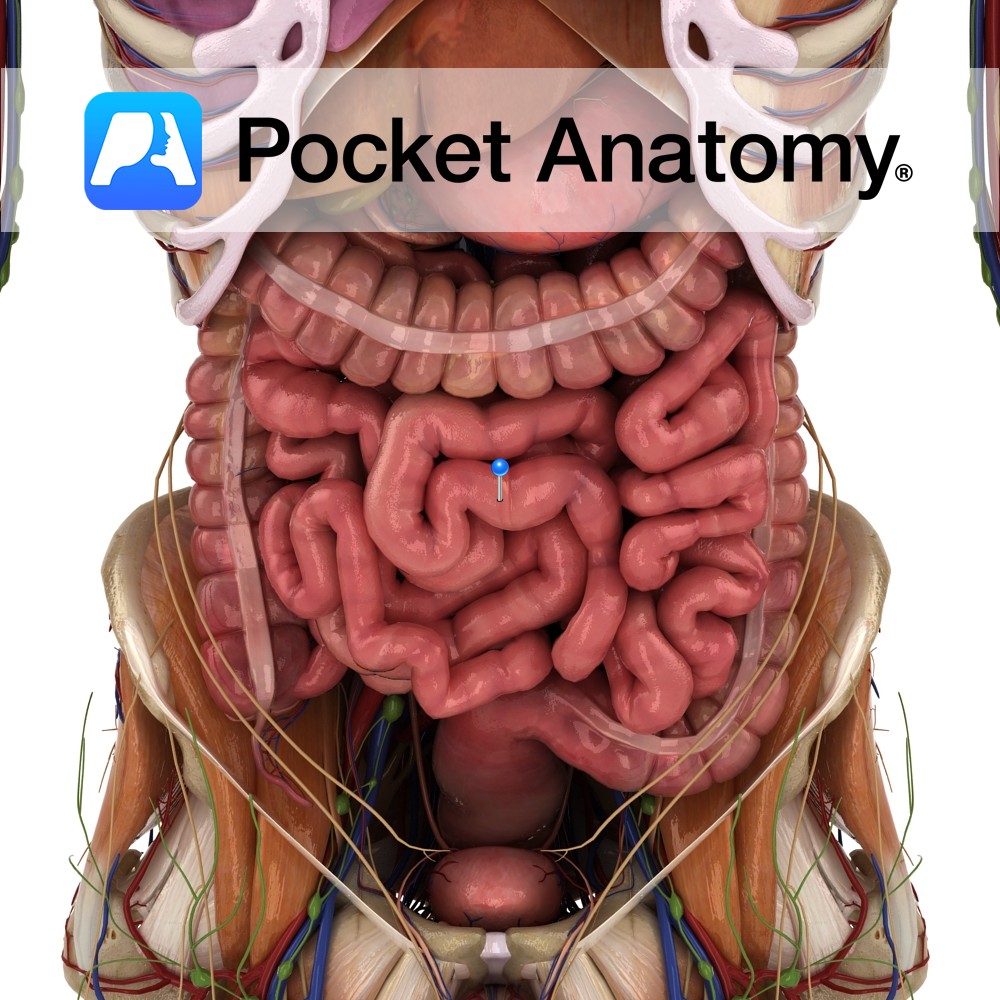
Anatomy Between stomach and colon (pyloric sphincter to ileocecal valve), comprising duodenum, jejunum and ileum, convoluted coils occupying much of abdomen/pelvis, framed at sides and above by colon, c. 23′ long in adult), attached to posterior abdominal wall by fan-shaped mesentery (invaginated peritoneum, containing lymph nodes and vessels) other than duodenum (mostly retroperitoneal). Supplied by
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course Begins from a series of veins that drain the sigmoid colon. It drains into the superior rectal vein. Drain Drains the sigmoid colon. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins